Most beginners have an underdeveloped lower leg that lags far behind the rest of the muscles. This asymmetry significantly affects the athlete's overall appearance. If a beginner has a broad torso and matchstick-thin calves, there is a clear disproportion that needs to be corrected in order not to appear ridiculous. This situation can be easily corrected with certain exercises that are suitable for both men and women.

- Physical therapy for osteoarthritis
- Specific physiotherapy for osteoarthritis
- Which muscles and joints need to be stressed?
- exercises in the gym
- Shin splits and knee extension
- Technique of exercise
- Variations of quadriceps exercises.
- Classic fitness exercises.
- Fitness training for trainers.
- Back to knee extensions in the trainer
- How important is quadriceps strength in relation to functional performance?
- Functional coordination between the vastus femoris muscles
- Why the knee hurts
- What happens when we bend the knee
- Anatomy and function of the lower leg muscles
- Front lower leg muscles
- Lateral shin muscle group
- Recommendations for training the lower leg muscles
- The 4 best exercises for the shins
- signs of injury
- Causes of a quadriceps sprain
- Which doctor should I see?
- Calf sprain in the gym
- Standing shin splints
- Alternatives
Physical therapy for osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a joint disease characterized by degeneration and wear of cartilage, often accompanied by salt deposits. As a result, any movement in a painful joint can result in pain and injury. Physiotherapy (exercise therapy) for osteoarthritis is recommended by orthopedists and rheumatologists as part of the treatment of the disease. Regular exercise can halt cartilage wear, improve ligament flexibility, and strengthen the muscles that support the joint.
Physical therapy for osteoarthritis has various tasks:
- Elimination of pain symptoms and stress on cartilage tissue.
- Improving blood supply to the joint and restoring cartilage integrity.
- Relief from muscle tension.
- Strengthening of ligaments and muscles.
- Improving the patient's well-being, joint mobility and range of motion to enable them to return to normal life and self-care.
- Reducing the frequency and severity of exacerbations.
- Improving the trophism of the cartilage tissue and stopping cartilage destruction.
Specific physiotherapy for osteoarthritis
The aim of physiotherapy for osteoarthritis is to partially relieve the joints and distribute the load evenly across the musculoskeletal system in order to rebuild the cartilage tissue. Therapeutic exercises should be performed regularly and daily to achieve lasting results. The initial exercise time is at least 20 minutes, which can later be increased to 40 minutes. The best time for the exercises is in the morning and evening. Each complex begins with a light warm-up period to warm up the tissue without tension. The movements during training should be smooth, jerk-free, pain-free and with little muscle tension.
Severe pain is a signal to stop the exercise. Exercises that directly affect the joints are excluded from the complex.
This exercise improves blood circulation in the joints and periarticular tissues, increases trophicity, which prevents degenerative processes in the joints, and strengthens the muscles and ligaments.
The load is increased gradually by increasing the number of exercises. No weights are used during the exercises. Pay attention to your breathing during the exercises: it must be even and rhythmic.
Any location and form of osteoarthritis can cause serious complications, so treatment should not be postponed.
Which muscles and joints need to be stressed?
The largest muscle in the lower leg is the triceps. This muscle forms a pronounced muscle mass on the back of the lower leg, which we call the calf. The triceps muscle is composed of the superficial calf muscle and the deep cambium muscle. Both are responsible for flexion, supination and adduction of the ankle. The triceps muscle is best used in exercises that involve raising the toes. Depending on whether the lifting is done while standing or sitting, the load is transferred to either the calf muscle (when standing) or to the cambium muscles (when sitting). In addition to strengthening the muscles, toe raising also has a positive effect on the ankle joints and improves their mobility and flexibility.

Gyms have special training equipment for the lower leg muscles. These machines allow you to train your lower leg muscles with additional weight by placing the appropriate weight on the machine. Such devices are practical and effective, but at home you have to do without them. At the initial stage of training, girls can limit themselves to training the lower leg muscles with their own weight. Later, you can increase the load by taking the weight in your hands (standing lift) or placing it on your knees (seated lift).
