The patient's quality of life in such cases is impaired due to the limited function of the foot and the inability to properly distribute body weight when walking or running, which can lead to damage to the spine and internal organs in the future.

- Valgus deformity
- | Where does hallux valgus come from?
- Design features of rehabilitation shoes
- Indications for the use of rehabilitation shoes
- How to treat
- When is a bunion on the foot removed with the laser?
- Arthrodesis for valgus deformity
- Hammertoe surgery
- Preparing for surgery
- Surgical technique
- Rehabilitation after surgery
- Types of surgery
- Proceedings
- Causes of nodule formation on the foot
- Non-surgical treatment of clubfoot
- Surgical technique
- Rehabilitation after surgery
Valgus deformity
We have unique, minimally invasive surgical techniques to correct hallux valgus in the forefoot. Just 15 years ago, 'removing the heel bone' in the big toe meant several months on crutches. Today this is a thing of the past; Even in the most difficult cases, our patients can leave the hospital independently the day after the operation. How is that possible? Read more…
Hallux valgus is the Latin word for the most common forefoot deformity: hallux valgus. If we translate the combination of words into Russian (hallux, big toe; valgus, outward deviation), we get 'outward deviation of the big (first) toe'.
You can find many different names for this deformity on the Internet: Hallux valgus, 'lump' or 'bone' on the feet. Sometimes it is also called gout, although gout is a metabolic disease in which the joint of the big toe can become inflamed, but if it deviates outward, this is by no means caused by gout.
| Where does hallux valgus come from?
The most likely explanation is a genetic or familial predisposition. However, this does not necessarily mean that your mother or grandmother had this deformity. It may be that the genes that are responsible for the development of hallux valgus are not active separately in the father and mother (scientifically speaking: recessive). And when two recessive genes come together in a common child, they become active, i.e. dominant, and lead to the deformity.
Many patients and doctors attribute the appearance of thickened feet to wearing tight high-heeled shoes and being overweight.
This is not true, although such explanations are much easier for patients to accept. But where does hallux valgus come from in young people or people who have never worn model shoes? Apparently, in tight, high-heeled shoes, the painful sensations may appear earlier. However, this does not mean that shoes or excessive weight are direct causes of the deformity.
In fact, statistics show that by the age of 60, about 60-65 % of women (the deformity is much less common in men) suffer from some outward deviation of the big toe, regardless of their weight or the shoes they wear have carried throughout their lives.
Design features of rehabilitation shoes
Although there are many different models of rehabilitation shoes, they all share common design and fitting features. When choosing the best footwear, the doctor pays attention to the following features and properties:
- heel – The rigid heel helps keep the joints firmly in place and prevents deformities from recurring. The height is calculated individually depending on the foot size. Most experts recommend choosing shoes with a heel height of at least 3 cm.
- Anatomical supinator – This part of the shoe has the task of supporting the arch of the foot and distributing the load evenly. This prevents injuries and damage to the joint structures.
- Shoelaces or Velcro – After surgery, it is advisable to wear shoes that provide better support for the foot. Models with laces or Velcro fasteners, which can be used to regulate the fit of the shoe on the foot, are preferable.
- Metatarsal pads – Special silicone pads placed at the front of the shoe to reduce friction between the toes, protect the toes from deformation and blisters and prevent the foot from slipping in the shoe.
- Hammertoe correctors – Special devices that fit over the toes and separate them from each other. This reduces the pressure of the crooked toe on the rest of the toe.
- Soft toe – The noses of the rehabilitation shoes should not be too narrow and should not pinch or stiffen the toes, and the outsole in the forefoot area should be relatively soft and flexible.
- Sole and heel – The soles of orthopedic shoes should be profiled and designed to distribute and reduce the load when walking and running. Heels: People who have had bone removed from their feet through surgery can wear shoes and sandals with a sturdy, wide heel no higher than 4 cm.
- Material: – Protective shoes should have good air permeability. This prevents the accumulation of moisture in closed shoes and prevents fungal infections of the foot, which are unacceptable in the postoperative period. For this purpose, rehabilitation shoes should be made of high quality, preferably natural materials such as leather, suede, soft fabrics, etc.
