In the general population, these unexplained fractures are rare and indicate a serious health problem as they are pathologic fractures.

- fractures
- diagnosis of pathology
- causes for the emergence
- risk groups
- How the marching foot manifests itself clinically
- diagnostic methods
- Bone fracture symptoms
- Classification of fractures
- First aid for broken bones in the foot
- Principles of treating foot fractures
- Related articles:
- Algorithm for first aid
- Shoulder and limb fractures
- fracture of the scapula
- fracture of the humerus
- Wrist bone fracture
- Fractures of the metacarpals and finger bones
- Other articles
- Classification of fractures
- Causes of incidence fractures
- Depending on the nature of the displacement of the bone fragments
- In relation to the surrounding skin:
- Along the fracture line:
- diagnosis
- How to recognize a fracture: main symptoms
- First aid after a fracture
- Can multiple myeloma be detected at an early stage?
- Prognosis of Multiple Myeloma
- Treatment in the Medical Center:
fractures
A fracture is a break in the integrity of a bone that results in dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system at the site of the injury. The symptoms of a fracture depend largely on the cause, location, and extent of the fracture. The vast majority of fractures also involve soft tissue damage, leading to inflammation and severe pain.
Statistics from the World Health Organization show a worrying trend in the prevalence of home and sports injuries: the number of injuries in German medical practices has doubled in the last 30 years. Young people's love of extreme recreational activities has led to an increase in reported spinal fractures and intra-articular compound fractures. Bone damage due to osteoporosis is also important, accounting for more than 20 % of the clinical cases.
diagnosis of pathology
Severe pain and swelling, changes in bone mobility and axis, and crepitation on palpation allow an experienced technician to make a diagnosis even without special examination methods. At the same time, a successful treatment of bone fractures can only be guaranteed by correct repositioning of the bone fragments and their subsequent immobilization. The diagnostic tasks are therefore quite extensive:
- It is important to determine the type of fracture and the location of the fragments. This factor is of paramount importance in the treatment of intra-articular fractures and compression fractures, where only surgical intervention can restore bone shape.
- The causes of the disruption in bone integrity often determine the choice of treatment methods. For example, in women over the age of 40, a high percentage of fractures are caused by minor domestic injuries that indicate osteoporosis and poor bone healing. In Germany, fractures are always treated with intramedullary osteosynthesis or fixation of the fragments with artificial bone cement.
- Today's high-precision diagnostic modalities, most notably MRI, help to determine the condition of the tissue and correctly perform the manipulation of fracture reduction. The leading modality is MRI, which produces 2mm images that, when juxtaposed by computer programs, allow a millimeter-accurate simulation of a complete fracture.
However, there are a number of important contraindications for MRI. The procedure is prohibited if there are metal implants in the patient's body, with claustrophobia and neuropsychiatric disorders. Post-traumatic shock can also be a contraindication. In such cases, German specialists take x-rays in several planes in order to get a detailed picture and be able to choose appropriate methods of treatment.
causes for the emergence
There are several causes for the development of a condition like march foot:
- High level of physical activity with constant stress on the foot.
- A sudden increase in physical activity with maximum traumatic loads on the feet in untrained individuals.
- Presence of chronic and acute diseases associated with bone pathology.
- Metabolic disorders, abnormal hormonal function of the body.
- Excessive or insufficient body weight. You only need to determine your BMI to find out if you are at risk. An index above 30 is a real reason to be concerned about your health.
Interesting fact!!! In medicine, there is an official term for the march fracture. It is Deutschlander's disease, named after the doctor who first described the disease.
risk groups
The marching foot can theoretically occur in any person, regardless of health and age. Even young children who are calcium deficient can suffer fatigue injuries to the bones of their feet from high levels of activity. However, there are several groups of people who need regular medical examinations and a balanced diet with nutrients and micronutrients:
- Competitive athletes, especially track and field athletes, weight lifters, gymnasts and others. Constant, long-lasting training leads to dystrophic changes in bone tissue.
- People who are overweight or underweight.
- Older people due to age-related changes and disorders in bone structure.
