During visual examination Note the presence of a mass (infiltrate) with 1 purulent rod.
- Keratosis: symptoms, treatment, prevention
- What is seborrheic keratosis?
- diagnosis
- Treatment
- What should I do if my child gets chickenpox?
- What should you do if your child has a fever?
- symptoms of calcification
- diagnosis
- How is a boil treated?
- surgical treatment
- Treatment directed at the pathogen (aetiotropic treatment)
- Local treatment of boils depending on the stage of development
- Stage of infiltration
- Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
- complications and consequences
- prevention
Keratosis: symptoms, treatment, prevention
Recently I posted on Instagram and VK an interesting encounter with a colleague about the diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis. The topic sparked a lot of interest, so I decided to write an article about this phenomenon. In it we will take a closer look at the causes of seborrheic keratosis (and of course the myths), its variants, possible health complications, treatment and prevention methods.
For the sake of simplicity, the terms seborrheic keratosis and keratoma are used synonymously below.
What is seborrheic keratosis?
One of the most common benign skin cancers in humans. It usually develops in old age due to epidermal hyperplasia with pronounced keratosis. [1]
The epidermis is the top layer of the skin that continually peels off and completely changes in about two weeks. Their thickness varies between 0.07 and 1.4 mm. Keratosis is therefore a very superficial mass. Although the foci of seborrheic keratosis can be very large, they do not penetrate deeply into the skin.

diagnosis
The disease is diagnosed through examination and consultation with a neurologist. More detailed information can be obtained through additional examinations:
- X-ray: It helps to confirm the presence of cavus foot and determine the extent and characteristics of the deformity;
- Plantography: This involves examining the impression of the foot on paper; cannot give a clear picture;
- CT scan: used for older injuries.
Electromyography and MRI may also be necessary. If the patient has no previous neuromuscular problems and no characteristic lesions, a newly diagnosed cavus foot may be a reason to suspect the development of a tumor in the spinal cord. If this is the case, the patient must make an appointment with an oncologist.
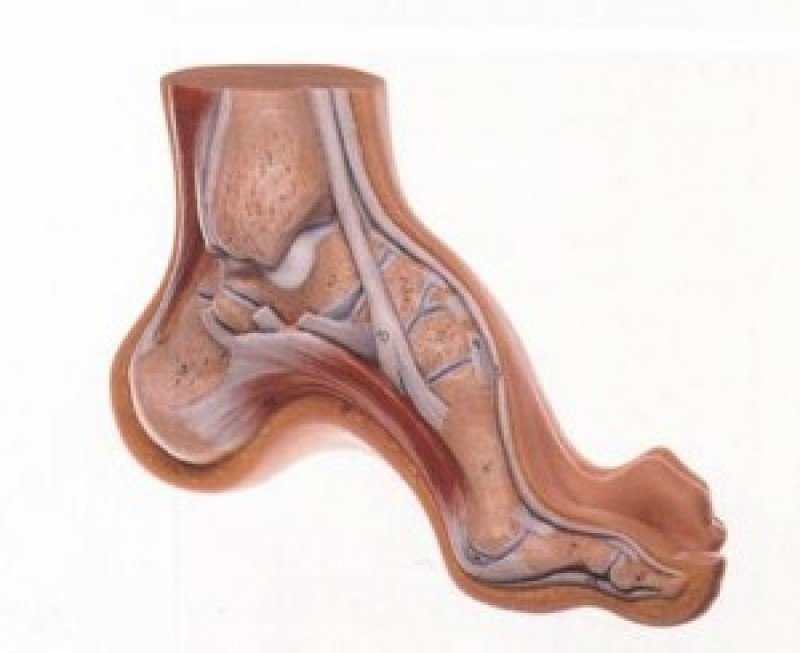
Treatment
For moderate or less severe disease, conservative treatment is recommended, the main aim of which is to strengthen the vault components. The treatment is carried out by trauma surgeons and orthopedists using the following techniques and procedures:
If the condition is neglected, surgical intervention is required:
- tendon transplant;
- Arthrodesis – immobilization of the joint;
- division of the plantar fascia;
- Osteotomy – cutting and shaping the bone.
With timely referral to a specialist, the prognosis for treatment is always positive.
What should I do if my child gets chickenpox?
Has your child been infected with chickenpox? Of course, this acute viral illness can also cause fever. What should you do in such a case?
The most important thing is that you find a fever reducer for your child. Under no circumstances should Nurofen be used. Products containing paracetamol can be used to treat fever in chickenpox.

What should you do if your child has a fever?
Does your child have a fever? If so, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Especially if it is accompanied by fever:
But don't panic: Fever occurs with most typical viral respiratory infections, and the maximum temperature is around 40 degrees. This is how our body reacts to an infection. The pediatrician will simply examine the child and select the appropriate treatment for the child, taking into account the severity of the disease.
symptoms of calcification
In the initial stages, it is very difficult to detect the disease because it is asymptomatic. However, some species have a fairly distinctive clinical picture.
In systemic calcinosis, that is, when the skin and joints are affected, the epidermis is covered with small blisters and there is no change in texture or color. As the pathology progresses, the calcium conglomerates swell, become denser when touched and change color. Fistula formation is possible.
Calcium deposits can be found during routine examinations by specialists or during instrumental examination of teeth, bones, vessels, muscle and nerve fibers. The accumulation of macronutrients on organ tissues leads to impaired organ function.
If the heart muscle and vascular system are damaged, the patient experiences pain in the sternum, arm, neck and back that lasts for a long time. Blood flow is also impaired, leading to an increase in blood pressure and a feeling of coldness in the extremities.
If the kidneys are damaged, the symptoms of intoxication increase, urine excretion is impaired, and the skin becomes dry and flabby. When the gastrointestinal tract is calcified, the gastrointestinal tract is affected, resulting in nausea, vomiting, abdominal heaviness, and constipation.
