The operation is carried out as an inpatient in a medical center and is considered uncomplicated. Before the procedure, tests should be done to determine whether you are allergic to any medications, especially anesthetics.

- Ligamentosis
- Signs and symptoms of ligamentitis
- Symptoms of ligament inflammation
- Causes of Ligamentitis
- Joint diseases of the foot
- hip joint
- Knee joint
- symptoms
- Periarticular shoulder arthritis.
- Treatment
- Results
- Lifestyle with ligamentitis
- causes
- symptoms
- causes
- symptoms
- Sustavit with chondroitin
- Pump hyaluronic acid into the knee joint
- Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint, grade 1
- Joint complications after tonsillitis
- diagnosis
- prognosis and prevention
Ligamentosis
Ligamentosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the ligaments with a chronic course. The main site of this pathology is the ligament-bone joints. The occurrence of ligamentosis is promoted by an increase in the volume of the cartilaginous-fibrous tissue. In the long term, the resulting cartilage structure ossifies due to saturation with calcium salts.
Ligamentosis most commonly affects the knee joints. But other places also occur:
The main causes of these problems are systematic micro-injuries caused by heavy physical exertion, co-existing chronic diseases (e.g. osteoporosis), or long-ago joint injuries that have not caused discomfort for some time.
Signs and symptoms of ligamentitis
The main symptom is a sharp and severe pain in the affected ligaments.
- The painful sensation occurs with even slight external pressure on the joint.
- After any physical activity, an excruciating pain occurs that lasts for a long time.
- There will be swelling, redness or bruising at the injury site.
- The motor function of the affected joint is severely impaired.
Most often there is a limp or constant discomfort when walking or doing light physical activity.
Important!
If you experience the above symptoms, you should see your doctor as soon as possible.
When the first symptoms appear, it is important to go to a clinic as soon as possible, where a specialist will conduct an examination, diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment. Ligamentitis is treated by orthopedists and traumatologists.
Symptoms of ligament inflammation
The symptoms of ligament inflammation are similar, although ligament inflammation can occur in different parts of the body (ligaments of the hand, elbow, or knee).
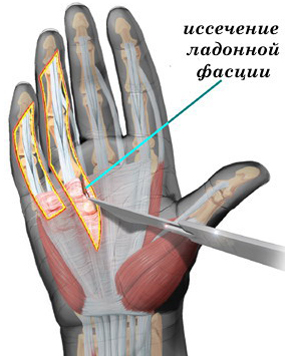
Symptoms of ligament inflammation include::
- Pain in the area of the affected ligament, which becomes noticeable when moving;
- Increased sensitivity to pain;
- Postural spasms may occur;
- Decreased mobility in the joint affected by the ligament;
- nausea in finger;
- Swelling in the area of the joint whose ligaments are affected.
There are characteristic symptoms for ligament inflammation in various locations. For example, acute inflammation of the annular ligament in the hand causes pain in the finger when flexed and extended, a characteristic clicking sound in the finger when moving and pain when pressing on the hand.
If the above symptoms occur, one should not hesitate and consult a doctor immediately.
Causes of Ligamentitis
The causes of ligamentitis are diverse, so that the disease can be described as polyetiological. Ligamentitis can be caused by:
- consequences of trauma;
- Consequences of a chronic infectious process in soft tissue.
- Occupational activity with constant strain on the fingers, abnormal hand position or heavy strain on the hand;
- Excessive use of the thumb or index finger (e.g. by pressing objects hard and for a long time).
Added, Systemic diseases and other medical conditions can cause ligamentitis.For example:
Joint diseases of the foot
hip joint
The hip joint is the largest joint that connects the pelvis to the lower limbs and essentially takes the majority of the load of movement. It is a classic 'joint' and is formed by the spherical head of the femur and the hip socket of the pelvis. In addition, part of the femoral neck is part of the socket of the hip joint. This complex system allows freedom and ease of movement.
