Wearing a compression stocking after a phlebectomy is mandatory. Bandaging the leg after phlebectomy is recommended on the first day to avoid thromboembolic complications. Bandaging with elastic bandages continues until the sutures are removed, that is, about ten days.

Osteoarthritis of the elbow: monoarthritis, inflammation and treatment
Osteoarthritis is a group of joint diseases that are inflammatory in nature. In this case, virtually any component of the joint can be affected: capsule, cartilage, synovial membrane, etc.
If the inflammation occurs in two or three joints, it is called oligoarthritis; if the inflammation occurs in four or more joints, it is called polyarthritis. Depending on the type of disease, different groups of joints are affected. In gout, for example, the inflammation first develops in the joint of the big toe, while in psoriatic arthritis the end phalanges of the fingers are affected.
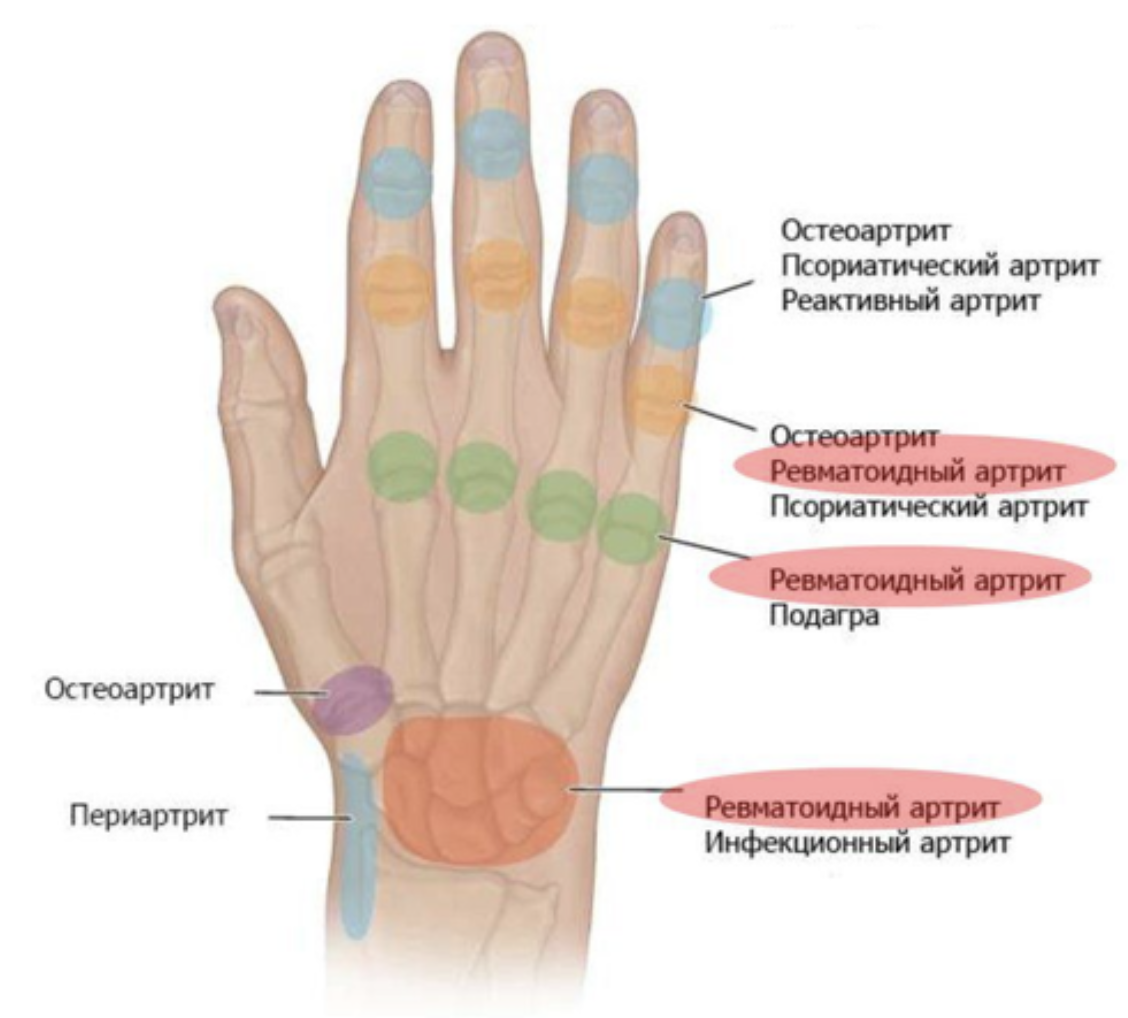
Monoarthritis - a disease in which only one joint is affected - is usually classified according to its location, among other things. A variant is elbow arthritis.
