The supplement can be taken with the symptoms of magnesium deficiency: insomnia, muscle pain, hyperactivity or, conversely, constant fatigue and drowsiness.

- Anatomy of the muscles that control the foot
- tissue of the hindfoot
- What is it.
- How does a nerve get pinched?
- muscles that move the foot
- Balance and coordination exercises
- The complex consists of ten coordination exercises:
- Video
- dosing regimen.
- side effects
- Doctors' opinions on vitamins for the nervous system in adults
- Popular questions and answers
- When should adults take vitamins for the nervous system?
- What ingredients should the best vitamins for the nervous system in adults contain?
Anatomy of the muscles that control the foot
The human skeleton is surrounded by fibers that perform important functions in the body. There are also many tissues in the foot. What is the anatomy of the muscles of the human foot?
Muscle tissues are important elements that perform specific tasks in the musculoskeletal system. In the foot, they are essential for leg control and toe flexion and extension.
In addition, the fibers support proper blood circulation in the limbs. Thanks to the fabric, various injuries to the feet are prevented. However, in order for them to be able to fulfill their full function, they must be constantly under tension.

tissue of the hindfoot
The muscle fibers of the hindfoot are located under the connective tissue sheaths and extensor tendons.
| Surname | Location | function |
| Short tendon | Begins at the anterolateral border of the heel bone and extends to the dorsum of the foot, terminating at phalanges 2 and 5. | Extends the 2nd and 5th toes |
| Extensor shortus Extension of the big toe | Extends from the heel bone to the tendon of the big toe | Extends the big toe |
What is it.
A pinched nerve in the lumbar spine is pressure on the nerve roots that exit the spinal cord in that area. They can become compressed due to spinal abnormalities, spinal diseases, and muscle spasms.
Statistics show that most patients with this condition are elderly. As we age, bones and muscles weaken and are more prone to injury and breakdown. The body lacks calcium and the metabolism slows down – hence the back pain.

When a person has a pinched nerve, he always suffers severe pain of various kinds. The pain can be stabbing, sharp or burning. Depending on how much and where the nerve is compressed, experts distinguish between Lumbodynia – (lumb. back and lumbar pain; lumboishyalgia – pain in the legs and buttocks; sciatica – with localization in the legs, sacrum and buttocks.
The symptoms are often not just limited to pain. These syndromes are accompanied by sensory disturbances in the limbs, numbness and disturbances in certain internal organs. It depends on which nerve was pinched.
How does a nerve get pinched?
A pinched nerve cannot develop by itself. The most common causes of pinched nerve branches are:
- intervertebral prolapse. This is the most common cause. A herniated disc is a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus from the fibrous ring of the disc. This bulge can create pressure and pinch nerves as a result. The longer the nucleus pulposus remains in the bulge, the more the nerve root is compressed, resulting in severe, persistent pain and numbness in the limb.

- disc protrusion. One form of disc protrusion is complete bulging of the disc. In this position, she also puts a lot of pressure on nearby nerve plexuses.
- osteochondrosis. Approximately 80 % of the world's population suffers from this condition. The discs in the spine shift slightly back and forth due to age-related problems or lack of exercise.
- postural defects. Lack of postural control can also lead to spinal stiffness.

