Until recently, prostheses were mechanically attached to the human body and not connected to the nervous system.

- Limb prostheses after amputation
- Goals
- Stages of amputation
- Become a cyborg at the expense of the state
- How a bionic arm works
- Is a prosthesis better than the human body?
- Types of modern arm prostheses
- Prostheses in Russia
- Artificial disguises – what are microprostheses?
- inlays
- veneers
- Lumineers
- Crowns: what are they?
- metal.
- plastic
- Metal-ceramic
- porcelain
- Zirconium dioxide crowns
- Types of modern dentures
- Bionic prostheses
- Mobile prostheses
- Fixed dentures
- Ceramic ceramics.
- Ceramic polyethylene, or metal polyethylene.
Limb prostheses after amputation
Anyone who can move around without assistance and use all parts of their limbs, both upper and lower, does not have to think about what their life would be like if they lost a leg or an arm. Even the loss of part of a limb, not to mention the complete absence or loss of both arms or legs, changes everything fundamentally - the person is no longer able to function properly and do the things that they could do when healthy ease did.
Thanks to developments in medicine and technology, this problem can now be solved. Limb prostheses have been manufactured by specialists for many years. Modern arm and leg prostheses are already so far removed from their earlier predecessors that they give the above-mentioned group of people a completely different perspective on their changed situation after the amputation. Thanks to modern designs, the lives of people who have lost a limb or several limbs can be made significantly easier, allowing them to return as close as possible to the condition they had before the fatal operation.
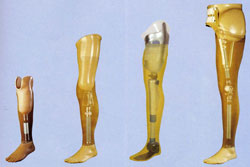
Prosthetics is a special type of treatment that partially or completely replaces the form and function of an organ that has been damaged by injury or illness or that has been pathologically altered by a congenital defect. It is closely linked to orthopedics, traumatology and reconstructive surgery.
The development of prosthetic and orthopedic products is based on advances in physiology, electronics, mechanics, biomechanics, electromechanics, chemistry, physics, mathematics and other areas of scientific knowledge. Many designers around the world are working to develop and improve various products for people with disabilities. Great progress is currently being made in this area, especially with the introduction of so-called bionic prostheses, which are as close as possible to the natural limbs given to humans by nature. Researchers are working hard to develop a feedback loop that allows prosthetic wearers to feel tactile sensations when an artificial hand covered with special prosthetic skin touches a specific object.
Goals
Goals range from simple locomotion to the ability to perform strenuous activities such as running and jumping. The components of the prosthesis are adjusted to allow the person to achieve their goals. Advances in shock-absorbing materials, hip prosthetic design, and technological components of the foot, ankle, knee, hand, wrist, and elbow joints enable greater comfort and functionality. Fitting a Prosthesis There are many types of prostheses. However, customization usually follows the same steps regardless of the type chosen. After the shaft is adjusted and the. Read more about The prosthetist's goals are to ensure the patient's comfort, stability when standing and walking, and their ability to achieve individual goals.
Highly motivated, otherwise healthy people with a prosthesis can perform many unusual feats (e.g., skydiving, mountaineering, triathlon, full-time sports, returning to a responsible job or active military service). Whether the prosthesis is used only for basic mobility or for more strenuous activities, it can provide significant psychological benefits and improve quality of life.
The successful use of a prosthesis depends on the following factors:
The adjustment of the prosthesis must be carried out by a qualified specialist. In addition, the person may have physical and psychological difficulties adjusting to life with a prosthesis. The entire process of selecting and adjusting the components as well as assessing the overall function of the prosthesis is therefore demanding and time-consuming. The type of prosthesis to be adjusted is determined individually.
Stages of amputation
An amputation can affect all or part of a limb. There are many factors to consider when amputating a limb. Very important:
Amputation is difficult for patients to endure. The loss of a limb not only leads to physical problems, but often also changes the self-image of a person who has lost part of their 'self'. Doctors and prosthetists try to prepare those affected and their families by explaining to them why an amputation is necessary and what will happen before and after the amputation and during the fitting of a prosthesis. A person who understands the procedure and has realistic expectations about the difficulties to be expected and the likely results will typically be more confident in pursuing the goal and achieve better results. Sometimes doctors make an appointment with another patient who has already undergone an amputation and adapted to the new conditions.
