It usually takes a few days before you can leave the clinic. At this point, patients are able to move around independently, sometimes with additional assistance. If all recommendations are followed, it is possible to return to the same level of activity within a few weeks. After a month it is even possible to do sports with practically no restrictions.
- Knee Arthroplasty
- Benefits of Arthroplasty
- First aid and treatment of a cruciate ligament rupture
- Rehabilitation after cruciate ligament surgery
- course of the operation.
- postoperative period
- What complications can occur?
- postoperative period
- Cost of knee surgery in Moscow
- classification
- auto transplant
- Legamis Plasticization
- Cost of knee surgery in Moscow
- classification
- Cost of arthroscopic surgeries on the knee joint in Moscow
- indications
- Possible complications
- cost of the operation
Knee Arthroplasty
The joints in the legs are subjected to enormous stress. It is therefore not surprising that these types of joints cause problems. Modern medicine offers a solution that allows a return to active life, even with severe damage to these joints.
Knee arthroplasty is an operation in which the natural tissue of the joint is replaced with artificial tissue. The result is a reconstructed and fully functional limb that allows the patient to return to an active life.
Total or unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, standard (no cost of arthroplasty)
– from 180,000
Surgery, anesthetic advice and anesthetic assistance, bandages, medication, meals and hospital stay, postoperative aftercare by the doctor treating you for one month (longer if necessary).
The price for the endoprosthesis (varies depending on the manufacturer) and the preoperative examination are not included in this price.
- osteoarthritis and arthritis of any etiology;
- Complications after fractures of articular bones;
- ligament damage that cannot be repaired conservatively;
- tissue necrosis within the joint;
- tumors of any kind.
- presence of decompensated chronic diseases;
- autoimmune diseases
- severe diabetes;
- Presence of infectious or inflammatory diseases.
The knee joint is the largest joint in the body. It is the body that carries a significant amount of weight when walking and also undergoes a tremendous amount of stress when running and exercising. Unfortunately, it is not always able to cope with them.
Anatomically, this joint is formed by the fusion of two bones—the femur and the tibia. It consists of numerous tendons and ligaments as well as hyaline cartilage. This system gives the joint strength, stability and sufficient mobility. On the side of the thigh is the kneecap, which is also considered part of the joint.
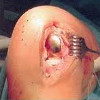
Benefits of Arthroplasty
Knee arthroplasty is considered to be technically complex. The procedure requires a surgeon with a sub-specialty - a professional who deals specifically with arthroplasty.
There are two main options for performing the procedure:
- Unipolar prosthetics.
An implant is only placed in a damaged area. Often the entire joint is not affected by the pathology and a unipolar prosthesis is sufficient to restore functional mobility. - A total endoprosthesis is the replacement of the entire joint.
The prosthesis is designed after an X-ray and taking into account the anatomy of the patient. The surgeon removes the damaged fragment and inserts a biocompatible endoprosthesis that takes over the function of the removed tissue. After the main part of the operation, the wound is drained. This is done to avoid blood pooling in the joint area. In addition, infections are prevented and blood loss is compensated for if necessary.
The operation is complex, but safe when performed in a modern clinic. Joint replacement allows you to live an active and fulfilling life and forget about joint pain.
First aid and treatment of a cruciate ligament rupture
First aid in an accident with a suspected cruciate ligament tear:
- Immobilization of the injured limb, immobilization, elevation of the position;
- apply a bandage
- apply cold
- give anesthetics if the pain is severe
- Transfer to a medical facility.
After the diagnosis, the doctor will recommend treatment - therapy or surgery of the cruciate ligament in the knee, which is performed in the hospital. Conservative methods include:
- Immobilization of the affected joint (plaster or bandage)
- Painkillers, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs
- Measures to restore mobility of the joint
- spa treatment
The therapy is indicated for minor injuries, in children and the elderly. However, most athletes experience joint instability and pain after conservative treatment. In severe cases or when therapy fails, surgical treatment is indicated.
Ligament reconstruction usually requires reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee joint. Autologous or allogeneic transplants such as tendons, patellar ligaments, artificial prostheses or donor ligaments are used as connective tissue reconstruction material.
The minimally invasive arthroscopic ligament reconstruction is performed through tissue sections a few millimeters in size and takes one to two hours. Surgical instruments and an optical device called an arthroscope are inserted into the joint, through which doctors monitor the procedure.
