Excessive or insufficient pronation of the feet is not a life-threatening condition, but it should not be ignored. If you have signs of a pronation disorder, try to prevent it from developing further — watch your weight, exercise, and wear the right shoes.
- What is hypopronation and hyperpronation: Types of foot pronation
- types of pronation
- PRONATION
- And there are three types of pronation:
- Older shoes
- Wet' test
- Understand the types of pronation: overpronation, underpronation, and neutral pronation.
- How can I tell what type of pronation I have?
- Step Cycle and Supination
- Causes of anomalies
- Determination of the type of pronation
- Selection of running shoes after pronation
- Normal pronation
- overpronation
- The choice of the coach
- Features when choosing sports shoes
- rotation
- How to choose trainers and orthotics for hypopronation?
- hyperpronation
- Exercises to correct pronation
- stretching the feet
- spin your feet
- Tiptoe walking
- heel walk
- Lift toes
- How do you determine your pronation?
- How do you choose running shoes when you know your pronation type?
What is hypopronation and hyperpronation: Types of foot pronation
Foot pronation is the flexing of the foot when walking and running. Good pronation is very important as it controls the stress on the musculoskeletal system. It also helps prevent discomfort when the foot hits the ground while walking. It also helps to relieve the feet when running and adapts to different ground conditions.
In everyday life, few people come across the term foot pronation. It should be noted right away that this is not a disease, but a term that describes the movement of the foot, its ability to turn inwards or outwards. Pronation is very important because without it a person cannot move. It also makes the foot much more flexible.
There are two main functions that allow the pronation movement. The first is the spring function, which cushions the impact of the foot on the surface. The second, the compensating function, serves to compensate for the various irregularities in the contact of the foot with the ground.
When the foot makes contact with the ground, the arch of the foot is flat and flexible. This reduces the impact force. This process can be compared to a spring in a car. In addition to the arch of the foot, the tibia is also involved in this process. As it moves inward, the foot swings out and increases cushioning. With normal pronation, the load is evenly distributed. However, in the case of various diseases, the body reacts immediately. He immediately takes the damaged parts under his protection, which leads to tissue build-up and bone deformation. Most biomechanical problems are caused by pronation abnormalities.
types of pronation

People with neutral pronation have no discomfort walking and do not need correction. However, you are advised to wear shoes with a slight stabilizer, where a thicker material that does not extend into the main part of the sole is responsible for arch support.
Hyperpronation is characterized by the foot turning inwards too much when walking, which has a negative effect on the ligaments, which are stretched and therefore offer less cushioning. This weakening of the foot muscles often leads to the development of flat feet. Athletes with hyperpronation who train in sneakers need stability - a stiff insole and a secure heel hold.
The main feature of hyperpronation is insufficient flexion of the foot, which significantly increases the risk of injury. The foot becomes stiff, loses the ability to rotate inward naturally, and is no longer able to transfer body weight to the arch of the foot. People with insufficient pronation should wear shoes with high cushioning that do not have stiff support elements on the inside.
PRONATION
People often ask about pronation, and many people don't even know what it is. So today's post will be about it.
Pronation is the way the outside of the foot straightens up when walking and running.
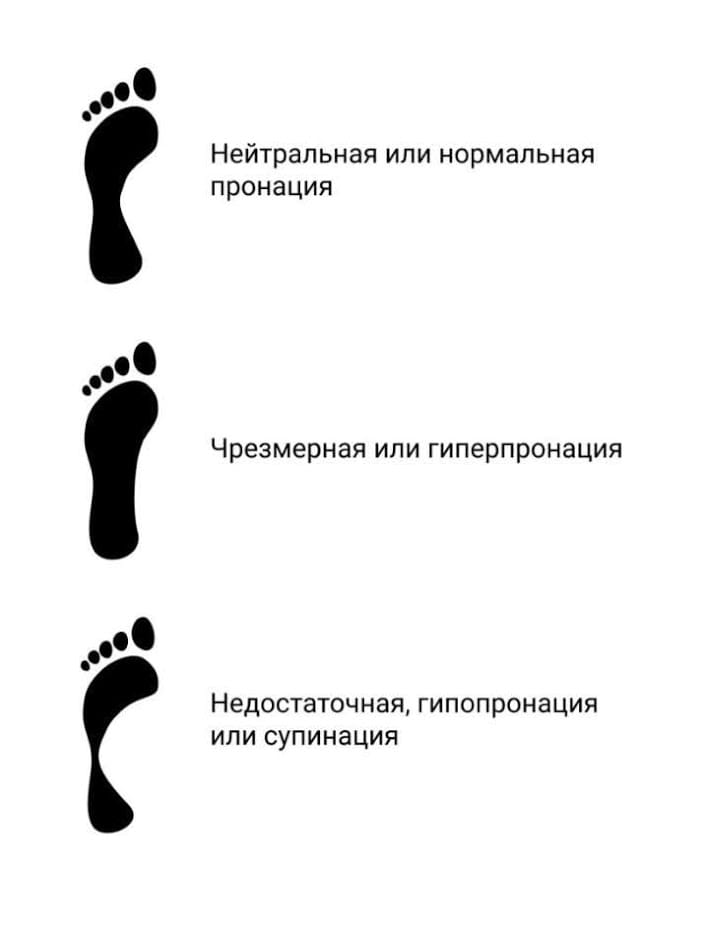