You can improve the shape of your calves with the following exercises:
Execution technique: Stand straight, straighten your back and lower your arms along the body. Raise yourself onto your tiptoes by counting to one. Don't move up for a moment. On the count of two, place your heels on the floor. Take 3-4 steps, 30-40 steps each. If you feel a burning sensation in the lower leg muscles during the last repetitions, it means that the load is sufficient. Once you've increased your fitness level, you can try a more difficult version of the lifts - on one leg. Use dumbbells to increase the load.
exercises in the gym

Gyms have special calf trainers for doing toe raises. The principle is the same as the lifts mentioned above: after lifting the toes as high as possible, lower the heels over the edge of the platform until the calf muscles and cambialis are fully stretched. If the exercise is performed while standing, the arms are placed under special pads and the lifts are combined with weight lifting, thereby increasing the load on the target muscles. The knees should not be bent - only the ankles are stressed. In the sitting position, the resistance caused by the load is also overcome, but here the knees are placed under the rollers. To work the entire triceps muscle evenly, you should train both standing and sitting. Remember that the calf muscle is well trained when sitting and the biceps muscle is well trained when standing.
To train your calves, you can use a leg press machine. Stand in a 45-degree inclined position with your toes resting on the bottom edge of the platform. The distance between your feet is equal to or slightly less than the width of your shoulders. Once you have removed your weight from the supports, you can begin the exercise. It consists of flexion and extension of the foot and looks like a toe press with the knees at rest. First the toes push the platform up, then the foot bends and the platform lowers. At the highest point there is a pause of 1-2 seconds. After you have completed all the planned exercises for the lower leg muscles, stretch the stressed calves with stretching exercises.
Shin splits and knee extension

Another variation of the shin splits and knee extension is performed with the barbell - the lifter places a disc on the shins and carries out the movement with it. This is considered less dangerous than the 'classic' trainer. Stretching on a trainer has been linked to anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries. However, the risk is greater if a person mindlessly lifts a weight, 'pushes' it up and then lowers it with a jerk.
Extension of the lower limbs is anatomically correct only in the plane of hip flexion, which for most people is a toe point outward. Additionally, this movement is not suitable for heavy weights. The good thing is that quadriceps relief can be done through repetitive work.
If you're worried about sustaining an ACL injury, you can train with a light elastic band or perform one-legged lunges with your toes in an anatomically natural plane.
Technique of exercise

Beginners are usually recommended to perform lower leg squats on a trainer because it is impossible to make mistakes with this exercise. This is where the internet experts are wrong. A beginner can make a mistake anywhere. For example, some people don't know that the backrest is adjustable and that the cushion back can also be adjusted. They sit on the edge of the seat and 'slide' their ankles firmly under the seat of the machine. From this position, the ACS is overstretched during takeoff. Therefore, such 'techniques' are not recommended in the fitness sector.
To perform the exercise correctly, you should:
- Adjust your back so that it is supported. Most fitness equipment has an adjustable backrest tilt and the ability to move it inwards and outwards;
- The correct starting position is one in which the back rests against the backrest, the thigh rests on the seat, the shin rests on the cushion and the angle between the thigh and the shin does not exceed 90 degrees;
- In rehabilitation, incomplete amplitude is allowed when the shaft is fixed higher than 90 degrees;
- The socks must point slightly inwards; it is better to start the exercise by tensing the quadriceps muscle.
The movement is carried out as follows:
- The downward move should not be forced; it is better to descend smoothly and gently stretch the lower leg;
- The back should be completely pressed against the backrest, including the lumbar spine;
- The extension should occur when you breathe out and the flexion should occur when you breathe in.
The variations are actually very diverse. The easiest one is to straighten one leg at a time. A version for those who have an imbalance in the development of their legs and always 'start' with one hip and only insert the other. This version of the exercise is also more appropriate if the lifter is concerned about PCC or already has an injury.
The second variant is stretching with a rubber band. Sitting on a chair, the athlete stretches the shin with the help of a rubber cushion attached to the foot. This variant is suitable for people who need to strengthen their ligaments and protect themselves from injuries.
Variations of quadriceps exercises.
Classic fitness exercises.
Squats.