Three bones meet in the elbow joint: the humerus, the ulna and the radius. In fact, this joint consists of three joints connected by a common capsule. Thanks to this structure, it is possible not only to bend and straighten the arm, but also to rotate the forearm. The entire structure is stabilized by a well-developed ligament and muscle system that is controlled by nerves. The inflammatory process in the joint severely impairs the function of the entire limb.
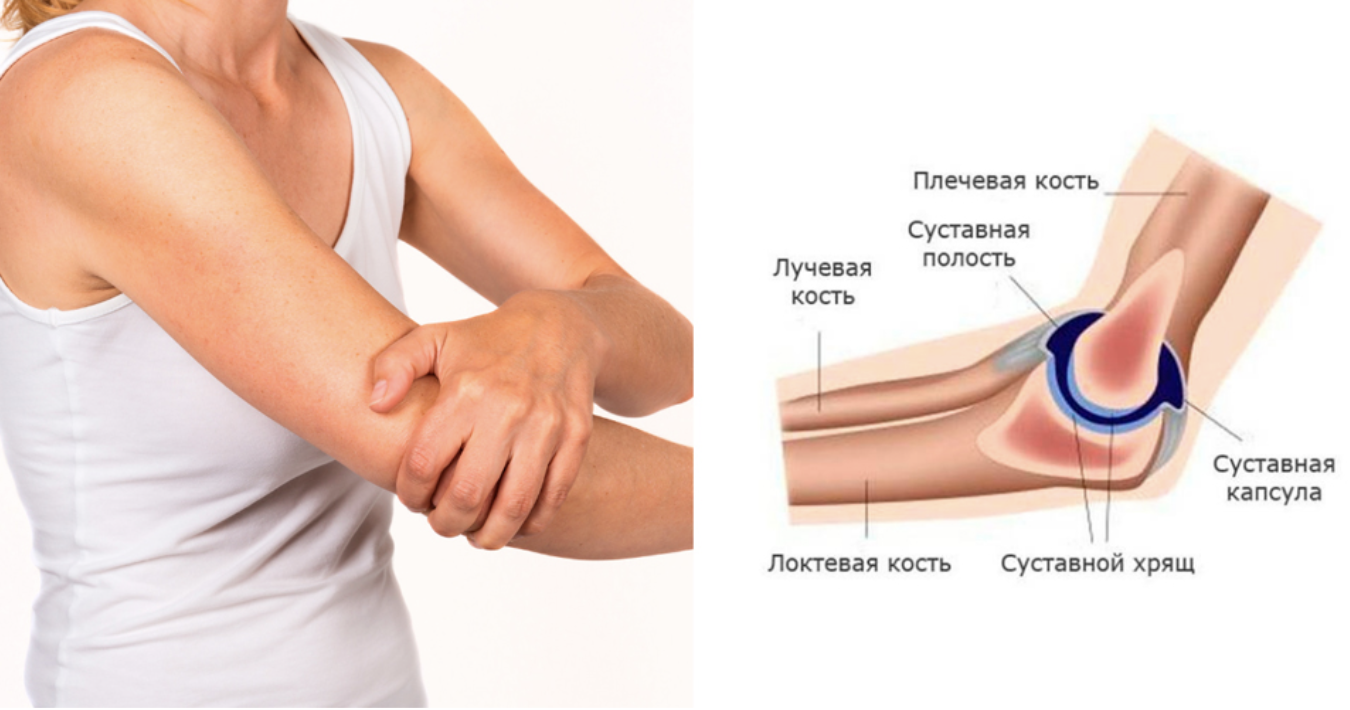
The frequency of arthritis varies depending on the form of the disease. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis it is 0.5-1 % in the population of developed countries. The highest incidence occurs in the fifth decade of life. The incidence is higher in women. The frequency of rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow is between 20 and 70 % of all locations.
causes
Like inflammation of other joints, arthritis of the elbow can be classified as follows:
- Arthritis, as an independent form of
- Rheumatoid arthritis, caused by autoimmune, systemic damage to connective tissue in the body;
- rheumatoid polyarthritis (the elbow joint is affected at the same time as other joints);
- infection specific (e.g. tubercular, viral, etc.).
- infectious-allergic;
- psoriatic;
- juvenile (chronic inflammatory joint damage in children and adolescents), etc.
- allergies;
- metabolic disorders (e.g. gout);
- bronchopulmonary diseases;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- tumors;
- osteomyelitis;
- Infections of the gastrointestinal tract or genitourinary tract (reactive arthritis), etc.