Indications for the use of rehabilitation shoes
Orthopedic shoes are indicated for the prevention and treatment of all types of foot deformities, including valgus deformities. For children and teenagers, the right footwear can completely solve the problem.
Specialists prescribe orthopedic shoes for patients with the following pathologies:
- Valgus deformity of the foot (valgus) – The formation of a bunion on the lateral surface of the foot is accompanied by a number of anomalies and abnormal load distribution. Wearing orthopedic footwear reduces pressure on the nasal side of the foot, eliminating inflammation and pain in this area and reducing the protruding bump.
- flat feet – A flattening of the arch of the foot, which is often associated with a valgus deformity. With flat feet, the arch of the foot is unable to absorb the shock and stress of walking and running. Orthopedic shoes with special insoles and supinators can reduce the load on the foot and protect the patient's musculoskeletal system from injuries or serious illnesses.
- Weakness of the ligamentous system – This pathology underlies all foot deformities. When wearing orthopedic shoes, the foot must be fixed in the correct position, which in turn puts strain on the muscles and ligaments. Regularly stressing the weak structures of the musculoskeletal system through walking and running helps to gradually strengthen them.
- overweight – Being slightly overweight can be very stressful for painful feet. Orthopedic shoes distribute the load evenly across the strongest and most resilient parts of the foot.
- Joint deformities – Pathological changes in the joints occur in diseases such as arthritis and arthrosis, but also when the feet are under heavy strain and wearing high heels for long periods of time. By regularly wearing orthopedic shoes, the joints are brought back into the correct position and can thus become healthy again.
- diseases of the spine – Scoliosis, osteochondrosis and other musculoskeletal diseases can cause severe curvature of the foot structures. In such cases, orthopedic footwear reliably protects the lower limbs from deformity.
- Diabetic foot – If a diabetic patient develops a valgus deformity, it is advisable to wear orthopedic shoes for life to avoid hyperkeratosis and loss of tissue sensitivity.
How to treat
In stage 1. The disease is successfully treated conservatively with physiotherapy.
Patients are recommended to exercise, maintain a normal weight, and wear orthopedic shoes or comfortable shoes with insoles and rubber boots to reduce pressure on the problematic joint.
Illness Stages 2 and 3. Can only be treated through surgery.
During the operation, the orthopedist removes the excess bone and joint tissue and eliminates the deformation of the first metatarsal bone - the patient is completely and permanently relieved of the problem.
When is a bunion on the foot removed with the laser?
Valgus deformity most commonly affects women over 30 years old. There is no clear cause for this condition, but experts believe that hereditary and hormonal factors play an important role. Uncomfortable high-heeled shoes, obesity, a history of osteoporosis, trauma, and damage to the foot can also contribute to bunion formation.
As soon as you notice a bony protrusion on the side surface of the foot, you should consult a specialist. In the early stages of the pathology, the doctor is likely to suggest conservative treatment in the form of massage, physiotherapy, wearing orthopedic shoes and taking medications. Surgery is performed if the patient has the following symptoms
- pain when walking and at rest;
- the deviation angle of the metatarsophalangeal phalanx of the big toe is more than 30° and the other toes are dislocated;
- Swelling of the feet and inflammation of the surrounding tissues with the formation of ulcers and purulent skin lesions;
- Inability to wear comfortable shoes as bones barely protrude;
- Gait disorder accompanied by spinal curvature.
Practice shows that timely removal of the bursa significantly improves the patient's quality of life, eliminates pain, prevents spinal deformation and serious joint diseases.