The quadriceps muscle works in the eccentric phase when lowering and bending the knee joint. This function is primarily performed by the lateral, medial and middle heads. Their job is to prevent rapid flexion of the knee, to partially counteract the 'forward sliding' of the thigh against the tibial heads and to counteract gravity. The quadriceps work concentrically as they lift upward, thus extending the knee joint. Its fibers shorten and create strong tension on the patellar tendon, which helps stabilize the knee joint in the sagittal plane.
Frontal squat.
A variant in which the center of gravity is shifted slightly forward. This is usually achieved by holding a projectile (barbell, kettlebell, dumbbell or rubber dampener) in front of the body at the level of the sternum or shoulder girdle. The quadriceps muscles are worked in the same way as traditional squats, but the load is slightly heavier.
Split squat or scissor squat. In this variant, the legs are brought into a spread position. The quadriceps muscles are used in a similar way, but the main load falls on the front leg.
Lunges.
There are different variations of lunges: backwards, forwards, sideways and cross-legged. It makes sense to do the training and progression of this exercise in this order. The quadriceps are trained in the same way as described in the previous exercises, but the emphasis is shifted to different levels and the stress on different myofascial circuits.
Leg press (platform press).
The quadriceps muscle is worked in the same way as in the squat. However, in this exercise the body position is very stable and requires practically no postural control of the body. It offers the opportunity to work more concentratedly and intensively on contracting the leg muscles.
Fitness training for trainers.
For fitness trainers looking for courses that will increase their income, make them even better, and ensure they never have to worry about getting a job, we recommend the following distance learning courses:
upgrade – Tailor-made topics and targeted income increase.
Fitness trainer course – For those who want to become a personal fitness trainer.
architecture of the body – Dmytro Gorkovsky's signature full-day practice and distance theory course for fitness trainers, massage therapists and physicians.
Pregnant women – Training techniques for pregnant women and postpartum recovery.
pilates – Jekaterina Vasilenko’s online Pilates course.
Back to knee extensions in the trainer
Are knee extensions really as bad as you've been told? Maybe not when you look at the research and know how important quadriceps strength is for knee health, recovery from anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, improvement in patellar pain syndrome (PFPS) symptoms, and even physical function in the elderly .
- Lower torque, total volume, and cross-sectional area of the quadriceps muscle were observed in patients with unilateral PFBS (Kaya D, 2011).
- Bodyweight-based exercises to develop quadriceps strength increase the contact area of the patellofemoral joint, which can reduce mechanical stress on the joint, thereby improving pain and function in people with PFBS (Chiu JK, 2012).
- The most effective and convincingly proven treatment for patients with PFBS is a combined physical therapy program that includes strength training of the quadriceps and hamstring adductors as well as quadriceps stretching (Rixe JA, 2013).
How important is quadriceps strength in relation to functional performance?
- High-resistance strength training (using a knee extension machine) results in significant increases in muscle strength, size, and functional mobility in frail nursing home residents under the age of 96 (Fiatorone MA, 1990).
- Quadriceps muscle strength is an important determinant of both performance-related physical function and self-assessment in patients with knee osteoarthritis (Maly MR, 2006).
- After total knee arthroplasty, quadriceps strength was the most important correlate of functional performance (Mizner RL, 2005).
So what exactly do all these studies tell us? Decreased quadriceps strength is an excellent predictor of decreased function after PCC reconstruction, correlates strongly with PFBS, and correlates very well with poor knee function in older adults.
Functional coordination between the vastus femoris muscles
The myoelectric balance of the quadriceps muscle is essential for normal movement of the kneecap.
The muscle's proprioceptive afferents help maintain correct posture. Recent studies suggest that activation of these afferents allows the contralateral quadriceps muscle to improve coordination and therefore balance.
The PM of the thigh can activate its fibers longitudinally. It can also activate the proximal fibers when the distal fibers do not contract. When quadriceps activity is maintained, the most distal fibers are activated in the absence of the most proximal fibers (likely due to a mechanism that delays the onset of fatigue).
The contribution of the femoral MSM to the patellar tendon is small, so it is unable to generate sufficient force to medially stabilize the patella during knee extension. Rather, it stretches the femoral SMP aponeurosis during its contraction, thereby counteracting the lateral forces on the patella generated by the femoral LSM. The femoral LSM acts as an indirect stabilizer of the patella, concentrating its force along the medial axis of the thigh.
