The patient remains in this state until the injury has healed. After the cast is removed, it is fixed with a special splint, and the splint is removed for physiotherapeutic and hygienic treatments.

- TREATMENT METHOD FOR BRIDGE in the lower trunk area with violation of the SYNDESMOS of the BETH HEAD Russian patent of 2006, according to MPK A61B17/56.
- Similar patents RU2282411C2
- Symptoms of a fracture
- treatment of the fracture
- Home ' Directions ' Fractures of the Lower Extremities ' Treatment of Fractures of the Tibia.
- Fracture of the fibula
- Restorative physiotherapy
- types of surgical techniques
- rehabilitation
- rehabilitation
- treatment of fractures
- Immobilization methods
- With positive repositioning.
- In case of a fracture with dislocation
- With the transversal type.
- When both bones are affected
- surgical treatment
- stages
- Consequences after treatment
TREATMENT METHOD FOR BRIDGE in the lower trunk area with violation of the SYNDESMOS of the BETH HEAD Russian patent of 2006, according to MPK A61B17/56.
The invention belongs to medicine, especially to traumatology.
It is known to treat a fracture of the lower third of the fibula with damage to the intertibial syndesmosis and outward displacement of the foot by closed manual repositioning and immobilization with a plaster cast [1]. The disadvantages of this method are that it is not possible to accurately position the fibular fractures, bring the tibia close to the syndesmosis and completely eliminate the displacement of the foot. In addition, compression of the cast can cause epidermal blisters to form, followed by infection. This can lead to misalignment of the fibula, instability of the ankle joint and severe dysfunction with pain syndrome.
Open reduction with fixation of the fibula with a spoke and clamping of the tibia at the level of the syndesmosis with a lag screw is known for the treatment of this injury [2]. However, with this method, a closed fracture is converted into an open fracture, which can also lead to inflammation and osteomyelitis, and overtightening of the lag screw through the syndesmosis can lead to synostosis between the tibia with significant restriction of movement in the ankle joint and subsequent development of deforming osteoarthritis .
The transosseous osteosynthesis method with the Ilizarov device was chosen as a prototype because its technical solution comes closest to the reported method [3]. This method involves assembling a device consisting of two annular and one semicircular supports connected by threaded rods and a semicircular support of a movable reducer. An olive spoke is inserted externally through the middle third of the tibia and secured in the proximal annular support. A second spoke with an olive is inserted 6-8 cm above the epiphyseal joint on the inside of the tibia and anchored in the distal annular holder. The olive spoke on the outside of the heel bone is pushed through the heel bone and anchored in the semicircular bracket. Congruence at the supraspinatus joint is restored by traction. A spoke with an olive from back to front (in the sagittal plane) is inserted through the distal fibular fracture at the level of the syndesmosis and anchored in the semicircular holder of the mobile repositioning node. The disadvantage of this method is that during syndesmosis repair, the radius is inserted through the distal fibular fracture in the sagittal plane and bulges, creating pressure on the soft tissues and causing wounds with possible infection. This can also lead to osteitis. With this type of distal fixation, the angular displacement of the fibula in the sagittal and frontal planes is not eliminated. This leads to a disproportion in the intercondylar syndesmosis, the development of osteoarthritis with pain syndrome and functional restrictions in the ankle joint.
Similar patents RU2282411C2
- Pankov Igor O.
- Emelin Alexei Lvovich
- Vladislav Rustemovich Nagmatullin
- Khachatryan Azat Gagigovich
- Vasily Ivanovich Rusanov
- Andrei Gennadievich Chibrikov
- Chekulaev Yevgeny Anatolyevich
- Anatoly Barabash
- Yuri Anatolyevich Barabash
- Balayan Vardan Dzhivanshiovich
- Magomedov Umar Akhmedovich
- Ramil Saudatovich Salikhov
- Pankov Igor Olegovich
- Plakseychuk Yuri Antonovich
- Solovyov Vyacheslav Vsevolodovich
- Ilya Sutyagin
- Burtsev Aleksandr Vladimirovich
- Sergei Nikolayevich Khoroshkov
- Ilya Sutyagin
- Burtsev Aleksandr Vladimirovich
- Gilew Mikhail Vasilievich
- Yuri Valeryevich Antoniadi
- Pomogaeva Elena Vyacheslavovna
- Elena Alexandrovna Volokitina
- Dmitri Nikolayevich Chernitsyn
- Fyodor Zverev
- Dmitri Shiryakov
- Ivan Tsybulko
- SN Khoroshkov
- Sergei Nikolayevich Khoroshkov
- Bogdanov Aleksandr Vladimirovich
- Chemianov Georgi Ivanovich
- Valery Galukhin



Symptoms of a fracture
The tibia is the part of the leg from the knee to the heel that is made up of two bones: the fibula and the tibia. The fibula is a long bone that, together with the tibia, allows us to move our leg.
