These exercises are really top notch and can help correct the shape of your legs. However, to maximize the effect, you also need to change your diet: cut out fast carbohydrates (sweets and flour) and add fats (omega-3) and proteins to your diet. This is complemented by regular endurance training and massages. All this together will give excellent results.

- Leg length discrepancy: can it be corrected, techniques, indications and contraindications, side effects and consequences
- causes
- How to correct leg curvature in 19 days.
- How to lengthen legs by 5 cm in 2 months?
- Approximate extension time by different values:
- Causes of pelvic ring deformities.
- Clinical and external manifestations of pelvic obliquity
- Who can be prescribed these procedures?
- What are the side effects of these surgeries?
- walking on towels
- chair exercise
- An orthopedic surgeon, an orthopedist and traumatologist with 44 years of experience, operates.
- frequently asked Questions
- The 3 phases of leg straightening in our clinic
- General information about leg straightening surgery
- causes and symptoms.
- diagnosis
- Diagnosis of leg height changes
- Approaches to treating lower limb deficits
Leg length discrepancy: can it be corrected, techniques, indications and contraindications, side effects and consequences
Consultation with an orthopedist for leg length discrepancies is not uncommon, and a doctor's consultation may be necessary in both children and adults. This problem is far from harmless and even with a small difference in the length of the lower limbs and without proper treatment, it can lead to dangerous consequences. With different segment lengths, the femurs and/or tibias are different, and the defect present can result in highly undesirable adjustments to the patient's overall musculoskeletal system.
Sometimes there is a slight difference in the length of the lower limbs, which does not exceed 5 mm and is not visually noticeable at all. Such a condition is normal and does not require special observation or treatment. According to some statistics, such a leg length discrepancy is detected during medical examinations in about 51 % of the soldiers. If the difference is more than 5 mm, then a visit to an orthopedist should be mandatory for both children and adults.
Why is the length of the lower limbs different? How is this expressed? Can different leg lengths be corrected? Can all be corrected and what are the consequences if left untreated? You can find the answers to these and other questions in our article.
causes
We divide the causes of leg length discrepancies into:
- anatomical (or structural) – the shortening of a leg is real and is caused by abnormalities in bone development;
- functional (or reversible) – a change in the length of a leg is caused by muscular imbalance or displacement of the surfaces of large joints.
Various factors and causes can contribute to different lower limb lengths:
- congenital anomalies: manifestations are visible immediately after birth;
- Infections: Impairment of bone growth zones leads to reduced function of growth cartilage and premature closure of growth zones;
- Osteoarthritis (coxarthrosis, ankle or knee joint pathologies, etc.): atrophic processes in the muscular apparatus around the joint lead to shortening of the leg;
- Injuries: Growth zone injuries resulting in dysfunction or abnormal bone fusion after bone fractures;
- neurological pathologies: disorders of the innervation cause the growth zones to stop functioning;
- Pathologies (chondrodysplasia with multiple exostosis, Olier's disease, neurofibromatosis, etc.): abnormalities lead to deformities and shortening of the limbs;
- Hemihypertrophy: In most cases, it is a congenital pathology in which the development of one side of the body predominates over the other, causing anomalies in limb length.
In addition to the causes described above, lower limb length discrepancy may also be due to unspecified (i.e., idiopathic) causes.
The following predisposing factors causing abnormalities in bone growth zones may contribute to leg length differences:
How to correct leg curvature in 19 days.
With the classic Ilizarov method, the curvature can be corrected quite quickly. However, the bone fragments in the area of the osteotomy must be rejoined in order to normalize. On average it takes 55-90 days. The express methods allow for a much faster transition to the rehabilitation phase - almost immediately after insertion and removal of the external fixator. This requires several treatment steps:
- Day 1 - operation: corrective osteotomy and internal fixation with an Ilizarov apparatus;
- Day 2-5 - early postoperative period, evaluation of the correction result;
- Day 5-11 – final shape correction with braces against the background of reducing pain syndrome and reducing postoperative edema;
- Day 12 - Internal fixation of the intramedullary pedicle, removal of external staples;
- Day 12-19 – postoperative period, suture removal.
After this period, rehabilitation can begin gradually, increasing the load. The bone is fixed with a pin and the external clamp is removed.
How to lengthen legs by 5 cm in 2 months?