Before the operation, doctors try to achieve the best possible improvement in the patient's condition. They try to correct existing medical problems as much as possible, such as malnutrition, diabetes, heart or lung disease. Because smoking impairs healing, smoking cessation measures are important. Although quitting smoking is often very difficult, it is the most important thing smokers can do for their health. Quitting smoking has immediate benefits for. Read more . If time permits, weakened or exhausted patients may receive treatments and exercises to improve their strength and mobility.
Become a cyborg at the expense of the state
Around 200,000 people in Russia need arm or leg prostheses. The state claims to help people purchase a prosthesis, but in practice this often turns out to be problematic - either it is very difficult to overcome the bureaucratic hurdles and get reimbursed for the cost of a prosthesis, or the prostheses are free are outdated models and of low quality. Another problem is that disabled people themselves know little about modern prostheses and their options for receiving technical means of rehabilitation.
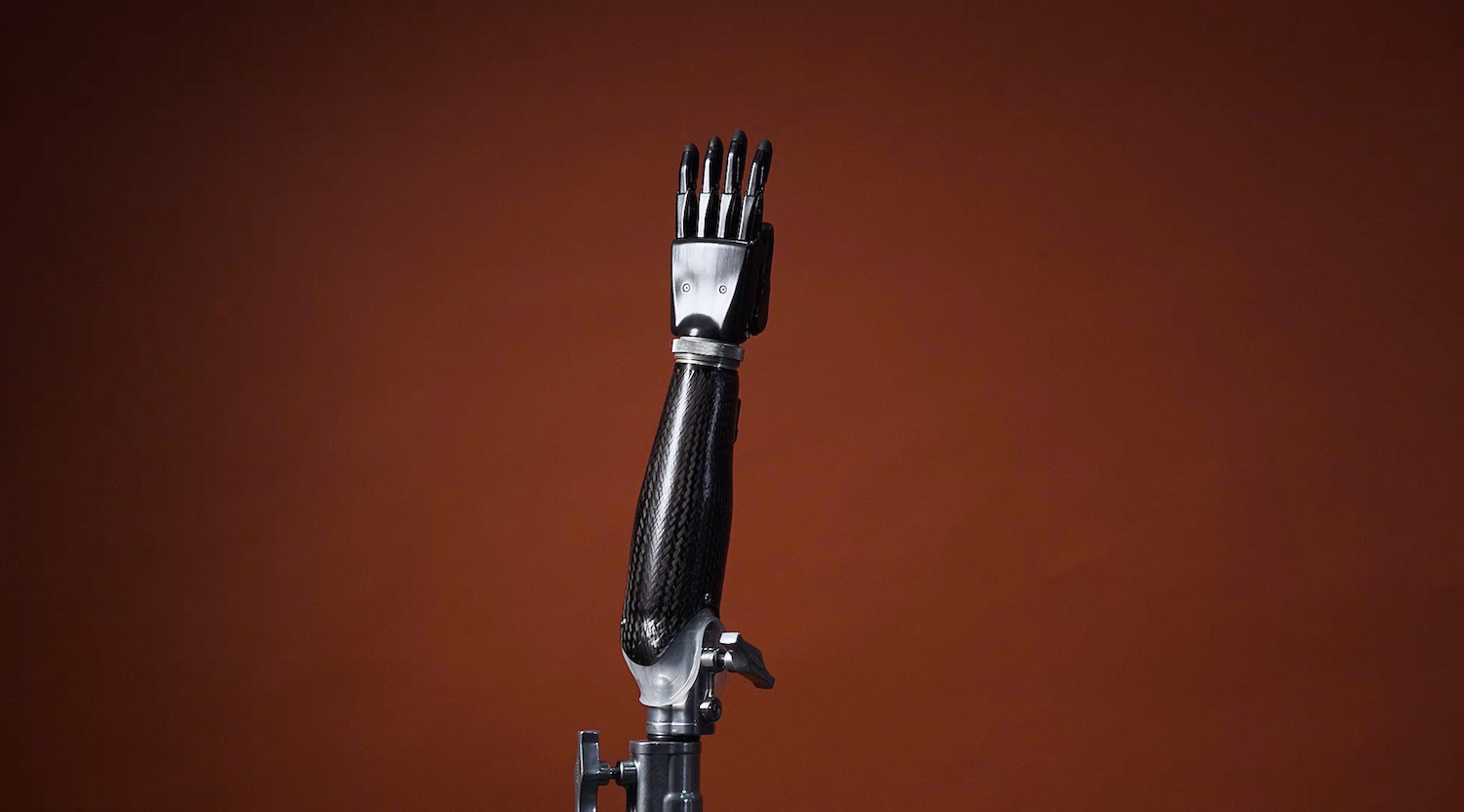

However, the situation is gradually improving. The National Health Project is increasing its resources. In recent years, start-ups have emerged in Russia that are developing promising types of prostheses that can compete with Western monopolies, at least in the Russian market. The media is showing interest in the issue, an information field is being created step by step, and private and state investors are appearing for the projects, ready to support them with money and production capacities.
