Fractures of the fibula are primarily caused by a tear in the femoral head or neck. The nerve in this bone can be damaged and severed. This leads to complications such as loss of limb function.
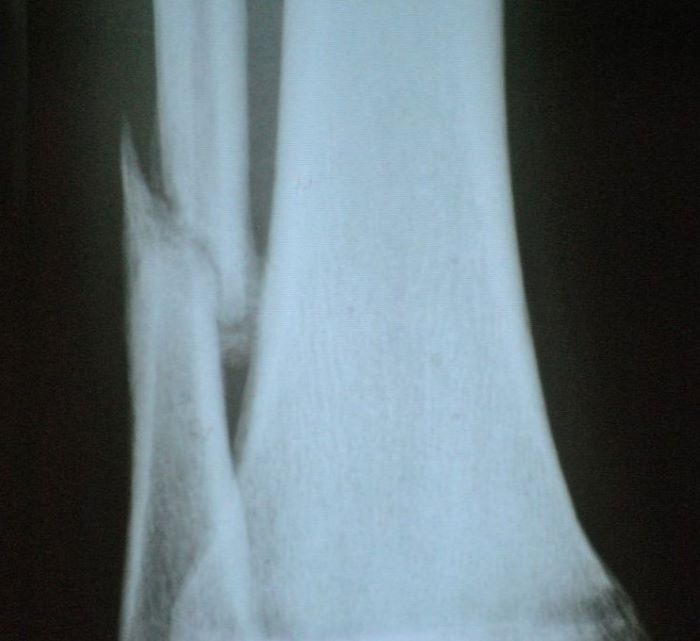
- Shinbone: where it is + photo of the fracture and how long it has been in the cast
- fibula. General information.
- place in the human body
- From anatomy
- Structure of the fibula
- The shaft or diaphysis
- Types of fractures of the fibula
- Treatment of fibular fractures
- reasons
- signs
- Osteotomy of the tibia at SM Clinic Surgery Center
- Find a doctor to treat shin fractures
- Offers
- Treatment of a fractured tibia
- Information for patients: Types of tibia fractures
- Types of fibula fractures
- How a doctor treats a fibular fracture
- Treatment of open fibula fractures
- types of injuries
- Characteristic Symptoms.
- Characteristics of the disease
- causes
- Treatment of fibular fractures
- Rehabilitation period after treatment
Shinbone: where it is + photo of the fracture and how long it has been in the cast

Man (Latin: Homo sapiens) is not just a rational being, but an extremely complex organism consisting of many cells, bones, tissues, etc. When we develop health problems, we must look for the cause in order to prevent its effects. And this requires an excellent knowledge of the structure of the body in order to distinguish between organs and parts of the skeleton. For example, if we talk about the feet, you need to know not only what distinguishes the small tibia from the tibia, but also its structure.
fibula. General information.
place in the human body
The tibia is composed of the tibia and the fibula. The fibula looks like an elongated tube and is the smaller bone of the tibia.
It has its own body and two vertices. The lower part is called the lateral malleolus and is involved in the formation of the ankle joint. It is a specific stabilizer of this joint.
The fibula is subjected to little strain when walking. Its main function is to participate in the formation of the ankle and knee joints. The appearance of the bone makes the foot appear more massive than the hand, but it is susceptible to injury.
An injury to the fibula often also affects the shinbone, causing complications such as dislocations and osteoarthritis. If only the fibula is broken, healing is quicker and more efficient.
From anatomy
The adult musculoskeletal system consists of passive and active parts.
Read also: Acromion – what it is, how it works, main diseases and treatment + photo
Active – are the muscles and ligaments.
Passive – Bones and their joint connections.
The adult human skeleton consists of 208 bones. In order to distribute the weight of the body appropriately, the bones are hollow inside. Therefore, all bones weigh less than the weight of the body. Nevertheless, the bones are strong and can withstand appropriate stress.
Structure of the fibula
Topographically, the fibula is located between the femur and the foot in the lower part of the leg. It borders the knee at the top and the ankle joint at the bottom.
The shaft or diaphysis

