MRI is used when a mass is detected on CT scan for differential diagnosis. In older patients, hygroma can be confused with age-related brain atrophy because in this disease the subarachnoid spaces are secondarily enlarged.

X-ray of the shinbone
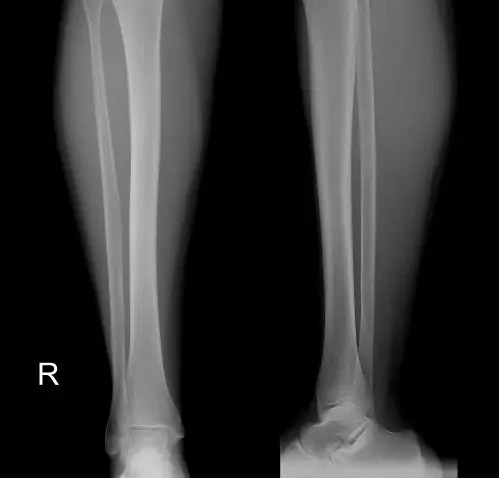
Shin x-ray is a non-invasive diagnostic method that can detect abnormalities in the bone structure. X-rays are most often required for fractures of the tibia and fibula.
This diagnostic procedure is very informative, precise and fast - it takes no more than 15-20 minutes to prepare, photograph and transcribe the recordings. This is very important, especially in a field such as traumatology, where surgical decisions are often made about the patient's health status.
Indications for.
X-rays of the lower leg X-rays of the lower leg can be performed for various indications and are recommended by various specialists.
Fractures of the lower leg or foot can vary greatly in location, size and complexity. X-rays help identify the characteristics of the fracture and determine whether bone fragments are present and their location. X-rays are also used after the broken bones are fused and cast. In this case, it is important to observe how the bones heal over time.
Brain subluxation on CT scan
Computed tomography is a modern X-ray diagnostic procedure that can be used to create layer-by-layer sections of the structures to be examined or to project a 3D model. The procedure is quick and painless. Computed tomography is suitable for most patients:
A CT scan can be performed at the Magnet Clinic on Krasnoarmiejska Street 7 6.
The CT scan can be used to determine the exact location of the hirgroma, which is important for further treatment. The growth rate and volume of the mass are recorded to determine whether surgery is required. A series of CT scans at regular intervals is used for dynamic monitoring.
A contrast-enhanced CT scan is performed to increase image intensity and differentiate the diagnosis from other masses (cysts, tumors, hematomas). According to the standard procedure, a substance containing iodine is injected, which reaches the brain via the vessels. The CT scan provides additional information about the part being examined.
A CT scan with contrast medium requires special preparation. A blood test to determine creatinine levels and, if necessary, a visit to an endocrinologist are mandatory.
- allergy to iodine and iodine compounds;
- Decreased glomerular filtration rate;
- Continued use of metformin;
- Excessive synthesis of thyroid hormones;
- Under 12 years (only if intensive care and specialists are available).
Symptoms of head hypersensitivity on a CT scan
A CT examination is essential for making a diagnosis and determining treatment tactics. The CT scan allows the precise location, boundary and size of the hygroma, as well as determining the relationship of the hygroma to the surrounding structures.
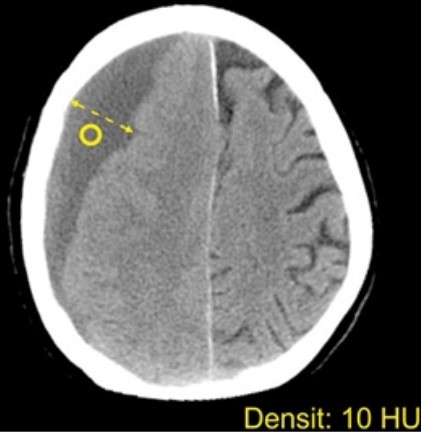
Hygroma on contrast-enhanced CT: The index does not accumulate
For the differential diagnosis, it is crucial to determine the presence of the capsule, invasion into the surrounding tissues, and the composition of the contents. The hygroma is filled with cerebrospinal fluid, that is, the intensity of the cavity in the images is consistent with the degree of turbidity caused by the cerebrospinal fluid. The shape is arbitrary, more often elongated, sickle-shaped and can be rounded. If the hirgroma spreads throughout the hemisphere, a collection of fluid can be seen running parallel to the meninges along the contour of the skull.
The mass is separated from the adjacent structures, does not form anastomosis with them, and often has adhesions. It can fuse with the cysts at the base of the brain via a so-called 'pathway'. A valve mechanism is created here through which liquid enters the cavity; there is no backflow. When this happens, the volume systematically increases, which can lead to brain compression and requires urgent surgical treatment. Such a development is rare because the hirgroma is usually stable in size.
In traumatic brain injuries, hemorrhages, hematomas and foci of contusion are often found nearby.
The contrast agent enhancement does not lead to a change in intensity because, unlike malignant tumors, the hirgroma does not accumulate drugs. The vessels running through the mass can be visualized so that a differential diagnosis with a cyst can be made.
causes
It is not uncommon for outpatients to report: 'I don't feel well, I've had dizziness and weakness for two days or a week'. But every person writes different feelings into this definition. For some, they are directly related to physical discomfort, while others note a sharp decline in mental performance, a slowdown in work.
It is also important to pay close attention to any accompanying symptoms to determine whether the patient has a serious illness or not [3]..
causes
It is not uncommon for outpatients to report: 'I don't feel well, I've had dizziness and weakness for two days or a week'. However, each person will fit a different feeling into this definition. For some people, they are directly related to physical malaise, while others notice a sharp decline in mental performance and a slowdown in work.
In addition, all accompanying symptoms should be carefully examined to determine whether the patient has a serious illness or not (3).
There is a clinically important difference between persistent or frequent mild malaise with dizziness and the sudden and abrupt onset of weakness and fatigue throughout the body with additional symptoms that should be investigated before initiating treatment.
Let's take a closer look at the situations that can cause such malaise in a person.
Read more:- Child has a bump on his foot.
- Anatomy of the heel bone x-ray.
- The so-called lateral foot bone.
- From where you can measure your leg length.
- If your soles and heels hurt.
- Which muscle extends the lower leg and flexes the thigh.
- lower leg prosthetics.
- What is the name of the ankle bone?.
