Ligaments tear during sudden movements when the connective tissue is stretched beyond its normal size. Partial or complete damage to the fibers leads to loss of the ability to move independently. Statistics show that one in five people worldwide have suffered a severe sprain.
- Ligament damage in the ankle joint
- Classification of ankle dislocations
- Anatomy of a sprain
- Severity and duration of treatment
- Clinical signs.
- causes
- Symptoms of an ankle sprain
- Mild degree
- Moderate to severe
- Very difficult
- Diagnosis of an ankle sprain
- causes
- Which doctor should I see?
- Our specialists
- Prices for Services
- Therapeutic exercises and calisthenics
- How to forget about joint pain?
- Symptoms (signs) of a torn ligament
- causes of injuries
- Which doctor should I see?
- Find a doctor for ligament tears and injuries
- Signs of a torn ligament
- Gymnastics for the ankle after a ligament tear
- Kinesio taping for torn knee ligaments
Ligament damage in the ankle joint
sprain of the ligaments – This is the most common ankle injury presented to the emergency room and perhaps causes the most treatment errors. Surprisingly, most emergency physicians have a very limited understanding of sprains, even though they occur more frequently than any other type of limb injury. A sprain is the result of inversion or extension of the foot in a plantar flexion position.
Inversion (varus) injuries Ankle ligament sprains account for up to 85% of all ankle sprains. There is a specific sequence of structural damage depending on the increase in applied force. During inversion, the anterior ligament of the ankle is first damaged, followed by tearing of the calcanofemoral ligament and finally the posterior ligament of the ankle. During plantar flexion, the anterior talofemoral ligament is perpendicular to the action of the inversion load on the ankle joint.

Sequence of damage to the ankle joint structures in inversion and eversion injuries
Inversion injuries (valgus) Inversion injuries (eversion) of the ankle are much rarer and usually involve a tear of the medial malleolus rather than a tear of the strong elastic deltoid ligament. Further exposure causes rupture of the anterior talocrural ligament and intercondylar membrane.
The most common inversion injury The most common ankle sprain injury is a sprained ligament, and the most common sprain injury is a fracture of the lateral malleolus. Regardless of the direction of force, an injury to the lateral malleolus is the most common.
Classification of ankle dislocations
Ankle ligament sprains are divided into grades I, II and III depending on the clinical symptoms and the instability of the ankle, which can be determined by stress tests. The diagnosis of the degree of rupture of the ligament is the basis for the subsequent appropriate treatment of a simple sprain. Grade I injuries are easy to diagnose, while Grade II and III injuries are difficult to distinguish.
Under Grade I If the ankle is intact, patients rarely need to see a doctor and usually heal at home. You have little or no swelling of the ankle joint and pain with normal movement, and little pain occurs when tested in the direction of the damaging force, usually inversion.
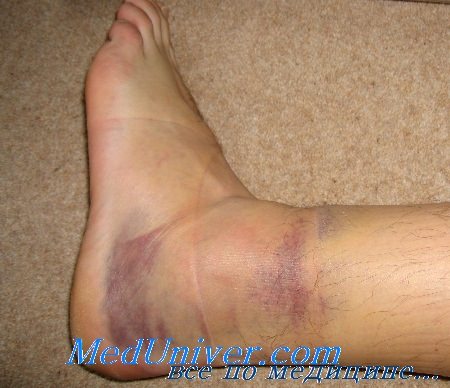
Anatomy of a sprain
The ligaments are made of strong connective tissue. They usually stretch to some extent and then return to their normal state. With a severe sprain, the ligament tears, which can be heard or felt as a pop or crack.
An ankle ligament sprain is a common injury. Twisting collateral ligament injuries account for approximately 85 % of all cases. According to statistics, the frequency is highest at the beginning of 2020 between the ages of 15 and 19. Half of all ankle ligament sprains occur during sporting activities, such as: B. in basketball (41.1 %), football (9.3 %). And in relation to all sports injuries, it occurs in 77-83 % cases.
The most common risk factor is a sprain. It can compromise the strength and integrity of the stabilizers by disrupting sensory nerve fibers. Gender, height, weight, limb dominance, postural sway, and foot anatomy are internal risk factors that can also influence injury potential. External causes include the fastening features of the protective system, the type of footwear, the duration of the competition and the intensity of the activity.
In addition to sports injuries, ankle injuries can also result from simply stepping on the foot incorrectly. For example, when a person steps on the side of the foot instead of the sole of the foot. This can happen when climbing stairs or running.
Severity and duration of treatment
Ankle sprains are classified according to their severity:
- Grade 1 – mild sprain and microscopic damage;
- Grade 2 - partial tear;
- Grade 3 - the ligament is completely torn.