Arthrodesis for valgus deformity
During arthrodesis, the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is completely immobilized by stiffening the bones that form it. The operation is performed on patients with transverse spinal deformity and hallux valgus with hypermobility of the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
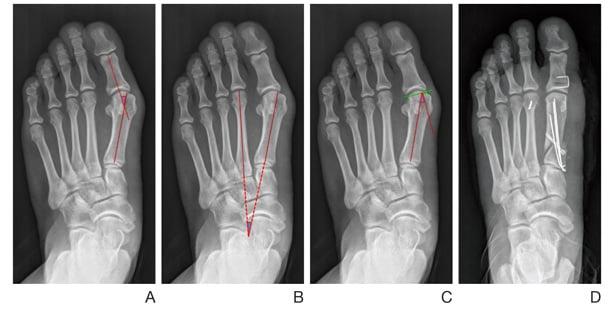
Test to detect pathological mobility:
- With the fingers of one hand, hold the II-V metatarsals;
- Hold the 1st metatarsal bone with the other hand and try to move it in a dorsal-plantar direction;
- Check how far you can move it;
- Displacement of the bone by more than one sagittal dimension of the thumb indicates the presence of hypermobility..
Arthrodesis is the most traumatic procedure and involves the complete removal of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe. It is only performed as a last resort when other methods prove ineffective.
Hammertoe surgery
In the advanced stages, hallux valgus is known to be combined with a hammertoe deformity of the II-V toes. This looks unattractive and affects the function of the foot. There are various surgical procedures to correct them.

- Closed reduction. This technique involves forcibly correcting the defect in a non-surgical manner. Unfortunately, reduction has little effect and relapse often occurs.
- Tenotomy or tendon transposition. The operation is performed on the ligaments of the foot. The hammertoe deformity can be corrected by cleverly crossing or repositioning the ligaments.
- Bone resection. During surgery, doctors cut out the base of the middle phalanx or the head of the main phalanx. This removes the excess bone mass and corrects the misalignment.
- Weil or Wilson osteotomy. Similar to the Scarf and Chevron operations, but performed on the II-V metatarsals. The surgeons cut them and then fix the bone fragments with titanium screws.
Osteotomy is most effective in treating hammertoes. It is carried out in the most serious and neglected cases.
Preparing for surgery
Before orthopedic surgery, a detailed examination of the body and the pathological area of the foot is required. This allows the operation to be planned and possible complications to be prevented.
Preoperative diagnosis includes the following examinations:
- Examination of the foot using x-rays and CT scans.
- Laboratory tests – general clinical blood and urine tests, blood chemistry, coagulation tests, Rh groups and factors, infection status (HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis).
- Instrumental screening – electrocardiography, chest x-ray (fluorography is acceptable but must not be older than 6 months).
If comorbidities are present, consultations with specialists and advanced preoperative diagnostics (cardiac ultrasound, vascular ultrasound, abdominal ultrasound, etc.) are indicated.
Surgical technique
Depending on the severity of the misalignment, the orthopedist uses different surgical techniques.
The surgeon splits the first metatarsal bone lengthways and then corrects the position of the head of the first metatarsal bone and fixes it with screws. In some cases, excess bone tissue in the metatarsal head is removed. The tendon and joint capsule are then restored.
Take advantage of this unique opportunity for a free consultation about elective surgery. Learn more.

Sock surgery can dramatically correct a deformity. This reshapes the inner edge of the foot, completely eliminating pain and restoring functionality to the lower limbs.
Rehabilitation after surgery
In the early postoperative period, dressings must be applied before sutures are removed. The doctor determines the frequency individually, depending on the condition of the wound and the general well-being of the patient. On average, patients stay in our hospital for 1-2 days and then continue with outpatient rehabilitation.
The sutures of the surgical wound are removed after 2-3 weeks. During this time, the patient is allowed to walk on crutches in special shoes (Baruca shoes) and put some weight on the operated foot. The intensity of the rehabilitation measures (gradual increase in load) is determined by the doctor based on dynamic examinations and X-rays of the foot.
After 1-2 months, the patient can wear normal, comfortable shoes with individual orthopedic insoles, and the operated foot is fully resilient without additional support.
After surgery, the risk factors for recurrence of the deformity should be eliminated. It is advisable to normalize body weight, avoid physical stress on the lower limbs (long static standing and lifting heavy objects) and not wear tight and/or high shoes for a long period of time. The orthopedic-traumatological specialists of SM-Clinic Surgery also recommend wearing comfortable shoes with individual orthopedic insoles and special interference insoles, as well as exercises to strengthen the muscles of the lower limbs and foot. Proper prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, diabetes and other related diseases is important.
