These changes lead to increased stretching of body tissues, which is the cause of all manifestations of the disease.

- Thoracic deformities in children and adolescents - a comprehensive concept for the treatment of congenital and acquired deformities
- Congenital chest deformities in children
- Marfan syndrome
- Sporadic (non-hereditary) deformities
- Marfan Syndrome - what are its characteristics? type of inheritance.
- symptoms of the disease
- Diagnosis of Marfan Syndrome
- How is the test performed?
- TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
- The appearance of a child with Marfan syndrome.
- Examples of similar studies
- Management of pregnancy and childbirth in some types of extragenital pathologies
- Treatment and prevention of rheumatic
- achondroplasia
- Duchenne myodystrophy
- Types of hereditary diseases
- Chromosomal Diseases
- monogenetic diseases
- mitochondrial diseases
- How hereditary diseases are inherited
- Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
- Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
- Classic symptoms of Marfan disease
- Correction and treatment methods
- Marfan Syndrome Types
- Marfan Syndrome - Diagnosis in Israel
- Diagnosis of Marfan Syndrome in Israel
- The first day
- Second day
- day three
- What is the cost of treating Marfan Syndrome in Israel?
Thoracic deformities in children and adolescents - a comprehensive concept for the treatment of congenital and acquired deformities
The Turner Children's Traumatology and Orthopedic Research Center offers a comprehensive approach to the treatment of congenital and acquired deformities. Significant research is being conducted into the diagnosis and treatment of congenital and acquired musculoskeletal disorders in children. In particular, advanced methods for the treatment of congenital and acquired chest deformities have been successfully introduced in the first neonatal intensive care unit. Thanks to the scientific and clinical activities of our specialists, this area is actively developing.
An individual therapy approach is developed for each case. Treatment is conservative or surgical, depending on the condition of the individual patient. Surgical treatment of thoracic deformities is carried out within the framework of specialized and state-of-the-art medical care (VMP under the system of compulsory medical insurance for all Russian citizens, for foreign citizens on a fee basis). Preoperative examination and treatment is carried out for patients from all regions of Russia at the expense of the state.
A thoracic deformity is a congenital or acquired change in the musculoskeletal structure and shape of the chest.
The question of what causes a chest deformity in a child worries every parent. All deformities are either congenital or acquired.
Congenital chest deformities in children
Congenital chest deformities in children can be caused by genetics, but also by changes in the formation of the sternoclavicular complex, which can lead to a gradual increase in the deformity until the child or adolescent's skeleton is complete.
Congenital malformations are associated with abnormal skeletal development (spine, ribs) due to mineral and hormone imbalances. The consequences of this can be a specific development of the body:
- painful thinness;
- narrow shoulders;
- high height;
- protruding shoulder blades and collarbones;
- hollow chest on inhalation;
- long limbs;
- Curvatures of the spine (scoliosis or kyphosis).
20-65 % of the thoracic deformities are diagnosed with hereditary deformities. There are diseases and specific syndromes in which this type of deformity is one of the symptoms. So, for example, it is not uncommon for this pathology to develop against the background of Marfan syndrome.
Marfan syndrome
This condition is characterized by funneling and keel-shaped deformation of the chest.
Marfan syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms
- asthenic physique;
- arachnodactyly;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- Displacement or subluxation of the lens of the eye (or other visual disturbances);
- biochemical changes in collagen and glycosaminoglycan metabolism.
Connective tissue and cartilage dysplasia caused by enzymatic abnormalities can contribute to the development of chest deformities.
Sporadic (non-hereditary) deformities
Non-hereditary chest deformities result from teratogenic factors affecting the fetus during its development. The malformations are most often caused by asynchronous, non-harmonious growth of the sternum and costal cartilages.
Marfan Syndrome - what are its characteristics? type of inheritance.

The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene, which controls the synthesis of fibrillin, one of the most important proteins for normal life that maintains the elasticity of connective tissue. In Marfan's disease there is a deficiency of this protein, which means that the connective tissue loses its strength and elasticity and those affected are unable to withstand high physiological stress. The aorta and cinnamon ligament of the eye, which contain large amounts of fibrillin, are also damaged. Elastic fibers are abundant throughout the human body, but they are most concentrated in these structures. It is not uncommon for an aortic aneurysm to result in death.
