I had an endoprosthesis put in for my left hip at the hospital. The pain has subsided and after 2 months I can walk normally again, I just have to be careful and not carry heavy weights for a while.

- How to prepare for an orthopedic consultation
- What the doctor may ask during the visit
- You may need to talk about these questions:
- Consent to the processing of personal data
- Paying for a question (guarantee of a doctor's answer)
- What tests can a trauma surgeon prescribe?
- ROENTGEN
- angiography
- Ultrasonic
- diagnostic techniques.
- treatment methods
- What examinations can an orthopedic-traumatological surgeon prescribe?
- Which treatment methods are used in traumatology and orthopedics?
- When should a trauma surgeon be consulted?
- What does a trauma surgeon treat?
- What does the orthopedic surgeon treat in adults?
- arthrosis
- Our orthopedic surgeons can help you
- arthrosis
- Osteochondrosis of the spine
- osteoporosis
- Our doctors
- Injuries and medical conditions treated by an orthopedic trauma surgeon
- Diagnosis of orthopedic injuries and diseases
- Instrumental and apparatus-based examinations used by trauma surgeons
- Algorithm for patient admission
- treatment methods.
How to prepare for an orthopedic consultation
Joint pain that recurs with enviable frequency is a reason to see an orthopedist. If you have not previously been treated for osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis or any other musculoskeletal condition and you are about to see a specialist, prepare carefully so that you don't forget to ask important questions and don't lose sight of anything.
It's not enough to talk about your symptoms and conditions: you need receipts and everything you have on hand related to your condition:
- an ambulance card from the clinic or other medical facility where you were treated (a copy is also sufficient, e.g. a photo taken with a phone or tablet);
- Results of tests and examinations of any date (everything that affects the joints is important, including examinations of other body systems);
- a list of medications currently or continuously being taken (preferably a written list with dosage).
It is the patient's responsibility to provide as much documentary information as possible about their condition.
What the doctor may ask during the visit
The doctor will first ask you about your symptoms, so you should think about it beforehand and formulate your answer. How often does the joint pain occur, what is the nature of the pain, how often does it recur, and what is causing the pain to worsen or improve.
You may need to talk about these questions:
- whether you have ever been treated for osteoarthritis, arthritis or other joint problems;
- If so, what kind of treatment it was and what the results were;
- Do you have family members who suffer from musculoskeletal disorders in general and joint disorders in particular?
- What diseases have you suffered from in your life?
- Have you had any injuries, fractures or bruises?
- Any operations, when and in relation to what
- whether there have been any major changes in your life recently, e.g. B. in relation to your eating habits, your professional activity or possibly a change of residence, etc.
The orthopedist may ask you about allergies to medicines.
![]()
The attitude of the doctor: Irina. Email: [email protected]
Was the advice helpful? No. It just felt like a bridging. So what was the point of the consultation?
Would you recommend this doctor? Unfortunately, no.
Answer: The website says: the doctor will use the scans to explain the situation exactly, what to do and how it will be. All I got was the answer: it can hurt more after surgery. That's all? Even the questions asked in the message are not answered.
![]()
![]()
The attitude of the doctor: Excellent
Was the advice useful? Useful
Can you recommend another doctor? Yes, of course
Return message: Answered all interesting questions quickly and very clearly.
![]()
Answer: Thank you for your kind words. I wish you good health. We are glad to have helped you.
![]()
The behavior of the doctor: Incredibly human, friendly, prompt and very professional
Was the session useful: 100%
Would you recommend this doctor? I would definitely recommend him.
My opinion: Many thanks to the doctor who advised me in a difficult case. He was quick, clear, precise and to the point and created a very thorough treatment plan. In fact, it was only through this doctor that I understood exactly what happened to my mother and how she should recover, which I hadn't learned from the family doctor at the hospital. Many thanks and appreciation to Dr. Leontiev!
![]()
Consent to the processing of personal data
By filling in this form, I confirm my consent to the processing of my personal data entered in the form by the service provider on the basis of this form (hereinafter the operator ), including
1) FULL NAME;
2) email address;
3) phone number;
I authorize the operator to perform all actions (operations) with my personal data, including collection, organization, recording, storage, updating, modification, use, depersonalization, blocking and destruction.
