Tapes that line the outside of the surrounding the ankle.These include the anterior and posterior fibula ligaments, as well as the fibula ligament. The powerful deltoid ligament is found on the inside of the joint and is the only ligament in this joint that contains elastic fibers. The tibia and fibula are connected distally by the anterior and posterior tibial ligaments. The latter enhance the shock-absorbing properties of the ankle and connect proximally to the intercondylar membrane. The movement of the ankle and foot is described using a number of interchangeable terms.

- Injuries to the ankle
- Classification of injuries (fractures and dislocations) of the ankle
- Ankle fracture: symptoms and first aid
- First-class care: what modern diapers can do
- First aid and treatment for broken ankles
- Medical treatment of injuries
- treatment strategies
- Pharmacological treatment
- Physiotherapeutic measures
- Symptoms (signs) of a torn ligament
- causes of injuries
- Which doctor should I see?
- Causes of ankle sprains
- Types of ankle dislocations
- causes
- Which doctor should be consulted?
- Our specialists
- signs
- Treatment
- REAR ANKLE LIGAMENTS: WHO IS AT RISK?
- THIS IS WHAT A REAR ANKLE LIGAMENTS LOOK LIKE
- 1ST STAGE
- 2 STAGE.
- 3 DECISION
- Massage after a torn ligament in the ankle
- Massage for dislocated knee joints
Injuries to the ankle
The ankle joint carries the greatest body weight per unit area compared to other joints in the body. Injuries that are anatomically inaccurate often lead to the development of traumatic osteoarthritis of the ankle. It's important for the doctor to know that ankle fractures and ligament injuries very often occur together. Any treatment plan must consider both types of injuries.
Sir Percival Pott (Percivall Pott) was one of the first to study ankle fractures in 1768. He described a fracture of the fibula 8 cm proximal to the ankle in connection with a tear in the deltoid ligament. The term 'pott fracture' is still used (albeit imprecisely) to describe a double ankle fracture.
Since then, some researchers have investigated questions such as the following fractures Several researchers have since studied ankle fractures and attempted to classify them. In 1922, Ashurst and Vgoteg proposed a classification based on the mechanism of injury.
K UnfortunatelyThe increasing variety of injury mechanisms and associated ligament damage are not adequately accounted for by this classification, which is why it is not widely used in practice. In 1949, Niels Lauge-Hansen proposed a classification based on the position of the foot and ankle at the time of injury.
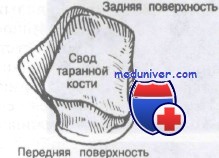
The hip block is wider at the front than at the back.
In this classification the first word indicates the position of the foot at the time the traumatic force was applied, and the second word indicates the direction of the applied force. Unfortunately, this classification does not include direct injuries such as embedding or axial compression.
She doesn't consider either. Combinations of differently directed forcesresponsible for most injuries. Wilson developed the classification by including combined forces. However, it became too cumbersome and also did not adequately reflect the position of the foot at the time of injury. After a brief overview of the functional anatomy of the ankle, the classification of ankle injuries proposed by the University of Chicago Critical Care Medicine is described in detail.
Classification of injuries (fractures and dislocations) of the ankle
For fractures There are several classifications for fractures and dislocations of the ankle. This classification includes several axioms that provide paramedics with comprehensive information about related injuries. In addition, the classification is easy to understand and is based on the increase in injury volume when an increasing force is applied in a specific direction. In general, three important elements are considered: (1) the position of the foot at the time of injury; (2) the direction in which the injuring force displaces the talus; and (3) the magnitude of the force and the degree of resistance of the support structures.
There are three basic powers(1) The main forces acting on the ankle. If the talus is taken as a 'reference point', the forces act medial, lateral or axial to the talus. Each of these 'primary damaging forces' can then be combined with secondary damaging forces (which are added to the primary forces in parentheses in the tables). The forces that displace the talar bone laterally are diverging or eversion forces (class A).
medial The talus is displaced medially by a driving force (class B). Adduction strength (class B). Class B fractures are the result of an axial shear force. The position of the foot at the time the force is applied determines the type and sequence of structural damage and is considered in the classification system.
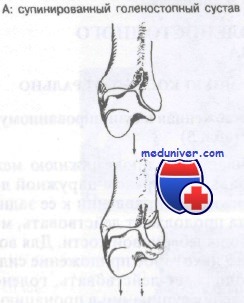
ankle fractures:
Class A: Force that displaces the talus laterally
Class B: Force that displaces the talus inward
Class C: force transmitting axial compression to the talus
Ankle fracture: symptoms and first aid

Ankle fractures are one of the most common injuries to bones and joints, especially in winter. Severe pain, inability to step on your foot, and numbness in your limbs are symptoms that may prompt you to see a trauma surgeon.
