In the past ankle joint The ankle joint has historically been referred to as the block joint, but it is more appropriate to call it the saddle joint. The block or saddle of the talus is wider in front than behind. In dorsiflexion of the foot, the thigh block enters the foramen formed by the ankles and provides more stability than in sole flexion. The only 'pure' movement in the ankle is plantar and dorsiflexion.
- Injuries to the ankle
- Types of ankle fractures and mechanism of injury
- How long does an ankle fracture hurt without a dislocation?
- Healing time for a non-displaced ankle fracture
- Rehabilitation after an ankle fracture
- Video reports about the treatment of ankle fractures in our center
- Class B: Fracture of the ankle from a force displacing the talar bone medially
- Class B: Type IA: Axial pressure applied to the ankle in dorsiflexion.
- Symptoms of a foot fracture
- causes of injuries
- Which doctor should I see?
- Main causes of injuries.
- The diagnosis.
- Classification: types of fractures of the ankle in children
- Symptoms of an ankle fracture in children
- Duration of immobilization in tibial trauma
- Methods for a successful recovery
- massage
- gymnastics
- How does the treatment of ankle fractures look like with our method?
- surgical treatment
Injuries to the ankle
Fractures of the ankle and associated dislocations are quite common. Most are due to a minor rotational injury. A smaller percentage are more serious injuries, including tibia fractures and ankle fractures, caused by severe trauma, e.g. B. by a fall from a height or a car accident.
The patient usually has a valgus foot in the ankle. Pain occurs immediately after the injury, followed by swelling. A little later there is a bruise around the ankle. The patient notices that he can no longer support himself on his leg.
The most obvious injury is a fracture of one or both ankles, but often the 'invisible' part of the injury, e.g. B. a rupture of the ankle ligaments, much more serious.
Types of ankle fractures and mechanism of injury
A person trips and falls. Typically, the foot is locked on the surface as the body tumbles forward. The ankle joint is retracted and the ankle bone (talus) is displaced and/or rotated in the ankle joint foramen, resulting in a fracture of one or both ankles with or without ligament damage.
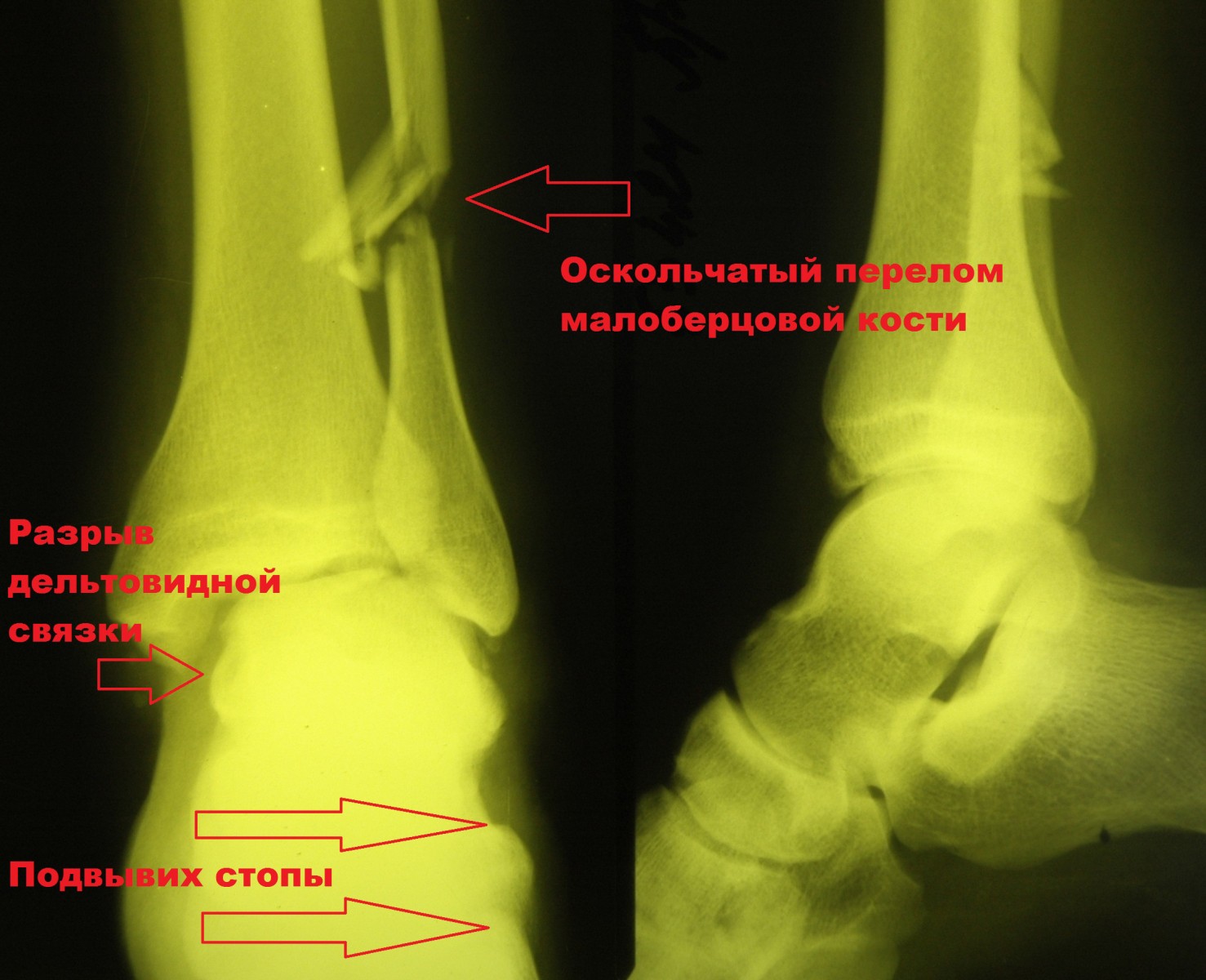
