Sometimes the weakness of the leg muscles is caused by the effects of toxic substances on the nerve and muscle tissue. Organophosphorus compounds and carbamates (insecticides) that inhibit cholinesterase activity adversely affect myoelectric synapses. The functioning of nerve fibers and ganglia is adversely affected by heavy metals: lead, thallium, mercury, arsenic, tellurium.

- Running Without Injury: How to Keep Your Joints Healthy
- The joint and cartilage: a little physiology
- 2 causes of cartilage wear
- Causes of lower limb weakness
- neurological diseases
- problems with the spine
- diagnosis
- Wear the wrong shoes
- What not to do
- How massage can help for blocked muscles
- What is a muscle block?
- Causes of muscle stiffness
- What to do if symptoms of muscle congestion are noticed?
- What should you do before training?
- What to do after training
- to eat and drink
- diagnosis
- How to strengthen your blood vessels through diet
- Vitamins to strengthen capillaries
- Swelling and Leg Pain: Disease-Related Causes
- Lower leg edema: causes and drug treatment
Running Without Injury: How to Keep Your Joints Healthy
Strange as it may seem, athletes, especially track and field athletes, are at risk of developing osteoarthritis. Regular stress on joints wears down cartilage, especially when athletes are prone to occasional injuries and micro-injuries. Is it possible to maintain healthy joints without giving up the popular jog?
Jogging is not just jogging: it is not always a risk for your joints
The joint and cartilage: a little physiology
A joint is a combination of bony surfaces covered by cartilage. It is surrounded by a joint capsule that seals it and protects it from damage. The function of cartilage is to absorb stress during movement. Synovial fluid is produced inside the joint capsule, which lubricates the surfaces and nourishes the cartilage. The latter has a spongy structure: under stress, it releases synovial fluid and absorbs it again.
2 causes of cartilage wear
If a joint is damaged, e.g. B. by a microtrauma, it begins to produce more anti-inflammatory substances, which in turn damage the chondrocytes - the cartilage cells. The latter react with the production of 'abnormal' and short collagen as well as small, low molecular weight proteoglycans. The content of chondroitin and hyaluronic acid in the cartilage decreases drastically - it gradually breaks down and becomes thin.
A sedentary lifestyle, lack of exercise or standing work impair the blood supply to the joint - the cartilage is no longer properly nourished. In addition, the cells no longer produce the right collagen and there is a lack of synovial fluid.
Worn out cartilage is the main cause of joint diseases
Causes of lower limb weakness
neurological diseases
Nervous system disorders are a common cause of weakness in the legs. Disorders of impulse conduction in the central or peripheral motor neurons cause an objective decrease in muscle strength - flaccid or spastic paresis. Either only the lower limbs are affected or the process spreads to the hands. In practical neurology, the following diseases are encountered:
- Stroke. Local damage to the frontal cortex leads to central monoparesis. Loss of motor function is associated with increased tendon reflexes in the lower limbs, abnormal foot symptoms, and spastic hypertonia.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. The degenerative damage to the motor neurons manifests itself in muscle weakness in the legs (one or both). There is ankle discomfort, stiffness in the foot, changes in gait, and patients stumble.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Acute autoimmune polyradiculoneuropathy begins with weakness of the buttocks and hips with paresthesia of the fingers. The flaccid paresis is accompanied by pain in the lumbosacral region and at the edge of the pelvis radiating to the legs and symptoms of radicular tension.
Limb paresis occurs as a result of trauma and is a consequence of compromised integrity of conduction pathways (wounds, fractures, surgeries). One-sided damage to the spinal cord in the lumbar spine area leads to weakness in one leg (lower monoparesis). If the peroneal nerve is damaged, the foot hangs down and the gait looks like a 'squatting' or 'stomping' gait.
problems with the spine
Spine diseases occupy an important place among the causes of leg weakness. Compression of nerve roots is caused by osteophytes in osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias and damaged vertebral bodies as a result of osteoporosis, tuberculosis or metastatic processes. This situation is observed with spondyloarthrosis and spondylolisthesis (displacement of vertebral segments).
diagnosis
To understand what disease caused the weakness in the legs, the data of the clinical examination, supported by the results of additional methods, will help. The neurologist determines a list of diagnostic procedures based on the information obtained during the examination of the patient and the neurological examination. The following tests can be performed:
- blood tests. A hemogram shows the red blood count, white blood cell count and blood sedimentation. Biochemical analysis reveals endocrine or electrolytic abnormalities, muscle enzymes, and specific antibodies.