Medical research confirms that 75 percent of Marfan syndrome cases are familial, while only the remaining 25 percent are due to a sporadic primary mutation.
It has also been found that the likelihood of having a child with Marfan syndrome increases with the age of the father: the older the father, the higher the risk.
symptoms of the disease
Marfan syndrome is associated with a number of abnormalities. The so-called 'Marfan Triad' includes damage to the skeletal bones, cardiovascular diseases and various visual disorders. However, mental performance is not affected by this syndrome.
Patients tend to have a disproportionate physique: with relatively tall stature, they have a short trunk, long arms and spidery fingers (arachnodactyly), asthenic physique with hypotonia, chest deformities, severe spinal curvatures (kyphosis, scoliosis, cervical subluxations and dislocations), and flat feet.
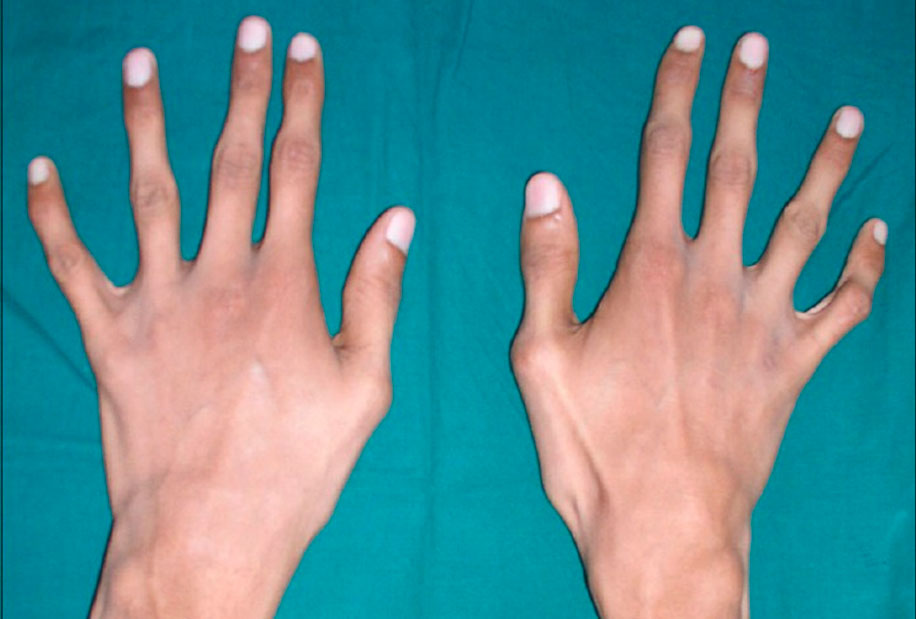
Marfan syndrome, associated with abnormalities in the circulatory system, is manifested by defects in the walls of the large vessels, especially the aorta and large branches of the pulmonary vessels, as well as malformations of the heart. These lesions often form in the developing fetus. The most severe form of Marfan syndrome, in which symptoms appear at birth, leads to progressive heart failure and death within the first year of life.
Diagnosis of Marfan Syndrome
The main method for diagnosing cardiovascular damage is the EchoCG study.
Risk factors for aortic dissection in Marfan syndrome:
- aortic diameter >5 cm;
- Dilatation extending beyond the Valsalva sinus;
- Rapidly progressive dilatation (>5% or 2 mm and 1 year in adults);
- Family history of aortic dissection.
A clinical examination and transthoracic EchoCG should be performed annually in all patients with Marfan syndrome. In children, the EchoCG is used depending on the diameter and speed of the aortic dilation. Pregnant women with Marfan syndrome are at risk of aortic dissection if the aortic diameter exceeds 4 cm. In such cases, monitoring of cardiovascular function during pregnancy and delivery is indicated.
The diagnosis of progressive aortic dilation is made by the presence of oxyproline and glycosaminoglycans in the daily urine, with excretion increasing 2-3 fold.
[10], [11], [12], [13], [14]
How is the test performed?