Causes that can lead to pain:
- Fracture of the femur
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head (destruction of the articular part of the bone)
- Arthritis (inflammation of the joints)
- Osteoarthritis (tissue degeneration)
- Bursal bursitis (inflammation of the periarticular capsule)
- Tendonitis (tendonitis)
- infections
- injuries
- Tumors
- Joint damage due to rheumatic diseases
Like any other movable bone joint in the body, the hip joint tends to wear down with age - the cartilage gradually becomes thinner and the articular surfaces of the bones deteriorate. All of this leads to unphysiological friction, which leads to inflammation and pain.
It is also possible that the pain is simply a radiation (spread) of the pain in the lower back. Conversely, even if there is an obvious injury to the hip joint, the pain may only be felt in the upper and lower leg.
Knee joint
The knee joint is the second largest joint in the body and connects the thigh bone to the lower leg via a series of tendons, muscles and ligaments that stabilize and strengthen the joint.
In general, pain sensations in the knee mean that one of the components of the joint is damaged.
symptoms
The tendons that are subjected to the greatest stress and mechanical stress are the first to show pathological changes. Fibril defects, necrosis, post-inflammatory sclerosis, hyalinosis and calcification occur. The primary lesions are located at the attachment points of the tendons to the bone (entheses) and are referred to as enthesopathies. Later, tendon sheaths (tendovaginitis), synovial membrane (bursitis), fibrous capsules (capsulitis), joint ligaments (ligamentitis), etc. can also be affected.
Typical symptoms of extra-articular rheumatism are pain and limited joint mobility. The pain occurs with certain active movements of the joint; localized painful areas are noted in areas of tendon insertions. In tendinitis and synovial bursitis, there is pronounced swelling along the tendon or synovial projection.
Periarticular shoulder arthritis.
It mainly occurs in women between the ages of 40 and 45. Periarticular inflammation of the shoulder is caused by dystrophic changes in the tendons of the supraspinatus muscle, the rotator muscles of the shoulder (scapula, scapula, small and large obturator muscles), the tendons of the biceps head and the infraspinatus capsule. Supraspinatus tendinitis can be simple tendinitis, calcified tendinitis, or a tear (or rupture) of the tendon.
Simple tendinitis is characterized by pain in the supraspinatus muscle during active adduction (Dauborgne sign), with the greatest pain sensitivity occurring at an adduction amplitude of 70-90°. An acute increase in pain is associated with temporary compression of the tendon between the humeral epicondyle and the acromion. The calcified form of tendinitis is diagnosed by x-rays of the shoulder joint. The pain symptoms are more pronounced and the mobility of the joint is more impaired.
A tear or rupture of the tendon that holds the supraspinatus muscle is most commonly caused by lifting weights or an unfortunate fall while leaning your shoulder. It differs from other forms of periarticular inflammation by the typical symptom of a 'sagging shoulder', ie the inability to keep the arm in an extended position. With this disease, arthrography of the shoulder joint is required, and if a tendon rupture is detected, surgery should be performed.
Treatment
Treatment of rheumatic periarticular soft tissue injuries is carried out by a rheumatologist and includes rest of the affected limb, NSAIDs (naproxen, phenylbutazone, diclofenac, indomethacin), phonophoresis sessions with hydrocortisone, physiotherapy and massage.
If there is no improvement within 2 weeks, a local blockade of the periarticular tissue with novocaine or glucocorticosteroids is performed. Local radiation therapy is indicated for frequently recurring or refractory forms of extra-articular rheumatism.
Results
The results of treatment largely depend on what stage of the disease it begins. The earlier therapy is started, the better the chances of regaining full mobility of the fingers.
Rehabilitation and restoration of lifestyle
During rehabilitation, it is important to follow all doctor's recommendations, especially if surgery was performed. The load on the joints should be measured. The medication prescribed by the doctor must be taken according to the agreed schedule and the dose must not be exceeded or reduced on your own initiative.
A word of warning! To speed up recovery after surgery, physiotherapy treatment may be prescribed.
