* The information is not suitable for self-diagnosis and treatment and does not replace a visit to the doctor!

- Clubfoot in children: treatment, prevention, massage
- Causes of flat feet
- How to massage
- Foot
- ankles and lower legs
- When and what type of massage
- Massage for osteoarthritis
- Massage of the periosteum of the lower limbs
- types of massage
- Techniques for massaging your baby's feet
- Symptoms of varus deformity
- Correction of valgus and varus misalignments
- Massage for deformities of the lower limbs in children
- Examples of massages and exercises
- Causes of flat feet
- Diagnosis of flat feet
- Varus knee
- Varus knee - when to see a doctor?
- Massage therapy for the varus foot in a child
- When Should You See a Massage Therapist?
Clubfoot in children: treatment, prevention, massage
Clubfoot in children It is a foot deformity that causes the arch of the foot to flatten. It is very rare for flat feet to be congenital. Statistically it's 2-3 %. As a rule, it is caused by various injuries that occur during the development of the foot in the womb.
Flat feet are more commonly acquired in children. One point that new mothers should be aware of is that the infant foot is flat because there is a pad of fat on the arch of the foot. Therefore, it can be said that there is no pathological change in the foot. An accurate diagnosis is usually made by the age of 5-6 years.
Flat feet are most common in boys. There are probably parents who have already noticed something about their son: for example, that the child tires easily, that he cannot lift weights, that shoes wear out strangely. All this can be successfully corrected from an early age.
Causes of flat feet
Causes for the development of of flat feet in children as young as 2 years old are very diverse. And parents should not only know what they are, but how to eliminate them if possible. If it is not possible to do it yourself, it is necessary to seek the help of a doctor who knows about all the causes of this condition, as well as the consequences that can arise if you do not take the time to treat it , advise and speak.
- weakening of the muscular system due to overexertion or illness;
- various injuries on the feet;
- ill-fitting footwear;
- heredity;
- consequence of rickets;
- joint mobility;
- overweight;
- cerebral palsy;
- Poliomyelitis.
How to massage
The massage should include techniques that stimulate the muscles of the foot, lower leg, knee joint, thighs and buttocks.
Foot
Two small pillows or two rolled up towels are needed for a foot massage. One is placed under the foot and the other under the knee joint. The child lies on his back or sits down with his legs stretched out.
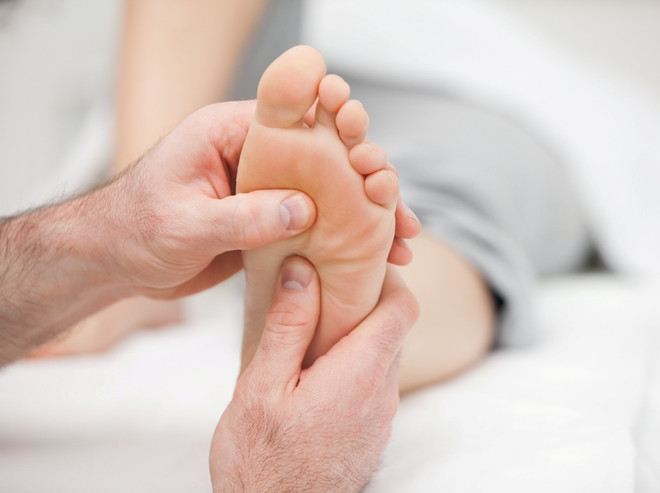

- With clean, dry hands, gently rub the sides of the foot. Try to keep hand movements in sync.
- One hand clenched into a fist rests on the foot while the other hand squeezes the foot tightly into the fist. Rub the foot intensely from toe to heel and back again.
- Place your thumbs on the top of your foot and the others on the bottom of your foot. Rub your child's thumbs from bottom to top. Then rub each toe, starting with your thumb and ending with your little toe.
- Rub the back of the foot and the sole of the foot in a clockwise direction.
- Rub the heel intensely with your thumbs. Then massage the heel area in circular, pressing movements.