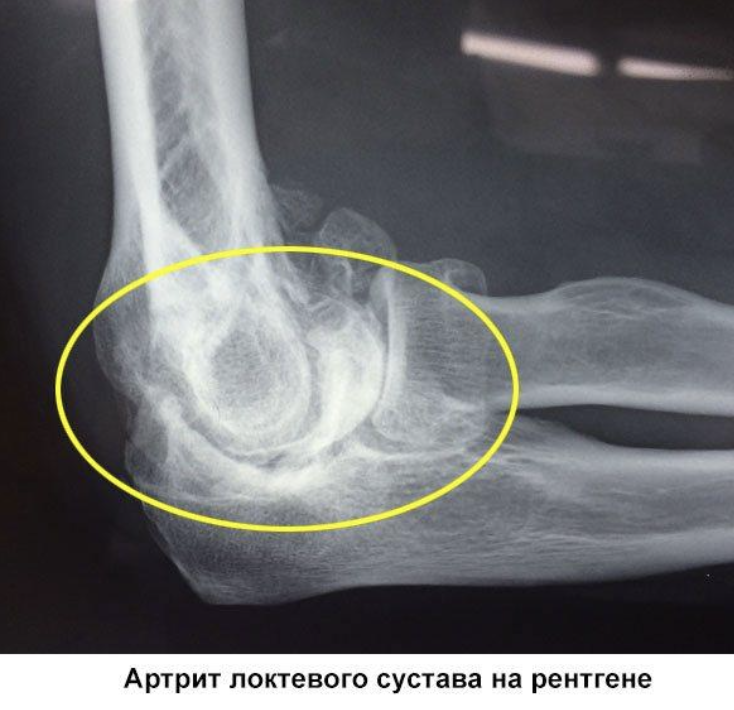
Need for rehabilitation
Surgery is a heavy burden on the body. Therefore, he needs time to return to normality. This period is called rehabilitation or convalescence. The patient is prescribed measures to restore normal blood flow in the veins and heal the damage. Rehabilitation is also necessary to prevent adverse effects of phlebectomy and, if they occur, to eliminate complications.
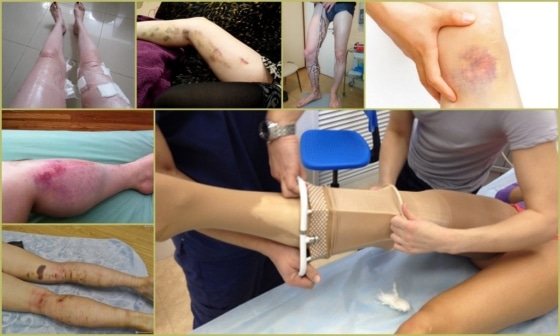
Like any surgical procedure, phlebectomy can be associated with a number of complications:
- Damage to nerve fibers leading to loss of sensation in the limbs;
- Bruises on the limbs;
- Inadequate wound care, presence of diabetes – high risk of abscess formation;
- Blood clotting disorders lead to bleeding or venous thrombosis;
- After a phlebectomy, eczema may form on the legs due to impaired blood circulation;
- The most unpleasant possible complication after a phlebectomy of the legs is pulmonary embolism, which is caused by a blood clot from the leg veins that enters the pulmonary vessels.
A not uncommon complication is recurrence of the disease.
Otherwise, the disease may recur.
The risk of undesirable side effects increases if rehabilitation is inadequate.
Recovery periods after surgery
The postoperative period lasts an average of 7-10 days. This period may vary depending on the course of the operation and the general condition of the patient. If there are additional pathologies, the doctor will determine an individual rehabilitation period.
The postoperative recovery period is divided into two phases – the early and late phases. The early phase begins immediately after surgery and lasts two days. This is followed by basic recovery, which can last up to three months after the operation.
Symptoms of a tibia fracture
The clinical signs of a tibia fracture may be as follows
- Pain that increases when palpating the leg or trying to move;
- swelling at the injury site and visible bruising;
- Poor posture of the leg, e.g. B. If the external condyle is injured, the leg tips outwards; if the internal condyle is injured, the leg tips inward;
- Severe limitation of leg mobility;
- Functional impairment – the lower extremity can no longer be supported because the integrity of the bone is compromised;
- Crunching of the bones (crepitations) when palpating or trying to move the leg.
If there is a simultaneous injury to the knee or ankle joint, hemarthrosis - an accumulation of blood in the joint - can occur in addition to the symptoms mentioned above. If this condition is not treated in a timely manner, it can lead to adverse consequences. In the long term, deforming osteoarthritis can develop, in which the cartilage plate is gradually worn away and persistent pain occurs.
