What can spoil a family's joy at the arrival of a little boy? Just concern for his health. In the first few days, no abnormalities can be found during examinations, but some may appear a little later, e.g. B. a torticollis.

- Scoliosis treatment – how to correct a crooked spine in children and adults
- – Let’s define what scoliosis is?
- Main types and causes of anomalies
- Associated diseases
- symptoms
- Methods of diagnosis
- How can candidiasis be prevented from recurring?
- What happens if thrush is not treated?
- Salon treatments at the effi clinic against hair loss
- Ozone therapy
- Mesotherapy
- Plasma lifting
- diagnosis
- How do you treat hormonal acne?
Scoliosis treatment – how to correct a crooked spine in children and adults
Why does almost everyone have a curvature of the spine? What is functional scoliosis and what is true scoliosis? How to treat scoliosis, what can be corrected and what cannot? Why does scoliotic posture develop and how do you stay healthy? We talked about this with the osteopath, chiropractor and neurologist Vladimir Germanovich Kosmin.
If you look at a healthy spine from behind, it is straight, like in the left half of the picture. A spine with scoliosis is curved, as in the right half of the picture.
– Let’s define what scoliosis is?
scoliosis – is a permanent lateral curvature of the spine. It is often accompanied by rotation, that is, a rotation of the spinous processes in the direction of curvature. As the spinous processes move to the side, the ribs on the side of the curve flatten slightly inward. In contrast, the ribs on the opposite side begin to bulge outward. If you place the person with their back to you and ask them to bend forward, you can clearly see that the ribs are sunken on one side of the spine and a rib mound is formed on the other side.

The curvature in scoliosis is usually compensated for. This means that the spine first curves to one side and then a compensating curvature occurs to the other side. This ensures that the body as a whole maintains an upright posture. A person cannot walk with a crooked body.
Scoliosis can be C-shaped, S-shaped, or even Z-shaped, depending on how much the spine is curved. If the curvature is directed to the left, it is left-sided scoliosis; if it is directed to the right, it is right-sided scoliosis. And there are different degrees of scoliosis: from the first to the fourth. The least curvature is the first degree, the most severe degree with a large angle is the fourth degree.
Scoliosis can take a very different course. Sometimes a person is born with altered vertebrae. For example, a vertebra may be wedge-shaped, higher on one side and lower on the other. And if the spine has even one of these wedge-shaped vertebrae, all of the vertebrae above it are already crooked. This type of scoliosis cannot be treated. If your doctor tells you that he can completely cure such scoliosis, he is deceiving you. However, it needs to be corrected so that it does not develop from a first to second degree to a third to fourth degree. So, scoliosis in children can develop from the first to the fourth degree within a month and a half. And the fourth degree is already disabling. Even chiropractic treatment is contraindicated for grade 4 scoliosis.
Main types and causes of anomalies
- Infections, poisoning, medications, chronic diseases, toxemia, lack of water;
- Unfavorable position of the fetus in the womb, compression of the head, its tension against the uterine wall or against the shoulder, transverse position;
- Shortening of the myoma due to intrauterine inflammation or other ontogenetic abnormalities;
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- Fetal hypoxia, insufficient blood supply to tissues.
It is not uncommon for torticollis to occur during childbirth or cesarean section when the child's head is pulled, even with forceps or a vacuum.
Acquired torticollis usually develops before the first year of life, but is not excluded in adults either.
Causes of secondary malformations in infants include.
- Inappropriate care of the infant: lying on one side - in the crib, while carrying and feeding;
- placement of lights, sound sources, toys on one side of the baby;
- Neck injuries, including thermal trauma, lymphadenopathy;
- Squinting, hearing loss.
Acquired torticollis can be more easily prevented or eliminated by treating the initial symptoms.
The occurrence of congenital torticollis is difficult to control and prevent except through medical care and careful preparation for birth. Neonatal torticollis is just one symptom that indicates a general imbalance. In some cases, it is associated with hip dysplasia and club foot due to skeletal deformity.