- With fingers joined in a half-ring, go up from the metatarsal to the ankle, stop and make gentle circular motions around the ankle.
- Cover the entire sole of the foot with gentle, vibrating strokes - from the toes to the ankle.
At this stage, the foot massage can be considered complete. This phase lasts no more than 10 minutes.
ankles and lower legs
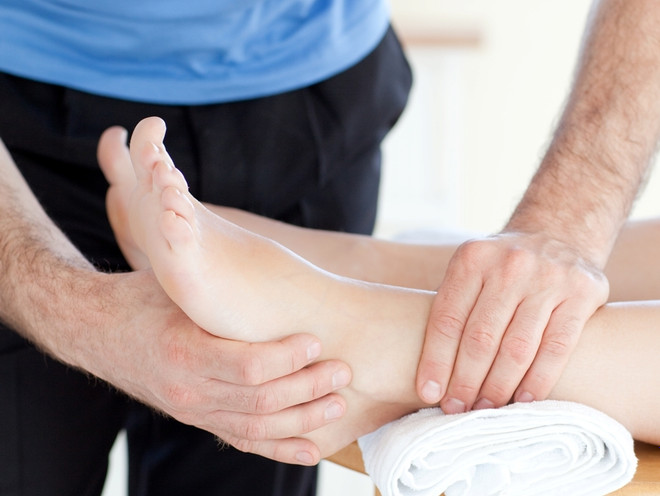
First gently stroke the ankle and then the shin up and to the side.
- Use your thumbs to gently massage the sides of the lower leg in an upward circular motion.
- Squeeze the muscles of the lower leg with your thumb and forefinger.
- Rub the upper part of the lower leg with the palm of your hand.
When and what type of massage
Children with physiological flat feet should not be massaged before the age of 2-3 years. An exception to this rule is. Congenital anomalies of foot structure. However, in this case, the massage technique is recommended individually by the orthopedist, who takes into account the degree and type of deformity.
At the With valgus deformities of the foot, the main part of the load falls on the inner part of the foot and ankle. The inner part of the foot, the ankle and the knee joint are stressed by the pronounced deformity of the foot. The aim of the massage is to relieve the musculoskeletal system in these areas of the body as much as possible.
Massage for osteoarthritis

arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is a dystrophy of the cartilage and other joint structures. The knee and hip joints are most commonly affected. In these areas, a primary arthrosis is more likely to be diagnosed, which develops without any previous illness.
In the ankle, osteoarthritis is rare and almost always secondary. It is usually caused by trauma, more rarely by inflammatory diseases. There is an excruciating pain, the intensity of which increases with exertion. Limited mobility of the joint follows. On palpation, the periarticular tissue is thickened. When moving, a crunching noise can be heard.
Massage is used as a symptomatic treatment method. It should not be viewed as a cure for osteoarthritis. Massage also does not have a significant effect on the progression of the disease. However, proper ankle massage techniques can contribute to the following
- reducing pain;
- elimination of puffiness;
- Avoiding the atrophy of muscles less stressed by the forced gait change;
- improvement of the function of the joint;
- Massage also reduces pain and swelling and prevents atrophy of muscles that are less stressed by the forced gait change.
The massage begins at the toes. The foot is then massaged by stroking and rubbing. Then you move on to the joint itself. Circular rubs, strokes and wraps follow. We massage the calves, the Achilles tendon and the area around the ankle.
The condition of the ankle differs from patient to patient at the time of the massage. Some have more pain, others less. The intensity is adjusted individually. It should be sufficient to induce hyperemia in the skin. However, excessive exertion should be avoided as it may cause discomfort or pain.
Massage of the periosteum of the lower limbs
Massage is used as one of the treatments for periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum. It is usually of traumatic origin. A single major trauma or permanent microtrauma triggers an aseptic inflammatory response. Periostitis or periostopathy is more common. One of them is subacute or chronic in nature. At first only the periosteum is inflamed. Muscles, bones, ligaments and tendons can also be affected later.