How the marching foot manifests itself clinically
It is important to realize that early detection of the pathological condition of the bone avoids the moment of maximum injury and avoids radical therapeutic measures. That is, how the march foot manifests itself clinically:
diagnostic methods
A march foot fracture is diagnosed similar to other fractures. The difference is that the patient's condition allows him to go to the emergency room on his own. The attending physician then asks the patient about their occupation, recent changes in physical activity, and the presence of chronic diseases. Then an X-ray and a general examination are performed to assess the current condition of the body. X-rays show fissures in various stages of development.
If damage to structures such as blood vessels, tendons, or nerve endings is found, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the foot is ordered. Based on a comprehensive examination, doctors make a diagnosis and decide on a treatment strategy.
Bone fracture symptoms
The main symptoms of broken bones include:
- Swelling that occurs quickly;
- pain syndrome;
- Bone deformity at the site of injury;
- subcutaneous bleeding; extensive hematomas with pulsation;
- restriction of mobility;
- numbness, tingling, cold over the injury site;
- crepitus;
- in the case of an open fracture, a laceration.
Most of these symptoms are also characteristic of other injuries, so the examination allows the trauma surgeon to make an accurate diagnosis. The general condition of the patient largely depends on the severity of the fracture. If it is an uncomplicated fracture, the condition is satisfactory. Traumatic shock is common in open fractures, compound fractures, and multiple injuries.
It is common to distinguish between relative and absolute fracture symptoms. Relative symptoms include:
Absolute symptoms in most cases indicate the presence of a fracture. These include characteristic grinding and cracking noises (crepitations), restricted movement and deformations. In open fractures, bone fragments protruding from the wound are visible.
Classification of fractures
Bone fractures can be open or closed and, depending on the joint damage, can be epiphyseal, metaphyseal or diaphyseal. Depending on the injury mechanism, a distinction is made between compression fractures, torsional fractures, compression fractures and flexion fractures. There are also broken bones.
Depending on the type of bone injury, experts distinguish between complete and incomplete fractures. The latter include fractures, breaks and perforations. With incomplete bone injuries, there is no displacement of the fragments. In complete fractures, there is displacement of the bone in length, angle, width, and axis.
Traumatologists also distinguish between multiple fractures and isolated fractures. Isolated fractures involve a single bone (hip or ankle fracture), while multiple fractures involve more than two bones or one bone in multiple locations (eg, shoulder and forearm fracture). If the bone fragment causes damage to internal organs and tissues, it is called a compound fracture.
Traumatologists also classify certain types of fractures, depending on the direction in which the bone was damaged:
When determining the treatment regimen, the doctor takes into account all the factors of the injury.
First aid for broken bones in the foot
The focus is on adequate pain relief by intramuscular injection of Promedol and Novocaine blockage of the fracture sites or 'box block' in the tibial area.

Transport immobilization in multi-fractures of the foot.
a – preparation of the splint; b - after immobilization.
Transport immobilization is carried out with the help of ladder rails. Patients can be transported in a semi-sitting position with the injured foot elevated.
Principles of treating foot fractures
Due to the low effectiveness of conservative methods, they should only be used as initial or additional treatment for multiple foot injuries. The use of distraction devices has significantly increased the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment of injuries at this site. Combination methods are the most promising.
The Ilizarov apparatus is used for closed repositioning of bone fragments of the foot. The spokes are then fixed percutaneously to the uninjured bone, the splint is removed and a circular cast is applied to the knee joint or to the upper third of the thigh (in the case of multi-fractures of the heel bone). For ankle bone and heel bone injuries, a cast is placed on the tibia (annulus and hemiplegia), ankle bone, and metatarsal bones. For multifractures and dislocations of the tarsal and metatarsal bones, distraction braces (mainly half rings) are applied only to the foot bones. As a rule, 1-2 spokes are inserted through each fracture of the heel bone and the ankle bone, which are fixed in separate half rings and can be shifted against each other. Spokes with thrust washers and interchangeable repositioning attachments are also used for repositioning.
