Depending on the injury mechanism, it is important for us to offer appropriate treatment at the highest level.

- Osteoarthritis of the knee, conversion osteotomy
- Indications for corrective osteotomy in arthrosis of the knee joint.
- How to recognize gonarthrosis: symptoms
- The 5 most common causes of knee osteoarthritis in athletes
- Principles of physiotherapy for osteoarthritis
- How do the exercises work in practice?
- need for surgery
- How is the operation performed?
- Causes of Osteoarthritis
- Types of surgeries for arthritis
- endoprosthetics
- osteotomy
- arthrodesis
- debridement
- Treatment of concomitant knee injuries
- Side effects and pain after graft removal
- Advantages of ACL plastic:
- CONTACT
- causes
- Osteoarthritis in the knee: treatment, medication, injections
- Intra-articular injections
- types of surgical techniques
- rehabilitation
Osteoarthritis of the knee, conversion osteotomy
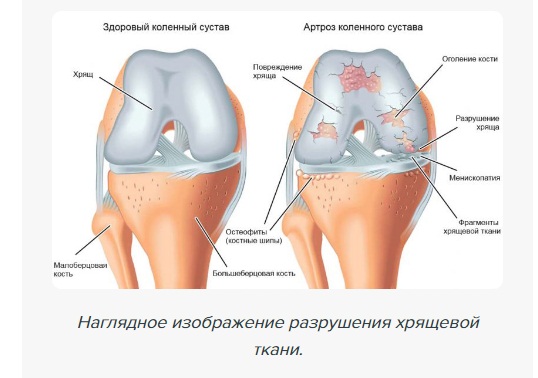
Arthrosis of the knee is one of the most common forms of arthrosis in the musculoskeletal system, along with hip arthrosis. By the age of 50, osteoarthritis of the knee is already occurring in 40 % of the population, and this number is steadily increasing with age.
Given the high prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, a progressive treatment algorithm has been developed that includes: modification of physical activity, physical therapy, physiotherapy, intra- and peri-articular injections of corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, and platelet-rich plasma, and surgical treatment when these conservative measures have failed.
Surgical treatment of primary knee joint diseases includes two main groups of surgeries - arthroplasty and corrective osteotomies. Arthroscopy for primary osteoarthritis of the knee is not very effective and often does not even provide temporary relief.
In the case of deformities of the knee joint, which usually affect one compartment (one half) of the knee joint, corrective osteotomies allow pain relief while preserving the original joint.
Below we will discuss the indications and contraindications for this procedure, the correct choice of patient, the surgical technique, methods of fixation and possible complications.
Indications for corrective osteotomy in arthrosis of the knee joint.
Disruption of the mechanical axis of the knee joint leads to uneven load distribution and asymmetric wear of the articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis with varus deformation of the knee joint (round feet) is more common; With this form of osteoarthritis, wear and tear occurs on the inside of the knee joint.

How to recognize gonarthrosis: symptoms
Knee arthrosis is a gradual disease that can only become noticeable after some time. Some of the first warning signs, especially if you play competitive sports, are
- stiffness in knee;
- pain after exercise;
- pain after sleeping or sitting for a long time;
- Crunching when flexing the joint.
These symptoms can plague you for years, from time to time. If left untreated, they get worse, the leg hurts when you step on it, and the knee joints deform with osteophytes – bone growths.
A stiff knee in the morning after waking up is the first warning sign
The 5 most common causes of knee osteoarthritis in athletes
- Injuries and micro-injuries that contribute to the slow and insidious destruction of cartilage tissue.
- Excessive physical exertion with intense sports.
- Metabolic disorders – the cartilage tissue is not sufficiently supplied with nutrients and cannot regenerate.
- Excessive weight puts additional stress on the joints.
- Persistent vascular spasms in the legs and resulting circulatory disorders.
Even small but frequent micro-injuries can sooner or later lead to gonarthrosis.
What are the causes of knee joint pain in athletes? Expert comment:
Principles of physiotherapy for osteoarthritis
A set of exercises for knee pain is not a panacea, but still gives good results. Provided that patients strictly follow the instructions of the specialist and follow certain rules.
Avoid sudden movements when exercising, even if they are part of a rehabilitation program. An awkward twist or bend can aggravate the situation and cause serious musculoskeletal problems. Although knee stretches are an essential part of rehabilitation, you should not do them if you are in pain. If your knee hurts, it means the exercise was not performed correctly.