The force generated by the femoral LSM increases as the knee flexion angle increases. This mechanism is due to the length of the fibers compared to the connective tissue structure of the muscle. Longer fibers have greater strength and better elasticity or resilience of connective tissue. When the knee is extended, the LSM of the hip generates a small force to maintain the position with minimal effort.
Why the knee hurts
The knee joint is one of the most resilient joints in our body. Nevertheless, it often develops degenerative processes. This can happen due to a genetic predisposition, for example in people whose relatives have already been treated for osteoarthritis. Many people suffer from pain caused by external factors such as an unhealthy lifestyle, unhealthy habits or injuries.
Pain in the extensor muscles of the knee often occurs after intense physical activity. They are particularly progressive in old age when the cartilage tissue wears down on its own. The most common causes of stretching pain are:
- intense running;
- carrying loads for longer periods of time;
- injuries;
- Bacterial infections;
- age-related changes;
- genetic predisposition;
- Circulatory problems due to lack of exercise;
- degenerative and dystrophic changes in osteoarthritis;
- Lack of synovial fluid in the body;
- Entrapment of nerve fibers.
Regardless of the cause of the pain when stretching, knee pads can never be a bad solution.
Osteopathic doctors, representatives of alternative medicine, have their own perspective on knee pain:
What happens when we bend the knee
When we perform normal flexion and extension movements, a variety of structures are involved - bones, muscles, cartilage, nerve endings, synovial fluid, etc. If the cartilage in the knee is intact and undamaged, a person does not even notice these movements. If the cartilage surface is damaged, the nerve endings are affected during stretching - resulting in pain and discomfort.
If the body lacks synovial fluid, the cartilage wears out quickly because there is no lubrication between them. Damaged areas form on its surface - the joint no longer functions normally and every stretching movement is painful.
Part of the collagen, which is involved in the synthesis of synovial fluid, can be supplied through food – meat and fish by-products, sausage products. However, this is usually not sufficient. To restore the function of the joint, it is more correct to inject a prosthetic synovial fluid - Noltrex - into the joint and eliminate friction.
Does straightening the knee cause pain? No self-healing with coolant or gelatin
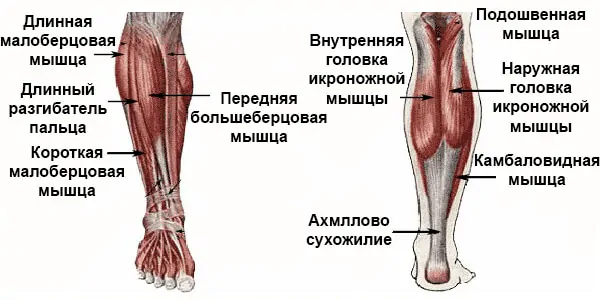
Anatomy and function of the lower leg muscles
Although the calves are considered a small muscle group due to their lack of function, the lower legs have a large number of muscles. Their structure is similar to the tightly woven bundles around the tibia and fibula. All muscles of the lower limbs and foot are usually divided into three groups according to their structure, attachments and function:
- anterior;
- laterally;
- The backstage area.
Each area has a different function, with the focus being on the rear area in terms of importance in sport. Most exercises for the lower leg muscles are specifically designed to develop them.
Front lower leg muscles
The entire anterior tibial muscle group is made up of three components:
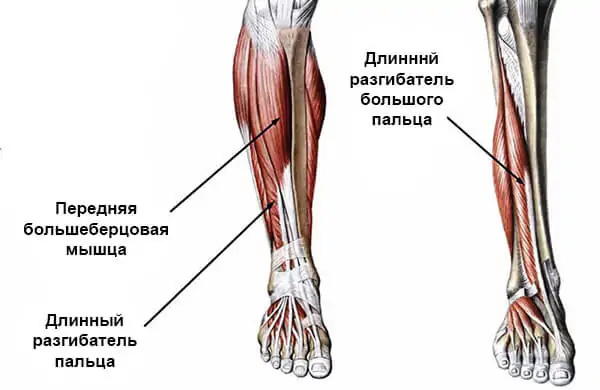
- tibialis anterior;
- Long stretch fingers;
- Long extensor thumb.
