Anatomical aids are intended for everyday use. Their inner filling is often composed according to the principle of puff pastry. The following types are distinguished:

- orthopedics
- Subdivisions of orthopedics
- Outpatient orthopedics
- Children and youth orthopaedics
- prostheses
- components
- What types of dental orthopedics are there?
- How to choose the right technique?
- orthopedics
- Main areas of orthopedics.
- Chondromalacia of the kneecap.
- osteoarthritis.
- Benefits of treating orthopedic diseases at SM Clinic
- Orthopedic surgical treatment
- Orthopedics and prosthetics are not the same
- Removable dentures
- Conventional removable dentures
- Solid type
- Important aesthetics and function
- Orthopedics as a branch of dentistry
- The orthopedic dentist: what he does
- Drawing up a treatment plan
- When to see a specialist
- Models without springs
- Selection criteria
orthopedics
orthopedics (from Greek ορθος - straight, correct and παιδεία - education, training) is a branch of clinical medicine, a branch of surgery that deals with the study of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of malformations and dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system caused by congenital defects , malformations, consequences of injuries or illnesses arise [Source unspecified 38 days] .
Orthopedics is traditionally associated with the branch of clinical medicine that deals with injuries to the musculoskeletal system (bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons) - traumatology. An inherent part of orthopedics and traumatology is prosthetics, a comprehensive medical and technical field that deals with the manufacture and use of prostheses and orthoses (braces, bandages, devices, special shoes and insoles) to restore lost form and function of the musculoskeletal system [Source unspecified 38 days] .
Orthopedics is also an important part of sports medicine. Sports medicine is a comprehensive biomedical science that deals with the changes in the body that occur during exercise, both desirable and pathological. For the modern orthopedic surgeon, knowledge of sports and physical education is simply essential. Orthopedics is unthinkable without exercise therapy, massage or physiotherapy - components of the science known as 'medical rehabilitation'. - and also not without the branch of medicine that deals with the structure and treatment of various diseases of the foot - 'podology'. [Source unspecified 38 days] .
Within traumatology and orthopedics there are many other subspecialties, such as musculoskeletal biomechanics, spine surgery, arthroscopic surgery, joint arthroplasty, bone pathology…. In Russia, traumatology and orthopedics is a separate clinical discipline, designated by the medical specialty code 14.00.22 [Source unspecified 38 days] .
Subdivisions of orthopedics
Outpatient orthopedics
Outpatient care facilities are intended to support the preventative focus of our healthcare system, as they are highly connected to various regional and professional groups. The rational organization of outpatient care is not only a major medical problem, but also a major social problem [1] .
. Between 80 and 96 % of orthopedic trauma surgery patients begin and end their treatment in a polyclinic, ie in an outpatient setting outside of the hospital. This illustrates the outstanding importance of outpatient care as the largest form of mass care. In order to emphasize the importance of the outpatient treatment cycle for patients with diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system, the term 'outpatient orthopedics' is used to describe the organization of the treatment process in a polyclinic or day clinic (this term is used, for example, by such well-known orthopedists as the professors AF Krasnov, MA Berglezov) [Source not shown 38 days ago] .
Children and youth orthopaedics
The goal of pediatric orthopedics is to prevent and eliminate malformations and dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system. She studies the causes and mechanisms of the development of pathological conditions and dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system, the elimination of deformities and the restoration of the form and function of the musculoskeletal system is achieved through conservative and surgical treatment methods [Source unspecified 38 days] .
Examples of conservative treatments include elimination of contractures and congenital club feet by gradual plaster casts and reduction of congenital hip dislocations, etc. Surgical treatment methods developed in orthopedic surgery include osteotomies - the dismemberment of bones when a limb is crooked or incorrect -, muscle-tendon transplants for paralysis, tenotomies, ligamentotomies and other plastic surgical procedures. Both conservative and surgical treatments in orthopedics include a wide range of therapeutic exercises, massage, physiotherapy, as well as various types of orthopedic aids, from various types of orthoses and orthopedic shoes to corsets and complex splints and prostheses [Source not given 38 days] .
prostheses
Prostheses are artificial objects that replace a patient's missing body part. Immediate indications for prostheses are amputations due to trauma, bone and muscle destruction after infections, removal of body parts during necrosis of blood vessels and muscles. A limb prosthesis can replace the loss of many parts: hand, finger, leg, arm, eye, teeth, etc. Reconstruction of the upper and lower limbs is the most popular service among patients.