As with leg curvature correction, treatment consists of several steps:
- Day 1 – operation: osteotomy, Ilizarov osteosynthesis, insertion of the stem;
- Day 2-5 - early postoperative period;
- Day 5-55 - Distraction (lengthening) with staples at a rate of 1mm/day;
- Day 56-60 - Locking (post stabilization), removal of the external clamp.
Thereafter, gradual initiation of rehabilitation against bone fixation with posts.
Approximate extension time by different values:
Causes of pelvic ring deformities.
The most common causes of pelvic ring deformity are functional and develops as a result of reversible The most common cause of pelvic ring deformity is functional and develops as a result of reversible displacement or torsion of the articular surfaces between the iliac crest and sacrum and pubic symphysis. There are also cases of organic damage to the pelvis due to trauma, congenital or other factors that lead to the development of severe structural anomalies and asymmetries.
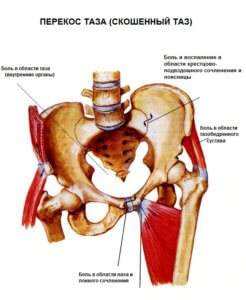
B the great majority В cases are functional and can be treated!
Clinical and external manifestations of pelvic obliquity
- change in leg length. The rotation of the pelvic ring and the reflexive contraction of the iliopsoas muscle on one side lead to a functional shortening of the leg.
- Chronic or acute pain component in the lumbosacral and pelvic region. The pain is usually caused by a dislocation of the joint surfaces of the 5th lumbar vertebra and the 1st sacral vertebra as well as the sacroiliac joint.
- postural abnormalities (Grade 1 scoliosis) are caused by twisting and tilting of the sacrum, the base of the entire spine.
- Osteoarthritis and arthritis in knees and hips. It usually occurs unilaterally due to a shift in the body's center of gravity and an unequal load on the joints due to different leg lengths.
- organ dysfunction. The organs in the pelvis are connected to the pelvis by ligaments. Changes in the normal position of the pelvic bones overstretch the ligaments of the internal organs and displace or compress the organs themselves, their vessels and nerves, affecting their function.
- Tension of the sigmoid mesentery and sigmoid-rectal junction often aggravates intestinal atony, constipation, and hemorrhoids.
- In women, uterine displacement and uterine fixation can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, gynecological problems, difficulties in conceiving and getting pregnant.
Who can be prescribed these procedures?
The two methods described above are intended for different groups of people.
Epiphysiodesis is more commonly used in children and adolescents who are still growing. This surgery must be timed to allow the unaffected bone to catch up (but not exceed) the length of the other bone.
Bone shortening surgery is often best for adolescents and adults who have completed their growth. Most people reach their final age between the ages of 18 and 20 - and only then can the doctor best assess how much bone needs to be removed to make up for the difference in length.
What are the side effects of these surgeries?
Bone shortening surgeries are not without risks. Potential side effects or complications of epiphysiodesis include:
- infections;
- bleeding;
- deformation of bone growth;
- continued bone growth;
- Over or under correction that does not eliminate the difference.
Potential risks or side effects of bone shortening surgery include:
- uneven bone healing;
- Infection;
- bleeding;
- over- or under-correction;
- Nonunion, or bones that don't grow together properly while healing;
- Pains;
- loss of function.
walking on towels
This exercise is a shock to your whole body; after just a few minutes you will feel your leg muscles burning! Perform the exercise on a slippery floor such as linoleum or tile. For the exercise you will need small waffle towels. Place these under your feet and assume a position as if you are trying to push yourself up with your arms straight. Change the position of your feet and slide across the floor as quickly as possible, imitating a running stride. This exercise is similar to 'rock climbing' and can easily be incorporated into a high-intensity Tabata workout.

It takes about 200 muscles to take just one step. Not surprisingly, walking is considered by some experts to be the best way to burn fat and improve posture.
chair exercise
This variant of the static exercise trains the muscles of the legs and buttocks, eliminates fat deposits and tightens the skin. Walk towards a wall, press your heels against it, place your feet shoulder-width apart and stretch your arms down. Inhale and lower yourself against the wall into a position that feels like you are sitting in a chair. Your knees should be bent at 90 degrees and your hips should be parallel to the floor. Your back must be straight. Stay in this position for as long as possible while keeping your whole body tense. As you exhale, return to the starting position as if pushing yourself up. To make the 'chair' more difficult, you can also do the exercise with a straight leg or without a wall.