Older people and people suffering from a bone disease belong to the risk group.
The ankle is a complex anatomical structure that allows the foot to move and walk. The ankle is the part of the leg that connects the lower leg and foot. The ankle is considered to be the area most prone to injury, for the simple reason that it is subjected to the most loads, supporting many times the human body weight.

First-class care: what modern diapers can do
First aid and treatment for broken ankles
For a broken ankle, first aid is to stabilize the ankle with a splint. The first thing to do with an open ankle injury is to stop the bleeding. If the bleeding is light, the wound should be disinfected and a sterile bandage applied, while if the bleeding is severe, a tourniquet should be applied.
Depending on the clinical picture and the complexity of the ankle fracture, appropriate treatment is carried out. For complex fractures with displacement, surgical repositioning of the bone is performed. After repositioning, the wound is sutured and a plaster cast is placed over the fracture site. The average duration of the plaster cast is 2 months. For fractures with displacement, the plaster cast can remain on the injured leg for up to 4-5 months.
The rehabilitation period after a broken ankle is as important as the treatment itself. Massage, exercise therapy and physical therapy are recommended to help the broken joint regain function as quickly as possible.
Medical treatment of injuries
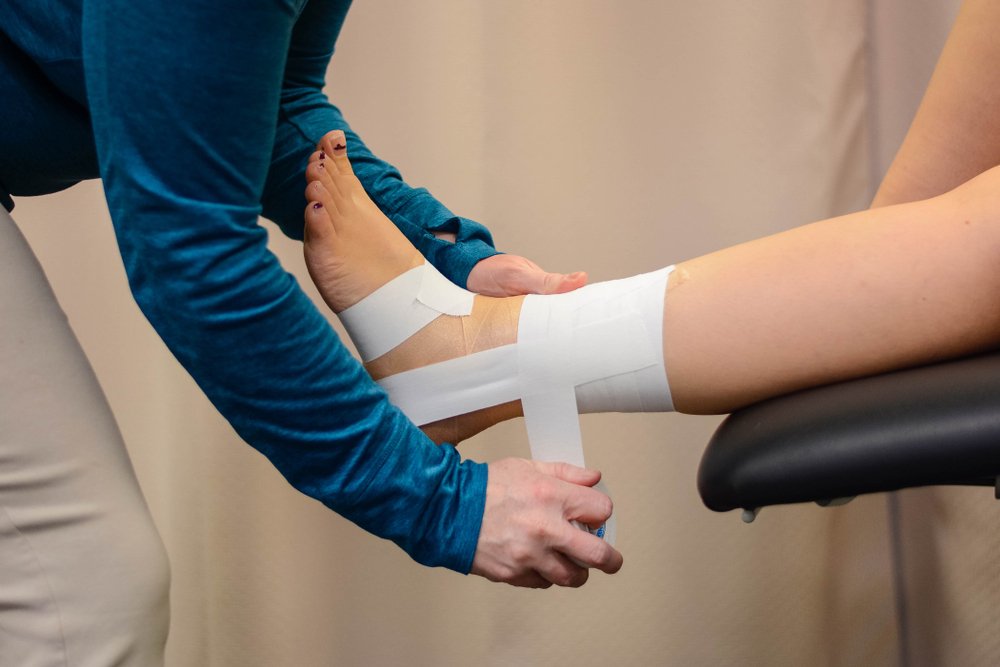
Cold treatment should be carried out immediately after the injury. It is advisable to fix the ankle joint with a firm eight-point harness. The more correctly the bandage is applied, the more effective it is. In addition, the load on the leg should be limited.
To relieve inflammation, pain and swelling, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of ointments, gels and creams.
In addition, a bioregulating ointment with various herbal and mineral ingredients - arnica, monkshood, deadly nightshade, echinacea, etc. - can be used. In 2016, researchers from the University Hospital of the Technical University of Munich published a paper demonstrating the effectiveness of this drug in diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
It is important to remember that the use of any medication is possible only after prior consultation with a doctor.
Physiotherapeutic treatment can be started around the second or third day after the injury. These can include magnet therapy, thermal applications with ozokerite or medicinal paraffin, and others.
When an ankle is sprained, the injured area is restored to function within an average of one to two weeks.
treatment strategies
An integrated approach to treating the sprain is taken to achieve rapid function recovery of the injured joint. The patient is treated with systemic and topical medications and comes to the physiotherapy office for treatment. Exercise or gymnastics under the supervision of the LFK doctor is recommended from around the 3rd to 5th day of treatment. Regular exercise improves blood flow to the ankle, promotes tissue regeneration and helps with swelling and bruising.