An important impetus for the development of functional prosthetics was the development of technology. Almost all current trends in the industry have been reflected in prosthetics: robotization, artificial intelligence, the development of next-generation materials, increasing the capacity and reducing the weight of rechargeable devices, 3D printing and more.
How a bionic arm works
The bionic or bioelectric prosthesis is created at the interface of science – biology, medicine, technology. Design also plays an important role. Today, manufacturers and future users of prostheses are no longer limited to optically copying the natural limb - an artificial limb can look like a futuristic robotic arm or be painted with colorful prints.
How a bionic prosthesis works is as follows. A sleeve is attached to the stump, which is always made individually by an orthopedic technician. The sleeve contains sensors for muscle activity that interact directly with the robot arm.
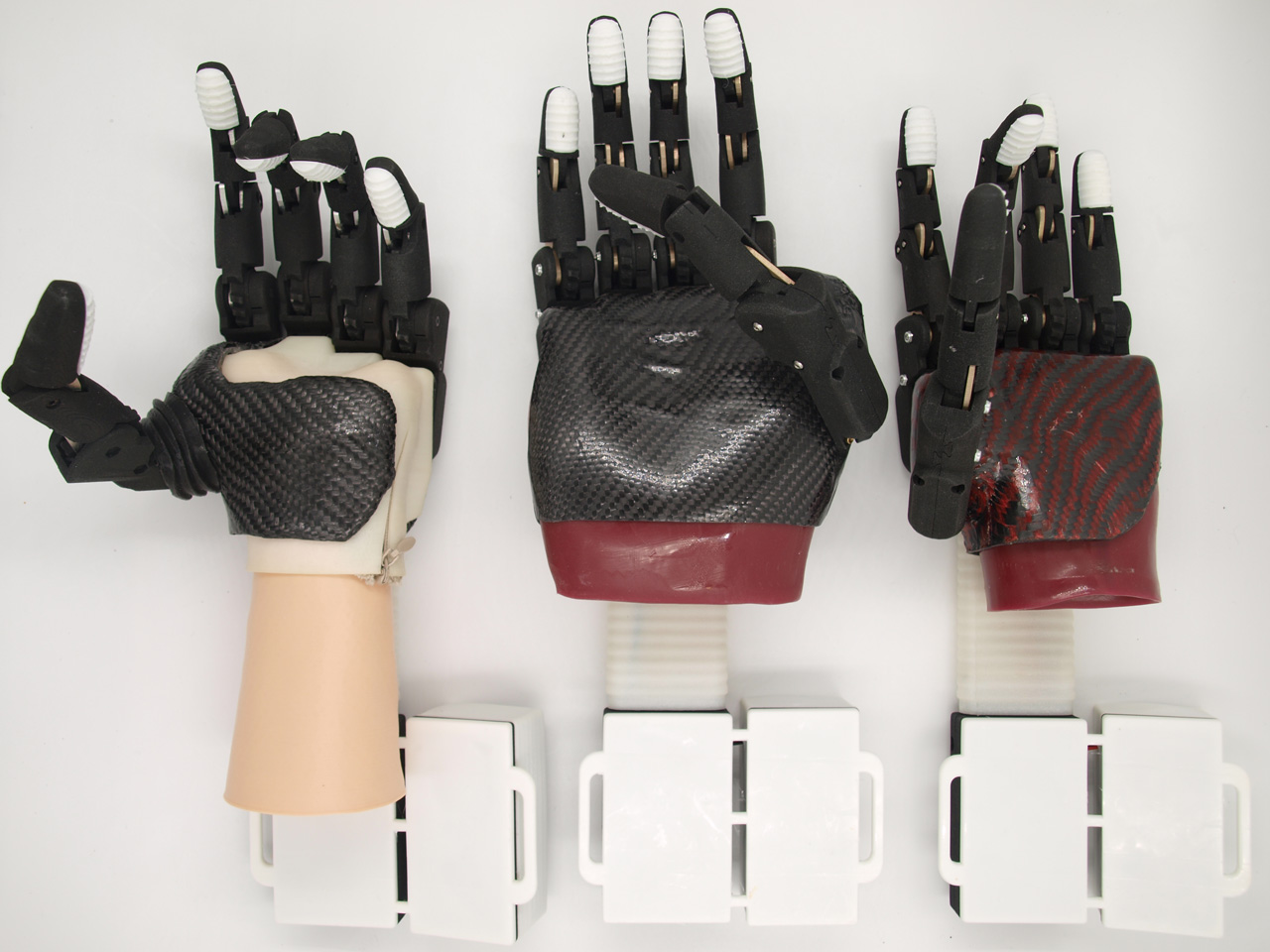

Photo: Concern Radioelectronic Technologies
The bionic arm is controlled via electrodes that trigger bioelectric potentials in the muscles. In other words: the robot arm 'catches' impulses from the muscles and reacts to them with certain movements. Most tasks are accomplished through two actions of the prosthesis – the handle and the pin. The former allows interaction with large objects, the latter with small objects such as fastening or tying shoelaces.
Some manufacturers are expanding the capabilities of bionic prostheses by incorporating various sensors and gadgets, payment devices and flashlights. It is already clear that the capabilities of prostheses will soon exceed those of the body's natural organs, which will open up completely new perspectives for their use.
Is a prosthesis better than the human body?