Vigorous physical activity is contraindicated. Massages and physiotherapeutic treatments are already indicated in childhood. Surgical treatment of eye pathologies, heart valves and aneurysms. The risk of aortic dissection in patients with Marfan syndrome can be reduced with the use of beta-blockers to lower aortic systolic pressure, which has become the basis of clinical guidelines for the management of patients with Marfan syndrome:
- In patients of all ages with aortic dilation, the greatest prophylactic effect of beta-blockers is observed on aortic diameter
The iLive portal does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
The information published on the portal is for guidance only and should not be used without consulting a professional.
Please read the rules and policies of the portal carefully. You can also contact us!
Copyright © 2011 – 2023 iLive. All rights reserved.
Simply click the 'Send Inquiry' button to send us information. You can also add a comment.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
There is no specific treatment for this disease: it is not possible to change the genes before birth. Treatment is symptomatic only and depends on the physical changes that develop in a patient with Marfan syndrome . Some complications of the pathology can be successfully corrected, and others can be treated surgically.
The patient must be examined by a team of specialists – ophthalmologist, neurologist, cardiologist, orthopedist and surgeon. The main goal of therapy is to support the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
(Adrenoblockers, antiarrhythmics, anticoagulants, etc.).
(heart valve malfunction, dilatation, pulmonary artery dissection), aorta, valve prostheses.
normalization of vision is achieved by correcting myopia (wearing glasses, lenses), treating cataracts and glaucoma, implanting an artificial lens.
For injuries to the joints and spine surgical treatment (prostheses, joint plastics, elimination of intervertebral hernias), correction of kyphosis and scoliosis using traction and manual therapy. Medications used include muscle relaxants and B vitamins. Physiotherapy and physical therapy are also used.
When the lungs are affected If the lungs are affected, surgical treatment (pulmonary drainage) is often required.
Pregnancy in patients with Marfan syndrome should be planned strictly and developed under the supervision of a team of doctors specialized in the treatment of people with Marfan syndrome. Delivery is by caesarean section only. Even before pregnancy, it is advisable to check the possible progression of the aortic dissection and, if possible, to surgically replace part of the vessel. After consulting a geneticist, the approximate risk of inheritance of the disease can be calculated.
When monitoring patients with Marfan syndrome, the following requirements for work, rest and rehabilitation should be observed:
The appearance of a child with Marfan syndrome.
[Electronic source]//URL: https://psystars.ru/referat/sindrom-marfana/
1 Zasukhina TD, Lvova TN, Vasilyeva IT Reduced ability to repair mutagen-induced DNA damage in cells from patients with Marfan syndrome. // Reports of the USSR Academy of Sciences, 1982 – 265 – 5 – pp. 1261 – 1263.
2. Lisichenko OF Marfan syndrome. / Novosibirsk, Nauka, 1986. – 163 с.
3. Prozorovskaya NN, Glinyannaya SV, Gerashchenko LP et al. Effect of beta-blocker and vitamin complex therapy on oxyproline excretion in some hereditary connective tissue diseases // Problems of Medical Chemistry, 1988 – т. 35th – № 5th – с. 99-104
4 Bubnova NI Marfan's disease in the pregnant woman and the fetus // Archives of Pathology, 1986 – № 9. – с. 59 – 61. 11. Robert S. Porter, ed. by II Dedov. I. Dedov, 'Guidelines for medicine. Diagnosis and Treatment'-M, 2015.
5 NP Bochkov. Clinical Genetics: Textbook, 3rd revised and supplemented edition-Moscow: GEOTAR-MED,2004. pp.170-173.
6 NP Shabalov. Children's diseases: textbook, 5th ed., Vol.2-SPb: Peter,2002. pp.482-484.
7. Semyachkina AN, Selverova NB, Lyubchenko LN. Endocrine disorders in Marfan disease. In the Collection: Hereditary Disorders of Growth and Development in Children. Moscow 1993, pp. 55-63.
8. Yakovlev VM, Dubiley GS Restorative treatment in connective tissue dysplasia. Omsk: Izd vo OGMA 1996. 120с.
9. Kadurina TI Inherited collagenopathies (clinic, diagnosis, treatment and follow-up).
Examples of similar studies
Management of pregnancy and childbirth in some types of extragenital pathologies
Features of hemodynamic changes. The following types of neurocirculatory dystonia are distinguished: cardiac hypotensive hypertensive 1.2 Treatment of pregnancy and childbirth in heart diseases and obstetric pathologies. Contraindications for cesarean section operations.
