At the Health Plus Medical Center, qualified specialists provide first aid, carry out all the necessary examinations and draw up a treatment plan to avoid irreversible damage in the future. X-rays, ultrasound examinations and surgical procedures are carried out in our clinic. However, the first and most effective method of ankle reconstruction is UWT. This procedure is carried out using the latest Swiss technology, which guarantees quick and effective results.
- Sprained ankle ligaments
- Physical examination
- ICD-10
- Ligament injuries: classification, diagnosis, treatment
- Diagnosis of a ruptured ligament
- What should I do if I have a torn ligament?
- Relevant symptoms
- types of disease
- Help with grade 3 ankle sprains
- Physiotherapy for ankle ligament injuries
- Possible complications of injuries to the external collateral ligament of the ankle
- What should the end result be?
- Video about our clinic for orthopedics and traumatology
- How long does the treatment in the joint clinic last?
- Damage to the ligaments of the ankle (ankle instability)
- Conservative treatment of ankle ligament injuries
- Symptoms of Ankle Injuries
- Treatment
Sprained ankle ligaments
This is a common problem across all age groups.
An ankle ligament injury occurs when these relatively strong anatomical structures are stressed beyond their load limit and tear or stretch. It is a common injury in all age groups. Depending on the severity of the ligament injury, sprains and strains can be mild or severe.
Most ankle ligament injuries are relatively harmless and can be treated at home by resting the injured limb and applying ice packs. However, if the ankle joint swells significantly and the support function of the limb is limited, or if you are afraid to stand on your foot, you should definitely see a doctor.
If not treated and rehabilitated properly, more or less severe ankle ligament injuries can lead to hypermobility of the joint, making the ankle vulnerable to new injuries. Repeated ligament injuries can lead to more serious problems, including chronic pain syndrome, degenerative damage, and chronic instability.

An ankle ligament injury is an injury to one or more of the ligaments that stabilize the ankle joint.
Ligaments are strong anatomical connective tissue structures that connect one bone to another. The ligaments of the ankle joint hold the bones that make up the joint in an anatomically correct position, thereby stabilizing the joint.
Most ankle ligament injuries are characterized by damage to the lateral collateral ligaments. These can range from mild sprains or tears of individual fiber bundles in the thickness of the ligament to complete tears of the entire ligament.
Physical examination
The diagnosis of an ankle ligament injury is based on the results of a thorough clinical examination of the foot and ankle. This process can be relatively painful.
- Scan. The doctor carefully feels the ankle joint to determine which ligament is damaged.
- Determination of range of motion. The doctor assesses the range of motion of the ankle in various directions, which is of course limited if there is severe swelling.
If there is no fracture, the doctor can assess the severity of the fracture based on the swelling, pain and bleeding.
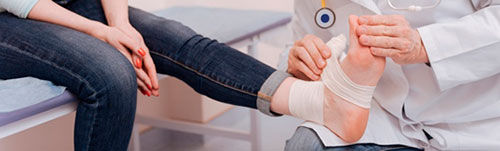
During the clinical examination, the doctor will carefully examine the soft tissues around the lateral malleolus and identify the area of greatest pain.
ICD-10
A ligament injury is an injury in which a ligament or its individual fibers are torn. Along with bruises, it is one of the most common traumatic injuries. It usually occurs as a result of domestic or sporting injuries and can occur in people of all ages. The lower limbs are affected more often than the upper limbs. There is some seasonality, e.g. B. the number of ankle ligament injuries increases sharply in winter, especially on black ice.
The immediate cause of the injury is excessive pressure or an amplitude of movement that exceeds the elasticity of the ligament tissue. The most common mechanism is rolling of the foot, less commonly twisting of the shoulder (e.g. as a result of an unfortunate fall or contact sports). The degree of ligament injury can vary greatly, from a mild sprain in which all symptoms resolve within 2-3 weeks to a complete tear requiring surgical treatment.

Ligament injuries: classification, diagnosis, treatment
In traumatology, three different types of ligament injuries are distinguished, regardless of the location of the injury:
- Grade I (sprain) – Some of the ligament fibers are torn, but continuity and mechanical integrity are maintained. This injury is commonly referred to as a ligament strain, although in reality the ligaments are rigid and inflexible. It is accompanied by moderate pain. There is no bleeding and only minimal swelling. There is a slight limitation of the musculoskeletal system.
- Grade 2 (crack) – Rupture of most of the fibers of the ligament. Swelling and bruising. Movement is painful and restricted. Mild instability of the joint may occur.