The exercises should be carried out regularly, preferably daily. This is the only way to achieve results and strengthen the muscles in the knee joint. It is these muscles that keep the knee in the correct position and allow it to function properly.
Despite regular exercise, physical stress should be kept to a minimum if you have osteoarthritis of the knee. That's why it's so important to alternate exercise and rest, and to do most knee joint exercises while sitting or lying down. It's important to make sure your spine stays straight during the exercises.
How do the exercises work in practice?
At the first stage of LFC, exercises for the knee joint should be performed only under the guidance of a specialist. The workout usually lasts no more than 60 minutes, half of which is spent warming up the muscles. This is very important as the muscles and ligaments need to be prepared. For older people, who are more likely to suffer from osteoarthritis and are usually no longer able to show their muscles as flexibly, the warm-up can take more than half an hour.
Since exercises for the treatment of knee arthrosis require a dosed load on the problem zones, the training usually takes place lying down or sitting. Therefore, a sports mat should be prepared in advance. Chairs with a rigid backrest are often used for the exercises.
The stronger the muscles become, the greater the load on the legs. If the patient is in good physical condition, then he performs at least 30-50 exercises in one approach, and the number of approaches can be up to 3-5 per workout. However, the body should be allowed to rest after each approach. The breaks are usually used for muscle relaxation and breathing exercises.
need for surgery
Arthroscopy is not performed before stage 2 osteoarthritis of the knee when 20-25 % of the cartilage is destroyed. Indications for surgical treatment can be limited joint mobility, recurrent synovitis or a chronic pain syndrome that cannot be treated conservatively. Surgery is also an option when a person does not want to take large amounts of anti-inflammatory drugs. It is known that regular use of NSAIDs can damage the gastrointestinal tract.
For people of working age whose knees have limited mobility, arthroscopy can help them get back to their normal lives. In patients with persistent pain, it can provide relief for several years and help wean them off all or part of their painkillers.
How is the operation performed?
The operation is performed under spinal anesthesia or peripheral regional anesthesia. During the arthroscopy, the patient is conscious and can follow everything that is happening on a screen.
Before the operation, the skin around the knee joint is treated with an antiseptic. Then the surgeon makes several small incisions. Through these incisions, the surgeon inserts surgical instruments and an arthroscope with a camera into the joint cavity. During the procedure, the image is displayed on a screen so that the surgeon can carry out the necessary procedures under visual control. The patient can also follow the progress of the operation.
Causes of Osteoarthritis
- Age-Related Changes. The cartilage tissue loses elasticity, regenerates less well and becomes more sensitive to stress. The risk of joint damage increases with age.
- Genetically conditioned. The development of the nodular form is due to a predisposition. Multiple joints are affected.
- birth trauma. Dislocation of the hip joint is common. If not treated properly, a severe form of deforming arthritis can develop.
- Congenital anomalies. The presence of connective tissue dysplasia, which weakens the structure, leads to hypermobility of the articular elements. The disease can appear at a young age, accompanied by a change in posture.
- injuries. Strained ligaments, bruises and fractures lead to arthrosis. Micro-injuries occur in athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor.
- Disorders of the endocrine system. Metabolic disorders lead to joint damage over time. Cartilage does not regenerate due to a lack of vitamins and minerals. Varicose veins are also dangerous.
- Obesity. Being overweight increases the stress on the joints, causing them to wear out and break down quickly.
- infections. Infections can cause joint abnormalities and irregularities in the joint surface.
Surgery is indicated in patients with severe deforming arthritis. Surgical intervention is performed when conservative treatment is unsuccessful. Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee and shoulder joints does not respond well to drug treatment and requires surgery.
- severe pain that cannot be relieved with painkillers;
- Infection – purulent cavities have formed in the joint;
- complete or partial immobilization;
- severe cartilage deformation;
- Internal damage to the joint, accumulation of bone splinters in the joint cavity.
Surgical treatment of osteoarthritis is a proven technique that provides relief to the patient. Surgery is performed when there is no alternative. The most effective is the endoprosthesis operation. In this procedure, the joint tissue is replaced.