- X-ray examination. The condition of the bony structures of the spine and skull can be assessed by conventional radiographs in two projections. However, this examination has low resolution and does not visualize soft tissue injuries.
- Computed Tomography. Computed tomography is the preferred method for imaging recent strokes, tumors, hematomas, and posterior fossa fractures. Diffuse pathologies of the spinal cord and brain substance can be better recognized with MRI.
- myelography. The permeability of the cervical canal is clarified by introducing a radiopaque contrast medium into the subarachnoid space. Myelography is indicated for intervertebral fractures, spinal injuries and tumors.
- electroneuromyography. Diseases associated with nerve conduction disorders are diagnosed with the ENMG. During the examination, the peripheral nerve is stimulated with electrical impulses and the muscular response is recorded.
Ultrasound angioscopy and rheovasography are prescribed to detect vascular diseases. Endocrinopathies require an ultrasound scan of the thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands, and in patients with myasthenia gravis, the size of the thymus gland is assessed. The diagnosis of hereditary diseases is made by cytogenetic, molecular genetic tests.

Wear the wrong shoes
As silly as it may sound, the cause of heavy feet can be the wrong footwear.
For example, anti-hypertension shoes tend to weigh more because they are structurally a little thicker and offer more support. Still, there is a wide range of stability shoes on the market. Try out a few models and do a few trial laps in the shop to make sure they're not too heavy for you.
On the other hand, shoes that are too light and don't offer enough support can also cause problems. If you don't have enough support in your shoes, there will be more strain on your body when your foot hits the ground. This can lead to muscle fatigue.
This can also happen with worn and old shoes. Therefore, change your sneakers every 300-500 kilometers.
What not to do
Some athletes ignore their body's warning signs and continue to train hard. Don't do this - if you overtrain an overloaded muscle, you put yourself at risk of overtraining and injury.
It is important to create a balanced exercise program that allows adequate time for recovery. It is also important that you monitor your symptoms closely. 'If you feel muscle pain and limited mobility five to seven days after training, you should consult a doctor,' concludes Yesenia Kalyuzhina.
Would you like to train online for your fitness? Train with lessons from the 'LIVE!' video library.
How massage can help for blocked muscles
Massage of blocked tissues helps to restore disturbed nerve impulses, increased metabolic processes and improves blood flow. A massage can make a world of difference when leg muscles are overworked after a hard run. At this point, when the body hasn't had time to rest, the muscles are full of lactic acid and toxins from protein breakdown.
If the relaxation massage is omitted, pathological degeneration and muscle contractures can occur. However, it is better to have permission of one medical professional.. So you know how to massage the blocked muscles yourself, which areas you need to massage and with what pressure. This massage should be done with special care if a child needs it. In this case, it is imperative to consult an experienced pediatrician or children's massage therapist in order to avoid injuries to the child if this treatment is carried out improperly.
What is a muscle block?

The physiological cause of a blockage (known as crepation in technical jargon) is elementary muscle fatigue. This means the muscles don't have a chance to relax. If you train too hard without training properly, if you increase the load too quickly, you can even tear a muscle.
Causes of muscle stiffness
- Muscles are swollen from lactic acid production (lactic acid production occurs whenever muscles are tense);
- contraction of a muscle without diastole prevents blood flow to the muscle in the required amount;
- excessive accumulation of blood in the legs;
- rarer: microtears and microtears of the muscle.
What to do if symptoms of muscle congestion are noticed?
This issue should be addressed in advance. To avoid overloading muscles during exercise, it is important to take care of it before training.