If the disease affects the brain and too much calcium accumulates, it may cause frequent headaches, dizziness, intracranial pressure fluctuations, incoordination, memory loss, vision and hearing problems. As the disease progresses, you may experience fainting spells.
Calcinosis leads to poor performance, constant dementia and fatigue, weakness and weight loss.
diagnosis
X-rays are taken to confirm the diagnosis. This allows the type and size of the deposit as well as the extent of damage to the organ in which the lime conglomerate is located to be determined. Other examination methods include Doppler ultrasound of the vascular system:
- Doppler ultrasound to examine the vascular system;
- ECG to study the heart muscle;
- Computed tomography with contrast agent;
- MRI.
To determine the cause of tissue calcification, additional examinations are prescribed in the form of general clinical and biochemical blood tests. The latter make it possible to determine the levels of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium in the blood. If renal function is impaired, a general clinical examination and bacteriological examination of urine are recommended to assess renal function.
A tissue biopsy is ordered to rule out a malignant tumor in the affected organ. In this method, biological material is removed and examined under a microscope under laboratory conditions. A biopsy also helps distinguish between benign and malignant tumors.
How is a boil treated?
There are several options for treating boils.
surgical treatment
Importantly, surgical treatment is indicated if the boil has formed a closed cavity filled with pus.
- The abscess (collection of pus) is opened.
- After the incision, it may be necessary to insert cotton and gauze into the wound to remove the liquid contents (drainage).
Treatment directed at the pathogen (aetiotropic treatment)
Aetiotropic treatment consists in the administration of systemic antimicrobial agents directed against the pathogen. These are given when symptoms of acute inflammation are present: fever, headache, general weakness, lethargy, and when boils on the face and multiple boils – furunculosis – are present 1,8.
Please note that it is strictly forbidden to squeeze the contents of the boil or massage near it!
Local treatment of boils depending on the stage of development
Stage of infiltration
At the stage when painful swelling begins, the skin is treated with 70% alcohol or povidone-iodine solution (Betadine®). Antibiotics and electrophoresis with antiseptics can also be used.
To accelerate the maturation of the boil, it is recommended to apply warming compresses with 20-30% ethanol or a 5-10% aqueous solution of ichthyol for 1-3 days. It is also possible to use ointments with the following active ingredients 10:
- Povidone-iodine (Betadine®) Has an antiseptic effect and helps to remove pus resulting from the presence of macrogallus. Helps destroy harmful microorganisms and reduce inflammation.
- Kalanchoe (phytopreparation) Has an anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect.
- Dimethyl sulfoxide Has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and pain-relieving effects.
- Tar and xeroform Has an antibacterial and regenerating effect.
- Pine oleoresin.Pine oleoresin, has antibacterial and regenerative effects.
- ichthiol Has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, keratoplastic effects (accelerates the formation of the stratum corneum) and pain-relieving.
- Salicylic acidSalicylic acid, which softens the stratum corneum and has an antibacterial effect.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
The diagnosis of scarlet fever in children is usually made at home based on the clinical picture of the disease. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may take a throat swab to detect bacteria.
Treatment is usually carried out at home. Treatment is comprehensive and includes antibiotics, bed rest and diet.
A person suffering from scarlet fever should be isolated in a separate room and contact with other people should be kept to a minimum. He or she should have his or her own dishes and towels. Isolation is required for at least 2 weeks after the first symptoms appear. If a healthy child has been in contact with a sick person, he or she must also be quarantined for a week, and if he or she has been in contact with a sick person, for the entire duration of the illness.
For more information about diagnosing, treating, and preventing scarlatina, see this article.
- Shulman ST. Group A streptococci. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 183.
- Bogadelnikov IV, Kramarev SA, Bezdolnaya TN Scarlatina // Journal of Child Health 3(30) 2011.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507889/Salvatore Pardo; Thomas B Perera. Scarlatina. February 28, 2019.
The information contained in this article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for advice from a qualified professional. Don't treat yourself on your own! A doctor should be consulted at the first signs of the disease.
complications and consequences
In the advanced stages of the disease, inflammatory damage occurs to other organs, including the heart, kidneys and joints. The most serious complications include:
- Mediastinitis – mediastinitis;
- Chronic bronchitis. – Inflammatory bronchial disease;
- Sepsis. Spread of infection through the bloodstream;
- joint inflammation – Arthritis;
- Glomerulonephritis severe kidney disease;
- purulent meningitis. Damage to the meninges of the brain;
- perianal abscesses – Sclerosis of the lymph nodes and peribronchial space.
Contacting the health center early will prevent negative health consequences.
prevention
By following preventative measures, the risk of developing the disease can be reduced. Effective prevention includes:
- Avoiding hypothermia (wearing warm clothing, controlling indoor microclimatic parameters);
- regular preventive visits to the dentist to detect the early stages of tooth decay and stomatitis;
- avoiding unhealthy habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- Moderate physical activity, regular outdoor walks;
- Normalization of nutrition, sleep and wake rhythms;
- Compliance with hygiene standards and requirements, cleanliness in the home and at work;
- Limiting contact with unknown people in times of an unfavorable epidemiological situation.
In order to avoid infections and get through a purulent sore throat better, it helps to strengthen the immune system through a healthy lifestyle.
![]()
If you are suffering from a sore throat, call us at +7 (499) 653-58-25 and we will help you!
Read more:- hole in the heel.
- arch of foot.
- Photo of the elbow on the foot.
- Orthopedic sports insoles.
- Heels for girls 12.
- A child begins to have clubfoot between the ages of 1 and 5.
- The person has an arched foot.
- Which doctor do you go to if you have joint problems?.