The patient lies on his back. A brace is placed under the knee. The leg is bent at the knee. The doctor massages the calf muscle. Movements are performed:
types of massage
There is no universal ankle massage technique for a specific age or situation. A technique that is appropriate for a 2-month-old child will not be effective for a 1-year-old child or for an elementary or preschool-age child.
There are the following types of massage for drumsticks and feet:
The mother or the masseur can use one of these methods. Manipulations can be performed manually or with the help of special devices such as massagers, orthopedic mats, balancing cushions, rubber-tipped balls, etc. Each of these tools can help diversify the massage technique and turn a boring and tiring manipulation into a health-giving and exciting activity.
The use of simple manipulations can be started from 5 weeks postpartum. Gradually, the list of movements on the child's foot and lower leg is expanded with the introduction of new techniques. As soon as the child can stand independently, a special massage mat with an orthopedic function can be purchased for a variety of massage exercises at home.
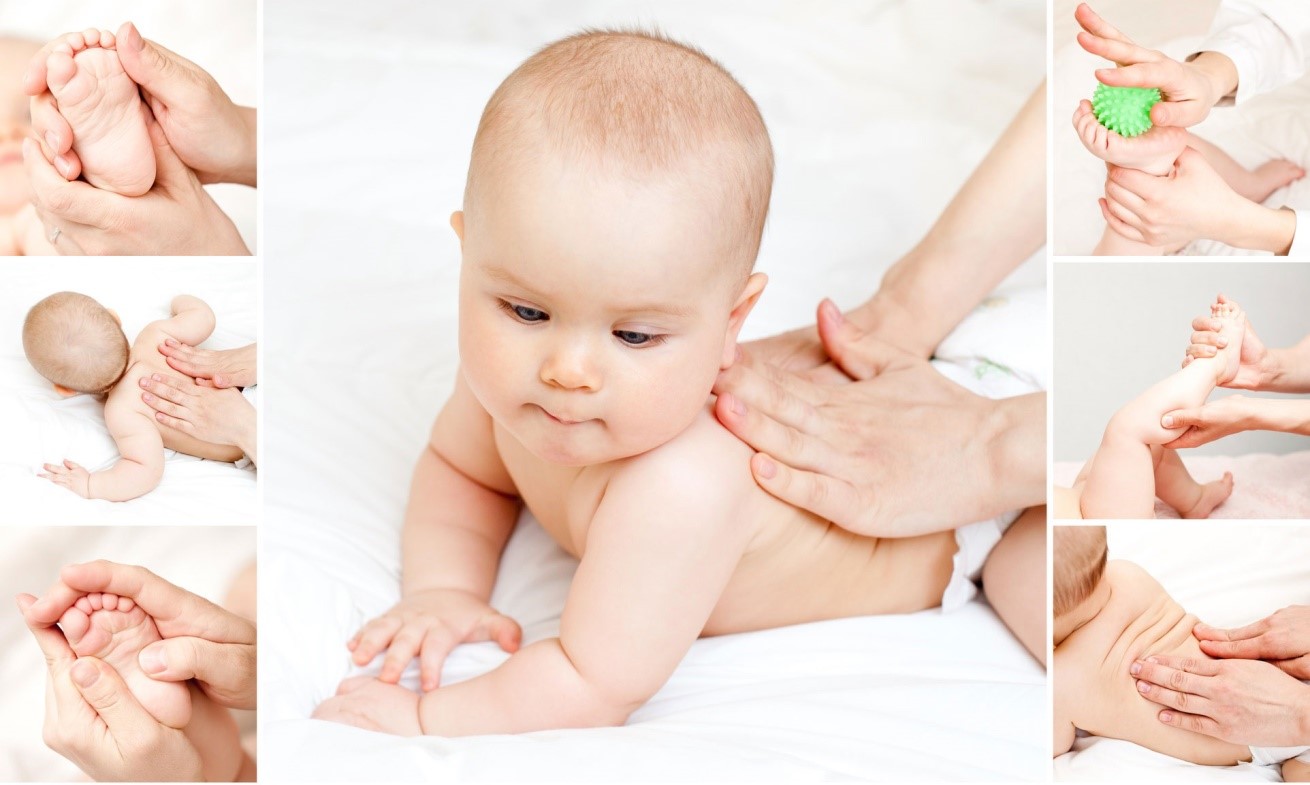
Techniques for massaging your baby's feet
Babies are of course massaged while lying down. The skin of the feet is previously greased with massage oil. The massage begins with stroking the soles of the feet and continues up to the arch of the foot. Then knead in the same way. It is important that the masseur proceeds in a targeted manner on the one hand and gently and not intensively on the other.