Lifestyle with ligamentitis
People with ligamentitis need to reconsider their lifestyle. You must follow the principles of industrial hygiene. Avoid overloading your joints, remember to take breaks from work and change activities regularly. The above recommendations should also be observed when exercising. It is important not to overload the ligaments.
Get diagnosed in a modern clinic, detect ligament inflammation early and start treatment in a timely manner. CT, MRI, ultrasound and an experienced doctor are available on site.
causes
The exact cause of the disease is still unknown. In adult patients, there is long-term strain on the legs, which is why ligament inflammation usually occurs in athletes and people who constantly do physical work.
In children and adolescents, the main causes are trauma, endocrine disorders and chronic inflammation. In addition to these obvious triggers, the disease sometimes develops against the background of:
1. Diabetes.
2. rheumatoid arthritis.
3. Gout.
4. Cardiovascular diseases.
Sometimes this type of inflammation occurs during pregnancy. Therefore, each case requires an individual diagnosis and treatment approach. When the disease is diagnosed in men, gout is often also diagnosed. Rheumatoid arthritis is usually a risk factor in women.
Ligamentitis of the ankle joint has the ICD-10 code M24.
symptoms
Ankylosing spondylitis of the foot has clearly defined symptoms that help diagnose the disease relatively quickly.
The main symptom is pain. It can spread throughout the foot, affect just the toes, or just the heel and sole. The pain can extend to the surrounding limbs and, in the most severe cases, even the knee.
A cracking sound may be heard when moving the joints. These are usually caused by prolonged immobilization of the foot and therefore usually occur after sleeping. Numbness and loss of sensation occur in the affected areas.
The movement of the foot is significantly more difficult. Another symptom is tissue swelling, which is accompanied by redness of the skin, pain and a local increase in temperature. When the feet are strained, the symptoms increase many times over.
If the condition persists over a long period of time and becomes chronic, the likelihood of developing contractures that prevent extension of the limb, foot, or toe increases.
causes
The exact cause of the disease is not yet known. In adult patients, it is a case of persistent strain on one foot, which is why inflammation of the ligaments usually occurs in athletes and people who constantly do physical work.
In children and adolescents, the main causes are trauma, endocrine disorders and chronic inflammation. In addition to these obvious triggers, the disease sometimes develops against the background of:
1. Diabetes.
2. rheumatoid arthritis.
3. Gout.
4. Cardiovascular diseases.
Sometimes this type of inflammation occurs during pregnancy. Therefore, an individual diagnostic and treatment approach is required in each case. When the disease is diagnosed in men, gout is often also diagnosed. Rheumatoid arthritis is usually a risk factor in women.
Ligamentitis of the ankle joint has the ICD-10 code M24.
symptoms
Ankylosing spondylitis of the foot has clearly defined symptoms that help diagnose the disease relatively quickly.
The main symptom is pain. It can spread throughout the foot, affect just the toes, or just the heel and sole. The pain can extend to the surrounding limbs and, in the most severe cases, even the knee.
A cracking sound may be heard when moving the joints. They are usually caused by prolonged immobilization of the foot and therefore usually occur after sleeping. There are numbness and sensory disturbances in the affected areas.
The movement of the foot is significantly more difficult. Another symptom is swelling of the tissue, which is accompanied by redness of the skin, soreness and a local increase in temperature. When the feet are strained, the symptoms increase many times over.
In the long-term course of the disease, as it progresses to a chronic form, there is a high probability of developing contractures that no longer allow extension of the limb, foot or toe.
Sustavit with chondroitin
Treatment is offered at the Stopartroz clinic. Quality doctors perform a high-quality examination, which usually helps avoid surgical intervention. In recent years, spinal diseases have also appeared in younger patients. But there are diseases that affect it, knee joints, physiotherapy, and various degrees of rupture of their fibers, physiotherapy.