The purpose of the processing of personal data. Providing services to me based on a completed form .
The operator has the right to exchange (receive and transmit) my personal data using computer media or communication channels, being secured against unauthorized access.
This consent is for an indefinite period and my personal information is not time-limited.
I reserve the right to withdraw my consent by issuing a written document to that effect, which I can send to the operator by registered post with acknowledgment of receipt or by handing it over to a representative of the operator for a signature.
Paying for a question (guarantee of a doctor's answer)
- ✅ Guarantee that you will receive an answer from several doctors to your question
- ✅ First Answer within few minutes
- ✅ Maximum medical activity: Consultations with several specialists, more detailed answers from doctors
What tests can a trauma surgeon prescribe?
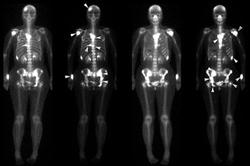
The trauma surgeon, like any other doctor, uses various tests and examinations in his practice. Most often these are additional diagnostic methods, less often laboratory tests.
ROENTGEN
The simplest and most commonly used diagnostic method in traumatology. In the vast majority of cases, the X-ray is the obligatory examination method. Even if the fracture is visible, the exam is done to assess the extent of the lesion—the presence of fragments, the length of the fracture, and the condition of the surrounding tissue. When conducting an X-ray examination, it is important to remember the basic principles of this procedure.
- Radiographs are always taken in two projections: lateral and front;
- The injury site must always be in the center of the X-ray;
- When examining skeletal bones, the radiograph should also include adjacent joints.
angiography
Method of examining and assessing blood flow in blood vessels using contrast media. The blood flow data, in turn, give the doctor information about the condition of the soft tissue, the periosteum and the bone. Without this data, recovery and consequences of fractures cannot be predicted.
The method takes place in two steps. The first is the administration of a contrast agent (Mayodil, urographer). The second step is direct imaging. In the darkened image, the blood vessels look like light, tortuous streaks. Narrowed areas where blood flow has stopped appear darker. This method is particularly revealing in the case of congenital anomalies of the musculoskeletal system.
Ultrasonic
Ultrasound is also a relatively simple and inexpensive examination method. It also has the advantage of being mobile. There are now portable devices (portable) Ultrasound devices are available that can be used in emergency rooms at the scene of an accident.
diagnostic techniques.

In traumatology, additional examination methods are used to make bones and joints visible. The traumatologist orders:
- X-rays of bones and joints – to detect breaks, fractures, inflammation, osteoporosis, changes in joint width;
- X-rays of the spine – to detect fractures, vertebral displacement, vertebral fractures, intervertebral fractures
- Joint ultrasound – to detect dysplasia, fluid in the joint cavity, damage to ligaments and soft tissues;
- Scintigraphy – determination of bone density, detection of osteoporosis.
Joint puncture is a diagnostic and therapeutic method. During the puncture, the traumatologist takes the contents of the joint capsule for analysis. In this way, an infectious cause of the inflammation can be determined and a malignant tumor ruled out. During the LP, the doctor can also inject medication into the joint cavity.
The laboratory tests are of an accompanying nature. General clinical blood and urine tests are recommended by the doctor in preparation for the operation.
treatment methods

The traumatologist treats diseases of the musculoskeletal system using conservative and surgical methods. An orthopedic trauma surgeon treats uncomplicated, non-life-threatening conditions conservatively. Surgery is performed when the injury is accompanied by bleeding or when conservative methods do not lead to healing.
Conservative treatment of fractures and closed uncomplicated fractures includes fracture fixation and plaster casts. For dislocations, the traumatologist sets the limb in place and applies a bandage.
Pharmacotherapy is indicated to reduce pain and inflammation. The following groups of drugs are used:
The specialist prescribes drugs in the form of tablets, ointments, patches, and also in the form of a solution for injection into the joint cavity.
Therapeutic exercise is indicated during the recovery period after injury and surgery. The exercises help to quickly restore joint function and prevent contractures. These exercises can be done at home or under the supervision of an LFC doctor.
Physiotherapeutic treatments are also indicated during the recovery phase. The doctor prescribes them:
Surgery is indicated for open and complicated fractures. During the operation, the trauma surgeon sets up the broken bones, sews up the bleeding vessels, and fuses the bones with metal plates and pins. In the case of deformed arthrosis and complete destruction of the joint, the joint is replaced. Surgery is indicated for large intervertebral hernias that compress blood vessels and nerves.