- overweight. Obesity puts a lot of strain on the spine and generally has a negative effect on the entire body. It is advisable to get rid of this weight as soon as possible.
- Excessive physical activity or lack of exercise. These two conflicting factors can cause a pinched nerve in the lumbar spine. It's important to find a balance and exercise moderately but regularly.
- spinal injuries. Even if the disease appeared earlier, the effects are visible for a long time. The nerves can still be partially pinched after an injury.
- Sprained muscles. The muscles in the lumbar spine can be tense for various reasons and cause unnecessary discomfort to the person concerned.
muscles that move the foot
The ability to execute and control precise, fluid movements using different muscle groups in sync is called hand-eye coordination. People who have successfully developed this ability have secure control over their bodies. They are responsive, can balance and move in any space. We tell you how and why you can develop coordination.
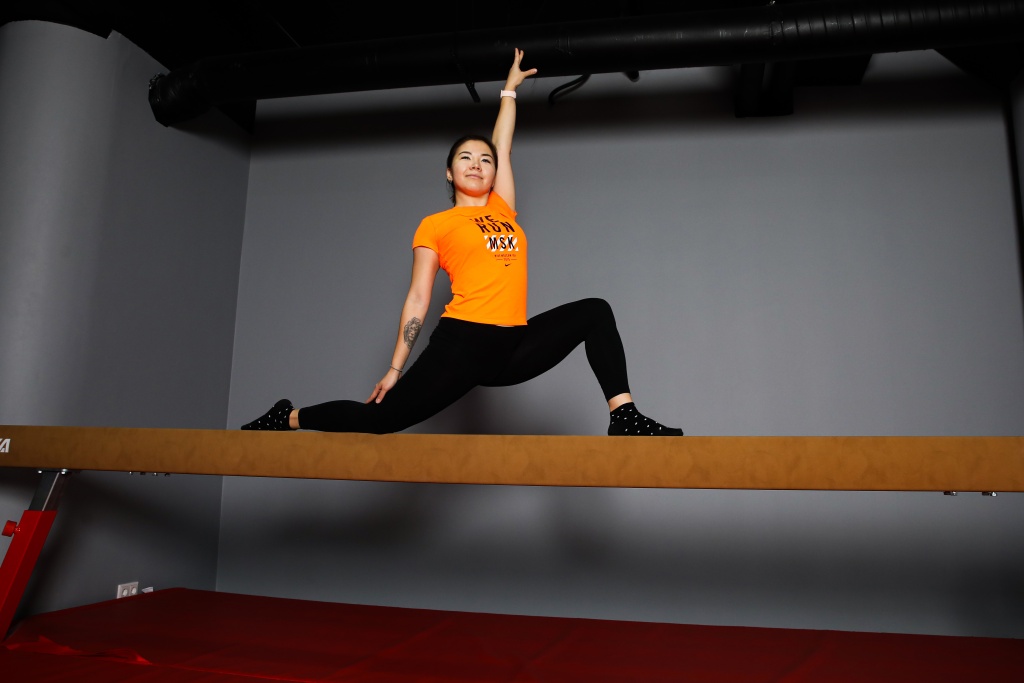

A person with good coordination has confidence in the flexibility and strength of their body. He or she quickly shifts the center of gravity, tightens the appropriate muscles, and avoids obstacles. This ability is best developed in people who practice complex coordination sports: figure skating, rhythmic and artistic gymnastics, synchronized swimming and diving. Spatial orientation is also part of the ability to coordinate. This is the ability to move by focusing your gaze and attention on a specific object that is either static or changing position. For example, this could be a hockey player tracking the location of a puck. Conversely, a person can perform an action on an object without looking at it. For example, a basketball player catches the ball without looking while running while keeping his eyes on the opponent's edge. Coordination is important not only for athletes, but for all adults and especially the elderly who are at increased risk of falling and fractured bones. Without a well-developed skill, equilibrium and body balance are lost and dizziness occurs. This is because the cerebellum and vestibular system are responsible for coordination. The former is located between the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem. The functions of the cerebellum include:
- Accuracy and smoothness of hand and foot movements;
- fluid gait;
- maintaining posture;
- Skill;
- regulation of muscle tone.
Balance and coordination exercises
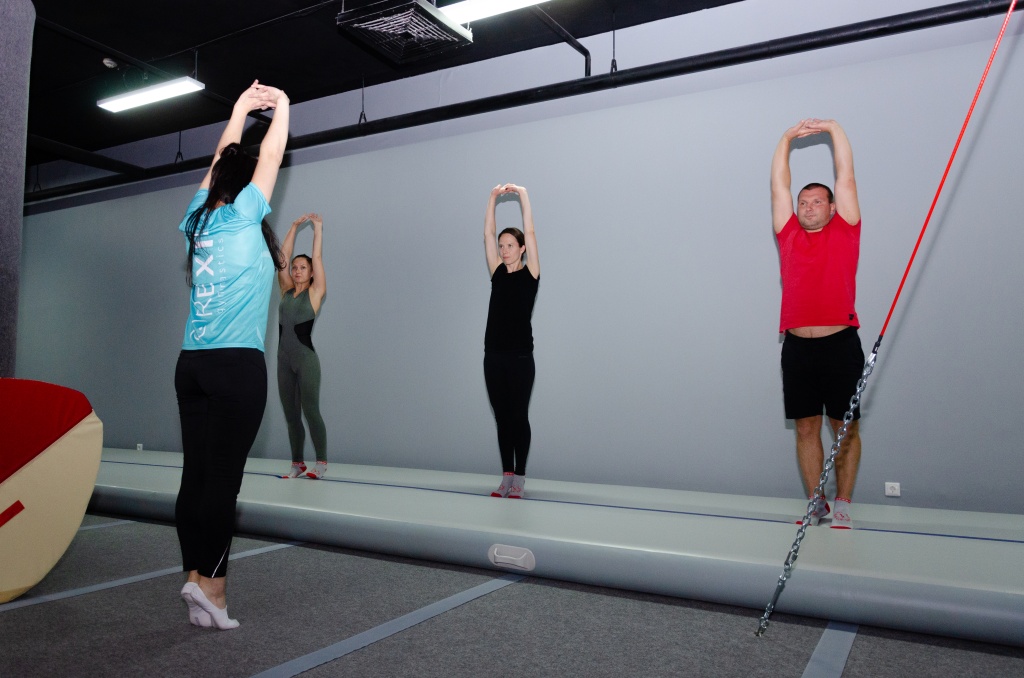