Bent backwards and curved along the axis. It is represented as a prism with three end walls:
The intercellular substance of bone consists of thin lamellae. They are all different thicknesses and shapes. However, most of them look like hollow cylinders with different diameters that are inserted into one another.
Types of fractures of the fibula
- Swelling,
- Pain when palpating the ankle region externally,
- Pain when moving the ankle joint,
- Pain syndrome due to axial loading of the bone.
The diagnosis of a fibula fracture – requires clinical examination of the patient by a trauma surgeon, and is the main diagnostic method X-ray of the ankle. In some cases, computed tomography of the injured limb is used for a more detailed examination, such as: B. in the event of a fracture of the femoral neck.
Treatment of fibular fractures
The main goal of conservative treatment of fibula fractures – is the correct anastomosis and preservation of the bone fragments. Repositioning by the trauma surgeon prevents displacement of the bone fragments and subluxation of the foot. If the fracture has been repositioned successfully and the position of the fragments is satisfactory, the shin and foot are protected with a plaster cast or an orthosis. If the bone fragments are displaced and the foot subluxates, surgical treatment of the fibula fracture is performed.
The surgical treatment of a fibula fracture takes place in several steps:
- open repositioning of the bony fragments;
- correction of subluxation of the foot;
- Immobilization of the bony fragments of the fibula with implants (plate, screws, pin).
Treatment of patients with fibular fractures in our center is based on our own and international experience, according to which surgical treatment methods should meet the needs of modern professionals at 100 %.
Individual care of each patient during surgical treatment with the use of modern fixators makes it possible to shorten the duration of treatment of fibula fractures and minimize the patient's rehabilitation time in the clinic.
reasons
Tibial aplasia (complete absence of the shinbone) or hypoplasia (underdevelopment) can occur for various reasons:
- The limb is wrapped around the umbilical cord. As a result, the leg does not receive enough nutrients for proper development and becomes deformed or stops growing;
- Fetal rupture. The leg gets caught in the opening and the edges overextend it. Amputation occurs;
- Genetic mutations. Sometimes the condition is the result of another pathology or poor heredity;
- Congenital pulling – excessive stretching of limbs in utero;
- Skeletal deformities resulting from connective tissue abnormalities. For example, chondroplasia – a change in bone formation or osteodysplasia – abnormal bone formation in the embryo;
Risk factors that can cause fetal anomalies should not be ignored:
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- Taking certain medications (the effects on the fetus are usually indicated in the package leaflet. It is therefore important to read the package leaflet and consult your doctor before taking them);
- Exposure to poisons and harmful chemicals, e.g. B. when working in hazardous industries;
- Radiation.
Regardless of the cause, the consequences of deformity are very unfortunate. They often lead to disabilities.
signs
Tibial hypoplasia is visible to the naked eye. The legs are deformed and do not fulfill their function.
During visual inspection, the following can be observed:
- Shortening and inward curvature of the tibia;
- deformation of the tibia and fibula;
- Abnormalities of the kneecap can be seen;
- atrophy of the thigh and shin muscles;
- Foot muscle abnormalities.
Accompanying symptoms include the absence of toes or bony duplication.
The patient complains of psychological discomfort, lameness and variable length of the limbs. Over time, pain may develop if arthritis or osteoporosis develops against the background of hypoplasia.
Osteotomy of the tibia at SM Clinic Surgery Center
Osteotomy makes it possible to change the length of the limb, redistribute the load on damaged joint areas and eliminate the effects of injury or disease. After the operation, the patient's claudication disappears, the pain in the knee or ankle joint is reduced, and the range of motion of the joint is increased.
Depending on the type of procedure, the patient will be hospitalized for three to seven days. During this period, drug therapy is carried out to prevent complications. After discharge, the patient is advised to avoid putting pressure on the operated leg, not to overheat, not to bathe, and not to swim in open or public pools. For 1.5 to 3 months the patient has to walk exclusively with crutches. The load is only increased under medical supervision. After 8-12 months, all restrictions are lifted. In some cases, after complete fusion, a second procedure is performed to remove the metal fixators.
To find out the current prices for tibial osteotomies and the cost of other operations at the SM-Clinic Surgery Center in Moscow, please call us or visit our website. Staff will answer your questions and help you schedule an appointment.
Find a doctor to treat shin fractures