- Grade 3 – torn ligaments. There is severe pain, severe bruising, severe swelling and instability of the joint.
The diagnosis of a torn ligament is based on the mechanism of injury and the examination findings. In general, the more pronounced the clinical signs, the more fibers of the ligament are torn. However, swelling and bleeding increase over time, so a recent tear may be less serious than one that lasts 2 to 3 days. To assess the extent of the ligament injury, an ultrasound or MRI scan of the joint is performed.
Ligament injuries are differentiated from fractures and sprains. A dislocation is a pronounced displacement of the bones in relation to each other, the joint is severely deformed, the normal anatomical relationships are disturbed, movements are impossible and a spring-like resistance is observed when attempting passive movement. In the case of a ligament injury, the appearance of the joint is only changed by swelling, the anatomy is intact, movement is possible but limited due to pain, and there is no spring resistance.
When a fracture occurs, deformation, crepitation, and abnormal mobility are usually observed. However, these are not necessarily signs of bone integrity and may be absent in some cases (e.g. lateral malleolar fracture without dislocation). Other symptoms of a fracture (swelling, limitation of movement, pain and reduced support) are similar to the clinical signs of a ligament injury, so radiological examination is required to make a definitive diagnosis. If necessary, an MRI or ultrasound scan may also be performed.
Diagnosis of a ruptured ligament
Only a qualified traumatologist with experience in treating such injuries is able to make the correct diagnosis. The examination usually begins with an anamnesis, in which the fact and type of injury play an important role. A clinical examination follows, which always begins with a healthy joint. A number of clinical tests are carried out that clearly indicate one or another intra-articular injury. In most cases, the tests provide a clear picture of the injury and a preliminary diagnosis is made. Additional examination methods are often used to confirm this
- X-ray – always done to get a picture of the joint and to rule out bony or traumatic injury. An x-ray of a healthy joint is also often recommended;
- MRI – allows you to view soft tissues and intra-articular formations in layers to determine the type, extent and degree of damage to ligaments, muscles, cartilage, etc.
- ultrasound examination
- Computed Tomography;
In difficult situations, when the injury is severe or old, or when clinical examination does not reveal a clear clinical picture, various additional tests can be performed to clarify the diagnosis.
What should I do if I have a torn ligament?

An accurate diagnosis cannot be made on your own after an injury, but if pain and swelling accompany the injury, there are some simple steps that should be taken immediately to provide first aid. These steps are as follows:
- The injured joint should be immobilized. This is best done with a rail - any longer solid object will do. This is one of the most important steps because any movement, even unintentional, of the injured joint not only causes pain to the injured person, but can also cause additional complications by aggravating the injury.
- The best way to prevent swelling is to apply cold to the injured joint. An ice pack is most effective.
- Another good way to reduce limb swelling is to elevate the injured limb.
- The injured person should then receive painkillers. This can be in the form of tablets or an intramuscular injection.
- Once these measures have been carried out, a specialist should be consulted.
Relevant symptoms
The characteristic symptoms of ankle bursitis are:
- Soreness. The pain is stabbing and throbbing. The pain may worsen if the sufferer attempts to move the joint, causing further pain and suffering.
- Swelling. This is caused by the dilation of blood vessels and entry of blood from the inflamed area. The swelling in this case is very severe. Occasionally it also happens that the skin peels off in small cracks. The swelling spreads very quickly.
- Redness of the skin. This symptom is caused by the dilation of blood vessels in the area of inflammation. The redness can be recognized by the clear shape of the tendon and then gradually spreads to the surrounding tissue. You may also hear a slight crunching sound when you feel the reddened area.
- General deterioration. When tendonitis develops, the patient may have a high body temperature, weakness, sweating, and loss of appetite. In advanced cases (with infectious lesions and purulent inflammation), vomiting, pallor and fever may occur.
- Impairment of the motor function of the joint. If the flexor tendon is damaged, the joint can no longer be flexed. If, on the other hand, the extensor muscles are inflamed, it is difficult to straighten the joint.
types of disease

Tendonitis can be acute or chronic. Each form is characterized by its own symptoms and course.
Acute tendonitis usually occurs after a joint injury or infection. The disease is accompanied by pronounced symptoms, acute pain and rapidly developing inflammation.
The chronic form of the disease follows acute tendinitis that has not yet completely healed. Repeated trauma to the joint can also contribute to this type of pathology.
Chronic tendinitis is characterized by an undulating course with periods of exacerbation and improvement of the patient's condition.
With such a disease, the patient suffers from excruciating pain, redness and swelling of the affected joint for many months or even years. There is a constant accumulation of clear fluid around the tendon.