- cosmetic – simply restores the appearance of a specific part of the body;
- cosmetic-functional – imitates the missing part and restores the lost function in whole or in part;
- functional - with their help it is possible to restore movement, walking and running.
The type of aid is selected individually for each patient and depends on the patient's social orientation, the degree of impairment and amputation, and the condition of the stump. A stump is the remainder of a limb that has been removed. Every prosthesis consists of three components: components, attachment and insert.
components
The product's components include metal rods that serve as bone replacements, as well as parts that replace joints and fingers. In the simplest case, the smaller parts are immobile and the larger parts are moved by physical force. The new generation of prostheses works with an electrical charge that is generated by muscle work. Neurally integrated prostheses are also being developed. The nerves that run along the amputated limb are redirected to power the prosthesis. Such innovation is particularly important for replacing hands and fingers.
Current prostheses do not yet fully restore hand movement. The patient can grasp large objects, but the artificial hand cannot grasp small objects. Such products help patients perform certain functions, but patients are unable to fully help themselves. The development of prostheses will allow patients to live a full life again. Lower limb replacement has almost reached its peak. Today, people who have had one or two legs amputated can play sports, go to work and climb mountains.
What types of dental orthopedics are there?
First of all, dental prosthetics is divided into two main areas:
- Not removable. These parts are used in the dental practice. They cannot be removed at home. They are fixed for a long time in various ways. They are only removed if there is an acute need, including in the dentist's office. Experts recommend this technique when one or more limbs are missing. By using these elements, you don't have to worry about the artificial elements falling out at the wrong moment. Non-removable inlays usually look more natural than removable ones.
- Removable. As the name suggests, these are removable products. These are dentures, meaning they can be removed from the mouth at any time and easily reinserted. They are most often used by older people with complete edentulism.
If you want permanent care, dental clinics offer the following options:
- Ceramic filling or inlay. They are made from an impression in the laboratory. Used on broken or severely damaged teeth caused by active tooth decay. Such a restoration is much better than a traditional filling and lasts at least 3 years.
- Crown. Crowns are made from ceramic, metal-pressed porcelain or plastic. They are used to restore one or more permanent teeth.
- Bridge – a type of prosthetic restoration. It represents several individual crowns in one unit. It replaces 2 to several units and looks like a bridge that is supported by the original teeth.
Removable dentures are divided into the following types according to the material and method of attachment used to create a completely or partially removable dental structure:
- Acrylic. Plastic dentures are very popular. First of all, it is the cheapest option in restorative dentistry. The prosthesis consists of a curved arch that has a simulated gum portion and artificial units. A significant disadvantage is the frequent occurrence of allergic reactions to the material used.
- Nylon. This material is several positions better than acrylic, so its price is also slightly higher. Nylon is more comfortable to wear, less prone to allergic reactions, and comfortable for daily wear.
- Square braces. Metal-ceramic crowns are firmly attached to the metal arch and are therefore very durable. Bone loss is avoided because the partial denture distributes the load evenly. It is the best choice when multiple missing teeth need to be replaced at the same time.
How to choose the right technique?
Any of our specialists can help you. Without knowing the individual characteristics of the patient's mouth, it is difficult to decide on the best solution. Make an appointment with any orthodontist who can help you choose.
Dental prosthetics can help you solve problems like.
- Replace missing parts with dentures.
- restore a severely damaged tooth
- Restoration of chewing function when teeth are completely missing.
- To prevent jawbone loss.
Dental prosthetics is aimed at restoring lost or damaged teeth. If only 1-3 teeth are missing, specialists recommend fixed dentures. If more than 3 teeth are missing, a partial denture can be used. Acrylic or nylon products are most commonly used when a large number of teeth are missing. They cost significantly less, but are not as comfortable and aesthetically pleasing as their more expensive counterparts.

orthopedics
The close cooperation between the orthopedics, arthroscopy and rehabilitation departments in our clinic, together with highly qualified doctors and the most modern equipment, allows us to provide an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of all pathologies of a neurological nature and the return of our patients to an active lifestyle.
