Ekaterina L. I had a back rub at Eden's. I received a lot of useful information about a healthy lifestyle and examples of short exercises that are easy to do in the office. I left Eden with a healed back and a boost of energy.
- X-shaped legs
- causes of this disease
- When is exercise therapy indicated?
- O-curvature correction exercises
- Useful Video - Dr. Artemiev on the dangers and consequences of X-shaped legs. Part 1
- Exercises to correct the X curve
- approaches to treatment
- massage therapy
- prevention
- Follow
- Treatment of pathological valgus deformity
- treatment methods.
- Conservative treatment
- Surgical methods to correct the curvature
- Causes of X-shaped lower leg bones
- Therapeutic massage for X-shaped shin splints
- signs
- diagnosis
- Treatment
- prevention
- Possible complications of the deformity
- prognosis and prevention
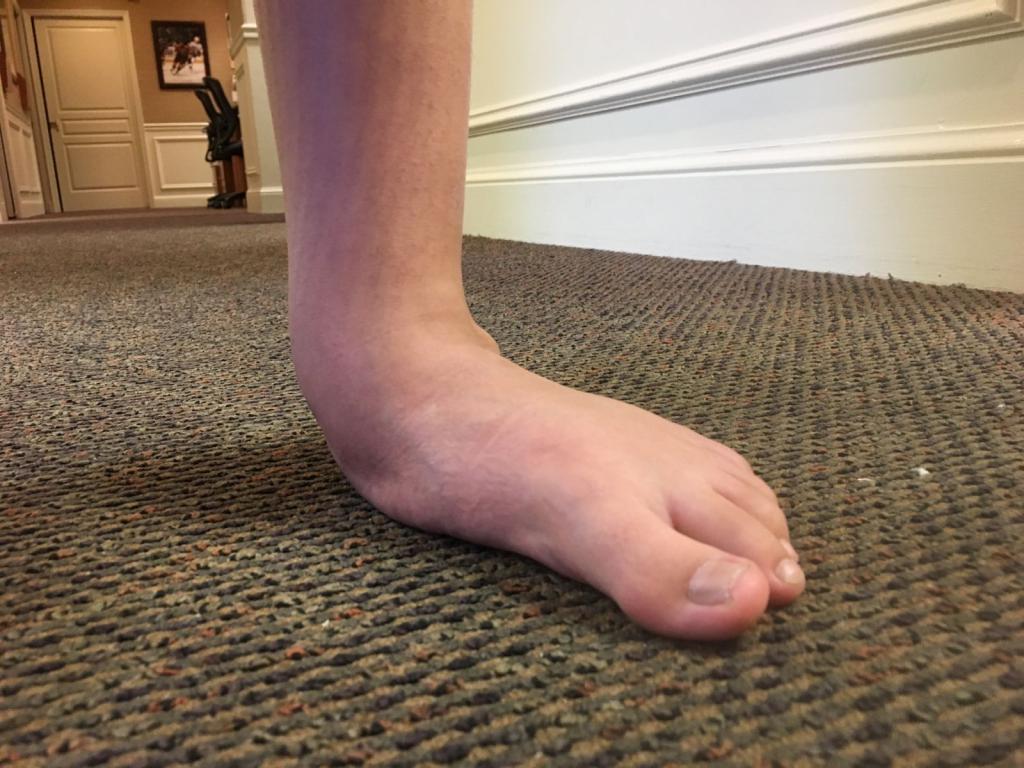
X-shaped legs
Clubfoot, or valgus, is a deformity in which the heels are more than 2 inches apart when the foot is straight and rigid. In most cases, X-shaped feet are an acquired pathology that developed as a result of excessive loads on the musculoskeletal system in the first years of a child's life. Diagnosis of this condition is not difficult: external examination and instrumental diagnosis.
