Every year, numerous people around the world are affected by diseases that cause severe joint pain. According to global statistics, joint pain is the most common cause of disability, which can lead to loss of function in society. Until 20 years ago, joint pain mainly affected older people. Today, these problems occur in both adults and younger patients, including school-age children.

- osteoarthritis of the knee
- Causes of gonarthrosis
- Why do my wrists hurt?
- Why do my leg joints hurt?
- Is muscle pain below the knee dangerous?
- Physical activity
- Pain in the front of the shinbone
- Pain below the knee on the front
- meniscus tear
- osteoporosis
- Alternatives to knee replacement surgery
- Preparation for physiotherapy
- Exercise
- Sentence 1
osteoarthritis of the knee
Gonarthrosis is a degenerative disease of the knee joint, a chronic, non-inflammatory disease characterized by progressive destruction of the articular cartilage, accompanied by abnormal formation of the bones that form the joint and changes in the synovial membrane and synovial fluid is.
Gonarthrosis is the most common form of osteoarthritis. Many people have pain in their knees, especially after long periods of inactivity, e.g. B. after a day in the office. It is very likely that the cause of these symptoms is gonarthrosis.
This osteoarthritis often develops with age because the strain on the knee that is unavoidable in various life situations inevitably leads to wear and tear of the cartilage over the years. Initially, after lying or sitting for a long time, there is pain when making the first movement, but this quickly subsides. However, as the disease progresses, the pain in the knees increases and significantly limits the ability to move normally in everyday life.
In more than half of the cases in which osteoarthritis affects the knee, both knees are affected at the same time. In the group of patients between 65 and 75 years of age, gonarthrosis occurs in 35 % women and 21 % men.
Causes of gonarthrosis
Healthy articular cartilage in the knee has a buffering and protective function and acts as a shock absorber during movement and impact. It ensures that the bones in the hip and lower leg do not rub directly against each other.
It is normal for cartilage to deteriorate due to wear and tear as a result of the natural aging process. However, under certain circumstances this wear and tear of the cartilage can become excessive. Excessive strain on the knee, for example through heavy physical work, sport or being overweight, can lead to excessive wear and tear of the cartilage. Improperly performed sporting exercises that lead to inappropriate mechanical stress (unpredictable for the joint structure) can also have an impact. Another cause is misalignment of the feet (e.g. due to anatomical anomalies), in which the knees hit each other when walking. Gonarthrosis can also occur as a result of joint injuries or bone fractures.
Why do my wrists hurt?
A number of patients who complained of severe pain in the wrists were diagnosed with various diseases associated with inflammatory processes in the upper limbs:
- synovitis (this disease involves inflammation of the periarticular joints);
- Arthritis (patients develop inflammation directly in the joints of the limbs);
- Arthritis caused by various infectious and allergic diseases;
- Arthritis caused by diseases of the blood, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Diseases of the upper limbs, in which patients have pain syndrome, are often accompanied by skin changes and an increase in temperature. Over time, many people's joints become deformed, resulting in loss of mobility in the injured arm.
Why do my leg joints hurt?
Severe pain in the lower limbs is the result of diseases that damage the periarticular capsules or the joints themselves.
The following diseases are often diagnosed in this category of patients (after a complete examination of the patient with hardware and laboratory):
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Very often, rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints of both lower limbs (foot and ankle). Modern medicine speaks of symmetrical arthritis of the legs in this case. Patients with severe joint pain due to rheumatoid arthritis show certain symptoms: swelling, skin changes, stiffness, redness, etc.
- Podagra.
- Osteoarthritis. It can occur in both children and adults. If not treated in time, the inflammation spreads to the upper limbs. In this category of patients, as a rule, there are no obvious symptoms, except for severe pain in the joints of the legs. Some patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis may experience pain in the hip joint area.
In any disease in which patients experience pain in the joints of the lower limbs during an exacerbation, signs of inflammation (swelling, redness, etc.) may appear. Those affected cannot stay on their feet for long or have difficulty walking even short distances.
Is muscle pain below the knee dangerous?