What should you do before training?

- Be sure to do a warm-up (5 minutes). This can be a brisk walk, light jumping jacks in place, squats, light stretches, circular joint twists;
- Eat at least half an hour before your workout. If you eat a heavy lunch or dinner, you should allow at least an hour between the meal and the workout;
- It is advisable to wear natural wool leggings during training;
- You can take amino acids or special vitamin complexes for athletes half an hour before training (we will talk about them separately below). You can buy them at pharmacies or sports nutrition centers. They help you maintain muscle volume during endurance training and reduce muscle recovery time, which in turn relieves post-workout muscle soreness.
What to do after training
- Take a warm shower. Only warm showers and no others;
- Place a warm heating pad or wool handkerchief on the affected area;
- Stand on an applicator (Kuznetsov or Lapko). This is especially necessary with muscle spasms;
- Massage the cramped muscle. Knead the rocky muscle with your fingers to stimulate blood flow and break down excess lactic acid;
- Remember to stretch the blocked muscle. While standing, stretch the pecs with arms extended perpendicular to the body, then 5-6 deep inhalations, then arms extended parallel to the body, also 5-6 inhalations, then arms extended with inhalations up and to the sides. Stretch the back muscles by bending forward, levitating for a few seconds, then straightening and bending again. Stretch the leg muscles by spreading them wide and alternately crouching on one leg and the other. Introduce stretching as a mandatory completion of your workout;
- If you have the opportunity to go to the sauna after training, use it! The sauna also helps your muscles relax. Remember that it is dangerous to go to the sauna immediately after a hard workout - there is a risk of overloading the circulatory system. Wait 15 minutes, relax, stretch and cool down. Only then go to a steam bath;
- Do a little exercise every day. This helps your muscles and circulatory system work properly and reduces the risk of muscle overload;
- Ensure sufficient physical rest. If possible, lie down. This can also include sedentary work. Ideally, a long, healthy sleep;
- Try to replenish your body's energy reserves by eating foods with easily digestible carbohydrates. Fruit or dried fruit is ideal. You can mix and take a protein and carbohydrate shake (make your own or buy a ready-made powder at a sports nutrition store);
- In emergencies, use special ointments, creams and gels for muscles that can be purchased in any store (for example, Ben-Gay, Diclofenac).
to eat and drink
You lose fluids when you exercise. Therefore, drink water, juice, compote or milk after the run. This should be done in small sips over many approaches so your blood volume doesn't increase drastically. A lack of water in muscle cells slows down their recovery after a run. Proper nutrition is also important.
Be aware of your food. Eat foods rich in vitamins (C, E) and micronutrients (potassium, calcium, magnesium). This improves the metabolic processes in the calf.
diagnosis
If none of the above reasons does not apply to you.you should see your family doctor. He will refer you to a surgeon or ask you to have tests and x-rays done. You may have symptoms related to your metabolism, your joints, or your spine. Your doctor will give you recommendations for treatment and continued physical activity.
If you have taken the available measures to prevent calf pain but it still occurs, here are a few things you should do after a workout:
- Take a shower. Point the spray gun at your right foot. Let the warm water flow slowly down to your knees. In this way you massage and relax the calf muscles. Repeat the movement 10-20 times, starting from the bottom. Massage your left leg in the same way.
- After finishing the water treatment, Lie comfortably on the sofa and lift your feet up.Put your feet against the wall. Stay in this position for 10-15 minutes and try to relax your leg muscles. You should feel the blood flowing through the blood vessels.
- for an hour keep your feet free from strain when doing housework or other chores.
It's a good idea if you have someone give you one a light calf massage. No special training is required: light kneading alternating with stroking in the direction of the heart helps to rebuild muscles.
Caution!!! Do not perform the massage alone. No matter how experienced you are, you will have to make an effort. Your calves will not fully relax.
How to strengthen your blood vessels through diet
The main enemy of the cardiovascular system is cholesterol. This substance causes the blood vessel walls to thicken. Therefore, it is useful even in moderate concentrations.