Most sprains take 4 to 6 weeks to heal. Recovery from a severe sprain can take several months.
If the ligamentous apparatus is damaged, the following symptoms occur
- Increased body temperature to subfebrile – 37.5°C;
- chills and fever;
- weakness and dizziness;
- local swelling around the injury;
- Hypersensitivity – the ankle is hot when palpated;
- localized hyperthermia;
- Pain on palpation and movements in one or more directions, and when walking.
In the event of a complete rupture of the ligament, in addition to the above-mentioned symptoms, the following occur:
- Excessive mobility in the joint projection;
- inability to stand on the painful leg;
- loss of consciousness;
- pain shock;
- Circulatory disorders, which are manifested by numbness in the fingers, numbness and tingling in the area of the injury.
Even if the clinical picture is normal, a trauma surgeon should be consulted. He helps in choosing treatment tactics and restoring the function of the joint and ligaments.
Clinical signs.
Acute pain occurs at the time of injury when the ligament is stretched to its limit. The crack is accompanied by a loud cracking sound similar to the plucking of a string. You can no longer move independently, and the ankle is no longer able to move independently.
There will be slight swelling in the first few minutes after the injury. After a few hours, there is severe swelling of the ankle, which is particularly visible at the site of the injury. A hematoma forms a few centimeters below the joint. At first a small bruise appears, but within a few days the bruise covers the entire surface of the ankle. The swelling and hematoma resolve within three weeks.
First aid to the injured person is taking painkillers (Ketanov, Baralgin, Next), cooling the joint and applying a tight bandage, which will help prevent severe swelling and reduce pain. After the injury, diagnostic workup should be performed at a trauma center to rule out a compound ankle fracture.
In traumatological practice, three degrees of ligament tears are distinguished:
- The first degree is classified as easy. The band maintains its anatomical integrity. If a force is applied that stretches the ligament against its natural, physiological direction, the connective tissue fibers are micro-damaged. At this point, there will be moderate pain and a small collection of fluid around the ankle. A hematoma usually does not occur with minor injuries. The joint's mobility remains, but is painful. The affected person can still walk independently, although with a limp and with the help of a cane or crutch.
- The second stage is characterized by a tear in the collagen fibers. The pain increases, the leg is severely swollen and subcutaneous bleeding is visible. Severe pain occurs when attempting to take a step and motor skills are severely limited. The joint becomes hypermobile and the damaged ligament is no longer able to hold the foot in a physiological position.
- The third stage occurs when the connective tissue is completely torn. The injury is accompanied by a loud crunching sound with stabbing pain. The affected person falls and can no longer step on the injured leg. Swelling and bruising occur immediately, indicating a serious injury. The joint becomes unstable and the foot is unstable.
causes
No one is safe from a torn ankle ligament, regardless of age or gender. The main cause of a serious injury is clumsy movement of the foot. The most common causes of hyperextension are turning the foot inward or outward while walking or falling, a hard blow to the foot from one side, or bending the toes inward during intense running.
- People who professionally pursue athletics, hockey, football or figure skating;
- the older generation is at risk of injury due to age-related changes;
- track and field athletes, ice hockey players, footballers and figure skaters; the older generation is at risk of injury due to age-related changes; – people whose professional activities involve great physical exertion;
- Skeletal muscle loss in untrained individuals.
Symptoms of an ankle sprain
There is usually pain and swelling in the tissue around the injured ligament. Occasionally, an ankle sprain causes muscle spasms, which are spontaneous contractions of the muscles around the ankle.
The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the tear. When nerve damage occurs, a person may have trouble feeling the position of the foot and ankle without visual control (this feeling is called proprioception).
Mild degree
Ligaments are twisted and torn, but the tears are so small that they can only be seen under a microscope. The ankle joint is usually not very painful or swollen, but it is weakened, increasing the likelihood of re-injury. Recovery takes a few hours to a few days.
Moderate to severe
A partial tear of the ligament occurs. The ankle joint often swells, bruising occurs, and walking is usually painful and difficult. The treatment lasts from a few days to a few weeks.
If the ankle is dislocated again, nerve damage can occur.
Very difficult
The ligament ruptures completely. Swelling and bruising may occur throughout the ankle joint. The ankle joint is unstable and the person cannot put weight on it.
It usually takes 6-8 weeks to heal. If you do not wait for the ankle to fully heal before returning to normal activity, you are at increased risk of further injury and the joint may not fully recover.
Very severe ankle sprains can result in fracture of the cartilage at the end of the bone in the ankle joint. This injury can cause persistent pain, swelling, and in some cases difficulty walking. The joint may become pinched or protrude (involuntary curvature). Sometimes ankle osteoarthritis develops in young patients.
Diagnosis of an ankle sprain
Your doctor will ask you about the circumstances of your injury and perform a physical examination.