All three muscles of the lower leg act as one mechanism in anatomy, with each muscle responsible for a different edge of the foot.
The main functions are extension, elevation, supination and pronation of the foot.
Although the anterior shin muscles are not often trained in strength sports, they play an important role in cycling sports (running, cycling, etc.).
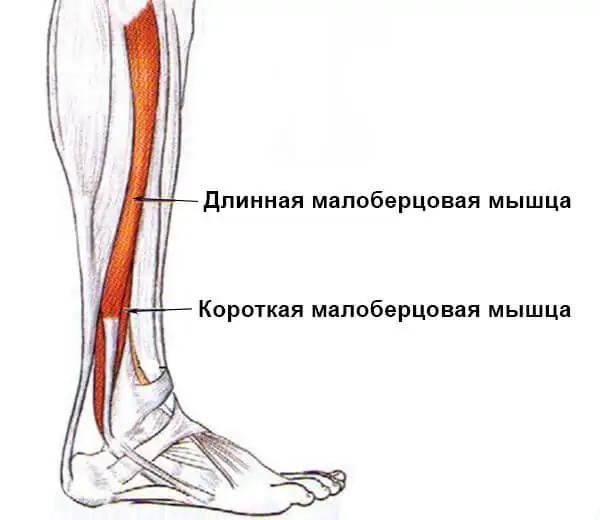
Lateral shin muscle group
Recommendations for training the lower leg muscles
The problem with training calves lies in the physiology of every athlete. For a long time it was assumed that the triceps (as the dominant muscle of the entire lower extremity) was dominated by slow muscle fibers. Therefore, the multiple repetition mode was suitable for this training. However, the MMW alignment and type of training did not promote hypertrophy, so even in some proscenium athletes calf volume remained significantly behind.
Later studies have shown that some people have up to 50-60 % fast muscle fibers in the hind limb. This made it possible to do not only repetitive training, but also strength training (i.e. work with heavy weights). So when it comes to how to pump up the lower leg, the ratio of GMV to OMV (fast and slow fibers) is crucial.
In addition to the physiological characteristics, there are also general recommendations that significantly accelerate progress:
- Alternate the types of training and monitor your progress. This will help you choose the best technique for the athlete.
- The most important indicator of well-functioning calf muscles is the burning sensation.
- When exercising, all other muscles in the body must be completely switched off. Only the ankle should be moved.
- All exercises should be performed in an elevated position to increase range of motion.
- When raising your toes, push the body up as much as possible, but the movement should be smooth and without jerks.
- The load time for shin training should be 36-45 seconds.
- Like any other muscle, the calves need rest. Therefore, you should not train this group more than 2-3 times per week.
The 4 best exercises for the shins
Anatomically speaking, the muscles of the lower leg and foot do not have many functions, so all movements are similar. The only difference is the effect, the weight and the posture.
signs of injury
The muscles of the hip include the posterior group, quadriceps, and adductors. The quadriceps muscle is the most commonly injured, especially in athletes. A quadriceps injury can be recognized by a number of features. The most common causes of sprains are incorrect, abrupt movements and exercises with excessive weight. When a dislocation occurs, the affected person feels it:
A characteristic sign is that the person is no longer able to perform the exercise that caused the sprain. It is almost impossible to determine the stage of the problem yourself. Dislocations are often accompanied by sprains, joint dislocations and fractures, so it is advisable to see a specialist as early as possible. The appearance of the clinical picture largely depends on the extent of the injury, which can be mild, moderate or severe and cause corresponding symptoms:
When the posterior muscles are stretched, swelling and limited mobility of the joint often occur. If the pain is severe, strain should be stopped immediately and the leg should be protected.
Causes of a quadriceps sprain
In most cases, a strain of the quadriceps femoris muscle is caused by a direct impact or an impact. This injury is common in sports such as football, hockey, rugby, martial arts, and others. A sprain can also occur accidentally during active games. Another cause is inadequate warm-up of the muscles before training. They are closely connected to tendons and joints, so heavy loading without proper preparation can easily result in an injury. Possible causes:
- direct and tangential impacts;
- lack of physical preparation;
- sloppy, sharp movement of the foot;
- home injury resulting from a fall;
- Leg sprain, side twisting.