There is a complex of foods that have a capillary protective effect. This includes:
- fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C;
- Legumes;
- buckwheat;
- herbs (especially sorrel);
- Fish;
- Milk;
- Seafood.
Decoctions of various berries, especially rosehip and black chokeberry, are very useful.
Healthy food doesn't mean tasteless. Olive oil, cayenne pepper, and turmeric can both improve circulation and add flavor to a dish.
Your diet should be adjusted if it contains unhealthy foods. It is not possible to strengthen blood vessels if you constantly eat fast food, drink coffee, drink alcohol and smoke. They have the opposite effect.
Vitamins to strengthen capillaries
There are many nutrients that are beneficial for cardiovascular health. The best way to strengthen the vascular epithelium is the vitamin groups:
- A (contained in carrots, beef liver, fish, broccoli, cheese, apricots, melon);
- B (contained in milk, kidneys, eggs, herring and cereals);
- C (contained in citrus fruits, leafy greens, rose hips, sea buckthorn, cabbage, tomatoes);
- K (contained in plums, cucumbers, olive oil, asparagus, cayenne pepper).
Vitamins E and PP also help improve overall vascular health. Their action is mainly aimed at normalizing lipid metabolism. If you cannot get enough of the nutrients from food, you can get them from supplements like Triovit.
Swelling and Leg Pain: Disease-Related Causes
Not everyone deals responsibly with a problem like leg swelling. However, the causes and treatment can be far more serious than just fatigue or overhydration — swollen feet can be a symptom of a disease as well as a core symptom.
They can indicate the presence of a number of diseases:
- Kidney disease - characterized by poor urination, lower back pain and high blood pressure;
- Heart failure - manifested by palpitations, shortness of breath, constant weakness and severe fatigue;
- Bone and joint diseases – accompanied by pain in the upper and lower limbs and impaired motor function;
- Nervous system disorders - Patients with neurological disorders complain of movement disorders, speech and coordination disorders, involuntary muscle spasms, tics, tremors, decreased sensitivity to touch, headaches, behavioral disorders and insomnia;
- Varicose Veins and CVI (Chronic Venous Insufficiency): The first symptom of venous disease is swelling in the legs. They are minor at first but get progressively worse as the disease progresses. Leg swelling associated with varicose veins or CVI is characterized by decreasing or disappearing at night and increasing during the day. Over time, the swelling is accompanied by stretching pains and night cramps in the calf muscles, as well as the appearance of small blue-red spider veins on the skin and later dark blue and tortuous veins. In advanced stages, the skin of the lower leg becomes dry and shiny, and pigmented brown islets are formed, preceded by trophic ulcers.
Any of the above conditions can present with symptoms such as swelling in the legs. The causes and treatment of swelling are determined by an experienced phlebologist of the Yusupovsky hospital on the basis of a comprehensive examination using modern diagnostic equipment in the clinic
Lower leg edema: causes and drug treatment
Treatment of edema of any cause in the phlebological department of the Yusupov Hospital includes a comprehensive approach. The therapy scheme is developed individually for each patient by phlebologists and a team of specialists from various medical disciplines, depending on the diagnosis and stage of the disease. In general, pharmacological therapy is chosen for patients with diseases of the veins, heart and kidneys, which are most often associated with the development of leg edema.
Severe leg edema caused by heart or kidney disease usually cannot be resolved with topical treatment (gels, ointments, or massages). Getting rid of such edema requires restoring the normal functioning of internal organs, which implies the normalization of water and salt balance.
Diuretics (potassium-sparing, loop preparations, thiazides) are prescribed, as well as cardioprotective agents and potassium preparations (the latter are contraindicated in patients with renal failure).
Leg swelling caused by venous disease can be treated with both external and internal (systemic) medications.