He will also perform movements of the ankle in different directions to determine the severity of the sprain. However, if the victim is in severe pain and has severe swelling or muscle spasms, the examination is usually delayed until X-rays can be taken to detect fractures.
To evaluate the ankle, doctors gently palpate the ankle to determine where the pain is most severe. If touching the skin over the ligament causes severe pain, you probably have a torn ligament. If touching the skin over the bone causes pain, you may have a broken bone. Swelling and cramps make it difficult to assess the condition of the ankle. In such cases, the doctor may immobilize the joint with a splint and examine it again after a few days.
The diagnosis of a sprain is based primarily on the results of the examination. However, sometimes the doctor will order an X-ray to rule out a fracture if the
causes
Athletes and people with a sedentary lifestyle are most likely to experience symptoms of an ankle sprain. The risk increases with:
- overweight;
- high physical activity at work;
- lifting and carrying heavy loads;
- Congenital anomalies of the foot;
- wearing ill-fitting footwear.
Ligament strain is caused by instability of the joint. The structure of the joint is changed by inflammation and osteoarthritis. Risk of injury:
The second most common cause after sports injuries is weakening of the ligaments due to hypodynamics. A sedentary lifestyle leads to a loss of tissue tension, so a short jog or even a sudden movement can cause a tear.
Which doctor should I see?
An ankle sprain should be treated by an experienced doctor. If you experience discomfort, pain, temperature changes and a feeling of tightness in the skin around the joint, you should consult a doctor. B. the
Our specialists
The prices stated on this page are not a public offer. Please call us at 8 (495) 255-37-37 to receive a quote for our services and to schedule an appointment with our therapist.
Prices for Services
In order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy, the doctor must obtain an objective picture of the disease. He:
Therapeutic exercises and calisthenics
Physical therapy is prescribed to patients to improve the function of the ligament-tendon apparatus. The exercises begin with light warm-up exercises. The complex is gradually being expanded and completed. The general principle of therapeutic exercises is freedom from pain at any intensity. The exercises should be done in moderation:
Patients are recommended to walk on their toes and then on their heels several times a day. Rehabilitation therapists recommend flexing and extending the foot and performing circular rotations to achieve a quick recovery.
| treatment methods | Medication, physiotherapy, exercise |
| Pharmacological drugs | Systemic NSAIDs (Celecoxib, Diclofenac, Ketorolac), topical NSAIDs (Fastum, Voltaren, Ketorol, Arthrozilen), chondroprotectors (Dona, Alflutop, Structum, Tereflex), Venotone (Troxevasin, Lyoton, Heparin ointment), drugs to improve blood circulation (Detralex, Venarus, Flebodia). |
| Physiotherapeutic treatments. | UHF therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin therapy, ultrasound therapy, magnet therapy. |
| Surgical procedures | Dry seams and bone seams |
| Gymnastics and therapeutic gymnastics | Walking on tiptoes and heels, lifting small objects from the floor with your toes, rolling a bottle with your feet |
Ankle ligament injuries, even Grade 1, can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. Complications such as flat feet, habitual sprains, arthritis and osteoarthritis develop within a few months. That's why it's important to see a doctor as soon as possible after the injury. Timely examination and competent treatment of torn ligaments can prevent irreversible consequences.
How to forget about joint pain?
However, according to orthopedist Valentin Dikul, there is a really effective remedy for joint pain! >>>
| First aid | 'There is actually an effective and inexpensive remedy for joint pain. |
| Treatment of minor to moderate injuries | First degree ligament injuries are rarely symptomatic. |
| Treatment of third degree injuries | 'The doctors are hiding the truth! |
| Physiotherapeutic treatment | Physiotherapeutic treatment of ankle ligament injuries is always recommended. |
| Therapeutic exercises and calisthenics | Physiotherapy is recommended for patients with ankle injuries to improve the function of the ligament-tendon apparatus. |
| How to forget about joint pain? | However, according to orthopedist Valentin Dikul, there is a really effective remedy for joint pain! >>> |
Symptoms (signs) of a torn ligament
Although this condition is quite common, many people confuse its symptoms with others. This leads to incorrect first aid measures and ineffective treatment, which can cause greater damage. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult a doctor who can accurately diagnose the disease. The main symptoms of a torn ligament include:
Signs of ligament tear are often seen in periarticular injuries, so the injury cannot be diagnosed based on these symptoms alone. To detect abnormalities, medical examinations are required, the results of which are crucial for the choice of treatment.