Pharmacological treatment
Long-term treatment with NSAIDs in tablet or capsule form is not necessary. Treating an ankle bruise with cold compresses for 2-3 days will help relieve pain. The discomfort is numb and dull, but increases significantly with walking due to soft tissue displacement. In this case, Naise, Ketorol, Nimulid, Ibuprofen can be taken, but no more than 3 tablets per day. NSAIDs should be combined with proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole is the cheapest and cheapest), otherwise this treatment of the bruise can lead to erosive gastritis. Comprehensive treatment of the violation involves the use of such external means:
- NSAIDS. Fastum, Voltaren, Finalgel, Diclofenac ointment and gel, Arthrosilen, Dolgit with pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects. They are applied thinly to the bruised area 2-3 times a day and gently rubbed in. They develop their pain-relieving effect within 15-30 minutes for 4-8 hours. Topical NSAIDs are not indicated for pregnant and lactating women and for children under 6-12 years of age (depending on the active substance);
- Ointments with a warming effect. Finalgon, Capsicam, Apisartron are prescribed to patients on day 3-4 of treatment, after the acute inflammatory process has subsided. The preparations contain ingredients that have a local irritating, analgesic and distracting effect. They compensate for the lack of nutrients and bioactive compounds and stimulate regeneration processes. Dosing regimen – 2-3 times a day for a week. The drugs have an extensive list of contraindications, which sometimes provoke the development of local allergic reactions;
Physiotherapeutic measures
In the case of bruises that are accompanied by fractures, ligaments, tendons and muscle fiber tears, a plaster cast is placed on the injured leg. In these cases, physical therapy is performed several weeks after the bandage is removed. If a simple ankle injury is diagnosed, an elastic or semi-rigid orthosis should be worn. They are easily removed so that physical therapy can begin once the inflammation has subsided. What are the most effective treatments?
- laser therapy, which accelerates the resorption of swelling, small and large bruises;
- UHF therapy, which stimulates metabolism and facilitates the removal of tissue breakdown products and inflammation;
- magnet therapy, which strengthens the walls of blood and lymphatic vessels and speeds up blood circulation;
- electrophoresis with NSAIDs, analgesics, and anesthetics to relieve pain, swelling, and inflammation;
- diadynamic currents that reduce the intensity of pain;
- application of paraffin, ozokerite, bischophite, which eliminate the lack of nutrients and biologically active substances in the damaged joint structures;
- Therapy with healing mud and mineral water to stimulate tissue regeneration.
Ultrasound therapy of the ankle.
However, the most common treatment for bruising patients is repeated cold therapy. Ether, chloroethyl, liquid nitrogen and ammonium nitrate are used as active ingredients. During the treatment, the excitability of the nerve fibers is reduced so that the conduction of excitation is partially blocked. The reflex muscle contraction is eliminated, and the intensity of the pain is reduced after 5 minutes by the application of coolants.
Symptoms (signs) of a torn ligament
Although the condition is quite common, many people confuse the symptoms with others. This leads to inadequate first aid measures and ineffective treatment, which can cause further damage. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult a doctor who can accurately diagnose the disease. The main signs of a torn ligament include:
Signs of a ruptured ligament are common with periarticular injuries, so the injury cannot be diagnosed based on these symptoms alone. Hardware testing is required to detect abnormalities, the results of which are critical to the choice of treatment.
For microfractures, symptoms can be very mild. However, the ligaments lose their strength due to the thinning, which increases the risk of consequential damage. In addition, the ligaments scar over time and do not allow regeneration. Therefore, even with slight signs of such a pathology, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
causes of injuries
Ligaments are made up of two types of fibers: one gives them elasticity and the other gives them elasticity. At the same time, the movements of the joint have a limited amplitude. If this amplitude is exceeded for any reason, ligament rupture will occur. A partial ligament rupture can be caused by:
Most commonly, ligament tears occur in the wrist, knee, and ankle. Most cases, of course, occur in athletes, but even at home this injury is not uncommon. Ligaments can tear if, for example, you slip on ice or your foot slips on a curb. Injury can also occur if you suddenly stand up from a chair or sofa, or bend or turn inappropriately. In all cases, the exposure exceeds the possible limits, even if it lasts only for a short time. A special case of rupture is an injury caused by bony abnormalities. The growth of new growths can damage the ligament.
Which doctor should I see?