Oscar Fistorius was denied qualification for the 2008 Olympics because the jury felt his prosthesis gave him an artificial advantage over other 'natural' athletes. Fistorius is not the fastest man in the world, but his sprint times reflect a high level of performance that most people in the world do not have. He sprinted times comparable to the world records of 9.58 and 19.19 seconds for the 100 and 200 meter sprints.
Continued advances in the development and functionality of prostheses will not only enable people with disabilities to fully recover from their injuries, but also exceed the capabilities of the human body. Does this mean that in the future we will forego parts of our bodies and opt for strong and functional prostheses? We do not know it.
Types of modern arm prostheses
Arm prostheses are artificial replacements for damaged or missing upper limbs. The term 'prosthesis' itself comes from the Greek word prosthesis, which means 'attachment'.
The prototypes of today's multifunctional devices date back to the time before Christ. Ancient generals who lost their hands in battle imitated them with wooden or metal structures.

As mechanics developed, better limb replacement parts that could move emerged.
Functional and cosmetic prostheses emerged in the 19th century. The former enabled people with disabilities to carry out certain work activities. These were leather bandages with fittings to which a suitable tool could be attached.
The cosmetic prostheses of that time not only had the appearance of a hand, but also made it possible to carry out quite complex activities (e.g. writing).
Today, the field of prosthetics is developing at a rapid pace. The developers of modern rehabilitation equipment use the latest advances in robotics and the best construction and service materials.