And there are three types of pronation:
- Hyperpronation – a sharp drop in the arch of the foot, with excessive inward rolling of the foot. To prevent injuries, we recommend sports shoes with Duomax technology (internal foot support), as found in models such as the GEL-KAYANO, GT-1000 and GT-2000, or the GT-4000 for extreme hyperpronation.
- Hypopronation is a lack of flexion of the foot, excessive outward tilting of the foot. For people with this type of pronation, a well cushioned shoe like the GEL-CUMULUS or GEL-NIMBUS is ideal.
- Neutral pronation: This type of foot flexion ensures optimal distribution of the impact load on the ground. Every trainer has a good fit.
Older shoes
people with hyperpronation The inner part of the sole is heavily worn, but the outer part hardly.
signs for Neutral pronation: A relatively evenly worn rear part of the sole.
In people with hypopronation (Supination) the outer part of the shoe wears noticeably.
Wet' test
No special equipment is needed, just paper. You need to wet your foot and stand on a piece of paper or cardboard. The outlines of the wet foot are recorded with a pen or pencil and compared to images of the pronation type.
Of course, only an orthopaedist/traumatologist can make a statement about your pronation type, but we have given you a little help in choosing sneakers.
Understand the types of pronation: overpronation, underpronation, and neutral pronation.
Pronation occurs in the joint below the ankle. This is the inward movement of the heel just after it hits the ground. When a person walks or runs, pronation helps cushion the initial impact. Without pronation, all of the impact with each step would be transmitted upwards, interfering with the normal function of the lower joints. In addition, pronation acts as a shock absorber, helping the foot to 'recognize' foot type by stabilizing and adapting to the type of terrain. Modern running shoes are modeled for different types of pronation. The type of foot pronation is a very important factor when choosing the right running shoe.
There are three types of pronation:

overpronation.
Overpronation occurs in about 70 % of the population, making it the most common form of pronation in runners. In this case, most of the body weight is shifted to the inner or medial part of the foot, and as the runner moves forward, the inner edge of the foot is loaded instead of the forefoot. Excessive pronation is most common in people with a low arch or flat feet. Runners with excessive pronation should choose the following shoes supportive shoes.