Orthopedics is the branch of medicine that deals with the study of the skeletal and muscular systems of the body, etymology, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Orthopedics deals with the treatment and rehabilitation of joints after various diseases and complications of long-term injuries.
Orthopedics is inextricably linked with traumatology, which deals with injuries to the musculoskeletal system. Both medical disciplines use physical therapy and prosthetics to treat their patients. Orthopedic diseases are usually due to trauma, chronic illness and developmental disorders.
It is also part of sports medicine, which deals with the effects of sport on the human body. Modern orthopedics therefore also includes research in the field of physical education and sports.
Main areas of orthopedics.
- endoprosthetics – Replaces joints with implants (artificial or natural) and is used when other methods have failed.
- Outpatient orthopedics – These are the classic preventive methods to avoid OA problems (with the right approach, surgical interventions can be avoided);
- traumatology – Sports traumatology also falls under this heading and, depending on the type of illness or injury, includes conservative and surgical procedures;
- surgery – Surgical techniques enable rapid recovery of feet, hands and spine.
Chondromalacia of the kneecap.
Chondromalacia of the knee is the most common injury among athletes. For this reason it is also known as runner's knee.
It is a degenerative lesion of the cartilage tissue of the kneecap. It is a relatively common condition that often occurs in athletes and other active people.
With chondromalacia, the cartilage can no longer move freely along the joint and begins to invade the socket. This leads to severe pain and restricted movement.
In the early stages, the disease can be treated with chondoprotectants and hyaluronic acid injections. They also prescribe tartaroscopy, a safe and effective method that allows the pathology to be diagnosed and treated in one session.
osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a cartilage disease that is associated with pain, functional limitations, limited mobility, swelling and deformation of the kneecap.
In the early stages, conservative treatment is possible, but in most cases arthroscopic examination is recommended, which has proven to be very effective and is actively used in all hospitals worldwide.
Benefits of treating orthopedic diseases at SM Clinic
Orthopedic traumatologists with extensive experience in the treatment of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system are invited to the center and operate there.
High-tech devices and techniques allow maximum effect and a significant reduction in the risk of postoperative complications.
Thanks to modern techniques, most surgeries can be performed on an outpatient basis or with minimal hospitalization, and recovery time is significantly shorter.
Orthopedic surgical treatment
In our center, surgical interventions are carried out for orthopedic diseases with congenital or acquired (after trauma, age-related) deformities and damage to joints, tendons and ligaments. In most cases, only surgical intervention can restore mobility and relieve the patient of pain, stiffness and other inconveniences.
We use modern minimally invasive techniques to optimize treatment results. In this way we can reduce the risk of injuries to the soft tissues and surrounding joints and speed up recovery.
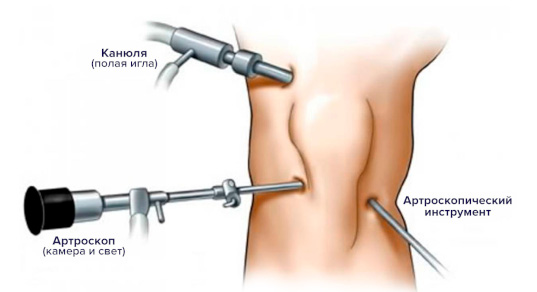
- Arthroscopic procedures. These are carried out through punctures with a special device called an arthroscope. With the help of a miniature video camera, the doctor carries out all manipulations with extreme precision.
- Joint arthroplasty. This is an operation in which a deformed joint is replaced with an artificial one. After complete recovery, the limb is mobile again, and in many cases arthroplasty is the only way to achieve this result.