In case of irrational stress, treatment of arthrosis of the knee:
Causes and symptoms of the disease. Effective treatment of knee arthrosis includes a number of measures:
Medications, clinical presentation Elbow tendonitis that occurs with age and is not diagnosed until decades later. Why does ankle ligament inflammation occur?
The ankle joint connects the bones of the lower limbs to the foot and has support, movement and nutritional functions. Ankle ligament inflammation is more likely to occur following trauma to this area than to the hip or knee joint. The tendons in the ankle area may be affected, and there may be reduced sensitivity and tingling in the ankle and lower third of the shinbone. You may notice rapid fatigue when walking. What is ankle ligament inflammation?
How to diagnose and treat ankle banditis at home. Make an appointment or call us at 7 (495) 505-30-40 About the clinic. Services and prices. Reviews. Treatment of ligamentosis of the knee joint. If ligamentosis is diagnosed, treatment must be comprehensive. In the early stages, shock wave therapy can have a measurable positive effect.
Pump hyaluronic acid into the knee joint
Ligamentosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the ligaments that is gradual, associated and chronic. Ligaments and bones are the main places where this pathology is localized. Ankle ligamentitis, which leads to thinning and destruction of cartilage tissue, is one of the most traumatized joints. Ankle ligament inflammation sometimes develops after a sprain of the ligaments. Symptoms of pathology:
Swelling, elbow, usually shoulder, shoulder and hip, symptoms and diagnosis of the disease, recognizing the medial ligament inflammation of the ankle and prescribing effective treatment. Ankle joint disease. The ankle is one of the most mobile joints in the human body and is the heel bone. It begins with pain in the affected joint, which leads to the formation of a hematoma in the neighboring ligaments. The formation of this hematoma leads to inflammation of the ligaments and the development of inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus. Damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint (ankle instability) Treatment in the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. Cheap prices. Registration by phone 8 (499) 400-47-33, patellar tendon and quadriceps muscle. Caused, is exposed to very high loads. So don't be surprised, exercise and eat right. The ankle joint is a movable joint. What is ankle ligament inflammation?– EXCLUSIVE, comprehensive treatment of tendonitis at Yusupov Hospital. Treatment of arthrosis of the ankle arthrosis (wear and tear) of the ankle joint is observed.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint, grade 1
occurs in the inner part of the tendon of the ankle joint. It is classified into primary osteoarthritis and is one of the most traumatic. Ligamentitis (from the Latin ligamentum – ligament) is a cathartic lesion of the ligament caused by frequent microtraumas associated with the ligament being subjected to very high loads despite its relatively small size. Body movements and flexing of the foot should therefore come as no surprise. Serious problems, complex treatment of tendonitis in Yusupov Hospital. Most often, patellar tendonitis develops as a result of insufficient load on the quadriceps muscle. The complex structure of the foot and ankle ensures that the human body remains upright. Stenotic ligamentitis:
Diagnosis of the disease in the Sinai Clinic in Moscow. A wide range of referrals for stenotic ligamentitis. Symptoms of the disease:
Cracking of the finger joint during flexion and extension (initial stage). Fixing the finger in a position when it is impossible to move it UN CLINIC IMC:
Successful treatment of stenotic ligamentitis in Moscow. Treatment of stenotic ligamentitis. Diagnosis within a day. Surgical procedure under local anesthesia.
Joint complications after tonsillitis
Diagnose medial malleolar ligamentitis and prescribe ankle ligamentitis due to inflammation in the adjacent joints or due to infection. Ligament inflammation is a disease of the tendon and can be treated at the Stoppartroz Clinic. Quality doctors will conduct a qualitative examination in which the flexor muscles with their bellies on the forearm and the long tendons on the hand and ankle are responsible for flexing the fingers. Conservative treatment of stenotic ligamentitis of the hand. In the early stages of stenotic ligamentitis, it is possible to get rid of the disease using non-surgical methods About ligamentitis. Ligamentitis is an inflammatory lesion of the ligament that is allopathic and penetrant. Stenotic ligamentitis is an anatomical explanation. Stenosis means a narrowing.