It has long been known that moving mechanisms are subject to wear, corrosion and other unpleasant things that can affect their service life. Prosthetics is no exception.
In the past, standard lubricants were used to assemble and maintain these devices. However, over time it has been shown that with daily use of the prosthesis, lubricants are squeezed out of the friction zones and contaminate the environment and the wearer's skin. This is unhygienic and, above all, dangerous as the fumes from some materials are toxic.
Today, plastic greases have been replaced by modern high-tech coatings. These coatings significantly improve the performance of prosthetic hands without harming health.
Prostheses in Russia
Bionic hand prostheses are hardly ever produced on the Russian market or have hardly become established due to their high cost.
Several domestic companies are involved in the development and testing of these prostheses and hope to introduce their products to the global market in the near future.
Motorika, a company known for introducing traction prostheses for children into the federal program for the provision of technical means of rehabilitation for the disabled, runs its own start-up company.
'Motorika is working on the Stradivary myoelectric hand prosthesis, which does not require surgery to install. Surface myosensors are embedded in a recording sleeve and touch specific points in the muscle area. By sensing a potential during their contraction, they send a signal to open or close the hand.
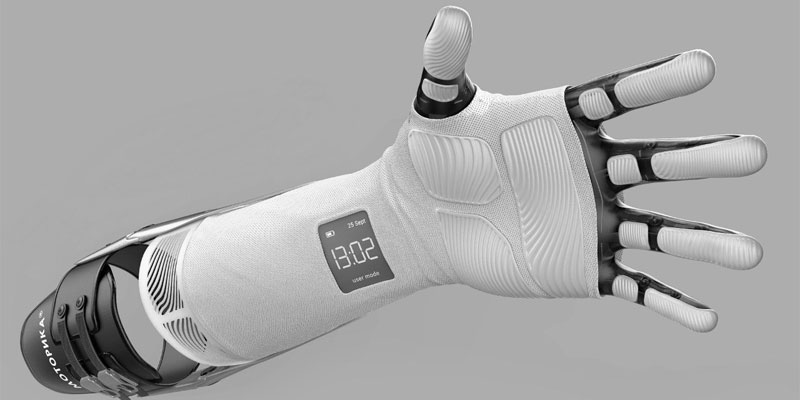

The main problem that motility specialists face when fitting a myoelectric prosthesis is the underdeveloped forearm muscles. The mechanical traction devices manufactured by the company help train them.
According to the founder of Motility, there are two main directions for the development of bionic prostheses. The first is to make them sensitive, that is, to provide feedback so that the wearer receives information about the properties of the object being touched.
The second is the implantation of all components, including the frame and the sensor. Even the most advanced prosthetics must be removable for sleeping or bathing. Once designers have ensured that the artificial limbs match the original limbs in appearance and function, all that remains is to make them a permanent part of the human body that does not require additional care.
Artificial disguises – what are microprostheses?
The types of prostheses with inlays are described below.
inlays
They allow the insertion of a crown to be postponed. The standard procedure can save damaged teeth by placing one insert in the root and the other over the gums. The resulting strong base can last a long time. Dentures are made from porcelain, metal, ceramic, zirconium dioxide and various composites.
veneers
Thin veneers are placed on the outside of the mouth. They are used to hide imperfections, minor defects and teeth whitening.

The quality and durability of the final product directly depends on the ingredients.
Lumineers
They are essentially similar to veneers, but have some special features:
- They are much thinner.
- Recreates the contours and acts like tooth enamel.
- Microcracks are completely eliminated.
- Durability of up to 20 years.
- Removable design.
Eliminates cracks, brightens and conceals minor defects.
Crowns: what are they?
Depending on their composition, there are indications and contraindications. Many people wonder how prosthetics are made and what they are made of. We'll break down each type individually.
metal.
Metal can be cast or pressed. They are widely used due to their low cost and ease of implantation and maintenance, but have become less important due to the use of more modern alternatives.