This type of injury should not be taken lightly. After that, the joint is weakened and there is a serious risk of further damage. You know exactly what to do when there are signs of a torn ligament:
Causes of ankle sprains
- Increased mobility of the joint
- Congenital hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the ankle
- History of repeated ankle sprains, habitual dislocations
- high arch
- Age-related changes and destructive degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
The clinical picture is acute ankle pain at the time of injury. Swelling, hematoma, and impaired movement and support of the limb follow. Vitality and tension of the tissue in the area of the injury, a cold foot, lack of pulsation and sensitivity indicate a neurovascular disorder. With subluxations, there is a moderate disruption in the relationship of anatomical structures, with dislocations, there is a pronounced deformity. Crepitations indicate a coexisting fracture.
Types of ankle dislocations
Posterior dislocation is the most common type of ankle injury. The talus is displaced backward toward the distal tibia as the force pushes the foot backward. When the lateral ankle is injured, a tear of the intercondylar syndesmosis or a fracture is diagnosed.
The anterior sprain is caused by immobilization of the foot and application of force to the tibia, forcing the ankle into dorsiflexion.
Lateral dislocation is caused by forced inversion (twisting), eversion, or external/internal rotation of the ankle. The injuries are associated with fractures of the ankle and/or distal fibula.
The ankle is a result of the upward displacement of the talus as a result of jumping from a great height. The patient is also evaluated for a heel bone fracture and spinal cord injury.
In 50 % of the cases, the dislocation of the medial malleolus is an open ankle where the bone fracture was interrupted by a skin fracture.
causes
The main causes of dislocations can be divided into two main groups: direct and indirect. The first category includes direct impacts on the ankle: sprains in certain situations, such as being involved in a traffic accident or dropping a heavy object on the foot. The second group includes unfortunate movements of the foot, most commonly when falling or slipping. Increased risk of injury:
The efficiency of all functions of the musculoskeletal system and the strength of the musculoskeletal system depend on many factors. An ankle fracture without a dislocation can also occur when one of these functions is compromised. This type of injury is more common in winter, when the likelihood of slipping on ice is very high. Older people are particularly affected because, in addition to the reduced cushioning properties of the skeleton, their muscles and ligaments are often weakened.
Which doctor should be consulted?
Even if the symptoms of the injury are quite tolerable and unremarkable, you should visit a medical facility as soon as possible. The danger is that small splinters of bone can form, causing much more damage. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of a fracture, consult the nearest doctor:
Our specialists
The prices shown on this page are not a public offer. Please call us at 8 (495) 255-37-37 to determine the cost of services and to schedule an appointment with a doctor.
signs
Symptoms of ankle injuries depend on the type and severity of the injury.
With a sprain, there is a sudden increase in swelling and severe pain when twisting the foot and palpating it.
- The lateral malleolus is painful below and at the ankle;
- In both ankles, any attempt to move the ankle is painful, and the pain is audible along with the crunching of the ankle joint with movement;
- The injured person can no longer get up on the heel bone due to severe pain in the heel;
- The middle portions of the metatarsal bones are severely painful when the forefoot is loaded and the foot is palpated.
A sprained ankle is characterized by visible deformity, pain, and swelling, and the foot is displaced inward, outward, or backward.
Depending on the severity of the injury, three degrees can be distinguished:
- I (mild) – slight swelling and tenderness without hyperextension, but no joint instability or noticeable impairment of foot function;
- II (moderate) – partial rupture of the ligament, characterized by moderate pain, swelling, slight impairment of foot function and instability of the joint (intra-articular bleeding is also possible and pain increases with exertion);
- III (severe) - complete ligament rupture with severe swelling, subcutaneous bleeding, severe pain, reduced foot function and marked joint instability (bleeding, inability to support the limb).
Chronic ankle ligament injuries are associated with ankle swelling, pain when walking and running, swelling and instability of the joint.
Treatment
At First Medical Clinic we offer conservative treatment of ankle injuries using the most effective and safe methods:
- drug blockages – Injection of anesthetics directly into the area of most pain
- Local injection therapy – injection of anesthetics, anti-inflammatory and other drugs into the joint cavity;
- intra-articular injections hyaluronic acid (relieves pain and accelerates function recovery in ankle fractures);
- Bio Osteo Bio Implant - injection of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from the patient's adipose tissue into the injured area, which promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing;
- Injection of platelet-derived autoplasma into the damaged joint or surrounding tissue (auto plasma therapy), etc.
The use of autografts not only heals tissue after injury, but also prevents the development of complications such as post-traumatic ankle arthritis. It is also effective in the treatment of an already developed degenerative-dystrophic process.