Types of surgeries for arthritis
Four main types of surgery are used to treat osteoarthritis. They differ in technology, possibilities, prognosis and costs.
The doctor selects the operation to treat arthrosis, taking into account the location and extent of the damage, as well as the presence of contraindications.
endoprosthetics
In this procedure, the damaged joint is replaced with an artificial joint. This procedure gives good results provided the prosthesis is properly fitted and the joint is properly designed. The problem will not bother you again for 20 or more years. Proper rehabilitation can restore musculoskeletal function. It is important to know that osteoarthritis cannot be completely cured, so the best solution is joint replacement. The disadvantage of surgical treatment with an endoprosthesis is the high cost.
osteotomy
In this procedure, a portion of the bone tissue is sawed off and the joint and bone are angled properly. This reduces the stress on the affected joint and slows the progression of the disease. However, the disease cannot be cured with surgery alone. It is a complex procedure that requires a long rehabilitation period.
arthrodesis
This is a radical treatment that involves removing tissue from the joint. This causes the bone and kneecap to fuse. Postoperative pain is reduced and the risk of recurrence is eliminated. The disadvantage is the limited mobility of the leg.
debridement
During osteoarthritis surgery, an arthroscope is inserted into the joint and the damaged cartilage is removed. The advantage of this method is that it quickly leads to pain relief in stage 2 and 3 osteoarthritis. The operation is used to treat meniscus tears and repair the ligaments. The disadvantage of arthroscopy is the short duration of the positive effect. Unpleasant sensations return within 1-2 years.
Each type of operation is indicated in certain cases. If the cartilage is completely destroyed, an endoprosthesis is indicated. When time is of the essence and osteoarthritis progression needs to be slowed, a periarticular osteotomy is indicated.
Treatment of concomitant knee injuries
A successful cruciate ligament reconstruction also includes the treatment of concomitant injuries. Twisting (twisting) the knee joint can injure other structures in the knee. An experienced orthopedist always examines the knee for meniscus tears and cartilage damage during cruciate ligament surgery. After treatment, the cruciate ligament implant is inserted into the knee through an arthroscopically prepared (minimally invasive) channel. The attachment of the cruciate ligament implant, its position and its function are checked several times under direct observation.
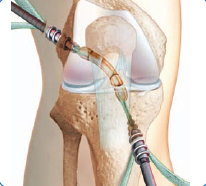
For stable fixation of the ligament, the transplant is fixed in the canal in a minimally invasive manner with resorbable (ie biodegradable) screws. In the case of poor bone quality (osteoprosis), titanium screws are used. © University of Applied Sciences Orthopedics.
To stabilize the transplant, it is fixed in the tunnel with special screws. These screws are made of self-absorbing material and will dissolve after about 2 years. Titanium screws are only used in cases of poor bone quality. Other methods of cruciate ligament reconstruction use slings for fixation, which are attached to the tunnel on one side and to the graft on the other side.
Alternatively, titanium screws or titanium clips can also be used in the lower leg, with which the fixation material can be removed without any problems.
Side effects and pain after graft removal
Advantages of ACL plastic:
- Partial weight bearing of the leg is possible immediately after the operation.
- Almost painless removal of the tendon.
- No complications
- High graft strength
- Small, cosmetically inconspicuous cuts.
- Rapid healing of the bone canal
- Due to the rapid healing of wounds, athletes can quickly start training again.
- Optimum stability of the knee joint is achieved by pre-stretching the implant.
Patellar tendon implants can cause pain at the implantation site in the first few months. During this time it is usually not possible to kneel as before.
If the semitendinosus tendon is chosen, the implant can stretch, so that a slight instability of the joint is possible despite the plication. The patellar tendon graft is more stable.
CONTACT
For comprehensive information on the treatment and prevention of orthopedic, rheumatological or neurological diseases, please contact us:
 Tel. +7(495)120-46-92
Tel. +7(495)120-46-92
 Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]
return form  Send us an email on Telegram
Send us an email on Telegram  Contact us on WhatsApp
Contact us on WhatsApp

Our address is 11, Trifonovskaya str.
causes
Osteoarthritis does not always have an obvious cause that can be characterized as idiopathic primary arthritis. Secondary osteoarthritis can be caused by:
- Trauma - fractures, dislocations, damage to the meniscus and ligaments of the knee;
- congenital defects;
- connective tissue weakness, hypermobility of the joints;
- autoimmune disease - rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus;
- infectious inflammatory process – purulent arthritis, tuberculosis;
- heavy exertion: running and heavy squats are especially dangerous for the knees;
- overweight.