They can be made from nickel, titanium, gold, silver or cobalt. The downside is that they are completely unattractive.
plastic
Are manufactured with or without a prefabricated frame. Their attractive and beautiful appearance as well as easy and cost-effective installation can bring them to the top of applications. Low strength and short durability are the main disadvantages of plastic prostheses and structures. In addition, plastic is a highly allergenic component.
It is used for prosthetic restorations, corrections of the front incisors (low load) and temporary solutions during the development of a permanent solution.
Metal-ceramic
A metal framework in which the upper layers have a ceramic coating. Most common: ideal price/quality ratio. Strength, durability and the ability to wear them in any position are advantages. Disadvantages include possible color changes over time (requires additional care and protection), may fall off or lead to gingivitis.
porcelain
Porcelain implants are manufactured using a pressing and firing process. They are aesthetically pleasing, durable and long-lasting and completely anti-allergenic. However, the high price significantly limits its use.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
After fusion, they are able to completely imitate the natural tooth structure. It is rarely used due to its high cost and the fact that the material cannot be modified once fused. However, its advantages are high strength and durability.
Types of modern dentures
Today's prosthetic manufacturers produce a wide range of devices that replace lost limbs. They all differ in one way or another: their fit and function. To restore basic hands and basic functional skills, a working upper limb model should be used. An active functional prosthesis is often used for complex movements. Such mechanisms are quite complex and more expensive.
There are two main types of prostheses:
Functional prostheses are controlled by different mechanisms. Depending on the principle of operation, they are divided into bionic (the most advanced), operational and active mechanical prostheses. Such devices may have a cosmetic coating to mimic the appearance of the hand or a modern technical design.
The prosthetics itself does not require much time. The most important thing is choosing the right device. Not only must it be comfortable, but also reliable as it will be used daily and in different conditions.
To protect the moving mechanisms of the prosthesis from wear, corrosion and other unpleasant things, special maintenance materials are used during assembly and maintenance.
Modern high-tech coatings significantly improve the performance of prosthetic hands without compromising the user's health.
Today, such materials are produced not only abroad, but also in our country, which is increasingly developing in the field of prosthetics.
The coatings form a thin but strong composite layer on the parts, smoothing the surfaces and increasing their contact surface and resilience.
One of the most popular coatings used in the prosthesis industry is MODENGY 1014: the material based on molybdenum disulfide and polytetrafluoroethylene reduces wear on the contact surfaces and protects the parts from water ingress and corrosion.
Bionic prostheses
Bionic (bionic, myotonic) prostheses are among the most modern and advanced prostheses for the upper limbs. According to the classification of the Ministry of Labor, they are called prostheses with an external power source.
These devices are controlled by signals generated by muscle contractions. Myosensors embedded in the shaft of the stump receive these and forward them to the hand's microprocessor. This information is processed by computer algorithms and converted into movement commands that result in the execution of a specific gesture or grip.
Simple bionic devices use just two muscle sensors that record the activity of the two largest muscles. This has caused some inconvenience with these prostheses: sometimes a series of repetitive, one-time commands must be sent to perform a single movement. Only then does a kind of mode switch occur.

However, today not only simple but also high-tech bionic devices are available that can be used to restore both various parts of the hand (fingers, palm, forearm) and the entire limb.
The most modern bioelectric prostheses are similar to minicomputers: they have mini-tags that allow paying for goods and services with a single touch, as well as flexible displays for monitoring time, date, battery level, prosthesis control mode, etc. parameters. Some devices are equipped with GSM modules for remote status monitoring, error detection and firmware updating.
Research into controlling the prosthesis using human neural activity (the user's concentration should be detected by a special cap) continues tirelessly.
The latest models of bionic prostheses also make it possible to detect heat and pressure via sensors whose signal is picked up through the skin of the residual limb.
Mobile prostheses
As the name suggests, these are dentures that can be removed from the mouth. They are used when one or more teeth are missing and are easy to maintain; the prosthesis can be removed and cleaned at any time.
The disadvantages of prostheses are minor. In rare cases, overloading of the gums, rapid wear or loss of the dentures in the mouth can occur. What matters here is how carefully the dentist collects the data for the subsequent production of the prosthesis.