'The SM Clinic in St. Petersburg invites you to a medical examination by an orthopedic traumatologist. You can make an appointment by phone or use the appointment form on the clinic's website. For the treatment and prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, go to a traumatologist.
What examinations can an orthopedic-traumatological surgeon prescribe?
Modern medicine has a wide range of methods for diagnosing injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Depending on the pathology and findings, the orthopedic trauma surgeon can recommend the following examinations:
- Radiological examination. Radiological diagnosis is the leading method in osteology. It allows not only accurate diagnosis of trauma, deformities, arthrosis and musculoskeletal tumors, but also observation of the dynamics of the pathological process in bones and joints.
- Contrast arthrography. Contrast radiography is often recommended for joint diseases and intra-articular injuries. With this method it is possible to diagnose intra-articular injuries: post-traumatic hypertrophy of periarticular tissue, meniscus tear, joint mouse' and other pathologies.
- Computed Tomography. A CT scan provides a layered view of organs and tissues in an axial projection, helps to study the structure of the bone substance, determine bone density, study the condition of the soft tissues, articular cartilage and walls of the spinal canal, as well as create a volumetric image of the skeleton. CT is recommended for both trauma and many musculoskeletal disorders.
- MRI. Since bone tissue does not emit MRI signals, MRI is mainly used to diagnose traumatic soft tissue injuries and to examine articular cartilage, intervertebral discs, periosteum, vessels, spinal cord and brain.
- Ultrasonic. Like MRI, ultrasound is the most conclusive method for examining soft tissues. Ultrasound can detect tendon ruptures, joint effusions, proliferative lesions of the synovial membrane, synovial cysts, abscesses, hematomas, and foreign bodies in soft tissues.
Which treatment methods are used in traumatology and orthopedics?
We divide the treatment methods for patients with injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system into two main groups: conservative and surgical.
In orthopedics and traumatology, various conservative methods are used in the emergency care and treatment of patients, including the following
- transport immobilisation;
- soft bandages and plaster casts;
- medicinal blocks;
- pharmacological treatment;
- Physical therapy;
- kinesitherapy;
- Massage;
- PRP therapy;
- acupuncture and other methods.
- Consultations with an orthopedist/traumatologist, neurologist, rheumatologist, physiotherapist, acupuncturist;
- laboratory and apparatus tests;
- intra-articular blocks, intravenous infusions, PRP therapy, acupuncture, physical therapy and massage.
When should a trauma surgeon be consulted?
A consultation with a trauma surgeon can be a primary or secondary consultation. The most common reason for a primary consultation is a recent closed injury (fracture, torn ligament, hematoma, etc.) with one or more of the following symptoms: pain, soft tissue swelling, bruising or discoloration of the skin, deformity and dysfunction of the affected area. The second most common injuries are open wounds: puncture, cut, laceration and crush wounds, more rarely gunshot wounds, burns and frostbite.
In all cases of recent trauma, it is important to see a trauma surgeon as early as possible. Early treatment shortens the patient's suffering and in some cases prevents complications such as: B. the further displacement of shrapnel, damage to blood vessels, nerves or skin by bone splinters, local circulatory disorders due to edema, wound infections, etc. An early visit to the trauma surgeon is particularly important in the case of open wounds, since the wound can heal within the first 24 hours (ideally 12 hours) closed and the tendon can be sutured within the first 6 hours. For recent injuries, a trauma surgeon is available 24 hours a day and no appointment or referral from another specialist is required.
An initial consultation with a trauma surgeon is indicated for pain, limitation of movement, limited mobility in the old fracture zone, deformity, shortening or dysfunction of the limb, extensive scarring, non-healing wounds, fistula formation at the injury site, and other symptoms. In such cases, admission is usually elective. The only exception is when an old injury is complicated by an acute pathologic condition (e.g., joint lock in a protracted meniscus injury). All patients will be re-consulted on a pre-arranged day and time.
What does a trauma surgeon treat?