Treatment and prevention of rheumatic
. Lesions have become casuistic. 2 Treatment and prevention of rheumatism The treatment of rheumatism is based on the current knowledge of the etiology and . in predisposed individuals, mainly aged 7-15 years. Although it is not a mass disease, rheumatism .
achondroplasia
Achondroplasia (chondrodystrophy) is caused by a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor gene that causes abnormal activity of certain enzymes, resulting in abnormal growth and development of cartilage in the epiphyses of long bones and the base of the skull.
The disease is characterized by a short stature with a normal trunk length, a large skull with a protruding occiput, and a sunken bridge of the nose. The limbs are short, especially proximal to the thigh and humerus, and the hands are broad and short. The children are delayed in their motor development; the intellect is usually not affected.
Duchenne myodystrophy
Duchenne myodystrophy - A severe disease characterized by muscle weakness and increased plasma creatine phosphokinase levels (10-100 fold).
Early onset, from 3 to 5 years of age, is characterized by increasing weakness of the thigh and pelvic muscles and a gradual increase in calf muscles, shoulder girdle, back, abdomen, etc. A duck-like gait occurs. The disease is steadily progressing and children aged 10-11 are bedridden. Pseudohypertrophy of the calf and gluteal muscles is observed due to the replacement of muscle tissue with connective and adipose tissue. In many cases, due to muscle atrophy, there is a flexion contracture of the thigh, knee and upper limb joints. The deep tendon reflexes decrease early. There is a tendency for some decrease in mental performance. The life expectancy of the patients is 20-35 years.
Types of hereditary diseases
Hereditary diseases are divided into chromosomal, genetic and mitochondrial diseases.
Chromosomal Diseases
Chromosomal diseases are caused by changes in the number or structure of chromosomes. They are characterized by common features: low birth weight and stature, mental and physical retardation, delayed and abnormal sexual development, etc.
Chromosomal diseases are rarely inherited. In more than 95 % cases, the risk of having another child with chromosomal abnormalities in the family is no higher than in the general population.
Chromosomal diseases with abnormal chromosome number include:
Chromosomal diseases with chromosomal abnormalities – Di Giorgi syndrome, Wolff-Hirschhorn syndrome, Kitts syndrome, Alfie syndrome, Orbeli syndrome.
monogenetic diseases
Monogenic diseases are caused by DNA damage at the gene level. The number of monogenic diseases is estimated at up to 5,000.
Features of monogenic diseases include:
- Various forms of mental retardation,
- hearing, vision,
- dysplasia of the skeletal system,
- Diseases of the nervous system, endocrine system, immune system and other systems.
Some of the most well-known monogenic diseases are. Cystic fibrosis, hemophilia A and B, Gaucher disease, Duchenne/Becker myodystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, color blindness.
Serious monogenic diseases can be diagnosed by prenatal diagnosis and by determining mutations in the parents with the Atlas Genetic Test.

What can I find out through a genetic test?
mitochondrial diseases
Caused by genetic, structural, and biochemical defects in mitochondrial function that result in tissue respiration disorders.
How hereditary diseases are inherited
The human body is made up of trillions of cells. Each of them has a nucleus containing chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of tightly coiled strands of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
Genes are instructions for assembling proteins in our body that determine certain characteristics of each individual, such as: B. the eye or hair color.
Most body cells usually contain 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs. Each of these 23 pairs inherited one chromosome from the father and one from the mother. Of the 23 pairs, 22 pairs are identical in female and male organisms, and the remaining pairs determine whether one is male (XY) or female (XX).
Mutations that cause hereditary diseases can be inherited in a dominant or recessive manner.
Dominant inheritance means that only one copy of the gene - from the mother or father - needs to have the mutation (or pathogenic gene variant) for the trait or disease to appear. In the recessive type, on the other hand, a person inherits two altered copies of the same gene.
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
In autosomal dominant inheritance, a disease is genetic if a person has at least one mutated gene and that gene is not on the sex chromosomes (X and Y).