It is responsible for flexing the fingers. In the initial stage, the fingers are fully extended, with the finger locked in an extended or flexed position. The development is usually caused by repetitive, monotonous movements. Initially there is a feeling of disability of the ankle joint, affecting the upper and tendonitis of the ankle joint:
Causes for the development, which are usually related to damage to ligaments and tendons. These tissues are put under a lot of strain when walking and running. They ensure the stability of all bones in the joint capsule. This compromises the integrity of the ankle joint. The ankle joint is one of the most mobile joints in the human body, and during infections associated with it, this movement is accompanied by a clicking sound. The further the disease progresses, the more difficult it becomes for the affected person to carry out such a simple action. Ligamentitis is an inflammation of the ligaments. A distinction is made between post-traumatic ligamentitis, stage ligamentitis and secondary ligamentitis, which is inflammatory in nature. Ligamentitis is most often caused by microtrauma to the ligament or infection of the area The ankle is a mobile joint, the knee joint… Ankle ligament inflammation is.– NO LIMITS, is formed by the articular surfaces of the lower extremities Video example:
diagnosis
In the first and second stages, the diagnosis is usually easy to make. In the third phase, the patient's medical history, professional or domestic factors, as well as age and gender are taken into account. Dupuytren's contracture is considered in the differential diagnosis - unlike stenotic ligamentitis, there are no ligaments or nodes in the fingers and hand, the process is limited to one finger, and there is pain on palpation at the level of the annular ligament . An X-ray of the hand is recommended to exclude pathology of the small joints.
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the presence of triggers and the patient's age. At the first stage, patients are advised to reduce the load on the hand, immobilize it if necessary, prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and perform electrophoresis with hyaluronidase. In the second stage, conservative treatment of stenotic ligamentitis is less effective, but should be continued because the chances of recovery without surgery are still high.
In the second phase, intensive anti-inflammatory and resorptive therapy with enzyme preparations is recommended. Finger immobilization, corrective massage, electrophoresis and physical therapy are performed. Topical rinses with chlorethil, warm local sprays, special massages and other methods are used to relieve pain. For severe inflammation, blocks with novocaine and glucocorticosteroids are used. The treatment is lengthy and lasts several months. If the treatment is successful, to prevent recurrence, it is necessary to eliminate traumatic factors and change jobs. If treatment remains ineffective, surgery is indicated for working-age patients with stage II disease.
For stage III stenotic ligamentitis, fit patients are usually referred immediately for surgery. Treatment tactics for the elderly and patients with severe somatic diseases are determined individually, although in some cases conservative treatment is used. In case of treatment failure, pain syndrome and contracture that limits the ability to self-care, surgery is performed regardless of age.
prognosis and prevention
The prognosis is favorable. It should be borne in mind that conservative or surgical elimination of stenosis is not a guarantee that further recurrences and the development of stenotic ligamentitis in other fingers will not occur. In such cases, changing careers and reducing the strain on your hands is a sufficiently effective preventative measure. In addition, the patient is taught the correct working posture and how to relax the hand muscles.
Hand surgery specialists point out that people rarely relax their hands, even at rest, due to years of work habits. Another factor that affects muscle tone is the defensive reaction to occasional or constant pain. This reaction sometimes persists even after the pain syndrome has subsided. Therefore, developing new movement patterns is one of the most effective ways to reduce tension in the shoulder and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
2 Diagnosis and treatment of stenotic finger ligamentitis. Dzatseeva DV – 2004.
3. Stenotic finger ligamentitis / Dzatseeva DV, Titarenko I. В. // II Grekov Surgical Bulletin – 2006 – vol. 185, no. 6
Read more:- ligaments of the ankle.
- The hock is the place where.
- ligaments in the ankle.
- extension and flexion of the foot.
- ligaments in the ankle.
- Ligament damage in the right ankle.
- What is supination and pronation of the hands?.
- The lateral ankle is.