Here are some simple exercises you can do at home. Do them in the first half of the day and warm up your body with exercises or a warm-up. If you feel unwell, have a headache or other discomfort, postpone the exercises.
The complex consists of ten coordination exercises:

- Throw a ball against a wall. Increase the difficulty, e.g. B. by clapping your hands or doing a body roll after a throw.
- Turn your head while fixing your gaze on a solid object. Choose an object that is at eye level. Keeping your gaze on it, gently rotate your head left and right for about 60 seconds. Can be done standing or sitting.
- ,Swallow'. Lean forward, extend your arms to your sides, lift your right leg and bring it back. Try to touch the ground with your left hand. Switch legs. Do three to five sets in total.
- 'Pistol Whip'. First try to hold on to a support. Slowly squat down, bend one leg and place the other leg in front of you, keeping your weight on it. Start with two or three attempts and gradually increase the number.
- Cross-legged jump rope. The left leg is in front for the first jump, the right leg for the next jump. Watch your technique and land carefully on tiptoe.
- Run with alternating postures. First, move as usual, then twist your back forward, then alternate left and right.
- head turns. Perform slow, alternating movements – clockwise and counterclockwise. It is important to turn your head evenly, preferably with your eyes closed.
- standing position. Stand up straight on tiptoe and stretch your arms overhead. Close your eyes and try to keep your balance in this position.
- ,Tree'. Place your hands above your head, palms together. Gently lift your left foot and place it on the inside of your right thigh. Stay in this position. Swap feet.
- Put an object on your head. Preferably a book. Put it on your head and try to hold it while keeping your back straight. To make the exercise more difficult, try walking without dropping the item.
Video
Tip 8: Get rid of a double chin with a thread
Probably the most effective method to get a quick chin without a scalpel. The results last for more than 5 years. The NAS lift with the iGuide system allows you to remove your chin in a week or even less: come to the clinic on Wednesday and go to work on Monday.
The NAS lift is only available in the Platinental Aesthetic salon. The price of the procedure depends on the scope of the intervention: the method shows the best results when combined with laser liposuction.






Chin enlargement effect without an implant! The patient underwent liposuction and a chin lift, where the chin was reinforced with i-Guide threads. The face now looks more elegant and sharp. The surgeon is AA Iskornev.