Depending on the fluid with which the tendon is filled, tendinitis can be serous, hemorrhagic, fibrous, or purulent.
The most severe form of the disease is purulent tendonitis. It occurs after an infection breaks out. The pathology is accompanied by rapid damage to healthy tissue.
Help with grade 3 ankle sprains

More serious injuries can result in a complete tear of the ankle ligament. This causes symptoms similar to those of a broken bone. The patient loses mobility, experiences severe pain and is no longer able to walk on the limb. These symptoms are caused by a change in the anatomical relationships of the joint components. The disease is also characterized by the rapid spread of hematomas and swelling throughout the entire ankle area.
In the event of a torn ankle ligament, conservative treatment is almost never recommended for the following reasons
- The healing ability of the damaged fibers is low;
- It may not be possible to completely restore the functional properties of the foot;
- If surgery is not performed, re-injury to the ankle due to instability is likely.
Planned surgery is performed when the ligament is completely detached from the bone. To restore the continuity of the ligament, bone and tendon threads are sutured. After the operation, the patient is recommended to wear a plaster cast for 21-28 days. During the entire rehabilitation period, the patient must take medications to improve the blood supply to the tissues in the ankle joint. The vasodilators Venarus, Detralex and Phlebodia are also prescribed.
Physiotherapy for ankle ligament injuries
Physiotherapy treatments are a must for anyone interested in treating sprained ankle ligaments. The benefits of such measures are more noticeable than those of medication.

For first and second degree injuries, physiotherapy should be carried out as early as 72 hours after treatment. It can also be carried out during the rehabilitation phase after surgery. An experienced physical therapist can help select the most effective treatments. The individual needs of each patient as well as the intensity of the damage are taken into account:
- intensity of damage;
- the regenerative ability of the tissue;
- History of circulatory disorders.
First of all, the patient is recommended to undergo treatment that involves the use of a constant electric current and special medications. To do this, a cotton swab soaked in a special medication is placed on the affected area and metal plates are placed over it. The electrical impulses allow the medication to penetrate into the deepest layers of tissue. A pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory medication is usually administered during treatment. In some cases, chondroprotective agents are recommended to accelerate the fusion of ligaments that have previously torn from their base.
Other techniques that can be used during the recovery period include ultrasound, paraffin compresses, magnetic therapy and UWT.
Possible complications of injuries to the external collateral ligament of the ankle
- Exacerbation of pain syndrome
- Restriction of the range of motion in the joint
- Chronic edema
- Chronic instability
- Damage to the superficial fibular nerve.
You can find our recommendations in this regard here. Ultimately, the responsibility in this regard lies entirely with the patient. A good way to check whether you can still drive is to place your right foot on the ground and press firmly to simulate a sudden application of the brake pedal. If you feel anxious or in pain, it is better not to drive as it can be dangerous. In addition, when you drive for a long time, your foot is forced into a forced position. This can cause the swelling to worsen and even become chronic.
What should the end result be?
In the vast majority of cases, the pain has disappeared and physical activity can be resumed fully.
This condition can occur when returning to work, sports, and other activities before the ligaments have fully healed and ankle function has been restored.
Video about our clinic for orthopedics and traumatology
How long does the treatment in the joint clinic last?
After the operation, a special shoe is made for the patient. You will need to use crutches for up to 12 days until the wound heals. In the following 3 weeks you will be able to walk without crutches but with the special shoe. After four weeks, the shoe is loosened to allow the leg to be bent and extended. After six weeks of treatment, walking without shoes is possible. During this time, intensive treatment is necessary to restore the muscles and mobility of the leg.
The staff at the Joint Clinic will be happy to advise you on the costs of the operation and follow-up treatment.
Damage to the ligaments of the ankle (ankle instability)
- SECTION MENU
- Allergology-Immunology
- Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (conjunctivitis)
- Allergy to grass pollen
- Allergic dermatitis
- Allergy to pets
- Allergy to house dust and its components
- Allergy to insects
- Allergy to pollen
- Allergy to tree pollen
- Allergy to grass pollen
- Eczema and other immune-mediated dermatoses
- Allergy to insect bites
- angioedema and Quincke's edema
- Atopic dermatitis
- immune disorders
- Allergy to drugs
- Acute and chronic urticaria
- Early signs of allergy
- Allergic alveolitis
- Why do my ovaries hurt and what can I do about it?