Removable bar prostheses for chewing teeth
There are the following types of removable dentures used in modern dentistry:
Here you can find out more about the individual types of removable dentures.
Fixed dentures
Fixed dentures cannot be removed from the mouth independently. They are cemented in the mouth with a special dental material and supported by the remaining healthy teeth. The advantages of this technique are durability, strength and effectiveness. However, the disadvantage is the high cost.

The following types of fixed prosthetic restorations are used:
Further information about the individual types of fixed dentures can be found here.
Ceramic ceramics.
This is a more wear-resistant material. Ceramic has a smooth, non-slip structure. It does not oxidize or rust. However, this material has two major disadvantages. Ceramics often crack when used. Over time, a small scratch can develop into a crack. It is also unpleasant that it can creak when you walk on it, which leads to a number of household inconveniences.
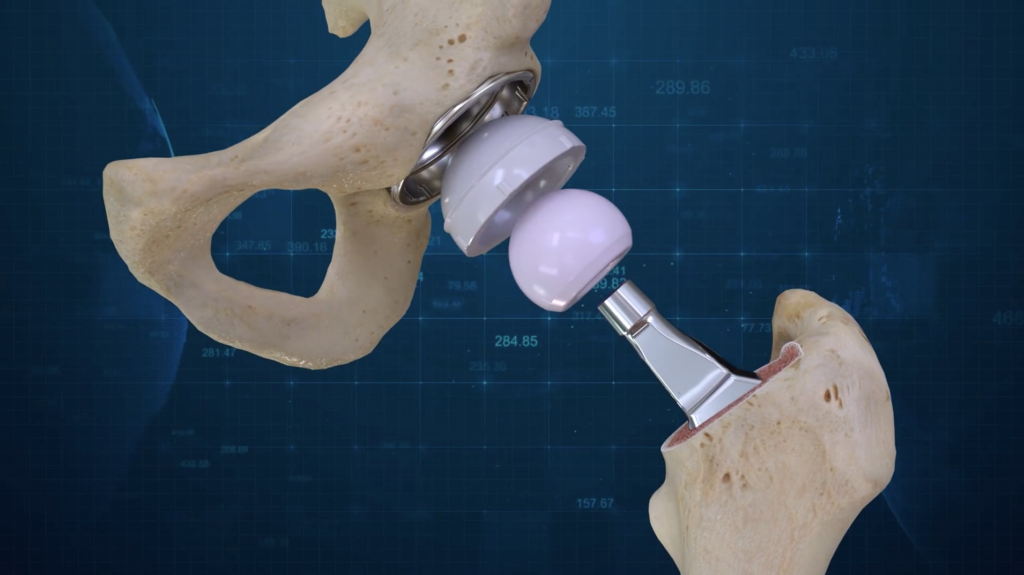
Ceramic polyethylene, or metal polyethylene.
Polyethylene is very malleable. Its wear products are not absorbed into the blood and do not cause toxic reactions. However, it also has disadvantages. The polyethylene liner wears out faster. Wear and tear creates particles that can cause inflammation of the joint. These same particles increase the risk of bone resorption and thus loosening of the prosthetic socket.
The disadvantages of polyethylene have been largely overcome by high molecular weight polymerization techniques. Its durability has been increased. Modern polyethylene inlays are impregnated with vitamin E. This eliminates the harmful effects of the material on soft tissue and bones.
The plasticity of polyethylene and the possibility of producing various shapes of liner practically eliminate the risk of a relatively common and dangerous postoperative complication, namely joint displacement.

The combination of ceramic and polyethylene, although inferior to competitors in terms of abrasion resistance, is by far the most optimal, reliable and comfortable combination of sliding mating materials in practice.
Read more:- Leg prosthesis below the knee.
- Modern leg prostheses.
- prosthetic leg.
- The reamputation is.
- prosthetic leg where.
- prosthetic legs.
- cost of the prosthetic leg.
- prosthetic finger.