The soles of the feet are then massaged in L and 8 movements. Then the arch of the foot and the heel are rubbed in lightly. The sole of the foot is then rubbed in from the heel to the base of the toes. The heel is rubbed with the thumbs in the same direction. The masseur then taps the soles of the feet with his fingers and pats them with the palm of his hand.
The next step is kneading your fingers. Each toe is kneaded individually. After these measures, the back of the foot is massaged. The masseur performs slight bending and stretching movements at the ankle. The massage ends by stroking the foot as it began. The device is also stroked between the individual movements.
Older children can also be massaged while seated. Younger children are placed on the back of a chair and a roller is placed under the lower back. This prevents the pelvis and feet from tiring and the child from leaning backwards or to the side. The massage also begins with caresses. Then the masseur rubs the foot. This is done in such a way that the toes bend slightly upwards. This stretches and mobilizes the tendons of the foot.
Once the foot is slightly warmed, the masseur rubs the sole with the thumbs from the heel to the middle and then up to the ball of the toe. It is important to keep the foot slightly elevated and the knee straight. Then massage the toes - first the I and V (thumb and little finger), then the II and IV and finally the III, which is the middle toe. Once the toes are warmed up, spread the foot again as you started and curl the toes. Then bend your ankle slightly. Then twist each toe in a circular motion.
Symptoms of varus deformity
A varus foot deformity is visually noticeable as follows:
- If there is no deformation, the child has no gap between the knees when the feet are pressed against each other while standing;
- there is a band shift on the outside;
- the hips are turned slightly outwards and the shins inwards;
- the knees cannot be fully straightened;
- With an asymmetrical deformity, the spine can also be curved.
Correction of valgus and varus misalignments
Clinic Ladisten diagnoses and treats these types of abnormalities, and you can learn more about varus deformities at https://ladisten.com/pathology/varusnaya-deformaciya-nog/. The latest diagnostic methods are used here. The doctors of the clinic have extensive experience in the treatment of these and other diseases, as well as certificates and diplomas.
Complex methods are required to correct the deformity. The complex must be made to speak:
- Massage is the main method that should not be discarded because its effectiveness is superior to others. Start with a full body massage, focusing on the lower back and legs. The next step is a varied massage of the limbs.
- Therapeutic exercises are also an important part of the program and should be repeated daily. With the right exercises, the ligaments become more flexible, the muscles stronger and the joints can move better. It also improves blood circulation and normalizes tissue metabolism.
- Orthopedic Devices and Mechanisms - Wearing specially made shoes, splints and special alignment aids.
- Physical therapy.
If you do not start at the first symptoms of all these procedures, various musculoskeletal complications such as osteochondrosis, arthritis, pain in the limbs, scoliosis, leg shortening and others can develop.
Massage for deformities of the lower limbs in children

In muscular torticollis, the child's head is constantly tilted towards the affected muscle. With severe torticollis, asymmetry of the face of the skull or the forearm is often observed. This condition is caused by underdevelopment of the sternocleidomastoid muscles, which are responsible for performing various head movements. Treatment of this condition should be started as early as possible:
storage treatment. It is important that the child's torso is symmetrical and straight in relation to the head. The child should lie on a semi-rigid mattress. The child should be laid on its side more often. If the child with a wry neck sleeps on its side, then a high pillow should be placed under the head, while no pillow is used on the healthy side. It is advisable to move the child frequently, approaching him from different sides of the bed. In this case, the light of the toy and communication with the adult should be on the side of the damaged muscle.