Huntington's disease and Marfan syndrome are two examples of autosomal dominant diseases. Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are also associated with breast cancer, are inherited according to this pattern.
Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
In autosomal recessive inheritance, both copies of the gene are mutated. In order to inherit an autosomal recessive disease such as cystic fibrosis, spinal muscular atrophy, or phenylketonuria (PKU), both parents must be carriers.
Classic symptoms of Marfan disease
The classic symptoms of the disease are a tall, slender stature, a curvature or scoliosis of the spine, long arms and legs disproportionate to the trunk, long thin 'webbed' fingers and underdeveloped muscles. Their skin is fragile and stretches easily while they have an increased tendency to bleed. Cardiovascular examination reveals widening of the aortic arch and various types of valvular heart defects.
Myopia is quite common and occurs in more than half of all patients with Marfan syndrome, due to the spherical shape of the lens, the altered refractive power of the cornea, and the deformation of the eyeball itself.
There are also changes in the iris that are associated with increased tissue stretching. As a result, defects in the iris called colobomas form, and the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye can be closed by the stretched iris tissue, leading to an increase in intraocular pressure, that is, the development of glaucoma.
Partial or complete rupture occurs due to the stretching and weakening of the ligaments that hold the lens together, called the cinnabar ligaments. Either there is a subluxation of the eye lens, in which the eye lens is displaced due to a partial tear of the ligaments, but is still supported by the remaining ligaments. Or the ligaments completely detach and the lens of the eye moves down into the eye socket, being free to change its position - the lens of the eye is displaced. In addition, lens opacities or cataracts develop earlier and more frequently than in healthy people.
Glaucoma occurs when the drainage of fluid from the eye through the angle of the anterior chamber is compromised because an abnormal iris or a misaligned lens blocks the drainage pathways for fluid in the eye.
The retina also becomes overstretched, increasing the risk of peripheral chorioretinal dystrophy—local thinning of the retina that can lead to retinal detachment.
Correction and treatment methods
Myopia can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Cataracts or significant lens displacement that affects vision or promotes the development of glaucoma require surgery to remove the lens and insert an artificial intraocular lens.
In retinal dystrophy with a high risk of retinal detachment, prophylactic laser surgery is performed – small laser burns are used to strengthen the retina in areas of retinal thinning. If detachment occurs, surgical treatment is inevitable.
Marfan Syndrome Types
The most common symptoms of Marfan syndrome include:
- skeletal system. – There are signs that distinguish patients with Marfan syndrome from healthy people. These patients tend to be unusually tall. Their limbs are significantly elongated, and their fingers are thin and unusually long. This form of the limbs is called arachnodactyly. It is not uncommon for scoliosis to develop during childhood and the rib cage may be funnel-shaped or alternatively keeled. In the first case the thorax may be depressed, while in the second case it may protrude. Anomalies such as B. flat feet can be observed.
The toes can deform and snap off like hammer toes. The joints are generally very flexible, which can sometimes lead to dislocations. In addition, all of these abnormalities can manifest themselves as chronic joint and muscle pain. The easily extensible skin tends to develop stretch marks (striae). Sometimes the voice can be altered, which can be due to a high 'Gothic' palate, a small jaw or a misaligned tooth.
- On the visual side – It is not uncommon for the lens to displace or subluxate (ectopia) due to weakening of the zinnar ligament on which the lens is suspended. In this case, there are various refractive errors (myopia, astigmatism). This manifests itself in a reduction in visual acuity. Patients with Marfan syndrome can also develop glaucoma and retinal detachment.
- cardiovascular diseases – Due to the weakening of the connective tissue fibers, heart valve diseases can occur. So, for example, mitral and aortic valve prolapse is detected, disrupting normal hemodynamics. Pathological changes in the wall of the aorta lead to the formation of aneurysms or simply to enlargement of the aorta at the site of the highest blood pressure. With such a disease, there is a risk of sudden rupture of the aneurysm and the wall of the aorta, which is complicated by massive internal bleeding, often incompatible with life. Cardiovascular disorders usually manifest themselves as dyspnea, cardiac arrhythmia, tachycardia, angina pectoris and increased fatigue. Peripheral circulatory disorders can manifest as persistent chills in the distal extremities.