- minor trauma
- rapid wound healing
- accelerated rehabilitation
- minimal risk of complications
- few contraindications.
Rehabilitation after cruciate ligament surgery
Proper rehabilitation after cruciate ligament surgery is essential for the patient's full recovery. A prerequisite for success are various rehabilitation measures (physiotherapy, massage, physiotherapy, orthopedic devices), early exercise (in the first days after reconstruction) and a gradual increase in the load on the injured limb.
For athletes, rehabilitation after cruciate ligament surgery consists of five phases:
- In weeks 1 through 4, measures are taken to reduce swelling and pain, and unaided movements are practiced.
- In weeks 5-10, joint balance is improved, leg muscles are strengthened, and full range of motion is restored.
- Weeks 11 through 16 include endurance training to prepare for a return to normal activity.
- Motor coordination is improved in weeks 17 to 24.
- In weeks 25 to 28, special motor skills are restored and there is a transition to sports training and a normal rhythm of life.
For those who prefer a moderate range of motion, the rehabilitation time can be reduced to 20 to 24 weeks provided they pay attention to their walking behavior.
course of the operation.
Spinal anesthesia or general anesthesia is used before the operation:
- spinal anesthesia. The anesthetic is given through a needle placed between the first and second lumbar vertebrae. With spinal anesthesia, the lower half of the body becomes numb and the patient is conscious.
- general anesthesia. Most commonly used in endoprostheses. Depending on the length of the surgery, general intravenous anesthesia may be recommended to maintain consciousness during the procedure.
The duration of a joint replacement surgery depends on which joint is to be replaced and takes an average of two hours. During the operation, the damaged cartilage and part of the bone are removed. The endoprosthesis mimics the shape and movement of the natural joint.
The hip replacement can be total, replacing all articular surfaces, or unipolar, replacing only the femoral head (rarely used in debilitated patients after a femoral neck fracture). A distinction is made between cemented and cementless arthroplasty, the latter being fixed by growing into the bone elements.
Knee arthroplasty can be total arthroplasty, in which all of the damaged cartilage is replaced with a prosthesis, unicondylar arthroplasty, in which half of the damaged structures are replaced, and point arthroplasty, in which the damaged cartilage is replaced directly is replaced.
In shoulder arthroplasty, the most important joint structures are replaced: the shoulder blade (scapula) and the humeral head. A functional examination is then carried out and the surgical access is sutured. The patient is transferred to the ward.
postoperative period
Activation of the patient begins almost immediately under the close supervision of the trauma surgeon - orthopedist.
After the operation, it is important to follow the instructions:
- Avoid strenuous physical activity, do not put pressure on the limb, apply ice for 20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
- Stick to the level and type of physical activity recommended by your doctor, gradually increasing the intensity.
- Elevation of arm and leg to reduce swelling and pain
- Care of the postoperative area. Bandages are performed on an outpatient basis. Keep the area around the seams dry and clean.
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain. Most patients experience pain after surgery. This is due to the traumatic nature of joint replacement surgery, which affects bones, ligaments, muscles and sometimes blood vessels. This pain will gradually subside over a period of two to three months.
What complications can occur?
After surgery, there is a risk of side effects. This includes:
- Contracture of the joint (can occur if the procedure is not performed correctly).
- Osteoarthritis, degenerative changes in the knee.
- pain, restricted mobility.
- Displacement or detachment of the transplanted tissue.
- Rejection of the material - very rare.
- Allergic reaction to the anesthetic.
Full recovery takes about four months. The operation is successful in 95 out of 100 cases.
postoperative period
The postoperative period is an important period on which the success of the patient's rehabilitation largely depends. The operation is only the first phase. This is followed by the post-treatment, which consists of several phases:
- For the first few weeks (usually up to a month), the patient stays in a special rehabilitation center and wears a cast to immobilize the joint. During this time, physical therapy and orthotics are used to protect the joint, speed up its recovery, and control muscle tone.
- After a month, the patient can begin to put weight on the joint. This is only possible with full muscle control and without swelling. After another two weeks, the patient can return to his normal life.
The total healing time of the graft is about three weeks. During this time, the ligaments remain vulnerable and weak. Handling should be as careful and gentle as possible. The patient should not kneel, squat heavily, or jump. An orthosis offers additional protection.