Contact a professional to effectively treat your foot deformity!
*Please note that surgical treatment prices are for operations only. Preoperative preparation, anesthesia, hospitalization and other related services are charged separately. The price indicates the minimum cost of the operation, the final price depends on the complexity of the procedure and is determined by the doctor during a personal conversation.
Types of surgery
There are many different techniques for correcting hallux valgus deformity. The choice of technique is made by the traumatologist or orthopedist, taking into account the severity of the pathology, the patient's age and the accompanying lesions in the adjacent parts of the foot. In modern traumatology and orthopedics, the following operations are mainly performed:
- Simple removal of a protruding bone fragment (Schede surgery). This procedure is called an exostectomy and is indicated for mild deformities.
- Hallux valgus surgery in which the ligaments surrounding the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint are repaired.
- resection arthroplasty. It ends with the removal of the head of the 1st metatarsal.
- arthrodesis. The joint surfaces are removed, the joint is immobilized and immobilized.
- Arthroplasty. The joint surfaces are replaced with plastic implants.
It is also possible to correct deformities through osteotomy. A fragment of one or more bones is removed. Most often a small fragment of the first metatarsal bone is removed, less often a fragment of the first phalanx of the toes. A technique is sometimes used that involves removing fragments of both bones; in some cases, a fragment of the tarsal bone (the tarsal bone to which the first metatarsal bone is attached) is taken out. This bone is partially removed to correct an angular misalignment. After the bone fragment is removed, the bone is repositioned anatomically.
Proceedings
The surgical procedure will be carried out as planned. Before hospitalization, the patient is examined, a general analysis is prescribed and x-rays of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe are taken. Anesthesia is administered either locally or through a conduit. General anesthesia is rarely used. An incision is made on the back of the foot over the affected area. A small chisel is used to remove bony structures. After the planned surgical procedure is completed, the wound is sutured and a rubber prosthesis is applied.
As a rule, the limb is fixed with a plaster or a plastic splint after the hallux valgus operation. The duration of immobilization can vary greatly depending on the type of procedure. The discharge time depends on the swelling, the condition of the surgical wound and the general condition of the patient. The stitches are removed on days 10-12. From this point on, the patient is advised to choose comfortable shoes, avoid wearing high-heeled shoes and do special exercises.
Causes of nodule formation on the foot
The growth of a nodule on the foot is associated with a deformity of the thumb joint. However, the exact causes of valgus foot deformity are not known. Several factors are likely to influence the development of hallux valgus.
If other family members have bunions on their feet, your risk of developing a valgus deformity increases. However, this is not a verdict. There are people who have healthy feet despite bad heredity.
Arthritis, an inflammatory disease of the joint, can be another cause of deformity. The following types of arthritis are considered to be particularly common in causing foot bunions:
- rheumatoid arthritis – pain and inflammation of the joints caused by an immune system attack on the joint capsule;
- Gout – a type of arthritis that most commonly affects the big toe;
- Psoriatic arthritis – one of the symptoms of psoriasis.
In some cases, however, arthritis develops secondary to foot deformity, while other diseases trigger the development of hallux valgus. Various congenital and acquired diseases related to weak ligaments, flexible joints and low muscle tone lead to a bunion in the foot. Examples of this are cerebral palsy or Marfan syndrome.
Uncomfortable footwear can be a cause of a bunion. Shoes that are too tight or the wrong size can worsen an existing bunion by wearing down the tissue of the big toe. Tight, high-heeled shoes compress the foot, causing the big toe to bend. This can stretch the toe and put pressure on surrounding nerves, causing pain. In addition, wearing high-heeled shoes puts a lot of stress on the front part of the foot, which leads to a lot of stress on the toe joints.
If the bunion is uncomfortable and painful, you should see a doctor. Below are the pros and cons of the different treatment methods so that you can easily compare them.