Offers

Treatment of a fractured tibia
The specialists at Lapino KG and MD GROUP KG will do everything to ensure that your shin bone recovers in the shortest possible time and you can walk again. We have every opportunity for this – experienced doctors and modern equipment. We approach each patient individually.
Uncomplicated fractures (fractures without displacement) can be treated conservatively with a plaster cast. All modern minimally invasive osteosynthesis techniques are used for fractures with displacement, as displacement often occurs
Manual reduction is often not possible. The risk of complications is particularly high with open tibia fractures. In these cases, the wounds are healed under the supervision of our doctors.
Information for patients: Types of tibia fractures
A distinction is made between closed and open fractures of the tibia. These can include line, comminuted, hammertoe and spiral fractures. Any of the large and small bones can be injured anywhere.
The fibula is characterized by fractures in the lower third, at the ankle joint. The bone itself is not solid. However, a fracture of the ankle joint results in subluxation of the foot. Treatment for a fibula fracture is aimed at immobilizing (immobilizing) the injured limb and correcting the subluxation of the foot. The traumatologists at Lapino KG and MD GROUP have extensive experience in treating these injuries.
If your shinbone has been injured or one or both tibial bones are broken, please contact us to schedule an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist. Please call reception to make an appointment.
Types of fibula fractures
Fractures of the fibula can occur in the ankle, knee, and metatarsal joints. There are different types of fractures, which can also impact treatment and recovery. The most important types are:
- Lateral fibular fracture – injury to the ankle joint
- Fracture of the head of the fibula, a fracture near the knee
- Fracture of the fibula – a fracture in which a small part of the bone is torn away
- Stress fracture of the fibula, hairline fracture due to repetitive trauma
- Diaphyseal fracture, a fracture that often affects the middle part of the leg and is caused by a direct impact.
With the exception of stress fractures, the types of fractures mentioned often occur as a result of trauma or greater pressure on the bone.
How a doctor treats a fibular fracture
Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture, its type, and the location of the injury. Fractures are often classified as:
Regardless of the type of fracture, the traumatologist performs bone fixation, and then puts a cast or splint on the leg. This will prevent movement so the fracture can heal.
Closed fibula fractures can, but do not necessarily require, surgery. A splint or cast to prevent movement is usually sufficient unless other parts of the leg are damaged. If the patient requires additional treatment to realign the bone, the trauma surgeon may order:
- Closed reduction: The doctor aligns the ends of the broken bone without cutting the skin
- Open reduction: The doctor performs invasive surgery on bones that may be broken in more than two places
- Bone grafting. If the bones do not heal on their own, various procedures and surgeries are used, including the insertion of special support pins.
Treatment of open fibula fractures
Rest, ice packs and elevating the leg are recommended while waiting for treatment. Open fractures require surgery because they can lead to associated injuries such as artery damage.
- Cleaning the wound to prevent contamination and infection
- Stabilizing the wound to keep the bone in place before surgery
- Imaging studies, the results of which allow the selection of a specific type of operation
- Antibiotics to prevent infections.
During surgery, the surgeon may repair the fibula fracture using internal or external fixation techniques. With internal fixation, the doctor inserts metal pins into the broken bone to hold the fracture together while it heals. Severe open fractures require external fixation, in which metal screws or pins extend above the skin to hold the bone in place.
types of injuries
A tibial fracture is divided into the following types depending on the type of injury
- Simple fracture – the lightest type of fracture in which there is no displacement and the number of fragments is minimal;
- Moderate fracture – it is accompanied by displacement of several fragments that can damage soft tissues and blood vessels.
Depending on the type of fracture line:

- closed fracture;
- Open fracture – the bone breaks completely, with bone fragments penetrating the skin and extruding, often with damage to blood vessels.
Characteristic Symptoms.
The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the fracture and the presence of complications such as a dislocation. General symptoms of a fibula injury:

- Severe, stabbing and acute pain occurring at the time of rupture;
- Overloading of the neighboring joints - knees and ankles - due to the pain syndrome;
- Formation of extensive swelling under the skin;
- hematoma;
- deformation of the limb in the presence of displaced bone fragments;
- The injured limb is shorter than the healthy limb;
- Restriction or complete absence of motor function;
- Numbness of the limbs.