Restoring leg function after transplantation takes effort and practice. Overall, it takes about a year for the patient to fully adapt. During this time, there may be some discomfort, warmth at the surgical site, and some swelling. The knee after plastic surgery is not exactly the same as it was before the surgery. However, with the right approach, it is possible to regain full functionality and even return to sports activities.
Cost of knee surgery in Moscow
- Arthrodesis of the knee ~ 43 751r. 59 cents
- Knee Arthrotomy ~ 27 974p. 25 cents
- Arthroplasty of the knee joint ~ 41.711r. 33 prizes
- Osteosynthesis of the knee joint ~ 40.610p. 177 prizes
- Surgery for habitual dislocation of the kneecap ~ 41 997p. 44 prizes
- Operation of torn ligaments in the knee joint ~ 37 934p. 23 prizes
- Ligamentoplasty of Knee ~ 34,130p. 51 prizes
- Periosteal Band Repair ~ 53.258p. 33 prizes
- Quadriceps femoris tendonoplasty ~ 46.877p. 28 prizes
- Removal of a Baker's Cyst ~ 20.615p. 261 price
- Patella meniscus removal ~ 23.487p. 38 prizes
- Removal of cartilage bodies of the knee joint ~ 27'430p. 33 prizes
- Distance of Goff particles ~ 26 179p. 33 prizes
- show more
Surgical treatment of chronic synovial lesions of the knee joint, Becker's cysts, etc.
Osteosynthesis of fractures of short bones, wrists and ankles, fractures (dislocations) of the clavicle, kneecap, elbow process
Surgery of the knee joint is a large group of surgical interventions that differ in terms of indication, scope and purpose of treatment. For ligament injuries, intra-articular fractures, and acute purulent arthritis, knee surgery is an emergency procedure. Planned surgical interventions aim to eliminate the consequences of an injury or disease of the knee joint and to improve the function of the joint or the support function of the affected limb. Knee surgery includes a wide range of techniques and methods of arthroplasty, arthrodesis, resection, internal fixation, meniscus removal, ligament reconstruction, etc.
classification
Emergency surgeries and elective surgeries
Emergency knee surgeries are performed urgently (within hours or days). The goal is to avoid complications and improve long-term outcomes. Surgical interventions for recent ligament ruptures, open kneecap osteosynthesis, arthrotomy for acute purulent arthritis, etc. belong to this emergency segment.
The aim of elective knee surgery in traumatology is to correct the consequences of the injury by restoring the integrity of the damaged structures (e.g. plastic surgery of old ligaments) or removing them (e.g. resection of a damaged meniscus).
In some cases, elective surgeries are performed to improve the patient's quality of life without restoring the normal anatomical shape or full function of the limb. An example of such an intervention is knee arthrodesis (eliminating mobility, fixing the joint in a certain, functionally favorable position), which is performed to restore mobility of the limb after severe trauma, suppurative disease, etc.
Soft tissue, bone and intra-articular structures
All knee surgeries fall into several categories based on the anatomical structures they are performed on:
- Soft tissue procedures (reconstruction of quadriceps femoris muscle, removal of Becker's cyst, etc.)
- intra-articular surgeries (synovectomy, meniscus removal, cruciate ligament plastic, etc.)
- Bone operations (osteosynthesis of the kneecap, etc.).
The elements of each operation can be combined in different combinations depending on the purpose of the intervention.
auto transplant
A part of the patient's tendon is transplanted, which the surgeon removes from the ligaments and tendons of the kneecap. A thin layer is cut out, which does not cause any further discomfort to the patient. In this method, the damaged tissue is removed and replaced with healthy ligaments. The edges of the harvested tendons are fixed in the holes of the tibia and femur, then stretched and fixed with biodegradable materials. After a few months, all the materials will have fused to the bone. Due to the great practical importance and high success rate of transplantation, specialists primarily prefer autotransplantation.
With this method, the ligaments to be transplanted are not taken from the patient but from the donor. A non-fused ACL of the knee cannot be repaired using this method. Since a foreign transplant is used, the risk of rejection is very high. There are no differences in terms of fixation and sequencing compared to autograft. Allotransplantation is recommended in rare cases when it is not possible to harvest a graft from the patient.