dosing regimen.
Take 1-2 tablets at a time 2-3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 6 tablets (equivalent to 240 mg).
No clinical studies have been conducted on the use of drotaverine in children.
- 6 to 12 years: Take 1 tablet 1-2 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 2 tablets (equivalent to 80 mg);
- Over 12 years: 1 tablet for 1-4 administrations/day or 2 tablets for 1-2 administrations/day. The maximum daily dose is 4 tablets (equivalent to 160 mg).
If taken without medical consultation, the recommended duration of treatment is usually 1-2 days. In cases where drotaverine is used as an adjunctive therapy, the duration of treatment without a doctor's consultation may be longer (2-3 days). If the pain persists, the patient should consult a doctor.
If the patient can easily self-diagnose his symptoms because he is well acquainted with them, he can also easily self-assess the effectiveness of the treatment, ie the cessation of pain. If there is moderate pain relief within a few hours of taking the maximum single dose, or if there is no significant pain relief after taking the maximum daily dose, it is recommended that you consult a doctor.
When using a vial with a polyethylene stopper fitted with a dispenser: Before use, remove the protective strip from the top of the vial and the sticker from the bottom of the vial. Place the bottle in the palm of your hand so that the dispensing hole at the bottom does not rest on your hand. Then press the top of the bottle so that one of the tablets falls out of the opening at the bottom.
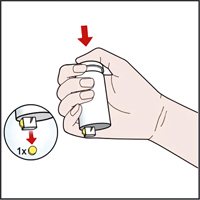
side effects
Adverse reactions observed in clinical trials are presented by organ system as follows, with frequency using the following WHO recommended categorization: very common (≥10%), common (≥1%, <10%), selten (≥0,1%, <1%), sehr selten, einschließlich einzelner Berichte (<0,01%), unbekannt (Häufigkeit kann anhand der verfügbaren Daten nicht bestimmt werden).
Nervous system disorders: Rarely headache, dizziness, insomnia; frequency unknown, dizziness.
Cardiovascular diseases: Rarely - palpitations, drop in blood pressure.
Immune system disorders: Rare - allergic reactions (angioedema, urticaria, pruritus, rash) (see section 'Contraindications').
Doctors' opinions on vitamins for the nervous system in adults
Doctors can prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the nervous system and to prevent and treat neurological diseases. However, experts note that fatigue, increased irritability, and sleep disturbances are not always associated with hypovitaminosis, but can also be symptoms of a disease. In such cases, it is advisable to consult a doctor and have yourself examined.

An anxiety disorder is a constant and uncontrollable feeling of fear that lasts for more than six months with no objective cause. Let's discuss with experts what medications are prescribed for anxiety disorders
Popular questions and answers
We asked our experts some questions about choosing and taking vitamins Nikolai Dubinin, health and nutrition expert i Nikolai Dubinin, Professor at the Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Toxicology, Mikhail Kutushov.
When should adults take vitamins for the nervous system?
– In general, taking vitamins to strengthen the nervous system is beneficial:
– students and pupils in times of high mental and emotional stress;
– competitive athletes;
– people with an intellectual disposition;
– Patients with neuritis and neuralgia;
– smokers;
– people who have suffered severe emotional disorders or are under stress;
– people working in difficult conditions;
– vegetarians and people following a strict diet;
– men and women over the age of 45;
- People recovering from a long-term serious illness, including coronavirus infection;
– Patients who are in the rehabilitation phase after a stroke.
Before taking vitamin complexes, always seek advice from a specialist doctor. Your doctor will select a product based on your age, gender, medical condition, and lifestyle.
What ingredients should the best vitamins for the nervous system in adults contain?
– Scientists have long discovered which vitamins, minerals and other bioactive substances are needed for a healthy nervous system. It is generally accepted that dietary supplements and vitamin-mineral complexes should contain:
– B vitamins (B1, B3, B4, B5, B6, B9, B12) regulate the functioning of blood vessels and the endocrine system and help restore energy balance;
– Vitamin C supports the functioning of the nervous system during high mental stress and strain, prevents destruction and loss of nerve cells, helps against depression and seasonal depression;
– polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids stimulate metabolic processes in nerve cells, promote glucose uptake by the brain;
– magnesium and calcium improve conductivity of nervous tissue, help fight stress;
– Glucose acts as 'fuel' for the brain and nervous system;
– Vitamin A improves nerve cell regeneration and helps protect neurons from damage;
– Lecithin improves brain function.
- Shin extensor muscles (tibialis extensor muscles).
- If the leather on your shoes is cracked.
- muscles of the soleus muscle.
- The muscles that move the foot.
- muscles in the legs.
- muscles and tendons of the foot.
- Muscles and fascia of the lower limbs.
- Muscles congest when running.