Inadequate pronation or supination
Inadequate pronation is a form of pronation in which the foot does not move inward enough. The outer or lateral edge of the heel hits the ground at a greater angle and there is almost no normal pronation, resulting in strong transmission of impact to the inside of the foot. This lateral loading of the foot continues throughout the stride and also affects running performance. This type of pronation is most common in runners with a high arch. Runners with insufficient pronation should opt for choose neutral shoes.
How can I tell what type of pronation I have?
The best way to determine your pronation type is to have a step analysis in one of our stores. However, if you cannot come to our store, there is a way you can determine your foot type yourself. This is the wet foot test. This method is used when your stride has changed since the last test (step analysis in our store). However, keep in mind that this test is only an approximation; it is best to repeat the step test while running.
Step Cycle and Supination
The stride cycle is the trajectory of the foot relative to the body. A single gait cycle consists of two phases: pronation and supination. Pronation is a function of load transfer, supination is a function of body transfer. The ankle, thigh, knee and hip joints are involved in the movement of the body. The pronator and supinator muscles play an important role: the better they are built, the less fatigue they experience.
When pushing off the ground, a rigid lever is formed and the joints lock, causing the human's body to rush forward. There is momentary supination just before pushing off as the heel is lifted off the ground. This increases the recoil force and leads to an increase in running or walking speed.
Causes of anomalies
Many factors can affect foot health and cause foot deformity due to the following reasons:
- weight gain;
- Unsuitable footwear – high heels, too flat soles, unsuitable size;
- High physical exertion;
- Musculoskeletal disorders - congenital or acquired;
- weak muscular corset;
- age-related changes in the skeletal system;
- Impaired neuromuscular transmission.

Wearing high-heeled shoes leads to foot deformation; walking in such shoes is acceptable for no more than 3 hours a day.
Defects in the feet result in a lack of motion cushioning. The spine and joints are the first to suffer as the imbalance of the feet increases the stress on the skeleton. The body begins to adapt to this position to protect all systems and organs from discomfort.
In the course of this conversion, the following pathologies can develop:
In addition to the above, pronation disorders can also cause such serious diseases as osteoarthritis. Arthritic changes resulting from poor blood supply are caused by hyperpronation and flat feet. This is the most common cause and leads to gradual destruction of the cartilage in the ankles.
The insidious thing about foot disease, and foot disease in particular, is its latent, hidden nature. Symptoms may not appear for a long time, but excessive physical activity or intense sport will aggravate them.
Determination of the type of pronation

There are three degrees of pronation. You can determine your pronation type at home by making an imprint of your wet foot on a piece of paper. Simply dip your foot in water and place it on a clean piece of paper. Look at the imprint. You can see where the sole of the sneaker rubs the most.
You can get three different footprints. Seen from left to right:

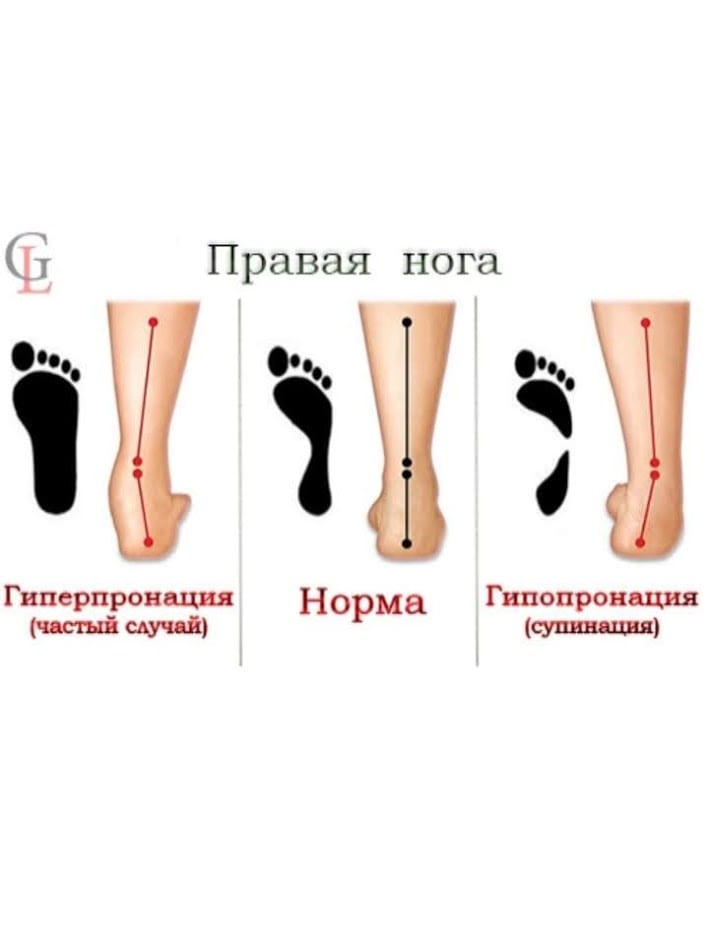
- High Arch - Hypopronation. A person with this footprint is a 'hypopronator'. (NEUTRAL). A very strong deviation of the foot can be seen. The foot is turned inwards (clubfoot). This is excessive pronation. Running stress is unevenly distributed and mainly affects the outer part of the foot, with ground contact occurring on the outside of the heel, ring toe and little toe. The big toe does not feel the stress as it is transferred to the little toe and fourth toe.
- The normal arch of the foot is neutral pronation. Most of us have neutral pronation, (SUPPORT). In this case, the flexion of the foot acts like a spring, ensuring optimal load distribution when striking the ground and optimal load distribution when pushing off. When walking or running, the outer part of the heel is in contact with the ground, the foot rotates inward no more than 15 %, then there is good ground contact. Body weight is evenly distributed over the entire foot and toes, with slightly more pressure on the middle and index toes.
- Low Arch - Hyperpronation (CONTROL). It occurs frequently and can be described as almost flat-footed. There is little or no inflection. The weight of the body is unevenly distributed. The running stride begins with the outer part of the heel in contact with the ground. The thumb and index finger (second toe) feel the most pressure. The other toes feel almost no pressure. The foot is turned outwards. Insufficient balance and stability when walking.
Selection of running shoes after pronation
Some running shoe stores will help you choose running shoes by measuring your pronation on a treadmill and running tablet with appropriate software. To do this, you just need to walk on the treadmill for 10-15 seconds. The software will then show you your foot angle. It's quick, convenient and easy. It is the safest way to determine your foot pronation.

Normal pronation
If you have a normal pronation, choose support shoes. You can walk in any shoe.
overpronation
If you have hyperpronation, look for 'Control' type shoes. This is a restrictive running shoe. The main feature of this shoe is its heavy weight and rigidity due to the many details in the thick sole and the straight cut.
The foot needs support on the inside – the so-called 'stabilisation'. stabilization .. This is ensured by running shoes that cushion the foot through the use of sole materials or parts with different stiffnesses - they 'complement' the part of the foot that buckles inwards.
Different manufacturers have different names for their technologies, but the bottom line is the same: Stabilizing running shoes for hyperpronators are equipped with cushioning zones on the inside and additional zones for arch support. An example of this are Asix – Gel – pulse-7. Here the midsole has stabilizing inserts on both sides as these shoes are suitable for a neutral pronation.