Legamis Plasticization
The procedure is carried out using a hypoallergenic steel sleeve and a polyethylene thread, which are combined into a single structure. The sleeve is attached to the tibia and the thread to the femur. The surgeon uses the thread to fuse and tighten the torn tissue, then fixes it to the end of the sleeve. This firmly fixes the knee joint, which significantly speeds up recovery after a serious injury. Legamysplasty is recommended only if the injury is recent (no more than 15-20 days ago). This method was developed by German surgeons and is mainly used in renowned medical centers in Germany.

Anterior and posterior cruciate ligament surgery at CELT Clinic is endoscopic and minimally traumatic. It is done through small punctures into which an arthroscope and instruments are inserted. This enables a diagnosis of the knee joint from the inside and shows any damage to the knee.
All data is displayed on a monitor. Our specialist removes what is left of the cruciate ligament, harvests tendons from the semitendinosus and hamstring muscles of the thigh and forms a ligament graft to replace the damaged ligament. The surgeon stretches it and fixes it in the bone canal with fixators. This allows the graft to develop into a full-fledged ligament over the course of healing and recovery.
With the help of highly sensitive optics and modern instruments, our specialists can operate on the joint without damaging the joint itself or the surrounding structures.
Cost of knee surgery in Moscow
- Knee Arthrodesis ~ 43.751p. 59 cents
- Knee Arthrotomy ~ 27.974p. 25 cents
- Knee arthroplasty ~ 41.711r. 33¢
- Osteosynthesis of the knee joint ~ 40.610p. 177 prizes
- Surgery for habitual dislocation of the kneecap ~ 41 997p. 44 prizes
- Operation of torn ligaments in the knee joint ~ 37 934p. 23 prizes
- Ligament Stiffness of the Knee Joint ~ 34,130p. 51 prizes
- Periosteal Ligament Repair ~ 53 258p. 33 prizes
- Quadriceps femoris tendonoplasty ~ 46.877p. 28 prizes
- Removal of a Baker's Cyst ~ 20.615p. 261 price
- Patella meniscus removal ~ 23.487p. 38 prizes
- Removal of cartilage bodies of the knee joint ~ 27'430p. 33 prizes
- Distance of Goff particles ~ 26 179p. 33 prizes
- show more

Knee surgery is a large group of surgical procedures that differ in indication, scope and treatment goals. For ligament injuries, intra-articular fractures and acute purulent arthritis, knee surgery is performed as an emergency procedure. Planned surgical procedures aim to correct the effects of an injury or disease of the knee joint and to improve the joint function or support function of the affected limb. Knee surgery includes a wide range of techniques and methods of arthroplasty, arthrodesis, resection, internal fixation, meniscus removal, ligament reconstruction, etc.
classification
Emergency surgeries and elective surgeries
Emergency knee surgeries are performed urgently (within a few hours or days). The goal of the procedure is to prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes. Surgical interventions for freshly ruptured ligaments, open kneecap osteosynthesis, arthrotomy for acute purulent arthritis, etc. belong to the group of emergency operations.
The aim of elective knee surgery in trauma surgery is to correct the consequences of the injury by restoring the integrity of the damaged structures (e.g. ligament reconstruction in an old ligament injury) or removing them (e.g. resection of a damaged meniscus). ).
In some cases, elective surgeries are performed to improve the patient's quality of life, and the aim is not to restore the normal anatomical shape or all functions of the limb. An example is knee arthrodesis (eliminating mobility and fixing the joint in a functionally favorable position), which is performed to restore mobility to the limb after severe trauma or suppurative disease, etc.
Soft tissue, bone and intra-articular structures
All knee surgeries can be divided based on the anatomical structures that are being operated on:
- Soft tissue surgery (quadriceps femoris reconstruction, Becker cyst removal, etc.)
- intra-articular interventions (synovectomy, meniscus removal, cruciate ligament plastic, etc.)
- Bone operations (osteosynthesis of the kneecap, etc.).
The elements of the different operations can be combined in different combinations depending on the purpose of the intervention.