Associated diseases
If torticollis is correctly diagnosed in a timely manner, it is easier to treat. The distinctions are:
- Myogenic torticollis, the most common form, which occurs due to shortening and contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, resulting in a curvature of the spine and asymmetry of the face.
- Idiopathic form. Often of undetermined origin, it is discovered after a difficult birth and presents irregular muscle tone. High risk of CNS abnormalities.
- Osteogenic type. This is an anomaly of the cervical spine in which the vertebrae are shortened and often fused into one. The neck is barely visible, rotation is limited, and cervical neuritis (inflammation of the nerve fibers) is also likely.
- Neurogenic. With this form of torticollis, cramp-like muscle twitches occur not only in the neck, but also in the entire torso, in the arms and legs on one side. This leads to a severe curvature of the body.
In addition to the anomalies and immediate consequences directly associated with torticollis, there is a high risk of developmental disorders in various body systems:
- The children have developmental delays, motor and language difficulties;
- Loss of appetite, sleep disturbances and crying are observed;
- Hearing and vision problems, often one-sided;
- Deformation of the head.
Long-term complications can occur many years later.
These include painful lesions in various parts of the spine, deformation of the lungs and trachea, facial and skull asymmetries, misalignment of teeth, narrowing of the carotid artery and resulting headaches and dizziness, brain dysfunction and excessive fatigue. In addition, the inner ear may be affected and the skeleton may become unbalanced and tilted to one side.
If this is an acquired manifestation of torticollis, the cause must be identified and eliminated in order to eliminate the negative factors and improve the overall quality of life of the child.
symptoms
- Squinting gets worse in bright light.
- The child is unable to focus on an object so that the pupils are in the same position and move synchronously.
- The child turns his head to look at the object with his squinting eye.
- When the child crawls, he or she bumps into objects on the side of the squinting eye.
- Older children experience frequent fatigue, headaches, double vision, and blurred vision.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
Strabismus can be acquired or congenital. In the latter case, symptoms appear soon after birth or within six months.
The squint can be vertical or horizontal. Horizontal pathology occurs most often. Draw a straight line between the pupils across the bridge of the nose - this is the place where the child's eyes squint. When they 'look' at each other it is convergent squinting, when they look in opposite directions it is divergent squinting. When squinting vertically, one or both eyes may squint downwards (hypotropia) or upwards (hypertropia).
Consider some other types of squinting.
- Monocular squinting – When only one eye deviates from the visual axis. There is often a loss of vision in the squinting eye, even down to zero. It is very difficult to cure this pathology, but it is almost always possible to return the eye to its normal position so that at least no cosmetic damage occurs.
- change – When both eyes squint one after the other, changing the axis both horizontally and vertically. This type of squint in children can be corrected without affecting the function of the eyes.
- Paralytic – Paralytic squint is characterized by the paralysis of one or more of the muscles responsible for eye movements.
- Squint – is the most common and simplest form. The amount of eye movement is maintained, both eyes see, but the squinting eye may see slightly worse. There is no double vision or blurred vision.
- Hidden – The child sees normally and the eyes are correctly positioned. However, when one of the eyes is 'off' (closed), it immediately begins to squint horizontally or vertically. Ophthalmological aids are required for diagnosis.
- Pictures – Both eyes can see and the image is not distorted. No treatment is required for this form of the disease.
Methods of diagnosis
At the first signs of strabismus, the child should consult a pediatric ophthalmologist. The doctor carries out an examination, takes the medical history and checks the vision using a table. Other Diagnostic methods:
- eye movement analysis;
- Mirrored Vision Test;
- visual acuity testing;
- skeascopy;
- Refractive examination of the eye;
- Examination of the fundus of the eye;
- Ultrasound examination of the eyeball;
- perimetry;
- Hirschberg-Schielwinkel;
- Ophthalmoscopy.
If the paralytic form of strabismus is detected, the child is referred for consultation to a neurologist. This form is characterized by damage to the eye muscle. This limits or prevents movement of the eye toward the paralyzed muscle. The cause is often neurological in nature.
Once the cause and form of the strabismus have been identified, treatment with various remedies is possible. If the squint is caused by muscle paralysis, surgery is indicated. It is best done when the child is between 3 and 6 years old. In some cases, botulinum toxin is injected. This acts as a muscle relaxant and can sometimes replace surgery. In addition, optical correction (glasses or contact lenses) is made and measures are taken to restore stereoscopic or binocular vision. Only the doctor decides on the treatment tactics.
How can candidiasis be prevented from recurring?
Candida is an opportunistic microorganism normally present in the microflora of the intimate area. In order not to provoke its excessive reproduction again:
- Strengthen your immune system;
- Do not wear tight, synthetic underwear;
- Maintain good personal hygiene;
- consume enough vitamins and limit fast carbohydrates;
- Limit foods and drinks containing mold and yeast;
- prevent;
- Avoid stress.