Related articles:
In the treatment of open foot injuries, the main difficulties lie in the limited possibilities of radical tissue excision, the strong immobilization of the fragments and the closure of the wound defect with local tissue. Much better results were obtained with the Krasovitov skin graft and the primary free skin graft. However, insufficient fixation of the fragments diminished the final treatment effect. The use of distraction devices also improved the results of foot skeletal reconstruction. Simple frame splints (2 half rings or braces, 2 rods and 2 spokes) in combination with a plaster cast ensure adequate immobilization of the fracture while the wound heals. The splints can also be inserted through skin-free areas, which are then closed by a secondary skin plication. External bone fixation devices should be used not only in very severe injuries, where there are doubts about the advisability of salvaging the limb, but also without destroying the soft tissues, since the distraction of the injured joints prevents the development of early post-traumatic arthritis.
Algorithm for first aid
If a stress injury is identified, first aid can be provided in the form of POLICE Therapytake place, which includes:
- Protection,
- optimal load,
- Ice – called cryotherapy.
Cold therapy is used for the first two to three days of the process.
Local compression with an elastic bandage and limb elevation are also recommended.
Physiotherapy treatments include diathermy, magnetic therapy, shock wave therapy and ultrasound.
From the second week, heat treatments, paraffin, ozokerite and mud packs and massages can be recommended.
Treatment is recommended by a doctor specializing in physical medicine and rehabilitation or a physical therapist.
Chiropractic is used to correct disturbed movement patterns.
Pharmacological treatment of stress injuries in athletes includes the prescription of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, nitrogenous bisphosphonates, parathyroid hormone preparations, vitamin D and calcium.
The drugs are administered by a sports doctor who formally agrees to the anti-doping guidelines.
Physical activity is an important element in the treatment and prevention of recurrent stress-related bone damage.
In February 2021, a study published in the prestigious journal Nature confirmed the importance of physical activity for bone repair.
Studies have shown that the vibrations generated by walking or running are transmitted from the bone surface to the bone marrow, allowing new bone cells to form, which not only help strengthen the bone itself, but also stimulate the immune system. That's why staying active is so important to recovering from a stressful bone injury as quickly as possible and preventing it from happening again.
Shoulder and limb fractures
They are common, especially in children. The typical point of fracture is the boundary between the inner and outer tercile; a fracture of the middle collarbone is less common. In children, fractures under the periosteum are most common, without significant displacement or angular displacement.
Dislocation of the clavicle at the clavicle-acromial junction (the joint between the clavicle and scapular processes) is quite common.
fracture of the scapula
Rarely. It is usually caused by direct violence. It is often associated with fractures of the adjacent ribs. A distinction is usually made between fractures of the scapula shaft and its processes. Such fractures are best diagnosed with computed tomography (CT).
fracture of the humerus
Can occur anywhere in the bone, but the most common fracture of the humerus is at the surgical neck and great cusp. Fractures of the humeral head are mostly fragmentary. A humeral head fracture occurs from a fall on an outstretched arm.
It occurs on one or both bones at the same time. Most fractures occur at the medial joint or at the elbow joint when the hand falls onto the arm (bent elbow).
Wrist bone fracture
Rarely occurs when subjected to direct force. Most often the navicular bone is fractured, more rarely the tibia or tricuspid bone, and occasionally other bones are fractured as well. These fractures are often combined with fractures of the radial bone. The umbilical bone usually breaks medial transversely into two almost equal parts. If the fractures are displaced and the bones are not nourished, aseptic bone necrosis can develop.
Fractures of the metacarpals and finger bones
Fractures most commonly occur from direct trauma. Of the metacarpal bones, fracture of the 1st bone is most common; a typical fracture of the metacarpal occurs at its base. The phalanges of the fingers break more frequently than the metacarpal bones and usually in the area of the tubercles.
Other articles
Everyone dreams of having beautiful, shiny and healthy hair. To achieve this, most people are constantly searching for the 'perfect' shampoo, conditioner or mask, undergoing expensive hairdressing treatments, etc. And few people realize that the root cause of poor hair and scalp condition is usually deeper lies than it first appears.
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis after pregnancy
Most new moms leave the maternity ward with an enlarged belly. After some time, the abdominal muscles tighten and return to normal, and the happy mother has become slimmer and more beautiful. However, it is not always possible to go back to the previous figure and have a flat stomach again. Under the influence of many factors, some women develop separation of the abdominal muscles. This condition is called diastasis.
Drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels, called statins, are the most commonly prescribed drugs in Europe and the United States to prevent and reduce cardiovascular disease. Unfortunately, in Ukraine, statistics on the prescription of statins and their use by patients are diametrically opposed. This is despite the fact that there is a solid evidence base (we're talking about the benefits of this class of drugs from clinical trials and meta-analysis).
Adhesions occur in 5-20 % of patients who have undergone surgery. Most adhesions result from surgical intervention, but treating the pathology also requires the surgeon's scalpel.
Classification of fractures
Causes of incidence fractures

1 Traumatic - caused by a traumatic factor. Bone structure and strength is usually normal. The power of the traumatic factor is high.
2 Pathological – occurs spontaneously or under the influence of an extremely small force of the traumatic factor (sneezing, changing body position, lifting an unloaded object).
The cause is a change in the structure of the bone and a decrease in its mechanical strength (osteoporosis, metastases of malignant tumors, bone tuberculosis).
Depending on the nature of the displacement of the bone fragments
- Without displacement.
- With shift:
- Along;
- along the width;
- along the perimeter;
- at an angle;
- with separation of fractures;
- fractions connected into a bundle.
In relation to the surrounding skin:
Along the fracture line:
diagnosis
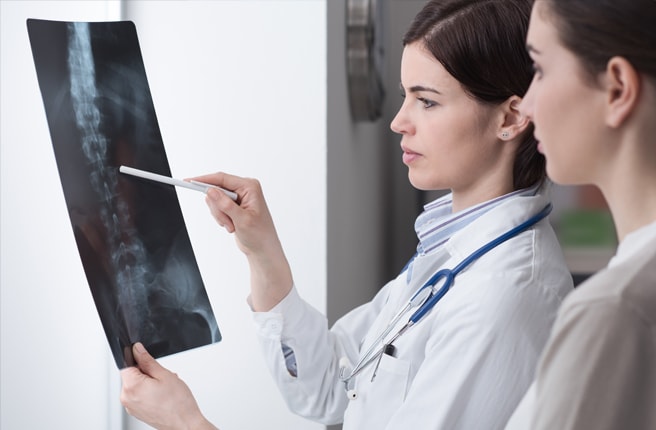
Diagnosis and treatment is carried out by a trauma surgeon, less often by a surgeon. The main diagnostic method is. the X-ray in two projections – straight and lateral. Special projections are used for some fracture types (e.g. iliac and obturator fractures in acetabular fractures). A more meaningful (and more expensive) method is. Computed tomography (CT scan)A more conclusive (and more expensive) method is computed tomography (CT). The following methods are used to further diagnose soft tissue injuries Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound (USG)less often. angiography, electroneuromyography.
The main principles of fracture treatment are. – Preserving the patient's life, eliminating anatomical damage that blocks the function of vital organs, restoring the anatomy and function of the injured limbs.
The following techniques are used to treat closed fractures immobilization – Immobilization of the injured section with plaster casts, plastic bandages or rigid orthoses. Displaced fractures are treated with skeletal traction (prolonged positioning of the fracture using a weight-loaded system). Many fractures require surgical intervention. The advantages are good fracture alignment and safe immobilization, early patient mobilization, shorter hospital stay, and less duration of transient disability. These include osteosynthesis, ie the stiffening of bone fragments with plates, pins or screws, and arthroplasty, ie total or partial joint replacement (the 'gold standard' for femoral neck fractures in the elderly).
Pharmacological treatment Pharmacological treatment is aimed at reducing pain and preventing the development of complications. Narcotics (hospital only - when there is serious injury and risk of traumatic shock) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to relieve pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as analgesics, ketorol and ketonal are preferred because of their predominantly analgesic effects. For the prevention of thrombosis (in fractures of the lower limbs and in bedridden patients), anticoagulants (to prevent blood clotting) – injectable derivatives of heparin (heparin, fraxiparin, enoxaparin) and modern tablets – Pradaxa, Xarelto – as well as anticoagulants (to improve blood flow) – are used. Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Trental - prescribed. In open fractures, prevention of infectious complications is essential. For this purpose, antibiotics (usually cephalosporins - ceftriaxone, cefotaxime) and antimicrobial drugs (ofloxacin, pefloxacin, metronidazole) are used.