A fibula fracture has very specific symptoms and clear signs that make it difficult to confuse it with a sprain or sprain.
- Severe pain syndrome.
- Severe deformity of the lower limbs.
- Inability to support yourself on the injured leg (combined with a tibia fracture).
- Swelling of the lower leg.
- The formation of bruises.
It should be noted that a fracture of the fibula in a child does not show such obvious symptoms, so the injury may only be recognized after some time.
treatment of the fracture
Of course, treatment depends entirely on the severity and type of fracture. The simplest treatment is a closed fracture without displacement or complications. Treatment is limited to applying a cast over the entire shin bone up to the knee joint.
The most severe form is the fracture of two bones: a small bone and a large bone. Compound fractures with displacement, spiral fractures and multiple fractures also occur. The level of the bone fracture also plays an important role. For example, with a transverse fracture, regeneration occurs faster than with an oblique fracture. Complex fractures of the fibula often result in skeletal traction, in which the bone is repositioned.
To avoid the consequences of the injury, the doctor's advice and the rehabilitation period after the main treatment of the fracture should not be neglected. Physiotherapy is very effective. To restore muscle activity and normal blood circulation, massage or therapeutic physical training is recommended.
- Necessity of fibula fixation in tibia fractures 2016.02.05 Necessity of fibula fixation in tibia fractures
- Cartoon of Orthopedics Kiev, Ukraine 02.07.2015 Cartoon of Orthopedics Kiev, Ukraine
- Treatment of the dislocation of the end of the clavicle 10/29/2014 Treatment of the dislocation of the end of the clavicle in the acromion
- Treatment of a luxated clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of a luxated clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of a luxated clavicle
- Treatment of fractures of the lateral end of the clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of fractures of the lateral end of the clavicle
- Intracranial internal fixation of collarbone fractures 2014.10.29 Intracranial internal fixation of collarbone fractures
- Treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the clavicle 2014.10.29 Treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the clavicle
- Treatment of clavicle fractures and dislocations of adjacent joints 2014.10.29 Treatment of clavicle fractures and dislocations of adjacent joints
- Postoperative treatment of fractures of the scapula 10/29/2014 Postoperative treatment of fractures of the scapula
- Surgical approaches in the treatment of fractures of the scapula 10/29/2014 Surgical approaches in the treatment of fractures of the scapula
Home ' Directions ' Fractures of the Lower Extremities ' Treatment of Fractures of the Tibia.
Treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the tibia without displacement. For isolated tibial fractures without displacement, immobilization is performed with a circular cast on the knee joint in the lower and middle third of the fracture and in the middle of the thigh in the upper third of the fracture. In the case of oblique fracture planes, no axial loading should occur until 2 months after the injury.
For transverse fracture planes, dose-dependent loading can occur 4-6 weeks after injury. The duration of immobilization is 2.5 to 3 months. Restoration of ability to work after 3-3.5 months.
For isolated fracture of the fibula The lower third of the fibula is covered with a U-shaped plaster cast up to the knee joint, and the upper and middle third of the fibula on the lower leg is covered with a plaster cast. The immobilization lasts 4 weeks, from the 2nd week onwards a measured load is possible. The ability to work is restored after 4-5 weeks.
Fracture of the fibula
A fracture is an injury that results in partial or complete loss of bone integrity due to excessive stress on the bone. One of the most common lower limb injuries is a fracture of the fibula. Like other fractures, it can be the result of a severe traumatic impact that exceeds the strength of the bone, or it can be the result of a disease that involves changes in the bone structure.
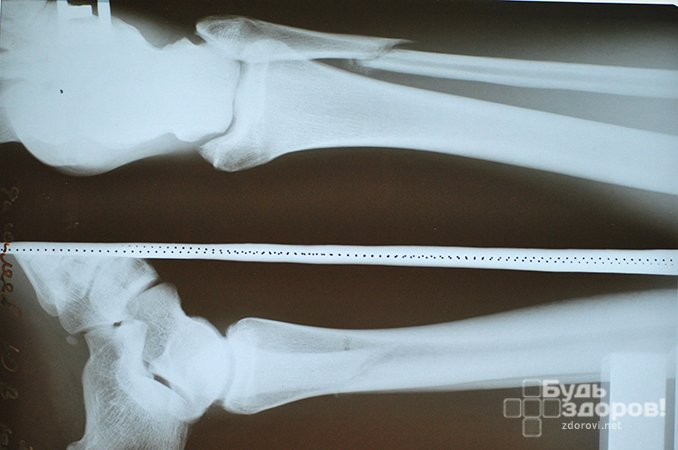
The legs are exposed to enormous strain every day. Increased weight, impaired motor coordination and muscle weakness make the situation worse. It is not uncommon for the shin bones to be unable to cope with this stress and begin to break. The result is a fracture.