With microfractures, symptoms can be very mild. However, the straps lose their strength as they wear, which increases the risk of subsequent damage. In addition, the ligaments scar over time and do not allow for regeneration. Therefore, even if there are mild signs of such a pathology, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
causes of injuries
Ligaments are made up of two types of fibers: one gives them elasticity, the other gives them elasticity. At the same time, the movements of the joint have a limited amplitude. If this amplitude is exceeded for any reason, a ligament tear occurs. A partial ligament rupture can have the following causes:
Ligament tears most commonly occur in the wrist, knee and ankle. Of course, most cases occur in athletes, but this injury is also not uncommon at home. Ribbons can e.g. B. if you slip on ice or if your foot slips off a curb. Injuries can also occur if you suddenly stand up from a chair or sofa or bend or turn incorrectly. In all cases the stress exceeds the possible limits, even if it only lasts for a short time. A special case of rupture is an injury caused by bony abnormalities. The growth of new growths can lead to damage to the ligament.
Which doctor should I see?
This type of injury should not be taken lightly. Afterwards, the joint is weakened and there is a serious risk of further damage. You know exactly what to do if there are signs of a ligament tear:
Find a doctor for ligament tears and injuries


Signs of a torn ligament
- A complete tear, where the ligament is torn in two because the integrity of all fibers has been compromised;
- A partial tear in which only some structures of the ligament are damaged but the function of the ligament is not affected (sometimes called a sprain).
Symptoms that indicate a ligament injury include:
- pain, both at rest and with movement;
- Restriction of movement in the area of pain (e.g., it is difficult to bend the leg or arm);
- Instability of the joint in the area of the injured ligament and changes in the external contours of the joint;
- Swelling of the joint
- bruises
- tingling and numbness in the affected area;
- Cracking, cracking, crunching in the joint.
Symptoms depend on the extent and severity of the injury. A partial tear is characterized by slight swelling. With a complete injury, the swelling is greater and extends to surrounding tissue. Older injuries cause significant swelling.
Gymnastics for the ankle after a ligament tear
Rehabilitation after a rupture of ankle ligaments is carried out by specialists at Yusupov Hospital. Their duration depends on the severity of the injury and the individual characteristics of the patient. The course of rehabilitation takes place in 3 phases:
- Physiotherapeutic treatments and massages - starting immediately after the acute phase, on the second or third day after the injury, with phonophoresis and electrical stimulation in combination with massage of the ankle, calf muscle and knee area;
- Physical therapy, initially passive, then active exercises that permanently reduce swelling in the joint, reduce the risk of muscle atrophy and promote primary mobility of the ankle;
- a final phase in which the load is gradually increased to the maximum so that the muscles can regain their natural tension and the joint can regain its normal mobility.
Rehabilitation is also essential after ankle surgery. Rehabilitation therapists at Yusupov Hospital select a set of exercises that will help reduce swelling as quickly as possible, develop normal mobility of the ankle, and strengthen ligaments to reduce the risk of re-injury.
Once the integrity of the ligaments is restored, general exercises are performed while sitting, such as: B. Breathing exercises with gradual rotation of the shoulders and tilt of the body in conjunction with diaphragmatic breathing. This puts you in a good mood and increases general body tension, which is important for the recovery process. Therapeutic physiotherapy is started 3 to 4 days after the injury. The main goal is to reduce the swelling of the ankle joint, develop the necessary flexibility of the ligaments and strengthen the muscles that move the ankle joint.
The patient performs the exercises of the first group while sitting:
Kinesio taping for torn knee ligaments
The rehabilitation therapists at Yusupov Hospital use kinesio taping for knee ligament tears as a method of physical therapy. It is used to treat osteoarthritis, joint injuries and patellar tendonitis. Kinesio-taping of the knee joints acts on all limbs at the same time in the mechanism of development of the pathological process and makes it possible to qualitatively improve the state of health without surgery. Bandaging a torn or stretched meniscus is one of the safest ways to fix the cartilage and prevent further damage.
For stiff knee joints, which may develop in the postoperative period, the effect of treatment can be enhanced by using a mesh. Taping is applied to the entire knee joint, including the anterior, medial and lateral surfaces. Rehabilitation therapists place the tapes on the knee in the shape of a cross, which has the additional positive effect of increasing the tension of the widest and straightest muscles of the thigh. As a soft orthosis, taping relieves the strain on the ligaments, improves microcirculation in the injured area and relieves pain.
Knee taping is performed on the kneecap:
Knee taping is used for torn ligaments with maximum tension, for knee injuries without tension and for quadriceps injuries with mild tension. For effective and affordable rehabilitation after a torn ligament, contact Yusupov Hospital.
Read more:- Rupture of the ligaments of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle.
- Injury to the ankle.
- Treatment of torn ligaments in the ankle.
- Partial tear of the ligaments of the ankle.
- Ankle ligament strain, ICD.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle photo.
- ligaments of the ankle.