How to recognize a fracture: main symptoms
A fracture is a break in the integrity of a bone caused by trauma or pathology. It can be open or closed. In the first case, the skin at the fracture site is damaged, and often even the bone itself is visible. In the case of a closed fracture, on the other hand, the skin is not injured. A bone can also fracture with or without a dislocation. A closed fracture without a dislocation naturally heals the fastest.
If the hernia is open, even a child can easily diagnose it. Closed fractures, on the other hand, are more difficult to diagnose. A fracture can easily be mistaken for a serious contusion, especially if it occurs without a dislocation.
- Swelling – occurs within a few hours after injury;
- Deformation of a body part - if it is displaced, there is a curvature;
- Mobility issues - moving the injured area is difficult and painful;
- numbness - not all people lose feeling;
- Hematoma – if the fracture causes internal bleeding, bruising occurs.
If the fracture is an isolated one affecting only a small bone, the condition is usually satisfactory. If there are multiple fractures or if a large bone is affected (such as a femoral neck fracture), the condition worsens due to the traumatic shock. In any case, you should go to the hospital and have an X-ray made. In this way it can be determined whether there is a break or not.
First aid after a fracture
If a person has suffered an injury, the injured area must be immobilized. It is advisable to call and wait for an ambulance. He will arrive and put on the splint himself. While waiting for the ambulance, you should not move the injured area. If necessary, cold water, hot tea, and painkillers can be gently applied.
If you decide to transport the person to the hospital yourself, you will need to stabilize the limb. A Kramer splint is placed around the arm and hooked into a sling. A Dieterichs splint is placed around the leg. If these are not available, boards, skis, poles and other improvised materials can be used. The aim is to fix the limbs to prevent deterioration.
Let's look at the instructions for applying a splint with improvised materials (boards, skis, poles) after a fracture:
- Keep the person's clothes on, prepare everything you need.
- Place two hard objects on each side of the arm or leg.
- Fix with a bandage (not too tight, so as not to cut off the blood flow);
- Fix the two joints above and below the fracture.
If sticks or other objects are not available, you can tie the arm to the torso and the injured leg to the good leg. If a spinal fracture is suspected, the person should lie on their back on a hard surface. The person should not be touched or transported independently. An ambulance should be called and waited for.
Can multiple myeloma be detected at an early stage?
It is difficult to diagnose myeloma in its early stages because symptoms are sparse or absent. In such cases, it is discovered incidentally when a normal blood test reveals an abnormally high level of protein in the blood. Therefore, all persons at risk (e.g. people with other plasma cell diseases) should have regular blood tests for monitoring.
Pharmacotherapy is the main treatment for myeloma. Many different drugs are used, including:
- traditional chemotherapy cytostatics;
- anti-inflammatory corticosteroids;
- immunomodulators;
- proteasome and nuclear export inhibitors;
- monoclonal antibodies, etc.
Symptomatic treatment of osteoporosis, correction of excess calcium in the blood, analgesics and styptic drugs are also indicated. Surgical interventions are very rarely used, while radiation therapy is mainly used as a palliative treatment in debilitated patients.
In recent years, bone marrow transplantation (more specifically, the transplantation of bone marrow stem cells from peripheral blood) has become increasingly effective in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Some experts recommend two autologous bone marrow transplants 6-12 months apart for myeloma. This approach is called a tandem transplant and reportedly leads to more reliable results.
Prognosis of Multiple Myeloma
According to statistics, the five-year survival rate for patients with this disease averages from 79 % to 58 %. This figure is primarily influenced by the stage of tumor pathology, but also by a number of other factors:
The diagnosis and treatment of myeloma is one of the specialties of Anadolu Medical Center. We have a team of highly qualified oncologists and hematologists who have advanced methods in the fight against this disease. Anadolu Medical Center has its own bone marrow transplant center with doctors who also successfully perform these operations in multiple myeloma.
Treatment in the Medical Center:
Read more:- tibia and fibula.
- tarsal bones of the foot.
- Bone structure of the navicular foot.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
- Metatarsal tarsal bones.
- The tarsal bone hurts from above - what to do?.
- tarsal bone in Latin.
- fracture of the elbow in the foot.