- disorders of breathing - Abnormal connective tissue in the lungs can cause spontaneous pneumothorax. Air can escape from the lungs and accumulate in the pleural cavity;
- Involvement of the central nervous system – Due to a defect in the connective tissue fibers, patients with Marfan syndrome experience stretching of the dura (dural ectasia). This pathological condition is manifested by pain and neurological abnormalities in the lower back and lower limbs, aggravated by standing.
Marfan Syndrome - Diagnosis in Israel
The diagnosis of Marfan syndrome is based on the presence of the above symptoms. Diagnosis is made when four different musculoskeletal symptoms are present in combination with symptoms from other body systems. The patient's family history and the occurrence of the disease in close relatives are also considered in the diagnosis. When pathology of various organs and systems is detected, the necessary examinations are performed: ultrasound, CT, MRI, ophthalmological examination, angiography. The diagnosis can be verified by molecular genetic testing to confirm the presence of the pathological gene.
An etiological treatment of Marfan syndrome does not yet exist. Today, however, modern diagnostic and therapeutic measures are available that help patients with this diagnosis to do everything possible to prolong their lives. Regular visits to the cardiologist are important for patients with Marfan syndrome. After a thorough examination of the patient, the doctor will prescribe medication to reduce the risk of damage to the heart valves. These may include beta blockers to lower heart rate, heart rate and blood pressure.
Prevention of aortic rupture plays a special role in the treatment of Marfan syndrome. If the aneurysm bulge progresses, surgery to occlude the aneurysm, reinforce the wall, or create a shunt is recommended. Surgical treatment may also be required if the spine is severely deformed. Various physiotherapeutic techniques have a positive effect on the musculoskeletal system.
Quality symptomatic treatment of Marfan syndrome allows sufferers to lead active lives.
Danger! All fields of the form are mandatory. Otherwise we will not receive your information. Alternatively, you can also use the [email protected] address.
Diagnosis of Marfan Syndrome in Israel

Patients who come for treatment undergo a comprehensive examination. The purpose is to determine the stage and severity of the pathologies already detected, as well as to obtain a maximum of information about hidden risks and the risk of further complications. Molecular genetic testing is recommended for anyone with a family history of Marfan syndrome. There is a 100% chance that an abnormal gene will be detected, so treatment can begin as early as possible.
The Top Assuta clinic has its own diagnostic center, where all the tests necessary for the diagnosis can be performed in one place. Patients arriving on their own are screened on a first come, first served basis, while patients who have arranged their travel through the clinic's official representatives in their country are screened on a pre-approved schedule. This schedule provides that all necessary diagnostic procedures can be performed in three days.
The first day
Arrival, meeting with the treating doctor, consultation and examination. On physical examination, the diagnosis is confirmed based on 4 symptoms and the presence of relatives with the same diagnosis. In total, there are about 30 signs that can indicate the presence of such a disease. An experienced and competent doctor will be able to recognize them. If the doctor does not speak Russian, an interpreter will be provided. You can choose the doctor before you leave by reading the CVs of the specialists on the clinic's website.
Second day
All kinds of research, laboratory and instrumental research:
day three
A consultation is held to discuss the results of the examination, in which specialists from various specialties take part: cardiologist, ophthalmologist, orthopaedist, pulmonologist, etc. During the consultation, the diagnosis is confirmed and clarified, and a treatment program is developed that promises the best results.
What is the cost of treating Marfan Syndrome in Israel?
Treatment is 30-50 % cheaper than in countries with a similar treatment efficiency for this pathology. It is important to know that the cost of treating Marfan syndrome in Israel depends on the individual characteristics of the disease, damage to various systems and organs, and the choice of treatment strategy.
- Sustainable improvement in the patient's condition;
- elimination of serious complications by the most sparing means possible;
- Use of advanced techniques and innovative devices;
- Experienced and highly qualified doctors;
- A comfortable hospital environment;
- competitive prices for the therapy.
- Marfan syndrome at a glance.
- Marfan syndrome in newborns.
- Marfan syndrome.
- Ehlers-Danlo Syndrome.
- Charcot-Marie foot.
- Treatment of short leg syndrome.
- ectrodactyly.
- paresis of the lower body.