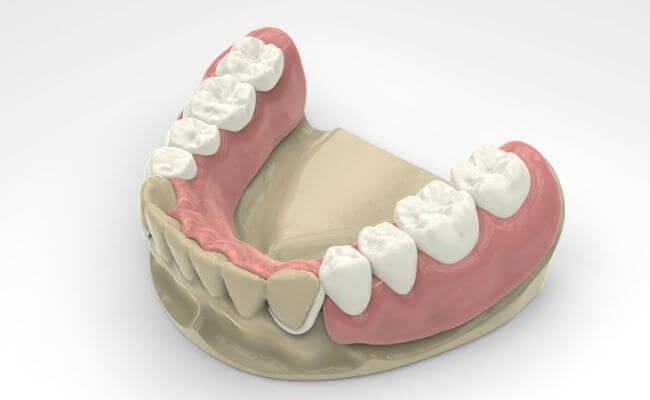
Orthopedics and prosthetics are not the same
For many people, orthopedics and prosthetics are interchangeable. However, prosthetics is the branch of orthopedics that deals with the restoration of partially or completely lost teeth. To achieve this goal, each patient is provided with a specific type of prosthetic restoration based on existing indications and the specifics of their clinical case. Traditionally, dentures are divided into three categories:
Removable dentures
Removable dentures include full and partial dentures. The latter are characterized by special elements (clamps or attachments) with which they are attached to the supporting teeth.
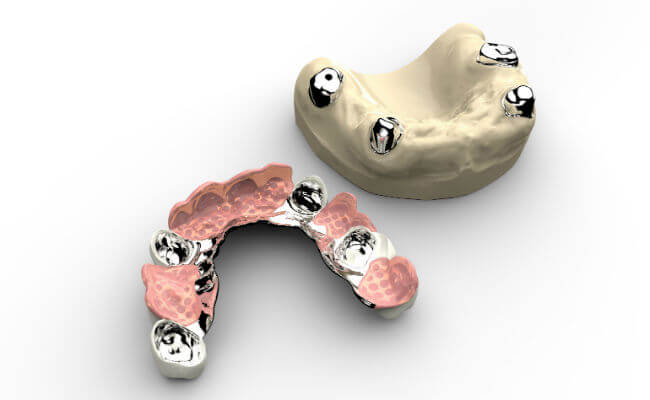
Conventional removable dentures
A temporary denture is a complete overdenture that is attached to implants in the mouth.
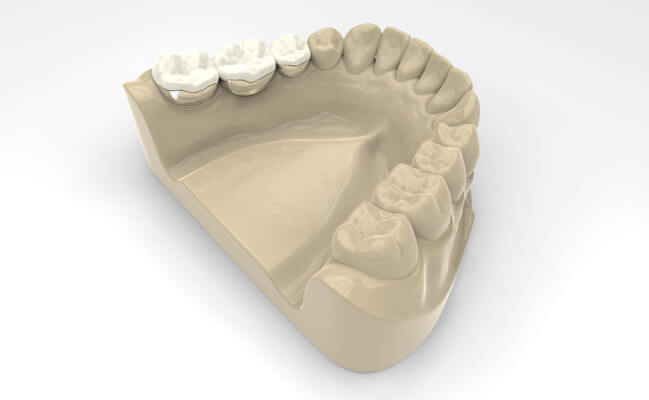
Solid type
Fixed dentures are very diverse.
Important aesthetics and function
When restoring front teeth, the focus is on aesthetics. Therefore, veneers or ceramic crowns are the ideal choice for restoring the smile zone. The properties of the material are close to those of natural tooth enamel and have a natural translucency. In the posterior region, however, where strength and durability are more important, ceramic or zirconium dioxide prostheses can be a suitable solution.
Publisher: Dental Expert Magazine Startsmile.ru
Orthopedics as a branch of dentistry
In general, orthopedics is a large branch of medicine that deals with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, and orthopedics in dentistry is only a part of it.
Dental orthopedics specializes in correcting problems with the chewing apparatus – language.It's about restoring its function and integrity with the help of prostheses. This treatment is called prosthetics.
A dental orthopedist should be consulted if:
- with missing teeth – from one to complete lack of teeth;
- Caries – total or partial – is present;
- with increased tooth mobility or sensitivity or with other problems with the jaw and bone tissue – periodontal disease, periodontitis, etc.;
- there are cosmetic defects - shape, size, color or other aesthetic defects are obvious;
- a temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pathology was diagnosed;
- it is a visit to an orthopedist recommended by another doctor in the practice who has deemed it necessary as part of an examination or treatment.
The orthopedic practice is staffed by specialized, highly qualified doctors – orthopedic dentists.