The child should either be held on the affected side, with the back to you, with the head supported with the hand and the healthy side raised, or held in the arms, with the back turned to you, with the cheek with the child's head facing the affected side and slightly tilted towards the healthy side. Another method is to hold the child to the chest with the arms in line with the adult's shoulders; turning the child's head to the sick side and holding the position with the cheek.
Therapeutic massage and gymnastics. Lying down and rotating from back to abdomen is usually done on the sound side, but can also be done on the wryneck side.
thorax. Relaxation techniques (stroking and rubbing) are applied to the affected side, first the upper and then the lower breast.
sternocleidomastoid. During the massage, the child's head should be tilted to the affected side. Only relaxation techniques should be applied to the affected muscle: gentle stroking (from the mastoid to the collarbone), rubbing (gently with the pad of a finger) and vibration (along the lateral part of the muscle).
Examples of massages and exercises
(age of the child 2 to 3 months)
- In pose - lying on your back. General stroking of the arms and legs. breast massage Stroking and vibration massage of the neck muscles on the wry neck side. Massage of the cheek muscles on the healthy side: stroking, rubbing, kneading. Corrective gymnastic exercises in rotation on the sick and healthy side. Stroking massage of the sternocleidomastoid muscles on both sides. Lie on your back.
- Starting position: prone. General caressing massage of the back. Reflexive crawling. Back and neck caressing massage. Reflex extension of the back in pose - lying on the right and left side.
- In pose - lying on your back. Tummy caress massage. Repetition of the special neck massage technique. Caressing massage and foot reflex exercises.
It is recommended to start the massage 40 minutes after a meal or 30 minutes before a meal. The duration of the session is 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the objective. The course of the massage is prescribed by the doctor.
The massage should be performed by a medically trained person with the appropriate specialization.
Causes of flat feet
Congenital flatfoot is nowadays a sporadic phenomenon. The disorder usually develops under the influence of environmental factors and many other features. The most common cause is wearing the wrong size shoes. Children's feet should develop naturally, which is why orthopedists recommend that children wear the correct size shoe, with a solid heel counter and a heel no higher than 0.5 cm.
Hereditary predisposition can also be a cause of the disease. Children whose parents have had the same problem should be checked regularly by an orthopedist. Overweight infants are also at risk due to the high stress on the foot. Various injuries and foot diseases (rickets, polio) increase the likelihood of flat feet.
Diagnosis of flat feet
Foot massage for flat feet in children is considered necessary. In older preschoolers, flat feet are diagnosed by pain when walking and prolonged standing. A clue to the diagnosis can be the condition of the shoes - worn tread on the inside of the sole.
The main symptoms of valgus flatfoot are.
- Painful sensations in the foot area;
- swelling of the feet in the morning;
- cramps in the calves;
- inability to maintain balance while crouching;
- shoes that have become too small;
- A dramatic change in gait;
- bad posture;
- Development of a transverse bone.
The doctor has his own diagnostic methods:
- Plantography – imprinting the outline of the foot on paper using a special dye;
- Podometry – measurement of all the basic values of the foot in order to compare them with the norm values, from which even a microscopic deviation indicates the development of the disease;
- Electromyography - the latest test with modern technology;
- X-ray – the most common method of diagnosing flatfoot, which gives a picture of the degree of damage to the foot.
The severity of the disease lies in its complications: impaired cushioning of the foot, increased stress on the joints and muscles. The abnormally distributed load becomes an additional burden on the spine, which can cause problems for the entire body. The increased load on the lower spine increases the risk of an intervertebral fracture. In young children, increased fatigue can affect mental and emotional well-being.