Put simply, all ankle fractures can be divided into three types (A, B, C). Type A is a transverse fracture of the fibula below the intertibial syndesmosis, possibly in combination with an oblique fracture of the medial malleolus. Type B is an oblique fracture of the fibula at the level of the syndesmosis; often with detachment from the inner malleolus or damage to the delta ligament. Type C is the most severe injury that is above the centesmosis and will inevitably result in damage to the interosal ligament and possible injury to the interosseous membrane.
How long does an ankle fracture hurt without a dislocation?
To say it straight away: It depends on the severity of the injury itself, the stability of the fracture, the quality of the bandage and the individual pain sensitivity threshold of each individual.
With a fracture of the 1st ankle (internal or external), you will have pain for an average of 5 days after the injury. Once the bandage is applied, the pain decreases many times over. If the bandage is tight, does not compress soft tissues, and is not loose, pain is rare. However, if the swelling is severe and the bandage is pressing on the soft tissues, the pain may be permanent.
If you are an individual and need to ask a trauma surgeon online, Ask me a question.I'm happy to help.
Healing time for a non-displaced ankle fracture
The average time it takes to heal an ankle fracture (internal or external) depends on the patient's age, the type of injury and underlying medical conditions, the stability of the fracture and its fixation in an ankle splint, and the patient's adherence to therapy.
For example, an external ankle fracture without dislocation in a 20-year-old patient, -. an average of four to six weeks to heal.. With severe swelling and a loose bandage that allows micromobility of the fracture (the patient arrives early), the healing time is longer and can last from six to eight weeks. Not to mention the cases where there is a secondary displacement of the fragment and a fracture that could not initially be displaced is to be operated on. To avoid this, it is necessary to strictly follow all the doctor's recommendations.
Rehabilitation after an ankle fracture
As soon as the cast is removed, the rehabilitation measures begin. For this purpose, electromagnetic therapy is recommended to restore blood and lymphatic circulation and reduce swelling in the ankle and foot area.