Muscle pain in the leg below the knee is common, especially if those affected were physically active the day before. However, if the pain does not subside within four days and occurs especially at night, you should see a doctor immediately.
Why does the front of my leg hurt below the knee? Often it is very difficult to distinguish between muscle pain caused by overwork and leg pain caused by an illness, so it is very dangerous to make a diagnosis while sitting in the kitchen with friends. It's better to go to the doctor every now and then and make sure everything is okay.
Interesting!!! In medicine, muscle pain is called myalgia.
Physical activity
The main cause of myalgia of the lower leg muscles remains excessive physical exercise. Pain under the front knee can occur for the following reasons:
- Lying your legs for a long time without moving, e.g. B. on a plane or in a car. Muscle pain of this type is caused by blood congestion in the limbs, with the risk of varicose veins. The pain is usually aching and stabbing. It usually subsides when you rest. It is particularly helpful to keep your legs above your head, for example by leaning them against the back of the sofa.
- Physical activity, especially running or long walks. This phenomenon in athletes is called crepitation and is caused by micro-damage to the muscles and the buildup of lactic acid. As a rule, crepitus disappears without a trace after a period of rest.
Some even believe that if the muscles don't hurt the next day after exercise, the workout wasn't effective. This is of course a misconception, because no crunch should be felt in the trained muscles.
Pain in the front of the shinbone
Pain below the knee on the front
Discomfort below the front knee should be considered separately, as there are many causes of this pathology:
- injuries after training;
- bacterial infections;
- tumors;
- ligament injuries;
- Injuries from bruises and falls;
- arthritis and periarticular capsulitis;
- softening of articular cartilage;
- Schlatter's disease.
Pain after ligament and tendon injuries has similar symptoms:
- characteristic cracking sound at the time of rupture;
- cessation of muscle activity;
- impossibility of moving the knee;
- Stitching pain when pressing on the knee;
- crunching when moving;
- Pain radiating to the lower areas, all the way to the foot;
- hematoma;
- Swelling.
Based on the clinical picture, the doctor determines the cause of the pain. If necessary, a more detailed diagnosis is made and treatment is recommended.
meniscus tear
A torn meniscus is a common cause of pain in the front of the knee. The main symptoms are:
If a meniscus tear is suspected, a surgeon should be consulted immediately, as even experienced surgeons cannot always make an accurate diagnosis in this case.
Important: An undiagnosed meniscus tear can go undetected for a while and only cause pain when climbing stairs.
Unfortunately, if a meniscus tear is diagnosed, it can only be treated with surgery.
Also read: When does my kneecap hurt?
osteoporosis
The disease mainly affects people over 40 years old. It expresses itself through:
- pain under the kneecap;
- rapid fatigue in the legs;
- difficulty moving the knee;
- swelling;
- deformation of the knee;
- Late-stage muscle loss.
Alternatives to knee replacement surgery
The aim of knee joint replacement surgery is for the implanted tissue to fuse perfectly with the rest of the knee joint tissue. In recent years, various procedures have been developed to repair joint damage, e.g. B. the use of chondrocytes and stem cells in combination with biological therapies such as tissue engineering and gene therapy.

Where he is admitted: LG Sokolov Federal State Hospital No. 122 of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia
- Akhtyamov IF Prevention of infectious complications of knee endoprostheses / IF Akhtyamov, DV Rimashevsky, E.-DT Kurmangaliev et al. // Practical Medicine. – 2014. Т.2, №4. C. 23-28.
- Volodin YS Peculiarities of knee endoprosthesis in patients with gonarthrosis of different etiology: dr. n. med: 14.00.22 / Volodin YS – Saint Petersburg, 2007. – 24 с.
- Kornilov NN Arthroplasty of the knee joint / NN Kornilov, TA Kuljaba. – SPb., BI – 2012. – 228 с.
- Tichilow, RM Comparative analysis of knee joint arthroplasties (review of the literature) / RM Tichilow RMNN Kornilov, TA Kulyaba et al. // Traumatology and orthopedics of Russia. – 2014. – №2 (72). – C. 112-121.