During the formation of the child's figure, up to the age of 2, the legs can take on different shapes. During the first few steps, the instability often results in 0-shaped feet, which eventually resolve on their own and do not require serious medical correction. Some children develop heavier X-shaped feet by age 2. In these cases, it is very important to see a specialist and make sure that this condition does not interfere with the child's normal forming process. An experienced specialist will immediately distinguish between a pathological curve and a physiological curve that resolves spontaneously by the age of 5 years. year of life disappears by itself. The doctor may suspect a serious condition if the curvature is more pronounced on one side or if there is a hereditary factor in the family.
causes of this disease
The development of X-shaped legs can be caused by a variety of circumstances. It is important to detect the development of pathology early and, if possible, to eliminate one of the possible causes. Foot deformities usually appear when a child is just beginning to walk. The most common causes are:
- an excessive load on the lower limbs;
- the child starts to walk too early (the muscular system is not yet sufficiently developed, so the child cannot keep his feet in the right position);
- Poor choice of footwear and clothing;
- obesity (stress on bones and joints);
- Disorders of calcium metabolism (decreased bone strength);
- rickets (vitamin D deficiency);
- hereditary disorders;
- fractures, trauma;
- Congenital malformations of the lower limbs;
- Tumors of cartilage and bone tissue.
In addition to serious real changes in the bone-joint apparatus, the development of false curvatures due to peculiarities in the formation of soft tissues is also noted. This condition does not require serious medical intervention; a cosmetic correction is sufficient.
When is exercise therapy indicated?
Therapeutic exercise is an excellent tool for treating pseudocurvature. This 'visible' curvature is not pathological since only the 'upper' soft tissue is altered. It does not affect physical health and causes only aesthetic problems.
If the curvature is the result of a genetic predisposition or a disease, it can only be corrected by surgery or by using special stretching equipment.
The effectiveness of the corrective exercises can be seen after 6-12 months. The recovery time depends on the degree of pathology: the smaller it is, the faster and more effective the exercises.
Danger!!!
The best results are obtained in the physical therapy of foot deformities in young children. In young children, the bone tissue is still soft and flexible, making it easier to correct.
After a course of therapeutic exercises, the following goals should be achieved:
- The weakened musculature of the lower limbs is rebuilt;
- Functionality of the ligament apparatus is corrected;
- the knee joint is corrected.
For best results, training should be done regularly and all exercises should be done diligently on a daily basis. The choice of exercises is best left to the doctor, as there are limitations due to the age and individual physical characteristics of the patient. With certain concomitant diseases, physiotherapy courses are contraindicated.

O-curvature correction exercises
Every workout begins with a 'warm-up' of muscle tissue. Here are some examples of warm-up exercises.
- The exercise is performed while standing. Pull your toes off the floor while supporting yourself on your heels. Repeat the movement 10-15 times.
- Sit in a chair and place your feet wide apart. Lift your feet off the floor and use your body weight to move them from side to side. Repeat the movement 10-15 times.
- Lie down on the floor. Pedal an imaginary bike vigorously for 3-4 minutes.
Useful Video - Dr. Artemiev on the dangers and consequences of X-shaped legs. Part 1
Exercises to correct the X curve
Correcting X-shaped legs also requires regular exercise. Before training, muscle tissue should be warmed up.
The goal of exercises to eliminate the 'X' on the legs is to develop and strengthen the adductor muscles of the outer thighs.
- Get on your knees and walk around the room in a circle.
- Get on all fours. Support yourself on your knees and elbows and lunge with your straight right leg and then your left leg one after the other.
- Squeeze the ball between your knees and do deep squats. If you find the movement difficult at first, crouch without the ball.
- Stand with one leg bent at the knee. Put your hand around the knee and pull it up as high as you can. Then turn it to the side with your hand. Stretch the muscle in this position for 30-40 seconds. Switch legs and repeat the movement.
- Sit on the floor and spread your legs into a squat position. Slowly put your hands on your knees, trying to get them as close to the floor as possible.
- Lie on your stomach. Pull your feet towards you and spread your knees as wide as possible. Try to stay in this position for 2-3 minutes. At each session, increase the time you remain in the static pose by 1 minute. In the end, you should stay in this position for 10-15 minutes.