The phases of medical rehabilitation following the treatment of a fractured ankle can be divided into two stages: immobilization and restoration of function to the injured limb. This phase lasts (in the case of two ankle fractures), complicated by subluxation of the foot, 2.5-3 months. In the case of external fractures of the ankle without dislocation, the immobilization period is reduced to one month.
The complex treatment of fractures of the ankle is usually carried out with immobilization. Patients focus primarily on therapeutic exercises that are general in nature. In addition, in the first period after the hernia has been repositioned (when the swelling has subsided and the cast has been replaced), special exercises of a training nature are prescribed.
Video reports about the treatment of ankle fractures in our center
Patient Lyubov M. – date of operation December 17, 2013.
Class B: Fracture of the ankle from a force displacing the talar bone medially
If this one mechanism The anterior ligament of the ankle bone, or lateral malleolus, is the first to tear. As this mechanism continues, the ankle bone is pressed against the medial malleolus, causing it to fracture or break off vertically.
axiomA vertical fracture of the medial malleolus is associated with either a fracture of the medial malleolus or a tear of the medial ligaments.
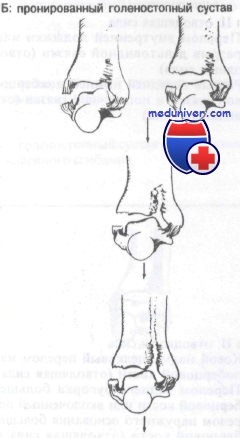
When a dorsiflexion component is present diffractionthe medial malleolus fracture can affect the anterior joint edge of the tibia. In plantar flexion, the internal fragment may involve the posterior articular margin of the tibia.
Class B: Type IA: Axial pressure applied to the ankle in dorsiflexion.
This mechanism usually leads to isolated or combined injuries. Puncture fractures and fractures of the anterior border of the heel bone can occur.
specific Print can lead to a fracture of the posterior border of the talus or a tear of the intertibial syndesmosis (tear of the intertibial ligaments). Severe diastasis can damage the inner and outer ligaments.
The patient complains about Pains Pain and swelling that is localized at first but can later spread to the entire ankle. The doctor should try to determine the exact mechanism of the injury and carefully examine the ankle for focal pain and swelling. The pulse from the dorsal foot artery and the posterior tibial artery should be palpated and compared to the pulse from the healthy extremity. Swelling or bleeding in the Achilles tendon area indicates a rear ankle fracture.
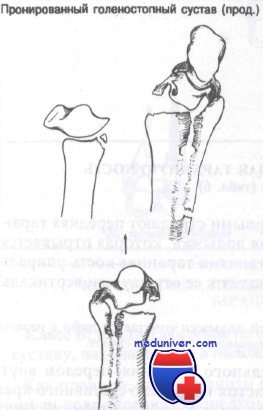
axiom: Any fracture of the fibula distal to the joint line should raise suspicion of a deltoid ligament injury. A lateral malleolus fracture with displacement is usually associated with a fracture of the medial malleolus or a rupture of the deltoid ligament.
axioms: An 'inversion fracture' of the medial malleolus must be accompanied by a fracture of the medial malleolus or a tear of the ligament. An 'inversion fracture' of the medial malleolus is usually associated with a fracture of the medial malleolus or a tear of the interosal ligament.
X-rays are usually taken X-raysincluding straight, side, and straight 20° foot-in projections. Fractures resulting from a tendon rupture are transverse—usually vertical, helical, or crushed—due to plate insertion. The rectilinear image should be carefully examined to detect internal or external displacement of the talus and fracture of the ankle. The space between the medial malleolus and talus must be carefully examined in a straight scan with 20° internal rotation; a tear in the ligaments can expand this space.