The necessary extent of therapy can only be determined by a specialist doctor after diagnostic procedures. For the treatment of ankle injuries, we recommend contacting the First Medical Clinic in good time.
You can make an appointment for a consultation and visit at the number below
REAR ANKLE LIGAMENTS: WHO IS AT RISK?
Anyone of any age can sprain an ankle. Sometimes it happens all of a sudden: a walk, a stumble and there it is: an attack of pain from a torn ankle ligament and the inability to kick the foot. However, there are some people who are particularly prone to injury:
- competitive athlete.
- Enthusiasts in ski resorts, roller skaters, skaters, etc.
- Gardeners with shovels: Digging up the ground in the spring puts an acute, unusual strain on the ankle.
- Patients with foot abnormalities: valgus foot, flat foot, etc.
- Patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system: scoliosis, posture and gait disorders.
- people with obesity.
- People with congenital diseases in which the connective tissue is particularly elastic (Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, etc.).
THIS IS WHAT A REAR ANKLE LIGAMENTS LOOK LIKE
1ST STAGE
Elongation of a small part of the fibers.
- Discomfort when putting your foot down, walking or running quickly. No pain at rest.
- Slight swelling over the lesion and on the forefoot.
2 STAGE.
Partial tear - significant fiber damage.
- Sharp pain with every step and at rest, especially on waking.
- Marked swelling, which is noticeable when putting on shoes (the painful foot is larger than the healthy foot).
3 DECISION
Torn ligament in extensive ankle injury.
The symptoms of a torn ligament are particularly severe:
- inability to put weight on the foot because it hurts;
- swelling of the entire joint, the redness may reach the middle of the shin;
- Hematoma over the damaged ligament.
If these symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately!
Massage after a torn ligament in the ankle
Severe ankle injuries require surgery or long-term immobilization in a cast. Massages are not indicated in the acute phase. However, it is used during the convalescence period to speed up the patient's recovery and relieve discomfort.
Operations are performed differently depending on the type of injury. Some require subsequent immobilization. Many ligament reconstruction surgeries do not require a cast. Therefore, patients can already put weight on the limb and perform physical exercises in the first few days. In the first two to three weeks, the burden of walking on crutches is reduced to a minimum. Later, a stick is used as a support.
Massages can already be carried out in the first days after the operation. However, it is not the joint itself that is massaged, but the soft tissues near the joint. During the long rehabilitation period, massage can also be used to restore range of motion in the ankle.
Massage for dislocated knee joints
The aim of the massage is to relieve knee pain and improve blood and lymph circulation. This will help to quickly restore the function of the joint.

Massage for dislocated knee joints
The massage should be started no earlier than one day after the injury. Until then, a complete functional rest is recommended. Cold can be applied to the knee to reduce swelling and pain.
Heat treatments can be carried out from the second day. This can be combined with a limb massage. This should be done in such a way that the patient does not feel pain.
If the knee ligaments are sprained, the thighs should be massaged. In the beginning, the massage should be performed once or twice a day for 5-10 minutes each time. The initial massage lasts 2 to 3 minutes: stroking the skin of the thigh, kneading and rubbing. The duration of each session is gradually increased and reaches 15 minutes.
After the acute phase of the injury, when touching the knee is no longer painful, the injured joint can be massaged directly. Massage is performed on the lateral surfaces of the knee, less often on the back of the leg. When the knee is massaged, the patient lies down and a roller is placed under the knee. Straight and circular rubbing movements with four fingers and the ball of the hand predominate.
If the hollow of the knee is massaged, the person lies on their stomach. The leg is bent at a 45 degree angle. Generally, circular strokes and rubbing are used. It should be remembered that there are numerous nerves and blood vessels in the popliteal fossa. Therefore, the area should not be overloaded.
Massage is a good, simple, and inexpensive way to relieve the symptoms of ankle or other lower limb injuries. It can be used as early as the second day after an injury. A massage can help a person feel better and recover faster. In most cases, however, it cannot be used without other therapeutic measures. Physical therapy, physical therapy, and medications to reduce pain and swelling are also used. In some cases, prolonged immobilization of the limbs with a cast may be required. Surgical treatment may also be necessary. In such cases, a massage alone should not be enough. With any injury, it is advisable to consult a doctor, undergo a diagnosis and undertake a comprehensive treatment, where massage can be part of the healing of the joint from the injury.
Read more:- Injury to the ligaments of the ankle.
- Ankle injury, ICD code 10.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle.
- Injury to the ankle.
- Structure of the human ankle.
- ligaments of the ankle.
- Rupture of the ligaments of the ankle.