If you have severe hyperpronation, shoes with a structural plastic sole on the inner arch work well. When hyperpronation is mild and the foot doesn't buckle severely, models with soles that combine foams of different densities and stiffer plastic on the inside of the foot provide support.
The choice of the coach
Professional runners choose their running gear, including shoes, with care. Amateurs should do the same to protect their feet and ankles from injury. When choosing running shoes, pay attention to pronation to distribute the load from the toes to the heel.
Why should you consider pronation when choosing running shoes? Running puts an enormous strain on the musculoskeletal system. If the foot is not positioned correctly, the pressure increases many times over. Shoe choice can help improve redistribution and reduce the risk of injury. Manufacturers today produce sneakers for athletes that take into account all types of pronation. Your feet get optimal support, cushioning and the necessary rigidity.
Features when choosing sports shoes
When choosing a sneaker, it is advisable to consider pronation, that is, the anatomy of the foot. It aligns the angle to the central axis and improves control, cushioning and stability on take-off and landing. Instep height, heel type and sole thickness are taken into account.
- For people with hyperpronation. Insole in the midsole and sometimes down to the heel area. Additional cushioning. Special projection on the inside, the so-called longitudinal vault. Provides stability, supports the foot and protects against tipping over.
- For people with hypopronation. Strong cushioning in the midsole area to absorb impact loads. flexibility of the shoe. Heel cushioning, outside.
- For people with neutral pronation. adaptation to the foot. Many models fit here, for people with neutral pronation it is better to choose models with cushioning.
Choosing the right trainer will help stabilize pronation. The result is cushioning that restores natural movement, comfort, and protection. It is advisable to buy the shoes only after trying them on to ensure that they fit perfectly, taking into account the nature of the foot.
rotation
Rotation is another type of movement, it means 'turning'. It occurs not only in the limbs of the human body, but also in some of its components, such as B. the vertebrae. Pronation and supination can be considered partial rotation. The range of motion of the upper and lower limbs is very different, which is something to keep in mind. All rotations serve to stabilize parts of the body during movement.
The rotator muscles (pronators and supinators) are small and don't deserve attention when building muscle mass. But they need to be discussed with athletes, and coaches need to teach beginners the importance of antagonists in building body composition.
How to choose trainers and orthotics for hypopronation?
Hypopronation trainers help maintain the correct physiological condition of the foot. To minimize the effects of the deformity, orthopedists recommend the following rules:
- Women should not wear heels higher than 4 cm.
- Children under the age of 14 should not wear shoes with a high platform.
- Shoes should be selected according to the size of the foot. Tight models lead to defects in the supporting part of the foot.
- Sports shoes should be supplemented with special insoles that help strengthen muscles and ligaments. This helps correct hypopronation. The symptoms of the disorder are alleviated.
- Flat soles are unacceptable. A slight rise in the middle and a moderately stiff bottom are acceptable.
- The material must be breathable.
- Flat shoes and platforms have no health-promoting effect (flatfoot prevention). Shoes with a power sole are a high source of stress for the feet. In this case, there is a risk of developing varicose veins.
- Shoes with a stretch in the toe area are suitable for men.
- For the big toe, an orthopedic pronator, a special insole or a supinator is suitable. The products help to avoid foot deformities.
Choose running shoes with special attention if you play sports (running, jogging, walking, etc.). A corrective insole helps to distribute the load evenly over the supporting surface of the foot. This normalizes the biomechanics of the foot and eliminates the discomfort. When the first symptoms of hypopronation appear, its further development should be ruled out. Participate in physical exercises and special gymnastics exercises, consult an orthopedist.
Today's sports shoe manufacturers (Nike, Adidas, Puma, etc.) offer consumers both high-quality and reliable orthopedic shoes. Special insoles correct the level of the foot and prevent the emergence of various defects. Don't skimp on your health!
hyperpronation
Hyperpronation is a lowering of the arch of the foot in relation to the floor. Visually, the foot is tilted inwards. Because the ligaments in the foot are loose and stretched, they cannot provide good cushioning. Hyperpronation is often, but not always, associated with flat feet, and decreased muscle tone in the foot contributes to this. Flat feet increase stress on the knees, spine, and pelvis.
In the first phase, hyperpronators touch the surface with the outer part of the heel. However, the foot then turns inwards significantly more than 15 %. The pronation phase is delayed so that the foot cannot assume a neutral position and supinates during the propulsion phase. The supination impression is made with the first two toes:

This condition of the foot does not provide adequate stabilization of the body. Supportive footwear and built-in supinators should be used to avoid injury and excessive fatigue.
Exercises to correct pronation
There is often an imbalance between pronation and supination, but this can be corrected. Excessive inward tilting of the feet results from weakness in the gluteal muscles, which stabilize the thighs, shins, and ankles. It is therefore worth strengthening the legs to correct this problem.
stretching the feet
Sit down, stretch out your legs and place your hands on the floor next to your buttocks. Pull your feet away from you, pause, and then pull your feet back toward you. Perform the same movements with the toes. Perform 15 to 20 repetitions and repeat the exercise for 2 sets.

spin your feet
Sit up, stretch your legs. Pull your feet towards you and then twist to one side and vice versa. Move slowly while maintaining maximum amplitude. Perform 10-15 twists to one side, then 10-15 twists to the other side, repeat for two sets.