When treating thrush, you need to change your diet
Thrush can occur regardless of lifestyle:
- During hormonal changes (pregnancy, taking birth control pills, endocrine disorders);
- After surgery;
- Associated with antibiotic treatment;
- in the course of serious illnesses;
- Vaginal dysbacteriosis;
- After hypothermia.
What happens if thrush is not treated?

If thrush is not treated on time, it can cause serious problems.
Once the disease is diagnosed, it must be treated. Although the Candida fungus is a conditionally pathogenic organism, the body needs help to cope with the overgrown colonies and neutralize the effects. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner:
- the immune system is weakened, which can lead to secondary sexually transmitted infections;
- provoke erosion of mucous membranes;
- does it disrupt the menstrual cycle;
- will cause cervical inflammation.
- Leads to prostatitis, cystitis, which can cause infertility.
Salon treatments at the effi clinic against hair loss
Ozone therapy
This is a method of treating hair loss in men and women in which a mixture of ozone and oxygen is injected into the scalp, the mixture containing a small amount of ozone (2-4 mg per 1 liter of oxygen). Ozone activates oxygen, making it more effective. Through microinjection with a fine needle, the gas mixture is applied almost immediately to the problem areas. The cocktail saturates the tissues with oxygen, improves blood microcirculation and lymphatic drainage. All this leads to restoration of hair growth.
This treatment is not suitable for everyone. It must not be carried out during the menstrual cycle or in patients with blood clotting disorders.
Mesotherapy
This is also an injection procedure, but in which a complex of preparations containing all the necessary vitamins, micronutrients, nutrients, useful amino acids, etc. is injected into the skin. Hyaluronic acid supplies the roots with oxygen and accelerates hair growth, copper and zinc improve the hair structure, coenzymes accelerate cell regeneration. All medications used in scalp mesotherapy are selected individually for each patient, depending on the existing problem, hair type and desired effect. Mesotherapy treats scalp baldness and improves hair structure by working at the cellular level. The treatment cocktails regenerate, nourish, moisturize, strengthen the roots and detoxify.
Treatment is not carried out during pregnancy and breastfeeding, in acute chronic diseases and in the development of inflammatory skin diseases. In addition, there are numerous contraindications to mesotherapy, which your doctor can inform you about.
Plasma lifting
The procedure essentially consists of injecting the patient's own plasma, obtained from the blood, into the skin. The blood is taken from a vein and, after processing in a special centrifuge, the doctor obtains the platelet-rich plasma. This is injected into the scalp using a very fine needle, making the Plasmolift procedure virtually painless. This awakens the body's own stem cells and renews the skin from the inside out.
diagnosis
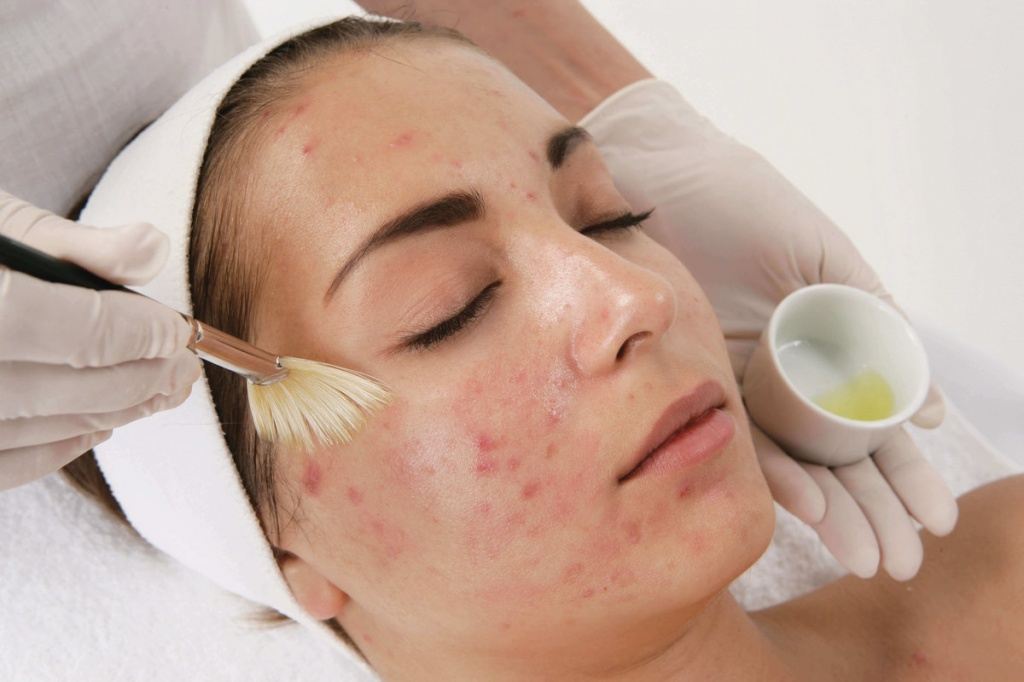
Since there are many reasons for the appearance of acne on the face of women, it is important to know the exact cause and eliminate it first before initiating treatment.
The first step is to see a doctor, such as: B. a dermatologist, endocrinologist or gynecologist. The specialist can assess the skin condition, suggest causes and prescribe the necessary tests. The standard methods for diagnosing acne in women are: Blood tests for sex hormones and thyroid hormones:
- blood tests for sex hormones and thyroid hormones;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and thyroid gland;
- General and biochemical blood tests;
- Urinalysis.
Based on the results, treatment is prescribed, a specialist from another specialty is involved, or additional examination is recommended, such as: B. Magnetic resonance imaging of the adrenal glands or other examinations.