Restorative physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an important step towards recovery. This can be UHF or Ray, but also any other physiotherapy that the doctor prescribes. This treatment focuses locally on a specific pain point and allows:
- accelerate bone fusion and healing processes;
- to relieve weeks of swelling and pain;
- to improve and restore blood circulation;
- Reduce muscle spasms and relax.
- Walk around the room for 5 minutes. If the healing dynamics are positive, the duration of walking can then be increased gradually from day to day, although you should consult your doctor beforehand.
- Abduction of the foot laterally at an angle of 30 degrees, hold for 5-6 seconds, 10 repetitions.
- Turn your foot left and right 10 times each.
- Swing your foot back and then forward, 10 times each.
- From a standing position, slowly and gently lift onto your toes (on two!).
- Supine exercises: leg raises, bicycle, scissors, foot rotation.
types of surgical techniques
The procedures are classified according to the location, the method of tissue removal and the type of bone graft. The structure of the shinbone or thigh is corrected. Classification according to the type of plasticity includes open, closed, lateral and straight osteotomies. The correction of the shinbone can be high or low. The specific surgical technique is selected individually by the doctor based on an initial examination.
- Closed wedge. A skin incision is made in the lateral or anterior area of the knee to gain access to the upper part of the tibial epiphysis or the lower part of the femoral epiphysis. Once the skin is removed, the exposed bone surface is secured with metal plates or staples.
- Open wedge. After cutting the skin in the front or side of the knee, an incomplete osteotomy is performed. The tip of the tibia is split in two and a diastasis is created. The bony areas are then fused with a metal plate and an autograft from the patient's pelvis.
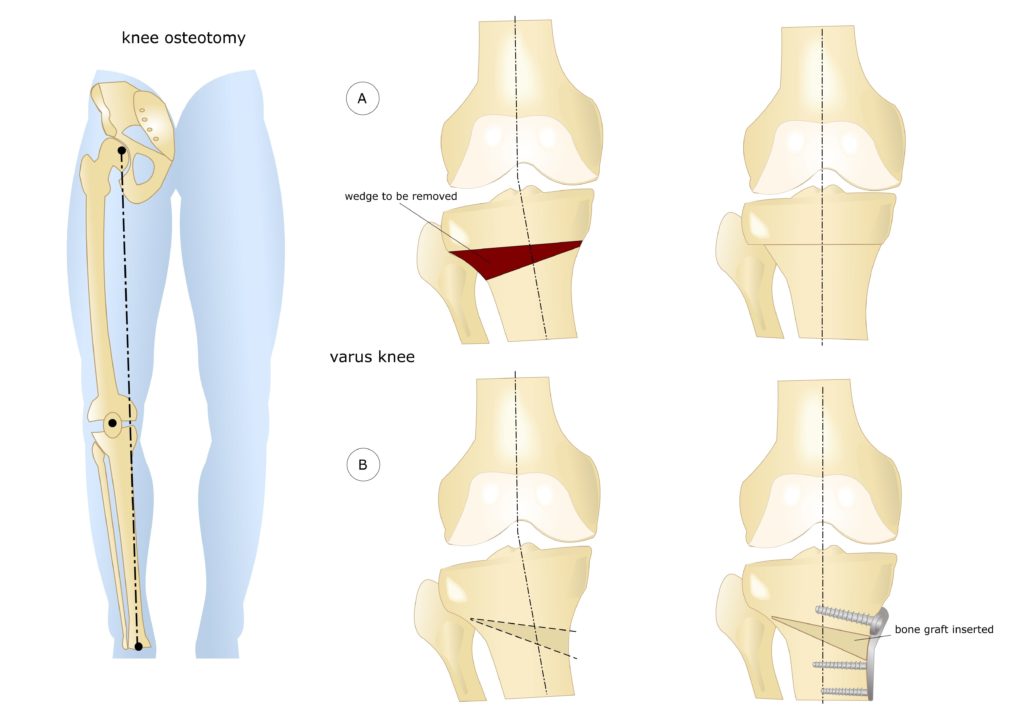
Osteotomy of the knee joint: a visual representation of the procedure.
The bone tissue is removed using an osteotome. To avoid damage to the blood vessels and nerves that run through the knee joint, the correction is carried out under X-ray or fluoroscopic control. After plication, the skin is sutured and the lower extremity is fixed with a cast or splint.