Do this complex three times a week. The exercise requires 3 approaches of 15 repetitions each.
Yoga, breaststroke, horseback riding and cycling are good additions to regular exercise.
approaches to treatment
Lower limb sprain: treatment approaches
An X-shaped lower limb sprain requires long-term and comprehensive treatment. The most effective conservative treatment is used in children up to 3 years of age. Surgical intervention is indicated when there are obvious changes in the knee joints.
Treatment begins once the cause of joint deformity has been identified. In the case of rickets and vitamin D deficiency, preparations based on vitamin D are used. Oil and water solutions can be used. Treatment begins with a high dose to quickly restore the level of vitamins in the body. The dose can be gradually reduced to a maintenance dose.
Self-medication is not permitted. Improper parenting can lead to worsening of symptoms and worsening of deformities.
In addition to the administration of vitamin D, treatment consists of applying plaster casts to the knee area. This keeps the joint in the correct position and allows the bones of the hip and lower limbs to form the joint properly. Plaster casts are very effective, but therapy can last more than a year.
Massages and therapeutic exercises are of supportive value for children. Both methods are aimed at normalizing muscle tone and strengthening the musculoskeletal system of the legs.
massage therapy
Therapeutic massage is performed as part of a series of massages. It should only be performed by a trained therapist. A child has to complete 4-5 courses per year. The duration of the massage is 15-30 minutes. This time will be gradually increased. Parents can also massage their child's feet at home after consulting the doctor.
The massage aims to strengthen the muscles of the upper and lower leg and relax them on the outside. This restores the alignment of the bones that make up the joint to their correct shape. In addition to the legs, the buttocks, lower back and upper back are also massaged.
prevention
To prevent X-shaped bones, it is forbidden:
- Getting your child up early, especially if they are overweight.
- Guided by two hands, the child should walk independently along the support.
If anyone in the family has had this deformity, parents should see a pediatric orthopedist. In addition, attention should be paid to a strong immune system, hardening of the body through swimming, exercise, active play and timely treatment.
Follow
If the curvature is within physiological and age-related norms, then all worries are unnecessary.
If the problem goes beyond physiology, then in the near future the consequences will be very serious:
- osteoarthritis of the knee. Excessive outward deviation of the tibia contributes to uneven development of the bearing surfaces of the joint. The branching of the joint is changed. It becomes wider on the inner surface and narrower on the outer surface. The knee joint is mechanically overloaded. As a result of these changes, a serious, chronic disease, gonarthrosis (deforming arthrosis of the knee), develops at a young age. This disease wears down articular cartilage, leading to progressive disability and the need for arthroplasty.
- Increased risk of injury. Injuries to the ligaments and menisci of the knee joint are common with valgus curvature of the lower limbs.
- coxarthrosis. The hip joint deforms along with the knee joint. The hip bone tilts inward, exerting mechanical pressure on the thinner cartilage of the hip joint. As a result, the cushioning in the joint is impaired and the cartilage wears out more quickly.
- flat feet. In connection with the knee joint, there is a deformation of the foot. Pathological flat feet develop, and later flat feet. The child's gait changes: it is unstable, the child often stumbles, leg pain and increased fatigue appear.
- scoliosis. The unphysiological curvature of the legs causes a chronic muscular overload of the entire musculoskeletal system, which always leads to the development of a spinal curvature.
- Disorders of the psycho-emotional state. The X-shape of the legs is visually very noticeable and can cause psychological discomfort and neurological disorders.
Treatment of pathological valgus deformity
The physiological limit state does not require treatment - it is not a disease! All you need is patience and careful observation of the development of your child's feet. It is important that you monitor your child's weight and physical activity. The 'golden mean' must be followed, as increased physical activity on the developing feet will not result in their spontaneous realignment and the cosmetic defect will remain for life. The frequency of consultation with a pediatric orthopedist - once every six months - should be strictly observed.