Varus knee
C.varus olana is a deformity in which the alignment of the lower limbs resembles an O-shape. The leg misalignment usually occurs around the age of three and worsens as the child grows. Rehabilitation in the form of corrective exercises is often required, and in some cases an orthosis may be necessary.
In this defect, the tibia forms an inward opening angle with the thigh – the legs form an O-shape. Varus is measured in degrees or assessed by measuring the distance between the medial condyles of the knees with feet fully closed. A valgus position is present when the distance between Kneel exceeds 4-5 cm when the feet come together and stretch. Varus knees usually deform the whole leg, but sometimes the flexion affects just the tibia (bow legs).
Varus knee - when to see a doctor?
All babies are born with a slight misalignment of their knees because their legs are stacked on top of each other in a very small space. Almost all cases of slight varus formation in the legs can be treated spontaneous correction, even if the condition lasts up to two years. Children over the age of three are most commonly affected. The defect increases mainly in the phase of intensive growth and, as a rule, is bilateral. Sometimes the disease also affects older women and is an indication of advanced degeneration of the knee joints.
In order to make the correct diagnosis, the orthopedist asks:
The most important diagnostic tests are x-ray, which may show deformation or damage to the bones. If there is a family history of varus or valgus knee, the condition is possible be genetic.
Massage therapy for the varus foot in a child
As with the valgus deformity, it is not only performed in the foot area. The lower back, sacrum, buttocks, hips, and lower legs are also affected.
The technique and intensity of the treatment depends on the severity of the curvature and the condition of the muscles. The specialist knows the intricacies of massage for varus deformities in children. In varus, the muscles on the outside of the shin, foot, and ankle are stretched while the muscles on the inside are shortened. So the goal is to tighten or shorten the muscles on the outside of the shin and relax or lengthen the muscles on the inside. The speed, intensity and strength of the movements are different for these two areas.
Infant massage is one of the best ways to prevent and even treat many infant ailments. At this age it is not always possible to use traditional medicines. However, the body of a one-month-old baby responds so well to a massage that the effect can be compared to that of a full course of medication.
The Ryazan branch of SM Clinic has qualified massage therapists who specialize in infant massage and are experienced in working with infants. A professional massage for babies up to 3 months old can help combat the effects of birth trauma. This treatment is helpful even without direct medical indication. The preventive massage relieves the increased muscle tension that occurs in many newborns and improves peripheral blood circulation, lymphatic drainage and strengthens the muscles.
Infant massage from 6 months to 1 year old is effective against:
- Disorders of the digestive tract (not in the acute phase), such as B. regurgitation syndrome or chronic constipation;
- Cardiovascular diseases, in particular circulatory insufficiency with shortness of breath and high or low blood pressure;
- Musculoskeletal disorders, such as hip dysplasia
- Diseases of the respiratory system, such as colds of various kinds involving the deeper parts of the respiratory tract
- Disorders of the hormone system and the central nervous system, such as obesity or hyperactivity.
When Should You See a Massage Therapist?
Preventive massages can be performed as early as a baby's first week of life. If you believe that your child also needs therapeutic treatment, please contact our pediatrician first.
The doctor of the SM-Clinic will decide which approach is necessary in this case. In most cases, a general massage will be prescribed as the standard treatment for your child. The specialist treats all parts of the body equally and, if indicated, adds passive or even active remedial gymnastics. And if there is a specific problem, the child gets a foot, leg, back or chest massage, depending on the area.
Such treatments usually take place in courses. The number of sessions and their duration are determined by our therapist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the young patient. Positive results are visible after just a few sessions.
Read more:- Massage for clubfoot in children.
- Massage for flat feet.
- Footwear for children's clubfoot.
- Orthoses for valgus in children.
- Toe movement in children.
- Orthopedic shoes for clubfoot in children.
- Do orthopedic shoes help children?.
- Clubfoot in children therapeutic exercises 7 years old.