Osteoarthritis in the knee: treatment, medication, injections
Conservative treatment is effective in stage 1 to 2 of the disease; in later stages, surgery is probably unavoidable.
Acute symptoms are relieved by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - diclofenac tablets, ibuprofen and their analogues. If NSAIDs don't help, corticosteroids are prescribed.
Chondroprotectors are used to slow down cartilage degradation.
To improve blood circulation and nutrition of the joint structures, agents for improving microcirculation – Normoven, Nicotinic acid, Cinnarizine, Pentoxifylline are used.
However, the best current treatment for arthritis is injection therapy.
- Non-Steroids – Flamax, Ketonal, Amelotex, Movalis, Lornoxicam, Diclofenac, Naclofen;
- Hormones - Celeston, Flosterone, Dipropane, Hydrocortisone;
- Vitamins – Neurorubin, Combilipen, Milgamma, Trigamma, Compligam.
Intra-articular, hyaluronic acid preparations are prescribed; the frequency of injections and the dose are determined by the doctor based on the diagnosis. Glucocorticosteroids can be injected intra-articularly, but should be administered with caution because, with frequent use, they can deteriorate cartilage and worsen arthritis.
Intra-articular injections
One of the latest developments of Czech scientists is carboxytherapy. It involves injecting carbon dioxide gas into the joint cavity, which causes intra-articular hypoxia. The gas is administered through a special device and causes an acute lack of oxygen in the joint structures.
The result is a sudden rush of blood to the affected area and rapid acceleration of metabolism. The gas is expelled again within minutes, and the mechanism operates over a long period of time.
Another modern method is the injection of plasma, a liquid containing blood cells, into the joint. In this case, platelet-rich plasma is used, which is great for reducing inflammation and pain, and in many cases slows down the process of destruction.
types of surgical techniques
- By type of access – open and closed. There are situations when open access is preferred, despite its high invasiveness (when the surface of the bone is exposed and the width of the incision is 10-12 cm). The need for this type of surgery stems from the increased risk of nerve and vascular injury during surgery;
- depending on the level of intervention. Depending on the localization of the pathological process and the purpose, excision is performed on the thigh or shin. Upper and lower tibia osteotomies are performed on the femur;
- in relation to the method of bone excision – wedge-shaped, transverse, straight, oblique, spherical;
- By type of correction – opening, closing.

Osteotomy of the knee: a visual representation of the procedure.
rehabilitation
rehabilitation rehabilitation measures After a corrective osteotomy of the knee with angle stabilized platesThe rehabilitation period is usually no more than four weeks. It is not uncommon for the rehabilitation period to be significantly longer. This is due to the individual characteristics of the patient, but the biggest reason for such cases is disregard for the recommendations of the attending physician and non-compliance with the conditions for the postoperative period. If the rehabilitation plan is strictly followed, the likelihood of complications or delay in healing is minimal.
The patient starts with the first exercises while still in the hospital (the stationary phase lasts from three days to a week). In the postoperative period after Corrective osteotomy of the knee This is the main goal of rehabilitation measures the recovery Rehabilitation measures focus on restoring blood circulation and maintaining a high trophic level of the limb. During this time, knee flexion and extension exercises, foot and hip massage, symptomatic, restorative, antimicrobial, and anticoagulant therapies, and leg cold are indicated. The patient walks on crutches (about three months), and it is absolutely contraindicated to load the operated limb.
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the rehabilitation process. The load on the joint should be gradually increased. The volume and duration of physical therapy exercises are increased, and at a later stage, sports cycling and swimming are recommended. Physiotherapeutic treatments are mandatory during the rehabilitation period.
The entire rehabilitation period and full recovery takes six months to a year.
Read more:- Orthopedic patella in osteoarthritis of the knee.
- How to wear a knee brace for osteoarthritis.
- The gait of the knee in osteoarthritis.
- Orthopedic knee orthoses for osteoarthritis when walking.
- Immobilization of the ankle.
- How to choose a knee brace for osteoarthritis?.
- Osteoarthritis trainer for the knee.
- Leg prosthesis below the knee.