- Cervical dysplasia
- How to prepare for a visit to the gynecologist
- Causes of abdominal pain
- ovarian apoplexy
- Bartholin's inflammation, cyst or abscess
- Ectopic pregnancy
- hematoma
- hydrosalpinx
- Hyperplasia of the uterine lining (hyperplasia, polyps)
- Leukoplakia of the cervix
- endometritis
- Uterine fibroids
- menstrual disorders
- Ovarian tumors (cysts and cysts)
- Prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina
- Polycystic ovaries
- cervical polyps
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy
- endometriosis
- Erosion and ectropion of the cervix
- Current approach to diagnosing cervical anomalies
- sinus infection
- Chronic rhinitis
- Nasal furunculosis
- pharyngitis
- tonsillitis
- Polypoid stomatitis
- otitis media
- acute rhinitis
- nosebleeds
- laryngitis
- Distorted nasal septum
- ENT diagnosis
- Opening of a parotid abscess
Conservative treatment of ankle ligament injuries
If the ligaments are only partially damaged, treatment is usually conservative - with a plaster or polymer bandage, special bandages or orthoses. Physiotherapy and physical therapy courses are also recommended.
Ineffective and incorrect treatment of this pathology can lead to serious complications such as arthrosis, chronic ankle instability, limping, etc.If all of these measures are ineffective - pain, swelling, instability, repeated trauma or complete damage to the external or internal ligament apparatus of the ankle - surgical treatment - ligament reconstruction (ligamentoplasty) - is indicated to prevent the above complications.
Depending on the extent of the damage, a surgical method is used:
- Band seam (if the bands are present but deformed)
- Periosteal flaps (if the ligaments are torn or not visible)
- Tendon and ligament transplantation using plantar material or replacement of tendons with 2-3 ligaments using absorbable materials for fixation
The operation is performed under arthroscopic guidance (with the help of a video camera inserted into the joint to view the joint cavity). This method can be used to diagnose problems not only with damaged ligaments, but also within the joint and correct them in one operation.
Immediately after the operation, the joint is immobilized with a plaster cast so that it is not put under unnecessary strain. This leads to a faster recovery. The stitches are removed on the 12th to 14th day. Once the stitches are removed, rehabilitation treatment can begin. After 4 weeks, the cast can be replaced with a semi-rigid U-shaped ankle brace. After a few weeks it will be possible to walk without crutches and put full weight on the joint.
Symptoms of Ankle Injuries
- Acute pain occurs at the time of injury;
- Swelling of the ligament immediately after injury;
- Bruises gradually appear on the skin;
- Moving the ankle is painful;
- The injured person cannot walk on the injured leg;
- If the ligaments are torn, you may hear cracking or popping noises when you move your ankle.
When an ankle is injured, the first thing to check is whether the bone is damaged. X-rays of the foot and an ultrasound scan will be taken to rule out a fracture.
For mild to moderate injuries, further diagnostics are usually not necessary. During the examination, the doctor will assess the condition of the joint and recommend appropriate treatment.
If a serious injury is suspected, the doctor will recommend an MRI scan. With this examination, clear layer-by-layer cross-sections of the ankle joint can be created and, if necessary, a three-dimensional model can be reconstructed.
Treatment
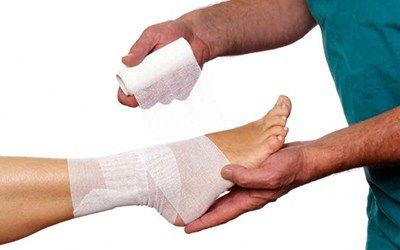
Treatment for an ankle sprain is simple and the injury is considered benign. The most important thing is the correct treatment of the ankle joint. The area around the joint is cooled and secured with an elastic bandage. You should then see a traumatologist for diagnosis.
Minor injuries include a partial ligament tear. You should be taken to a trauma center as quickly as possible. The doctor will anesthetize the patient with an anesthetic solution and apply an immobilizing bandage. After a certain period of time, physiotherapy and massage are recommended, followed by therapeutic exercises.
Ligament tears and tears are classified as more serious injuries. After anesthesia, a plaster cast is usually applied by a traumatologist and is worn for 6-8 weeks. Once the cast is removed, physical therapy, massage, and exercise are recommended. Recovery from ankle ligament injuries can take up to 1.5 months.
The experienced specialists of the multidisciplinary CELT clinic provide high-quality medical services to patients with ankle injuries and other types of injuries.
- Treatment of torn ligaments in the ankle.
- Rupture of the ligaments of the ankle.
- Injury to the ligaments of the ankle.
- ligaments in the ankle.
- Rupture of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle photo.
- Ligament damage in the right ankle.