Causes of tibia fractures
The causes of shin fractures can be traced back to accidents at home, during sports or at work. The type of bone fracture depends on the point at which the external force is applied and its direction.
- A fall from a height most often results in a fracture of the tibial condyles. These can be split or depressed (compression fractures).
- Direct and indirect injuries usually lead to fractures of the tibia or fibula shaft. If the connecting connective tissue membrane is not damaged, the fractures are not displaced.
- If the foot is abruptly turned outward or inward, hyperextension of the ankle can occur (a similar mechanism occurs with ice injuries). The latter can also be injured by direct impacts.
Stress fractures are a category of their own. They occur when the shinbone is subjected to mechanical stress for a long period of time, with the force almost comparable to the strength reserve of the bone. Such fractures can occur in athletes and military personnel who have been marching for many years.
Advantages of MRI of the elbow

MRI of the elbow is often compared to CT, ultrasound and X-ray. The MRI technology is unsurpassed in its informative value. In addition, it is safe and poses no risk of radiation exposure.
The main advantages of MRI scanning of the elbow region are.
- Clear representation of all anatomical structures in the study area.
- Ability to see not only the pathology, but also to determine the type, stage of development, exact size and volume, metastasis.
- Non-invasiveness, speed of implementation.
- Quick capture of visual results.
- No need for lengthy preparation for the examination and subsequent recovery.
- The frequency of the examination can be any and is determined by doctors depending on objective necessity.
- Early diagnosis of pathological processes, tumors, injuries.
- Can be used in children's medical care. General sedation is used for young children who cannot lie still for the required time.
- A specific area can be imaged in different projections so that the lesion can be viewed from different angles.
MRI uses modern gadolinium-based compounds instead of outdated iodine preparations. This avoided the typical complications of a contrast-enhanced examination and the risk of allergic reactions in sensitive people.
Where is magnetic resonance imaging of the elbow joint performed in Moscow?
Medscan Medical Diagnostic Center performs any type of hardware diagnostics, including all types of MRIs. The examination is carried out on modern, expert-level tomographs under the supervision of qualified, experienced diagnosticians.
The prices for MRI scans and other medical services are affordable for all patients. A price list can be found on the clinic's website. The final price of the examination is determined taking into account the type of CT examination, the need for contrast enhancement, sedation, detailed decoding of the results and additional consultations by highly qualified specialists.
In order to make an examination as pleasant as possible, an appointment must be made in advance. You can make an appointment for a consultation or diagnostics by calling the clinic or using the feedback form. Here you can also find out about special offers, features of diagnostic and therapeutic activities and doctors. Enter your contact details, the managers will contact you shortly.
- Isakova TM, Kolotova GB The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of the elbow joint in patients with chronic pain // VI International Congress of the Rheumatopedic Society. – 2022. – С. 43-44.
- Kudinski DM et al. Comparison of standard radiography and magnetic resonance imaging for arthrosis of the hand // Scientific and practical rheumatology. – 2021. – Т. 59. – № 4. – С. 418-425.
- Kochergina NV et al. Effectiveness of MRI in determining the presence of bone metastases with controversial SPECT/CT findings // Journal of Oncology: Radiation diagnostics, Radiotherapy. – 2020. – Т. 3. – № 3. – С. 93-100.
- Lobanov GV Surgical treatment of elbow injuries // VI International Congress of the Rheumo-Orthopedic Society. – 2022. – С. 72-74.
- Guseinova AR, Kaziev AY, Dadashova VA. Application of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors // Medical News. – 2020. – № 1 (304). – C. 72-75.
- Kochergina NV et al. The effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging in detecting bone metastases in the case of controversial results of SPECT/CT // Journal of Oncology: Radiation diagnostics, Radiotherapy. – 2020. – Т. 3. – № 3. – С. 93-100.
- Bocharnikova VA For the diagnosis and treatment of neuropathy of the ulnar nerve. A clinical case // Brain Universe. – 2021. – Т. 3. – № 1. – С. 5-8.
- Karateev AE et al. Periarticular soft tissue injuries in clinical practice: frequency, type and effectiveness of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs // Therapeutic Archives. – 2019. – Т. 91. – № 12. – С. 21-28.
- incision on the leg.
- Injury to the ligaments of the ankle.
- Ankle injury, ICD code 10.
- Injury to the ankle.
- Injury of shin ligaments.
- Injury to the navicular semilunar ligament.
- Injury of the tibial condyle.
- Injury to the shoulder joint.