- Ermolaev EK Endoprosthetics of the knee joint: Doctoral thesis in medicine / Ermolaev EK St., 1994. – 178 с.
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows the examination and treatment of injuries to various structures of the knee joint.
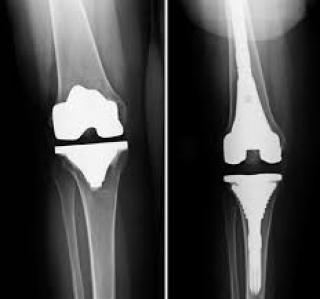
An artificial knee joint gives status 'D'. – not fit for military service. There are 5 categories of fitness for military service: A - fit for military service B - fit for military service with minor restrictions
Preparation for physiotherapy
Any exercise for the treatment of the knee joints should begin with preparation. Most exercises are performed lying or sitting, so the floor should be warm. The gymnastics mat should not be too stiff either.
A good warm-up of the knee joint will help avoid discomfort when performing more difficult elements.
The warm-up typically consists of lunges, stretches, and foot exercises if enough time has passed since the injury or if the ligaments and muscles in the knee need to be strengthened:
- Lunges. Bend one leg at the knee and push off with the other leg, stretching it forward and back, fully engaging the muscles of the limbs.
- Stretch. For this exercise you will need a chair or an exercise piece. Stand with a chair about three feet away from you. Move your leg to the side and lift it so that your foot rests on the back of the chair, pull your leg well. Then do the same with the other link.
- Simple side-to-side and upward pulls help stretch the joint.
As a warm-up exercise, you can perform a complex of several micro-movements developed by Vitaliya Gitt that put minimal strain on the joint but are still good for it.
These exercises are called 'Humpty Dumpty', and the name accurately describes the first exercise in the complex:
- You have to sit on a high bed or a chair. The height should be such that your feet do not reach the floor. The legs must be swung back and forth effortlessly - just a few centimeters.
- When sitting on a chair, place your feet on the floor and stretch them slightly forward. Alternately lift your toes without lifting your heel off the floor. Then lift the heel area without the toe.
The movement must be easy and painless.
Exercise
If your knees are in good condition, you can proceed directly to knee therapy. There are several options here: movements for chronic osteoarthritis or arthritis aimed directly at the knees, or physiotherapy, which is necessary as a rehabilitation measure.
For pain caused by osteoarthritis, the following movements are suitable.
A kneeling position is required, which can be supported by hand support. Perform a knee step in place. If the pain is not severe and you cannot help with your hands, sit up.
The specialist says that this exercise can be done for all diseases. However, in the case of rheumatoid arthritis, for example, doctors advise against such active strain on the knees. If you have osteoarthritis in the knee, the kneecap should not be actively stressed.
For your information! Special orthoses and knee pads must be used if the joint is unstable and has been severely affected by an illness.
Knee joint gymnastics will help you manage the residual pain after the injury and effectively restore the function of the knee joint. It should be carried out at least 1.5 months after the injury.
Below is a video with exercises to restore the knee joint.
Sentence 1
This LFC contains both warm-up exercises and effective movements.
First, sit down, bend your knees slightly and then massage the inside of your knees in a circular motion.
Then move on to the next set of exercises:
While sitting, wrap your arms around the limb just above the knee and bring it towards your upper body. Perform rotational movements of the ankle joint and then movements in the opposite direction.
- Place your hand on the back of the thigh, just above the bottom of the hamstring, and then bend and flex the leg. The hands should pull the leg towards the body.
- Sit upright and place your hands on the floor. Straighten your legs and pull your toes up. Hold this position for 30 seconds.
- Spread your legs to the sides, keeping as much distance as possible. The snake movement with both feet should be as relaxed as possible if the knee is severely weak.
- Pull your feet toward your body, tighten your thighs and knees, pull your shoulders back for support, and try to lift your foot off the floor.
- Knee splint for knee arthrosis.
- Lamb Muscle Soreness.
- lower leg flexion.
- The long fibula muscle hurts.
- muscles in the legs.
- How to wear a knee brace for osteoarthritis.
- Rupture of the medial collateral ligament.
- Femoral collateral ligament.