Tiptoe walking
Stand up straight, put your hands on your waist and feet shoulder-width apart. Stand on tiptoe and walk until you feel tired. About 15 to 20 steps on tiptoe are possible, repeat in 2 sets.

heel walk
Stand up straight, put your hands on your waist and feet shoulder-width apart. Get on your heels and walk until you feel tired. You can take about 15-20 steps on your toes, repeat for 2 sets.

Lift toes
Assume a classic stance and place your feet close together. Pull your heels off the floor, stand on your toes, hold them for a second, and return to the starting position. Perform 15-20 repetitions and repeat the exercise for 2 sets.
How do you determine your pronation?
Sports shoes must be light and comfortable, absorb the impact of landing well and relieve pressure on the foot. These qualities are represented by the Nike Air Max sneakers, popular among professional athletes.
For people with poor foot pronation and their correction, manufacturers of branded sports shoes offer special models with compensating mechanisms in the sole. When choosing training shoes, it is therefore useful to know whether and how severe your pronation problems are.
Ideally, a podiatrist or surgeon can determine the pronation of the foot, but when this is not possible, home remedies can be used. The 'wet test' is considered to be the simplest method. All you have to do is:
- Take a piece of thick paper and lay it on the floor.
- Soak your bare feet in water and step on the dry paper for about 2 minutes.
- After leaving the sheet, use a pencil to trace the wet outline.
- The results obtained can be compared with the image in the photo.
The appearance of old sneakers can also be used to complete the test or to determine the pronation of the foot. In a neutral pronation, the feet are parallel to each other and the sole is worn full-length. With hypopronation, the sole is worn more on the outside. With hyperpronation, the soles of old running shoes wear down on the inside of the feet.
How do you choose running shoes when you know your pronation type?
If you have weak pronation, you should choose running shoes with good cushioning, because the greater the impact load, the greater the risk of joint injuries. Therefore, adapt your running shoes to your pronation type and also buy orthopedic insoles. When the trainer is selected according to the anatomy of the foot, it helps improve medial support, create motion control, and increase stability and cushioning properties.
Knowing the nature of the pronation of the foot, running shoes can be purchased. With neutral pronation, the cushioning works well, so you can buy any shoes in the neutral category that do not have additional support for the foot.
In hypopronation, the arch of the foot is high and the foot contacts the surface in a smaller area and the load is poorly distributed. In this case, choose sneakers with good cushioning and a thick sole. Nike Air Max, Mizuno Wave Rider 9 (8) would be ideal.
With hyperpronation - a low arch - the foot absorbs the load well, but there are stability problems. In this case, you need to buy sneakers with good cushioning properties and significant foot support. Nike offers a range of shoes with these characteristics.
Before buying Nike Air Max sneakers or any other model, you should determine your height, the width of the insole and the instep. The shoes should fit your foot but not pinch, you should not feel that your toes are too loose in the nose of the shoe.
If you have problem pronation, before you buy a particular brand or model of running shoe, you should not only try it on, but walk, jump, and jog in them for a while. This is the only way to find a suitable and comfortable shoe model in which you do not feel uncomfortable when doing sports.
In the online store vse-krossovki.in.ua you can buy Nike Air Max or any other model of shoes, taking into account the pronation of the foot. Competent employees will help you to choose the right sneaker, try them on and advise you which model is suitable for you.
Read more:- pronation.
- Sneakers with hyperpronation.
- What is pronation and supination?.
- pronation and supination.
- What is a neutral pronation?.
- Pronation and supination in anatomy.
- hip pronation.
- These are the pronator muscles.