There is no single surgical technique that is suitable for all indications. When choosing the surgical technique, the doctor will take the planned correction angle into account. Imaging techniques help to reconstruct the axis of the lower extremity more precisely. In modern orthopedics, the most commonly performed technique is an open wedge osteotomy of the tibia above the tuberosity.
rehabilitation
The long-term results depend on the rehabilitation measures. After the operation, the doctor conducts follow-up examinations and selects methods to restore mobility of the knee joint. Rehabilitation goals include pain control, prevention of postoperative complications, and restoration of lower limb muscular system.
- Physiotherapy: electrical stimulation, cryotherapy and heat therapy. Physiotherapy relieves pain and reduces tissue swelling in the postoperative period.
- Therapeutic massage. Manual therapy improves blood circulation in tissues, relieves pain and normalizes muscle tension.
- Therapeutic exercises. The exercises can be done at home. The main goal is to restore flexion and extension of the knee joint.
- Orthopedic rehabilitation to prevent recurrence. The patient should wear a knee brace or elastic bandage to stabilize the joint. In the first postoperative period, a cane should be used and shoes with orthopedic insoles should be worn to reduce the load on the articular surfaces.
The rehabilitation plan is drawn up by the orthopedist and physiotherapist. Therapeutic medications are administered. Full recovery of motor activity occurs within a year.
rehabilitation
To avoid side effects and shorten the recovery time, rehabilitation of the fibula fracture should be carried out. This begins with the movement of the toes and the rotation of the foot immediately after the cast is applied. If horizontal walking is possible, it is recommended to walk short distances using crutches.
Rehabilitation after a fibula fracture begins after the cast is removed. The doctor prescribes physiotherapy to restore blood circulation to the injured leg and muscle activity:
- LFC;
- Massage;
- laser therapy;
- diadynamic currents;
- ultrasound therapy;
- Warming;
- Magnetic therapy.

Rehabilitation after a fibula fracture may include massage.
These are administered before the cast is removed. The patient then receives further physiotherapy, massages continue and swimming is recommended.
Massages help relieve muscle spasms and pain syndromes. Both the injury site and the immediate surrounding area are massaged with pain relievers and creams.
Physiotherapy also helps regenerate the damaged tissue and improve blood circulation.
Performing the LFK exercises selected by the instructor restores blood circulation and motor functions.
To prevent negative effects, pharmacological treatment continues during the rehabilitation period: calcium preparations, NSAIDs, chondroprotectors and analgesics are used to reduce inflammation and pain and prevent complications.
Various complications can arise if the sequence of treatment and rehabilitation is not followed:
- chronicity of processes in the lower limbs;
- Interruption of ligaments, tendons, muscles, vessels and nerve bundles;
- infection of the wound;
- development of a false joint;
- appearance of detached osteochondrosis and deforming arthritis;
- Onset of disability due to amputation of part of the leg.
treatment of fractures
All fractures are usually treated conservatively and, more rarely, surgically. Whenever possible, non-surgical treatment is used to treat injuries. A non-displacement fracture is the easiest to treat.
The conservative option is to fuse and immobilize the bone fragments. The traumatologist must first immobilize the fragments to prevent subluxation and displacement of the foot.
Immobilization methods
With positive repositioning.
and confirmed by x-rays, the ankle is immobilized with a plaster cast or orthosis.
In case of a fracture with dislocation
The type of fracture must be determined. Traction may be required.
A spoke is then inserted through the bone and a weight is placed on the leg. This is how a fracture in the oblique plane is treated.
With the transversal type.
A metal plate is inserted and fixed with a plaster cast. The therapy is the same as for a simple sprain.
When both bones are affected
This depends on the fragments. If the bone fragments cannot be brought together and held in place, a surgeon is required.
surgical treatment
stages
Treatment can be divided into several phases:
- The bone fragments grow together in the open air, i.e. an incision is made in the soft tissues, the muscles are removed and the fracture site can be reached.
- Elimination of subluxation and dislocation of the foot;
- Immobilization of bone fragments with implants – pins, screws, plates.
- The ankle joint is immobilized with a plaster cast in order to create the conditions for rapid bone healing.
Consequences after treatment
The following problems may occur after conventional or surgical treatment.
- ankle joint dysfunction;
- Persistent swelling at the injury site;
- deforming arthritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- Dependence on natural conditions.
Take care of your feet!!! Use shin guards, knee pads, etc. when cycling, inline skating, skating.
The strength of your bones depends on the amount of calcium in your body. A healthy lifestyle and care can protect against many injuries.
In the event of a broken fibula, you should not despair, but rather seek urgent medical treatment. After the injury, efforts should be made to protect the legs from re-injury for the rest of life.
Read more:- syndesmosis.
- tibia and fibula.
- The intercondylar syndesmosis is the.
- function of the fibula.
- fibula.
- The lateral ankle is.
- Anatomy of the syndesmosis.
- pelvic subluxation.