A valgus curvature already requires treatment. If the child is not yet of school age, there are good chances of success. The sooner the problem is identified and treatment is started, the easier and more successful the correction will be. But above all, orthopedic foot correction is a long and difficult task, which above all requires perseverance and regularity on the part of parents. It is necessary to develop a strong treatment habit in the child, which is easier to achieve through play.
treatment methods.
All methods of treatment can be divided into:
Conservative treatment

Conservative treatment is based on a combination of treatments and includes
nutritional therapy
The basis of nutritional therapy is a balanced diet. It should be rich in bone-building micronutrients and vitamins.
Foods containing calcium.
Calcium is the basic building block for bone growth.
- Dairy products: milk, cheese, cottage cheese, fermented dairy products;
- almonds;
- Leafy greens and greens: celery, collards, arugula, spinach;
- Root vegetables: radish, radish, beetroot.
Surgical methods to correct the curvature
If you have a true curvature, surgery can help straighten your legs. The most common methods of correction include:
If there is a need to correct the shape of the lower leg, the most effective option is curvatureplasty - an operation in which silicone implants are placed in the problem areas. The crookplasty helps to increase the volume of the desired areas and make them flatter. The procedure takes about 1.5 hours. During the procedure, the implants are inserted through an incision in the neck tendon. The sutures are removed after a week, and the full rehabilitation period after Crucoplasty takes 1.5-2 months. The first results of the operation can be seen after 2-3 months. The maximum effect of improving the shape of the leg can be seen one year after the lower back surgery.
Lipofilling can help not only to correct the shape of the legs, but also to eliminate excess fat in problem areas. This is a procedure in which the body's own fatty tissue is transplanted into areas where there is a lack of volume. Lipofilling is the least traumatic way to straighten legs, it even requires incisions and stitches. The procedure lasts no more than two hours, and the rehabilitation period can last from one to two months.
With complex curvatures, patients are advised to undergo external osteosynthesis, an orthopedic operation using an Ilizarov apparatus. It can radically straighten the legs with a true curvature of almost any degree. During the operation, the deformed bones are split and then fixed with a machine. The patient has to wear a special device until the bones are fully fused together - this can take anywhere from one to three months.
Causes of X-shaped lower leg bones
One cause is uneven leg tension that is not corrected in time. The outer muscles of the lower leg and thigh are tight. The inner muscles are relaxed. Therefore, when walking, the main load is on the inner ligaments of the knee. Also, the feet do not stand on the midline but appear slightly turned outward with the heel behind the midline defined by the centers of the ankle crease and the center of the knee.
Another reason is that many children are used to sitting 'between their legs', as well as weak ligaments and an inherited predisposition to this deformity.
Therapeutic massage for X-shaped shin splints
The therapeutic massage for X-shaped shinbone misalignment and valgus foot position is carried out to relieve the outer surfaces of the feet, tighten the inner surfaces of the feet and compensate for muscle tension. Exercise is recommended from the age of one and a half, with the easiest exercise being half-sitting, getting up from this position and walking on the outer surfaces of the feet. The number of sessions is usually 12 to 15, but can be up to 20 if needed.
Between the ages of 3 and 5, children develop the so-called physiological X-foot position, which does not require the intervention of a doctor or massage therapist. However, to distinguish between a situation where you can relax and do nothing and one where you need to act decisively and persistently (and correcting X-foot position does require persistence), you need to see an orthopedist in good time!
In addition to massage and physical therapy, he sometimes prescribes electrophoresis, vitamins and minerals that are responsible for the calcium-phosphorus balance in the body.
As the baby grows, everything must be done to ensure that it grows healthily.
signs
The first symptoms usually appear in the first year of life. The child cannot close the foot when the legs are straight. A distance of more than 5 centimeters between the ankles is considered abnormal. He complains of pain, tiredness easily, and a reluctance to stand or walk for long periods of time. An unsteady, clumsy gait can be observed. These children prefer the stroller and beg to be hugged. This is because the knee ligaments are stretched and weakened.
Over time, flat feet, knee misalignments and poor posture occur.
diagnosis
A valgus curvature should be diagnosed by a pediatrician or orthopedist. A nephrologist, oncologist, rheumatologist, endocrinologist and traumatologist can also be consulted.