Trauma surgeons treat bone and soft tissue injuries, which vary greatly depending on the location and severity of the injury. When the musculoskeletal system is affected at the same time as the abdominal organs, traumatologists work together with abdominal surgeons. In the case of simultaneous injury to the chest, thoracic surgeons are involved in addition to trauma surgeons, neurosurgeons are involved in damage to the brain, spinal cord and nerve trunks, and vascular surgeons are involved in damage to the integrity of the large vessels. The following groups of diseases that require consultation with a traumatologist can be distinguished:
- fractures. Injuries to the bones of the limbs, pelvis, spine, ribs, sternum and shoulder rim. Fractures can be closed, primary or secondary open, displaced, non-displaced, linear, helical, comminuted, etc.
- Closed soft tissue injuries. Sprains, strains and torn ligaments (commonly in the knee and ankle), torn muscles (commonly in the hip or shoulder), bruises and bruises.
- Open wounds. These can be bruises, lacerations, punctures, cuts or gunshot wounds (bullet, shot, shrapnel), with or without penetration of foreign bodies, violation of the integrity of muscles, tendons, vessels, nerves, joint capsules.
- Local thermal injuries.Frostbite and burns of varying severity from local and superficial with viability of underlying tissues to deep and extensive complicated by necrosis formation.
- Syndromes caused by compression. Persistent Compression Syndrome, caused by squeezing a body part with an object or other body part, and Myofascial Compartment Syndrome, caused by increased pressure in the fascia.
- consequences of trauma. False joints, contractures, stiffness, deformities of all kinds, post-traumatic arthrosis, functional disorders (restriction or inability to stand and walk, gripping function of the hands, etc.) as a result of the aforementioned causes, tendon or nerve damage.
What does the orthopedic surgeon treat in adults?
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system include a large group of pathologies associated with changes in the bones and soft tissues that make up the skeleton, joints and muscles of the body. They can be divided into inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic diseases, injuries and their consequences, pathologies resulting from autoimmune and endocrine disorders, tumors and secondary lesions of the musculoskeletal system.
Since it is impossible to cover all diseases of the musculoskeletal system in a single article, we will dwell on the pathologies that orthopedists most often deal with.
arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is a group of inflammatory joint diseases of different origins, which can occur in acute and chronic forms. Primary arthritis arises as a result of infections, trauma, immunological and metabolic disorders, secondary arthritis develops against the background of pathological changes in periarticular tissues, blood diseases, internal organs and malignant diseases.
The main symptom of arthrosis is pain in the affected joints, which can be moderate or severe. Pain syndrome is accompanied by swelling and redness of the skin and local hyperthermia. With inflammation of several joints, the local symptoms can be accompanied by general signs of intoxication: weakness, malaise and fever.
Our orthopedic surgeons can help you
arthrosis
Osteoarthritis is a chronic and progressive joint disease characterized by progressive destruction of cartilage, changes in the joint capsule, synovial membrane, adjacent bones and ligaments. The most common causes of arthrosis are degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joint, trauma, dysplasia, connective tissue pathologies and autoimmune diseases. The risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with age.
The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time. With the destruction of the articular cartilage and the formation of marginal bone outgrowths, patients develop the symptoms of arthrosis: crunching and pain in the joints, which are aggravated by movement and weather changes, morning stiffness, with further progression of the disease - limitation of mobility and deformation of the affected joints.
Osteochondrosis of the spine
Spinal osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of the musculoskeletal system, characterized by degenerative changes in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Almost every person develops more or less pronounced osteochondrosis with age, but heavy loads, micro-injuries and other chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system contribute to the earlier development of the disease.
The main symptom of spinal osteochondrosis is pain. The intensity and duration of the pain depends on the degree of impairment. Most of the time, the pain is dull and constant. During periods of exacerbation, patients may need to adopt forced postures, restrict movement, and be physically active to relieve their symptoms. Left untreated, spinal osteochondrosis can lead to herniated discs, compression, and spinal cord infarction.
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a chronic disease associated with a decrease in bone density and strength. It is more commonly diagnosed in women over the age of 50 and is usually asymptomatic or with delayed symptoms.
Our doctors





The 5 phases of treatment in the health workshop

A medical advisor will ask about your symptoms, select the right doctor, advise you on the cost of treatment and arrange an initial appointment.