Place your hands on the floor as if you are doing a push-up. Kneel on the floor with one leg bent at 90 degrees and the other leg straight. Gently raise the free leg to the maximum height, hold for 2-3 seconds, then lower to tiptoe. Switch legs and lift with the other leg. Look straight ahead and don't flex your lower back as you perform the exercise. Do not wiggle your leg backwards or lift the knee of the supporting leg off the floor. You can prop yourself up on your forearms if you want, which is a good option if your wrists are weak. You can use leg weights.
An orthopedic surgeon, an orthopedist and traumatologist with 44 years of experience, operates.
- – He has mastered the method of external fixation to perfection. He has developed numerous methods to use external fixation devices in the treatment of trauma and orthopedic defects.
- – He developed and introduced therapeutic and diagnostic technologies for the treatment of patients with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, including an original CT scanning scheme for the lower limbs, improved external fixation devices and his own computer program for operating the Ilizarov device.
- – Author of monographs, 58 scientific papers, 7 inventions and 5 rationalization proposals.
- – Awarded the Gold Medal at Euro-2002 for Achievements in Medicine (Belgium).
- – Since 2015 senior researcher at the Department of Musculoskeletal Injuries and Abscess Complications at the Priorov Scientific and Technical Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics.
The surgeon will examine you and determine the problem and the method of correction. The doctor will prescribe you diagnostic procedures and tell you how to prepare for the operation.
X-rays and CT scans are taken to create a computer model. Even before the operation you will see how your legs will look after the correction.
Surgeon Bagirov uses minimally invasive techniques to correct lower limb deformities. The procedure involves the insertion of an external fixation device into the lower leg and an osteotomy - cutting through the bone.
Depending on the type of deformity, the surgeon corrects the shape of the legs directly during the operation or gradually in the postoperative period. The final shape of the legs is refined using X-rays, CT scans and visual inspection.
In lower limb surgeries, modern Ilizarov staples are used to preserve the full range of motion of the joint. Patients are able to move easily and go about their daily activities.
You will stay in the hospital for five to seven days. During the correction and fixation period, rehabilitation includes walking with a walker, joint exercises and walking with the splint with full limb loading.
frequently asked Questions
Acquired deformities – sequelae of rickets and rickets-like diseases, Erlacher-Blount disease, post-traumatic conditions. Congenital deformities – genetically inherited varus (O-shaped) and valgus (X-shaped) curvatures in children and adults. Congenital and acquired shortening of the legs and arms. Multiplanar deformities of the foot - multiple curvatures at the same time. Bone deformities of the foot – valgus deformity of the first toe (hallux valgus), toe lengthening with congenital toe shortening.
Yes, the surgeon increases the patient's height by lengthening the lower limbs and/or the thigh.
Yes you can.
The success of the operation and the guarantee of its safety directly depend on the quality of the preoperative examination. We diagnose leg deformities using modern X-ray and CT equipment. So we can find not only the projection deformity, but also the rotational (twisting) deformity. A computer model is created based on the diagnosis so we can see what the feet will look like after the correction.
Surgeon Bagirov uses a minimally traumatic surgical technique to treat foot deformities. Surgical correction of the tibia deformity is performed through an osteotomy, in which the bone is severed through a 5-7 mm skin incision. An external fixation splint is attached to the outside of the tibia. We use an Ilizarov brace, which is smaller and more modern. These braces maintain the full range of motion of the knee joint and allow the patient to move freely. Depending on the type of misalignment and the goals set, the bone deformity is corrected immediately during the operation or gradually, taking into account the postoperative period. A special computer program is used to correct the deformity. After the correction, the final shape of the legs is refined through visual, radiological and computer-aided examinations. Patients stay in the hospital for 5-7 days and are then treated on an outpatient basis. During the correction phase and after achieving the form (fixation phase), rehabilitation is carried out.
The 3 phases of leg straightening in our clinic

Doctors perform the following steps on both legs at the same time:
- They insert the splint and thread the medical-grade steel spokes through the bone of the upper and lower tibia.
- They fix the spokes in the rings of the Ilizarov clasp and tighten them, connecting the rings with rods. A secure corset-bone system is created
- The bone is carefully cut through small skin incisions with a bone cutter to avoid damaging the surrounding tissue.
- The brace is firmly fixed and a cosmetic suture is placed over the surgical area.