Pathology can be seen with the naked eye, so diagnosis is not difficult. A medical history is taken, as the disease is inherited in most cases.
X-rays and MRI scans are done to detect complications, comorbidities, or underlying diseases.
Treatment
The physiological deformity is a cosmetic defect and does not require treatment. Other forms are treated as follows:
- Wearing orthopedic shoes is prescribed;
- The limb is immobilized with a device (joint orthosis, bandage or splint);
- treatment of the underlying and/or concomitant disease;
- Physiotherapeutic treatments (massage, physical therapy, applications, electrophoresis) are effective;
- Surgery is rarely performed when conservative methods fail.
prevention
For the prevention of X-shaped tumors it is forbidden to:
- Getting the child up early, especially if they are overweight.
- to lead the child by both hands; the child must walk independently on the support.
If anyone in the family has had this deformity, parents should see a pediatric orthopedist. A strong immune system, hardening of the body through swimming, exercise, active play, and timely treatment should also be considered.
The consultation of a specialist can take place in private or public clinics, the addresses of which can be found on medbooking.com. On the site you can choose the right medical center, make an appointment with a specialist, find out about the cost of services and read customer reviews.
Possible complications of the deformity
Without proper treatment, the foot will become permanently deformed, resulting in chronic bunions. Symptoms include pain in the joint, swelling and redness, limited mobility and a localized increase in temperature. The bursitis is accompanied by an accumulation of fluid in the joint capsule cavity. In this case, it is necessary to immobilize and elevate the joint, and occasionally apply cold to the affected area. Compression with elastic bandages relieves the pain. Chronic bursitis can be treated in the hospital.
A complication of the deformity can be Deichlander's disease (reconstruction disease). This is a pathological change in bone structure caused by excessive stress. The patient begins to limp, gait becomes unsteady, and the child may stop walking due to pain and discomfort. There is swelling, increased skin sensitivity and redness in the problem area. The disease is not accompanied by general symptoms such as fever, blood count changes, etc., but the pain can last up to several months. The disease usually ends with a complete cure.
prognosis and prevention
Children's legs can be severely twisted. In this case, the pathology is not only a pronounced cosmetic defect, but also leads to a severe impairment of the function of the limbs. The serious consequence of valgus deformity is disability in working age. Treatment must be done at an early age as it is almost impossible to correct the foot after the age of ten. If the foot deformity is minor and treated in time, the foot can become functional again.
Prevention begins as early as during the mother's pregnancy. The pregnant woman should eat a varied and healthy diet and take all the vitamins prescribed by the doctor in precise doses and according to a schedule. Long walks in the fresh air are very beneficial for all organs and systems. After the birth of the child, it is advisable to make every effort to introduce and maintain breastfeeding for up to a year, but only if the nursing mother follows optimal nutrition.
To prevent the development of deformities, it is necessary not to put stress on the feet of children up to the age of seven or eight months and to follow a daily routine that includes preventive massage, hardening, exercise, adequate sleep and long walks, and a nutritious diet includes. Vitamin D intake is important. You should see your pediatrician and get check-ups from specialists.
It is often recommended that the child wear shoes made of high-quality natural materials. But many doctors today have a different opinion. In order not to get 'knock-knocks' in your child (Komarovsky fully supports this opinion), it is not necessary to buy orthopedic shoes as a preventive measure. Also, it's better to learn to walk without shoes at all. The human foot is adapted to walking barefoot. People have been wearing shoes in our sense of the word for only 500 years, no more, and all of Russia until recently walked in clogs without ankle straps. In fact, most western orthopedists say that using special shoes as a method of correcting valgus deformities is pointless.
Read more:- X-shaped legs photo.
- What to do if your teen has crooked legs.
- Massage for varus deformities of the legs in children.
- legs 14 years.
- At what age do girls' legs grow?.
- Legs of different lengths in a child.
- The baby has short legs.
- Legs in adolescent boys.