Do you need a consultation with a neurologist, orthopedist or rheumatologist, but cannot come to the clinic? The doctors at the health studio are ready to offer an online consultation.
A comprehensive examination by a neurologist or orthopedist, during which the doctor takes a medical history, reviews the results of tests or prescribes a diagnosis, makes a preliminary diagnosis. *For more information on the terms of the free consultation, please contact the clinic's advisors or call +7 (812) 421-70-36.
Injuries and medical conditions treated by an orthopedic trauma surgeon
- Tissue contusions, ie damage to tissues without compromising their integrity but with functional impairment;
- sprains of ligaments and muscles;
- tears of ligaments, muscles and tendons;
- bone fractures;
- dislocations and other joint injuries;
- Consequences and complications of injuries (wrong joints, habitual dislocations, contractures, etc.);
- Congenital and acquired deformities of bones, joints, spine and limbs, including scoliosis, flat feet, heel spurs;
- Osteoarthritis - osteochondrosis, spondyloarthritis, deformative arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, aseptic bone necrosis and their complications;
- disorders of tendons, ligaments and muscles;
- Benign tumors and tumor-like diseases of the musculoskeletal system.

- Any injury, even if it seems minor at first glance;
- Visible deformation of the limbs, spine;
- pain in the bones, muscles, ligaments, joints and spine;
- limitation of mobility of limbs and spine;
- crunching and cracking in joints when moving;
- redness, swelling and enlargement of the joint;
- instability of the joint;
- valgus deformity of the big toe;
- pain in heel when walking;
- postural abnormalities;
- flat feet.
Each symptom on this list indicates that an orthopedist/traumatologist needs to be consulted. You can make an appointment directly with a doctor in this field in the network of general practitioners. Early and appropriate diagnosis and treatment will help you get back to a full life quickly and avoid complications.
Diagnosis of orthopedic injuries and diseases
The consultation of a trauma surgeon includes a detailed medical history, an analysis of the complaints, a general examination and a visual assessment of the tissue condition, anatomical structure and shape of the body parts, as well as determination of the range of motion according to the patient's perception.
Laboratory diagnosis is an indispensable part of the diagnostic search.
Instrumental and apparatus-based examinations used by trauma surgeons

Algorithm for patient admission
Whether you're the department's chief trauma surgeon or just a 'yesterday' med student, the algorithm for enrolling scheduled patients remains the same.
First there is an initial interview. In this conversation, the patient describes his complaints, presents his medical records and indicates whether he has a hereditary predisposition.
This is followed by the traditional external examination. This is usually insufficient, even if the trauma surgeon has a lot of experience. Further clinical investigations are required to refute or confirm the suspicion:
- X-rays;
- MRI;
- CT scan for suspected head trauma;
- general blood tests to exclude underlying inflammatory processes.
People with suspected osteoporosis must undergo a bone density measurement. In medical jargon, this procedure is referred to as densitometry.
Patients who come off the street and are classified as urgent are usually taken directly to the trauma or intensive care unit. Particularly long queues at the tram clinic can be observed in winter when the ground is icy. During this time, elderly people who are particularly vulnerable should be particularly vigilant. Their bones regenerate more slowly than those of younger people.
treatment methods.
One of the most modern methods of diagnosis and treatment is arthroscopy. A flexible guide with a miniature camera is inserted through a puncture. An image of what is happening near the affected joint is projected onto a screen. In this way, the source and cause of pain and inflammation can be localized.
If it turns out that a damaged meniscus is the cause of the knee joint pain, the damaged parts are removed on the spot or the previously disturbed integrity is restored. In this way, arthroscopy seamlessly transitions into endoprosthetics.
The latter refers to radical techniques to correct the damaged joint. A metal or polymer replacement is deployed to replace the worn mechanism.
In some cases, however, conservative treatment methods are sufficient. This includes tight bandages and various devices to fix the damaged area. The pharmacological treatment prescribed by the doctor is not a substitute.
- Free online consultation with an orthopedic surgeon.
- Consultation with an orthopedic trauma surgeon.
- Consultation of an orthopedic traumatologist.
- Online consultation on trauma.
- Online consultation with an orthopedist.
- Who is a trauma surgeon?.
- Consultation of an orthopedic surgeon.
- How to make an appointment with a traumatologist.