How do you treat hormonal acne?
Treatment should be approached holistically. In addition to prescribing medications and treatment procedures by a specialist after identifying the cause of hormonal disruption and acne, appropriate skin care, diet and lifestyle adjustment are essential.

The most important rule is: do not try to suppress the inflammation! The face has many shallow vessels, an infection that enters them spreads throughout the face and aggravates the situation.
Common supportive treatment for all causes of facial acne in women:
- Diet – limiting consumption of foods that cause high sugar emissions (flour products, dairy products, simple sugars, etc.);
- Retinoids – reputable medications with high concentrations of vitamin A that prevent the formation of new pimples and inflammation;
- Acids – help to effectively eliminate dead cells, penetrate the inflammation and easily dissolve its contents; not suitable for all skin types;
- Hydrocortisone – usually in the form of a mild steroid cream that helps reduce inflammation but should not be used for long periods of time;
- Isotretinoin, a drug that blocks sebum production and is used for severe tissue damage with signs of scarring;
- Spironolactone, a drug that reduces the production of male sex hormones.
Hormonal acne treatment should be supervised by a doctor, and skin care and cosmetic treatments should also be discussed with a specialist who, based on his knowledge, the patient's skin type and medical history, is able to achieve positive results in the short term.

- How to treat clubfoot in a child.
- Equinos pes cavus.
- squinting in adults.
- 2 year old child with clubfoot.
- How to correct a clubfoot in a child.
- A child begins to have clubfoot between the ages of 1 and 5.
- Torn ligament in leg how long will it take to heal.
- How to cure plantar fasciitis forum.