The topic of sprains is particularly relevant for weightlifters. It can happen to them through:
- exercising too quickly;
- Excessive weight lifting;
- incorrect movement sequences;
- Failure to comply with the rules of movement;
- improper warm-up.
It is well known that muscles work best when they are properly warmed up. That's why it's so important to stretch and warm up before training and to give your legs a break during training. This significantly reduces the risk of injury.
Which doctor should I see?
To diagnose and treat a hip sprain, you should see a doctor, such as: B:
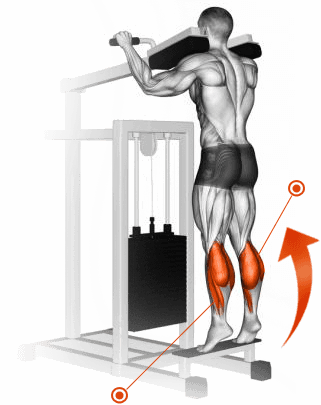
 Calf sprain in the gym
Calf sprain in the gym
To build muscle, you need fitness equipment. These are often available in 4 main variants, namely:
It is immediately noticeable that these models can be found in large sports centers and fitness clubs. In small rooms or at home, other bowls and designs dominate, which we will learn more about later.

Standing shin splints
A weighted shin splint or weighted shin splint allows you to stand on your toes to achieve the desired effect. This is handy because it allows you to position your body as needed for the best effect.
Since the technique is quite simple and the trajectory is fixed, the athlete can easily concentrate on the execution of a specific area of work. Ultimately, shins develop well through the application of heavy loads while lifting while standing. The timing of the contraction is extremely important in this exercise. The most important thing is to give the heel as much room to move as possible.
- Adjust the weight, then stand on the calf machine and adjust it to your height.
- Place your shoulders on the soft rollers that serve as supports.
- Place your feet on the platform so that your heels can comfortably go up and down.
- When exiting the device, stand on your tiptoes and after a short delay lower yourself back down.
The aim of this exercise is to push your body weight outwards. Experts advise against straightening your knees and rounding your back as much as possible. Instead, it is allowed to tense the hips. This tactic creates a stable muscular shock absorber.
Finally, you can move in a shortened amplitude until you feel a burning sensation, which is a sign of success. To transfer pressure to the medial head (inner part), curl the toes outward and splay the heels toward the lateral head (outer part).
 Alternatives
Alternatives
- In addition to highly specialized devices, other types of devices can also be used, such as: B. a wall leg press. In a semi-recumbent position, the calves are pumped up well. To do this, place your feet on the lower edge of the platform and press it together using the force of your fingers. Standing calves are loaded in a Smith machine. All you have to do is stand on some kind of elevation.
- An additional benefit comes from the leg extension machine, flexors, hyperextensors (straight, oblique), etc. Here the shins are indirectly stressed, but are quite strenuous, especially when combined with other isolation movements.
- If you don't have shin splints, you can exercise with a barbell. The barbell is placed on the shoulders (standing IP) or on the hips (sitting IP). You can also feel the strain by placing an exercise bar on the quadriceps. The dumbbells are taken in both hands if you want to raise your toes at the same time, or first in one hand and then in the other if you want to work alternately. Of course, the presence of a footrest is mandatory.
- The 'Donkey' is also possible without additional equipment, but with a partner on the back! You need to lean forward, support yourself securely on the support and let the helper jump on you. The closer you are to the lower back, the better the muscles are used.
Practice shows that the calf muscles can also be trained outside of the gym. Walking on tiptoes, jumping rope, climbing and descending stairs train this muscle a little. Only weight training will help them to be truly toned and well defined. The exercises don't have to be cyclical and repetitive - you can vary the foot rotation, body angle and exercises.
Benefit from our recommendations, be patient, and success is assured.
Read more:- Lift your heels off the floor during the squat.
- muscle work while running.
- The muscles that move the foot.
- Pain in short fibula when walking.
- Square soleus muscle.
- muscles in the legs.
- lower leg flexion.
- Exercises for the triceps tibialis muscle.