Gradual straightening of the legs begins 5-7 days after the procedure. The length of this period depends on the desired result and the size of the initial deformation.
The doctor constantly monitors the patient and gives instructions on how to correct the shin curvature with an accuracy of 0.1 degrees.
The orthopedic surgeon runs a simulation on the computer, examines the x-rays and decides with the patient whether they want to complete the phase.

The last phase lasts about 1 month.
The devices hold the bones in the correct position until the bones have healed. During this time, patients walk without crutches and hardly notice the splint on their feet.
Doctors take an X-ray of the lower leg to determine the density of the regenerated bone. If the bone density is sufficient, the specialist removes the brace.
General information about leg straightening surgery
Even the threads disappear 5-6 months after the operation

Surgical correction of the legs is performed under general or spinal anesthesia. Expected age for surgery: 16-60 years. The procedure takes place in the hospital or under outpatient supervision.
Patients return to work and daily activities 2 to 3 weeks after brace removal. Walking is not restricted during rehabilitation. Running and jumping are contraindicated. Swimming is recommended. More demanding exercises can be started after 2-4 months.
The total duration of treatment is 2-3 months. The exact time for foot correction depends on the speed of tissue recovery, age and physical activity of the person. Our record is 42 days.
causes and symptoms.
Bilateral leg shortening is caused by various genetic abnormalities. The unilateral form can be provoked by various pathologies and diseases:
A slight difference in leg length is often not even visible to the patient and is only detected during special examinations. If the leg length difference is more than 3 centimetres, the pelvis is noticeably tilted, which impedes normal walking and causes limping.
In children, shortening of the lower limbs is usually detected during an examination by an orthopedist. The presence of a pathology is indicated by a number of external signs (localization of the tendons, upper pole of the knees, etc.).
diagnosis
To determine the severity and nature of the pathology, the doctor measures the length of the patient's lower limbs, as well as its individual segments, focusing on the bony protrusions (ankles, knees, etc.). X-rays are also recommended.
Lower limb shortening is treated by specialists such as podiatrists and traumatologists. In the case of a slight shortening, conservative correction (wearing special shoes and orthoses) is indicated.
If the pathology is caused by a hip dislocation or subluxation, treatment consists of splinting, exercises and massage. In some cases, the dislocation is corrected with surgery.
A major dislocation requires surgery. The most common method of orthopedic foot correction is the use of an Ilizarov splint.
Legs that are not equal in length are a serious problem and can lead to serious joint and spine abnormalities if not properly managed.
- Open daily from 09:00 to 22:00
- All diagnosis rooms are open daily from 08:00 to 22:00.
- Trauma and treatment rooms are open 24 hours a day
- Open from 09:00 to 22:00 daily
- All diagnosis rooms are open daily from 08:00 to 22:00
- Trauma and treatment rooms are open 24 hours a day
- Open from 09:00 to 22:00 daily
- All diagnostic rooms are open daily from 08:00 to 22:00
- Trauma and treatment rooms are open 24 hours a day
- Open from 08:00 to 22:00 daily
- All diagnostic rooms are open daily from 08:00 to 22:00
- Trauma and treatment rooms are open daily from 08:00 to 22:00
- Open from 09:00 to 22:00 daily
- All diagnostic practices are open daily from 08:00 to 22:00
- Trauma and treatment rooms open 24 hours a day
Diagnosis of leg height changes
Computer-aided optical topography, computer-aided planoscopy and a podiatry consultation with special orthopedic examinations are used for the diagnosis.
Other diagnostic methods include X-rays, CT and MRI. The aim of the examination is to determine the severity of the leg length discrepancy and the causes of these changes, and based on the information obtained, a possible treatment is decided.
Approaches to treating lower limb deficits
Some patients refuse any treatment because they fear the need for surgery. In reality, the problem can often even be treated with orthotics. Chiropractic and osteopathy, massage therapy and physical therapy have shown good results.
Appropriate treatment can achieve the desired results: eliminating or compensating for leg length discrepancies and preventing the development of complications and comorbidities.
Read more:- How to determine leg shortening.
- Shortening of the lower limbs.
- difference in leg length.
- One leg is shorter than the other.
- From where you can measure your leg length.
- Different leg length after a hip prosthesis.
- Leg length proportions.
- Lift your heels off the floor during the squat.