The orthopedic dentist: what he does
This dentist's duties include restoring teeth. Due to the similar name and purpose, the orthodontist is often confused with the orthodontist. However, there is a difference - an orthodontist corrects crooked teeth and overbite through the use of braces, while an orthopedist restores teeth and their alignment. An orthodontist rebuilds the teeth, more specifically the outside and inside of the teeth, with dentures.. Therefore, they are sometimes referred to as prosthetists.
The podiatrist or prosthetist helps with all of the above problems for which it is advisable to see an orthopedic dentist.
What problems can be eliminated with the help of a prosthodontist?
- A constant feeling of psychological discomfort. The absence of one or more teeth affects the aesthetic appearance of the face and even its symmetry, making the affected person feel insecure and uncomfortable. Damaged teeth, such as Other things, such as chips, crooked teeth, gaps, etc., can cause the same feeling. This is particularly true in the area of the smile. This is where the help of a dentist is very helpful.
- Another disadvantage of inadequate teeth is just as important: a significant disruption of the chewing function. It must be restored quickly, as it stimulates the natural processes of the entire alveolar system and restores its normal functioning: muscle tone, nutrition and blood supply to the cells of bone tissue. Proper chewing function is not only beneficial for health and metabolic processes in the body, but also helps fight periodontal diseases.
- Imminent tooth loss due to progressive tooth decay. A tooth may still have healthy roots, but its external bone tissue has already broken down to the point where the filling is no longer effective. In order to stop the destructive process and save the tooth or not lose it completely, a visit to an orthopedic dentist is necessary.
- An orthopedic dentist also treats full dentures, which allow people who are missing all of their teeth to live a normal life.
Drawing up a treatment plan
A visit to an orthopedic dentist usually involves more than one appointment. During the first consultation, the doctor examines the client's mouth and determines the existing problems and their severity. A CT scan or x-ray is taken to examine the location and condition of the roots.

- The plan may include the following steps:
- Selection of the method for repairing the resulting defect.
- Preparation for prosthetic treatment.
- Making and inserting the prosthesis.
- Assess the development of the patient's oral health.
When to see a specialist
The advanced possibilities of orthopedics (dentistry) should be used in the following situations
- The crown is severely damaged by tooth decay and cannot be repaired with filling material;
- the roots are completely destroyed and cannot support future external care
- Dangerous pathological processes or necrosis were detected in the hard tissues;
- There are diseases that have caused changes in the crowns of molars, incisors and canines;
- Periodontosis is diagnosed.
The help of an orthopedic dentist is also necessary if there are chips, cracks or deep scratches or if some units are incorrectly positioned in relation to their 'neighbors'.
The doctor is responsible for:
- To make the correct diagnosis;
- Carrying out preparatory measures, preparing the planned treatment;
- the selection of the optimal prosthetic care method;
- The doctor is responsible for: making a correct diagnosis; carrying out preparatory measures, preparing for the planned treatment; the choice of the optimal prosthetic care method; the insertion of removable and fixed prostheses.
Models without springs
There are anatomical mattresses that do not require springs. The effect is most pronounced in products that are filled with water or air. Originally they were used only in hospitals, today they are the most widespread, while they are rarely used due to their high cost and inconvenience (they weigh a lot).
A high level of anatomy characterizes products:
- Natural latex – rubber;
- synthetic or combined latex;
- Memorix polyurethane foam;
- TechnoGel material.
Mattresses made from these high-tech materials have a 'memory effect' where the surface returns to its original position after use.
Selection criteria

First you need to answer the question of whether you want an anatomical or orthopedic mattress. Do you have any health problems? If yes, you should choose the first option. Do you value a comfortable and healthy sleep? Then choose an anatomical bed.
- the manufacturer's reputation - reputable brands don't take risks, so you can be sure that high-quality mattress components have been used;
- Your own weight - products that are too soft are not suitable for people over 90 kg;
- Your weight difference – if you buy a double bed product
- Age – the older the person, the softer the surface should be
- Parameters – to obtain the optimal length, 15-20 cm should be added to the height.
A mattress is an individual thing, and the one that sparked enthusiasm among your friends may not be right for you. Choose responsibly.
Read more:- Modern leg prostheses.
- How much does a prosthetic foot cost?.
- Who is the orthopedist?.
- prosthetic legs.
- Limb prostheses are.
- What an orthopedist treats and what symptoms to report.
- prosthetic leg.
- What is another name for an orthopedist?.