Symptoms of a foot fracture
The severity of the symptoms depends on how badly one area of the foot has been damaged. It is not uncommon for the minor symptoms of the injury to mean that those affected do not even visit a hospital. This leads to complications: severe pain, inflammation and unhealed fractures. Also, without a radiological diagnosis, the injury is mistaken for a soft tissue injury such as a contusion or dislocation. In order to identify the nature of the problem and seek help in a timely manner, it is important to know the main symptoms of a fracture:
- Stitching pain in foot, unable to kick foot;
- swelling, redness, bruising;
- increase in local temperature;
- inability to move toes;
- Deformation of the foot, hard thickening under the skin;
- In severe cases of fractures, abnormal bone mobility.
The symptoms of a foot fracture can vary in severity and location. This depends on how severe the injury is and which part is affected. The overall condition is also affected by possible damage to other connective tissues - cartilage, tendons, ligaments. Injuries to these bones are most common:
In severe cases, the injury can be aggravated by displacement, which can lead to an open fracture. This is a dangerous condition in which bone fragments break through soft tissues.
causes of injuries
Injuries can occur regardless of occupation and lifestyle. The fragility of the bones in the foot means that even minor mechanical impacts can compromise their integrity. Professional athletes and the elderly are at high risk. Causes of foot fractures include:
- Vertical or side impact;
- twisting and bending;
- bending over a hard edge;
- twist;
- crushing impact.
A foot fracture is not uncommon as a result of a fall in which the foot is twisted or struck by a heavy object. Foot injuries are a typical feature of soccer players and athletes. In children, on the other hand, these fractures occur much less frequently due to the high flexibility of the bones. In older people, injuries are often associated with osteoporosis or osteomyelitis.
Which doctor should I see?
Timely medical treatment can help control the symptoms – pain, swelling, inflammation – and significantly speed up the healing process. Therefore, if a fracture is suspected, you should not postpone a visit to the hospital. The doctor is responsible for treating these types of injuries:
Main causes of injuries.
There are general and local causes that slow down the healing process. This includes:
- Serious diseases (diabetes, osteoporosis)
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol)
- exhaustion
- Older age (over 60 years).
- Multiple fractures
- Dysmenorrhea in women
- Infection or foreign body entry into the wound
- Severe soft tissue injuries
- Poor circulation.
The diagnosis.
Delayed normal bone healing in the area of the fracture can be noted:
- by clinical examination (by bending and applying strong pressure to the injury site, the doctor determines whether there is pain and whether there is elasticity and resilience at the fracture site)
- X-ray (can only be used 16-22 days after the fracture, the X-ray clearly shows the fracture line and callus formation is indeterminate)
Classification: types of fractures of the ankle in children
Like any other fracture, an ankle fracture in children can be open or closed (with or without skin penetration), with or without displacement, uncomplicated or complicated by damage to adjacent structures.
The most important classification of injuries is based on the location of the injury. The most important classifications are isolated lateral or inner ankle fracture, double ankle fracture (both ankles are damaged) and triple ankle fracture. In the latter case, the edge of the tibia is damaged in addition to the ankle.
Symptoms of an ankle fracture in children
It can be difficult to distinguish the symptoms of an external or medial ankle fracture from other ankle injuries in children. Immediately after the injury, the child complains of severe pain that rarely subsides. Over time, there is swelling of the ankle and a hematoma that spreads under the skin of the foot to the heel and base of the toe. Because of the severe pain, movement of the joint is almost impossible, as is weight bearing on the foot. If the bone injury is accompanied by a dislocation, the joint will look significantly deformed.
The most common cause of an ankle injury is turning the foot inward or outward while walking, running, or jumping. Children often suffer such injuries while playing or doing sports. The injury can also be caused by a direct blow to the ankle.
Duration of immobilization in tibial trauma
Anatomically, the tibia is represented by the tibia and fibula. The duration of the cast depends on the type of injury. If the broken tibia is not displaced, the cast will stay in place for 5-6 weeks and you will not be able to step on the foot until the splint is removed.