Increased pain occurs when attempting to move or step on the broken leg. In an open fracture, the bone fragment tears the soft tissues and skin, creating a large wound that bleeds profusely.
With a dislocation, the patient cannot move the leg in the knee joint, while with a non-dislocation, movement is possible, but is accompanied by severe pain.
Numbness in the injured limb occurs when the fibula head has been damaged, resulting in nerve damage. If the nerve has been completely severed by bone fragments, the leg is numb, hanging like a whip.
Characteristics of the disease
Periosteum is a mild to acute inflammatory process of the periosteum, the bone layer that surrounds the leg. The ICD-10 codes for periostitis are as follows:
- If the pelvis or hip is involved: M 90.15;
- If the lower leg is affected, M 90.16;
- Periostitis of the calcaneus – M 90.17;
- At an unspecified location – M 90.19.
The foci of inflammation are located in the inner or outer layer and then spread to the surrounding tissue. Periostitis is treated by different specialists depending on the cause of the disease. It may require support:
The lesion can spread to different parts of the bone, distinguishing the following types of the disease:
- periostitis of the tibia;
- periostitis of the fibula;
- periostitis of the foot;
- periostitis of the lower leg;
- Periosteal inflammation of the Achilles tendon.
Please note.
The location of the disease process influences the symptoms and the choice of treatment.
- Acute inflammation of the periosteum (periostitis), which is characterized by the presence of a purulent process in the bone;
- Chronic periotitis, which is a specific complication of the acute process.
Doctors distinguish the following classification:
- The simple type often forms on the ulna or tibia and arises as a result of trauma, persistent inflammation in the periosteum;
- purulent forms on long bones, occurs after infections, penetration of bacteria, staphylococci, streptococci through a wound, hematoma;
- The fibrous bone develops against the background of long-term irritation;
- Sedimentary periostitis is caused by persistent irritation and subsequent bone hypertrophy;
- Posttraumatic periostitis is caused by trauma and is characterized by the presence of serous mucosa;
- Tuberculosis develops against the background of tuberculosis and is characterized by the formation of purulent clots and fistulas. It is commonly diagnosed in children;
- Syphilis occurs on the background of sexually transmitted diseases;
- The serous infection forms at the site of the injury and is characterized by painful swelling and fever, which usually subsides afterwards. In the initial phase the swelling is thick, later it softens and becomes liquid;
- Linear, which appears as a single line along the bone on an x-ray. This is seen against the background of long-lasting, low-grade periostitis, which represents the beginning of osteomyelitis formation;
- Stress periostitis occurs in areas of the foot and lower leg that are exposed to high stress as a result of trauma. It is characterized by pain and swelling.
causes
In medicine, the following causes of periosteum inflammation are mentioned:
- Trauma, which may present as bruises, dislocations, broken bones, dislocations, soft tissue wounds;
- Inflammation of the adjacent tissues from a pathological focus near the periosteum;
- Toxic. Some diseases produce toxins in the body that enter the periosteum. Toxic substances are produced in the diseased organ and transported throughout the body via the blood or lymphatic system;
- Allergic. The periosteum reacts in this way to allergens that enter the periosteum;
- Specifically, if the disease is caused by tuberculosis or syphilis.
Treatment of fibular fractures
The process is not too difficult for doctors if no bone structures are broken and there is no displacement. If the tibia and fibula are broken and there is no displacement, treatment is quick.
For these fractures, a cast is placed over the injured area to prevent the injured lower limb from moving to the side. This method prevents displaced bone fragments.

If there are displaced fragments of bone structures, i.e. there is a risk of uncontrolled displacement of the tibia and fibula, doctors try in the initial phase to restore their correct position. If the shinbone is pinched in the lateral direction, doctors use so-called periosteal plates. In other types of impingement, spokes are inserted into the area above and below the resulting crack. These serve to fix all fragments in a specific position while expanding the area where healing should take place.
To speed up the healing process, doctors can send the patient to physiotherapy to consolidate the effects achieved. At the same time, time is spent on special massages to strengthen the patient's muscles.
Rehabilitation period after treatment
It is one of the most important and crucial steps after healing a fractured fibula. Failure to include it in the list of corrective measures will dramatically increase the patient's recovery time. At the same time, neglect of the rehabilitation period often leads to various complications.
After the cast is removed after a period of time (usually 2 to 3 months), muscle structures and normal blood flow must be restored. Doctors prescribe a special program of therapeutic exercises for this period. These exercises can easily be done at home, eliminating the need for hospitalization.

To ensure an effective rehabilitation process for fibula fractures, the entire range of exercises is selected individually for each patient. Before putting any weight on the healed limb, the treating doctor must be consulted. The injured leg should be loaded gradually, increasing the physical load according to the doctor's recommendations.
The duration of recovery for the above-mentioned fibula fractures directly depends on the severity of the injury. The entire process of full recovery can take 60-90 days. During the rehabilitation process, a bony callus may form at the site of the former fracture after 1.5 months.
For a severe fibula sprain, the rehabilitation process may take longer, six months or more.
The patient's mental attitude plays an important role in the complete recovery of the injured limb. The patient must strictly follow all the doctor's recommendations. Special massages should not be omitted and the load on the injured leg should not be increased. Damage to the breaking point should be avoided. There is no specific diet for shin fractures, but in some cases doctors prescribe medications containing calcium and recommend eating more foods containing calcium.
Read more:- tibia and fibula.
- Lower third of the fibula.
- Pain in the periosteum of the tibia.
- fibula.
- Function of the short fibula muscle.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
- The lateral ankle is.
- Bone structure of the navicular foot.