Non-surgical treatment of clubfoot
Whenever possible, surgery should be avoided. Non-surgical treatments help relieve the pain and discomfort caused by bunions, but do not change the shape of the foot or prevent further deformation of the joint.
If the ball of your foot is causing you pain, you can take a pain relieverYou can take an over-the-counter pain reliever such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Before you take a painkiller, read the dosage instructions on the package insert.
Special reusable pads Gel, fleece or foam for the big toe joint help to relieve the pain associated with hallux valgus and are available from pharmacies without a prescription. Some are glued to the bump, while others are attached to the foot with a small ring placed over the big toe. The insole prevents the foot from rubbing against the shoe and relieves pressure on the enlarged joint at the base of the big toe.
The orthopedic insole is placed in the shoe and corrects the position of the foot bones, which can reduce pressure on the ball of the foot and relieve pain. Orthopedic insoles can be purchased at the pharmacy without a prescription, but the most important thing is that the insoles fit the foot perfectly. Therefore, it is better to consult an orthopedist when choosing an insole. In addition to off-the-shelf insoles, you can also buy insoles that are made according to individual dimensions and requirements. The choice between ready-made and custom-made insoles depends on the individual case and the severity of the misalignment.
or use a special railwhich is placed on the back of the foot above the big toe to promote its straightening. The splint can be worn both during the day and at night, although there is little evidence of its effectiveness. There are also toe separators that can relieve the pain caused by a bony toe. However, it is not always possible to use toe separators or insoles as the thickening causes the foot to cramp in the shoe.
Surgical technique
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The anesthesiologist determines the optimal anesthetic combination depending on the individual risk.
SM Clinic Surgery Center uses innovative methods to remove nodules on the feet. There are 2 different surgical techniques. Each technique has its own advantages. The orthopedist/traumatologist selects the best option after a detailed examination of the patient.
- The surgeon performs a layered approach to the first metatarsal bone.
- An incision is made along the long axis of the metatarsal bone.
- The correction is carried out in the horizontal plane.
- Fixing the new position with screws.
- Removal of the hypertrophic area of the first metatarsal bone.
- Plastic correction of the joint capsule of the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
- Seam application on the skin.
- A V-shaped incision is made in the transverse direction of the bone.
- The head of the metatarsal bone is moved in the appropriate direction and fixed in the new position.
- Plastic correction of the joint capsule of the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
- The operation is completed with a corrective osteotomy of the proximal phalanx of the first toe.
- Immobilization with a special screw.
- Insertion of a skin suture.
Take advantage of this unique opportunity and make an appointment for a free consultation about your planned treatment. Learn more here.

The operation leads to a complete recovery - the pain is eliminated and the shape of the foot is restored. The affected person can wear beautiful, fashionable shoes again, is free from pain and fatigue and can lead an active and fulfilling life.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Discharge from the hospital occurs on day 3 after surgery.
The average duration of the rehabilitation phase is around 5-6 weeks. Immediately after orthopedic surgery, the patient can put full weight on the foot, but must wear special footwear.
After 5-6 weeks the patient can wear normal footwear and the restrictions are lifted.
Foot nodule removal is a radical and effective method to solve a long-standing problem.
Bone reconstruction (corrective osteotomy, bone lengthening, bone shortening) (depending on complexity)
Bone reconstruction. Bone osteotomy with internal and external fixation devices (depending on complexity).
*Please note that the cost of the procedure is for the surgery only. Preoperative preparation, anesthesia, hospitalization and other related services are charged separately. The price list indicates the minimum cost of the operation, the final cost depends on the complexity of the procedure and is determined by the doctor during the direct consultation.
The administration of the clinic makes every effort to timely update the price list published on the website; However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we recommend that you inquire about the cost of the services at the reception or in the contact center at +7 (495) 292-59-87. The price shown is not an offer. The medical services are provided on a contractual basis.
Read more:- flatfoot μb.
- ICD 10 chalgus valgus.
- Stages of hallux valgus.
- chalgus valgus.
- Deflection of the first toe.
- First metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot (metatarsophalangeal joint).
- Shoes for hallux valgus.
- How much does crooked leg surgery cost?.