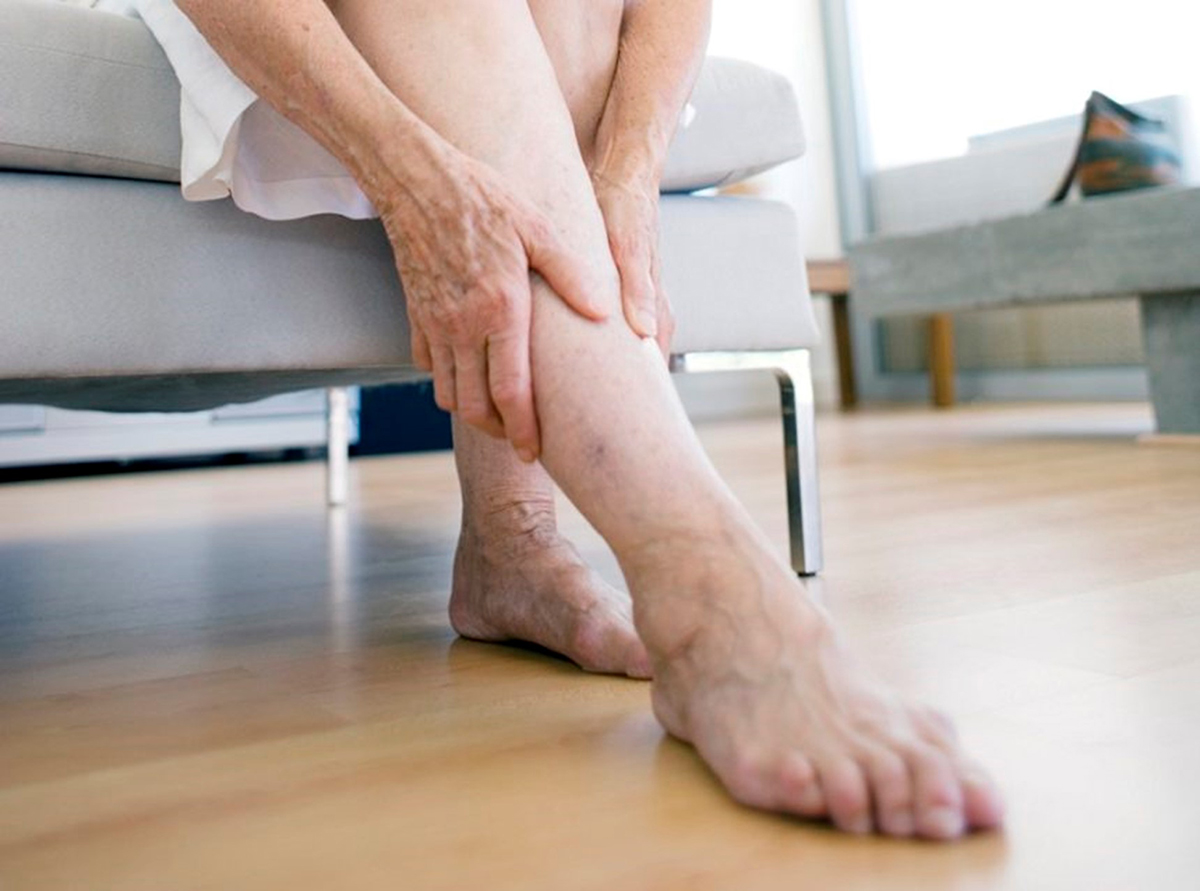
The use of external agents (phlebotonics) relieves symptoms, improves blood microcirculation, reduces the likelihood of blood clots, and reduces inflammation and swelling.
The use of systemic drugs (venotonics, angioprotectors, anti-aggregates of the latest generation) is recommended by the phlebologists of the Yusupov Hospital for the prevention or treatment of varicose vein diseases.
Swelling as a symptom should not be taken lightly, especially when the feet are acutely swollen. The causes of this symptom can vary widely, which is why early detection and treatment of the condition that caused the swelling is so important.
Read more:- Which muscles hurt after running?.
- muscle work while running.
- The calf is constipated when running.
- Why do your calves hurt when you run?.
- Shin extensor muscles (tibialis extensor muscles).
- running hurts.
- Acute pain in the calf muscle when running.
- muscles in the legs.