Cost of arthroscopic surgeries on the knee joint in Moscow
- Knee joint arthroscopy ~ 35 166r. 253 prizes
- Arthroscopic Meniscectomy ~ 42.851p. 159 prizes
- Arthroscopic Meniscal Suture ~ 56 221p. 104 prizes
- Arthroscopic knee arthrolysis ~ 46 427p. 30 prizes
- Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair ~ 75 092p. 136 prizes
- Arthroscopic posterior cruciate ligament repair ~ 64,994p. 67 prizes
- Collateral ligament arthroscopic plication ~ 52 809p 60 prices
- Arthroscopic combined ligament surgery of the knee ~ 102 140p. 23 prizes
- Arthroscopic combined ligament surgery of the knee joint ~ 21,050p. 8 prizes
- Arthroscopic medialization of the kneecap ~ 39,541p 40 prices
- Arthroscopic Stabilization of Dislocated Patella ~ 55.017p 35 prices
- Arthroscopic Knee Chondroplasty ~ 42.351p. 70 prizes
- Arthroscopic removal of loose intra-articular bodies of the knee joint ~30 270p. 99 cents
- Arthroscopic removal of synovial folds ~ 21.265p 37 cents
- Arthroscopic debridement of a knee joint infection ~ 37 454p 58 cents
- Arthroscopic external release of the kneecap ~ 38 520p 34 prices
- Microarthroscopy of knee joint with biopsy ~14,500p. 6 prizes
- show more
Arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Arthroscopic reconstruction of the posterior cruciate ligament of the knee (without implant costs).
Arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Arthroscopic reconstruction of the posterior cruciate ligament of the knee (no implant costs)
Arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction (at no cost for implants)
indications
Traumatology and orthopedics offer general and specific indications for arthroscopy. General diagnostic indications include unclear symptoms in diseases and injuries of the joint when the diagnosis cannot be made by less traumatic methods of investigation. The technique is also used when a patient has unclear symptoms after knee surgery and when it is necessary to assess the effectiveness of certain surgeries. The list of special indications for diagnostic and therapeutic arthroscopy includes:
- meniscus tear. Arthroscopy is performed to determine the location and nature of the tear, determine the need and extent of surgical intervention, and partially or completely remove the meniscus. Minor trauma to the joint reduces the risk of joint deformity after meniscectomy.
- torn ligaments. This technique allows to reliably confirm or deny the presence of damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint, select the optimal surgical tactics and restore the integrity of the ligaments.
- Deforming arthritis. The diagnostic examination provides a clear picture of the condition of the joint surfaces. The treatment removes abnormal tissue, creates optimal conditions for stabilization and prevents further progression of osteoarthritis of the knee.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. At the operation, villous hypertrophy of the synovial membrane, irregular lesions on the articular surfaces and narrowing of the articular stroma are clearly visible. During surgery, the synovial membrane can be removed and the articular surfaces treated;
- Fractures and dislocations of the kneecap. With this technique, the integrity of the kneecap and its ligaments can be effectively restored.
In addition, arthroscopic surgery is performed for diseases and injuries of the synovial membrane. With arthroscopy, it is possible to determine the extent of intra- and extra-articular interventions and to effectively remove damaged areas of the synovial membrane with little or no trauma to intact areas of the knee joint. This method is also indicated for articular cartilage damage and diseases. Arthroscopy makes it possible to examine all areas of the joint, including the kneecap, that are difficult to diagnose with other methods, as well as to efficiently and gently remove overgrowths and repair damaged cartilage.
Possible complications
If the patient neglects the corrective measures, a number of complications can develop:
- Painful sensations at the site of intervention, swelling
- Increased swelling in the operated area;
- high body temperature;
- damage to nerves;
- chest pain, difficult breathing;
- thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, etc.
If there are signs of discomfort during the postoperative period, the patient must immediately consult a doctor.
cost of the operation
The price of an arthroscopic operation on the knee joint depends on various factors. The main ones are the purpose of the procedure, the type of anesthesia, the complexity of the necessary procedures and the length of stay in the hospital. If performed correctly, the surgery can ensure a permanent cure and the patient's return to a full life.
With GP, the patient is cared for by the surgeon in comfortable hospital rooms after the operation. This supports proper recovery.
The basic pricing parameters are given below. Your doctor will help you calculate the exact cost at your consultation, which you can book through the call center, mobile app, or your personal patient account.
Dear patients!!!
Please note that the prices shown are not the final cost of the procedure.
If manipulation is carried out during the visit, the cost of this will be added to the cost of the visit (the cost of the visit will therefore be increased by the cost of the manipulation performed).
- How much does meniscus surgery cost?.
- How much does shoulder surgery cost?.
- How much does meniscus replacement surgery cost?.
- Axis of rotation of the knee joint.
- How much does a shoulder prosthesis cost?.
- How much does bunion surgery cost?.
- How much does a hip prosthesis cost?.
- Rupture of the medial collateral ligament.