For injuries with a displaced fracture, a plaster cast must be worn for at least 4 months. The traumatologist decides on the duration of immobilization of the limb depending on the type of injury, the radiological findings and the activity of callus formation.
Methods for a successful recovery
The rehabilitation that begins after an ankle fracture is very important to regain lower limb function. The scope of rehabilitation measures is determined by the traumatologist and physiotherapist, taking into account the severity of the fracture and the age of the patient.
Rehabilitation is occurring on several fronts. For pain, external and internal painkillers are prescribed. The drugs are prescribed by the attending physician. A good effect is shown by physiotherapeutic treatments, which lead to the following results:
Electrotherapy is complemented by other rehabilitation measures (mud or paraffin applications, radon baths, acupuncture) to achieve better results in restoring ankle function.
massage
The appointment of a massage can be justified at any stage of the therapeutic process. Treatment can begin as soon as the cast is removed from the leg. Various ointments or gels with an analgesic effect are used to relieve the symptoms.
The massage improves nutrition in the area of the injury, which leads to better repair of the damaged tissue and stimulates metabolism in the joint and surrounding muscles. The treatment consists of 10-20 sessions.
An elastic bandage is applied after each session to better immobilize the ankle and allow the tissue to retain heat longer after physical treatment.
gymnastics
Gymnastics for broken ankles is an integral part of rehabilitation. Classes are held in a special group after the cast has been removed. Specific exercises target the weakened muscles and ligaments of the ankle so that the joint slowly regains its function.
How does the treatment of ankle fractures look like with our method?
First stage. – The ankle fracture is reduced in a closed apparatus with the help of a hardening plaster of paris or a polymer bandage in a special patent apparatus.
Second stage – Once the bandage is in place, the patient is taught to walk with full support of the injured limb. On the 8th-14th day after the injury, when the risk of post-traumatic edema is eliminated, the shoe bandage on the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot is shortened.
If the fracture position is satisfactory, patients are discharged for outpatient treatment. The general appearance of the shoe bandage upon discharge from the hospital is shown in the figure below. The general appearance of the patients upon discharge from the hospital is shown in the figure below.
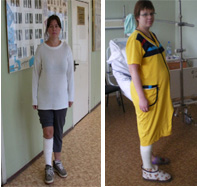
The general appearance of the patients upon discharge from the hospital is shown in the figure below. Until the primary consolidation of the ankle fracture, ie up to 4-5 weeks after the ankle fracture, the injured ankle joint is relieved of a plaster or polymer shoe bandage on the dorsal and plantar surfaces.

After the estimated ankle fracture consolidation time of 6-8 weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture, the remainder of the cast or shoelace polymer dressing is removed. Patients are not psychologically afraid to put weight on the injured limb without a bandage, put on ordinary shoes and start walking with full weight on the injured limb.
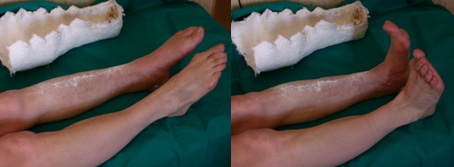
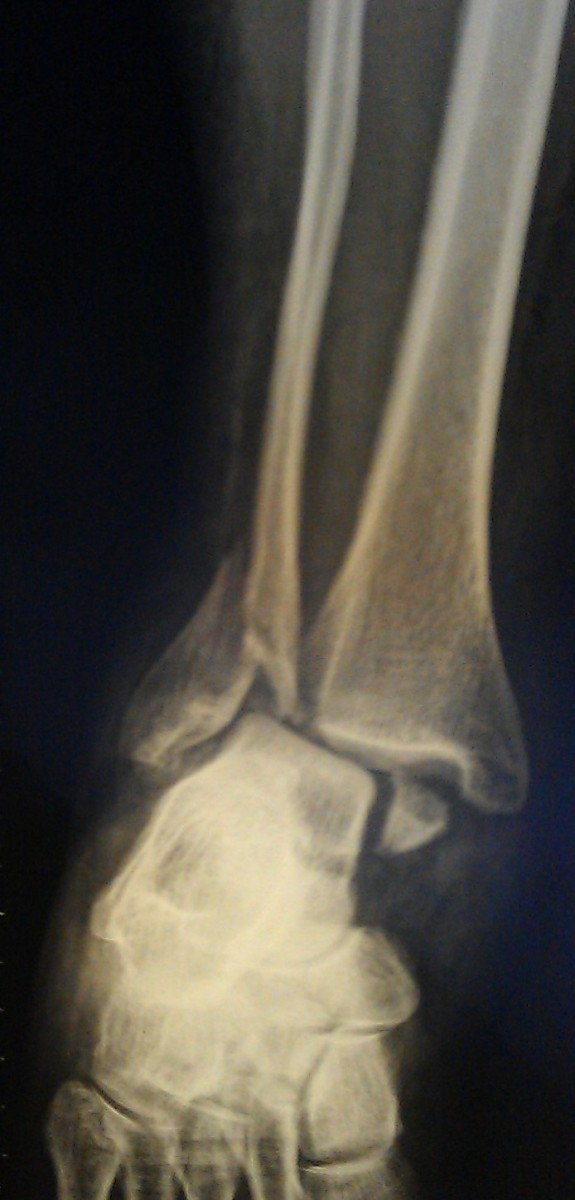
Patient M. 33 years old. She was injured in a fall on the street, twisting her left foot outward. Diagnosis: fracture of the medial malleolus, periarticular fracture of the left fibula with posterior displacement of the foot.
surgical treatment
It is not uncommon for bone fragments to remain in an unsatisfactory position after closed reduction. This fracture is also characterized by secondary displacement of bone fragments with subluxation of the foot after swelling subsides.

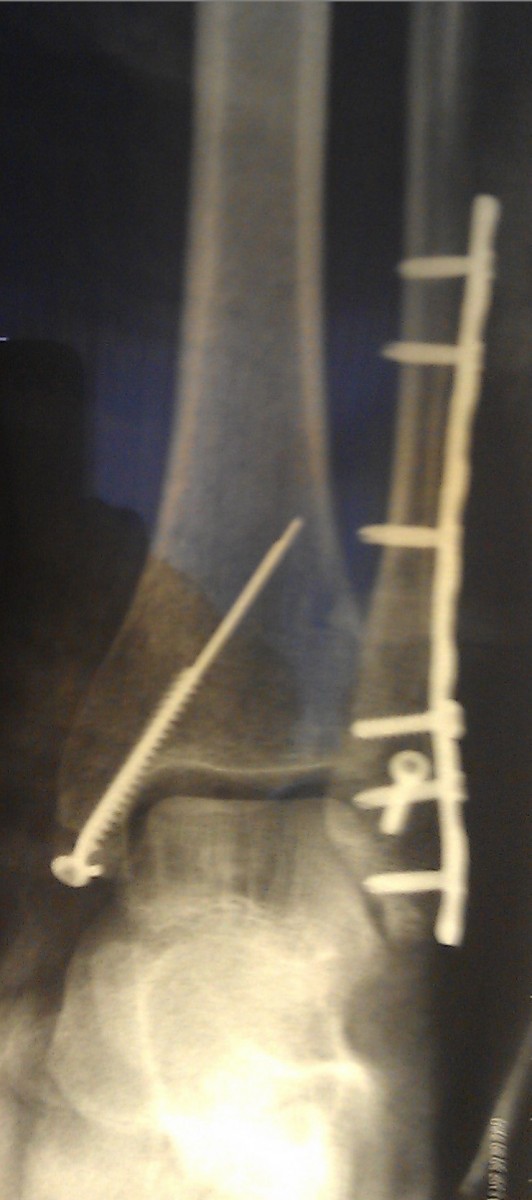
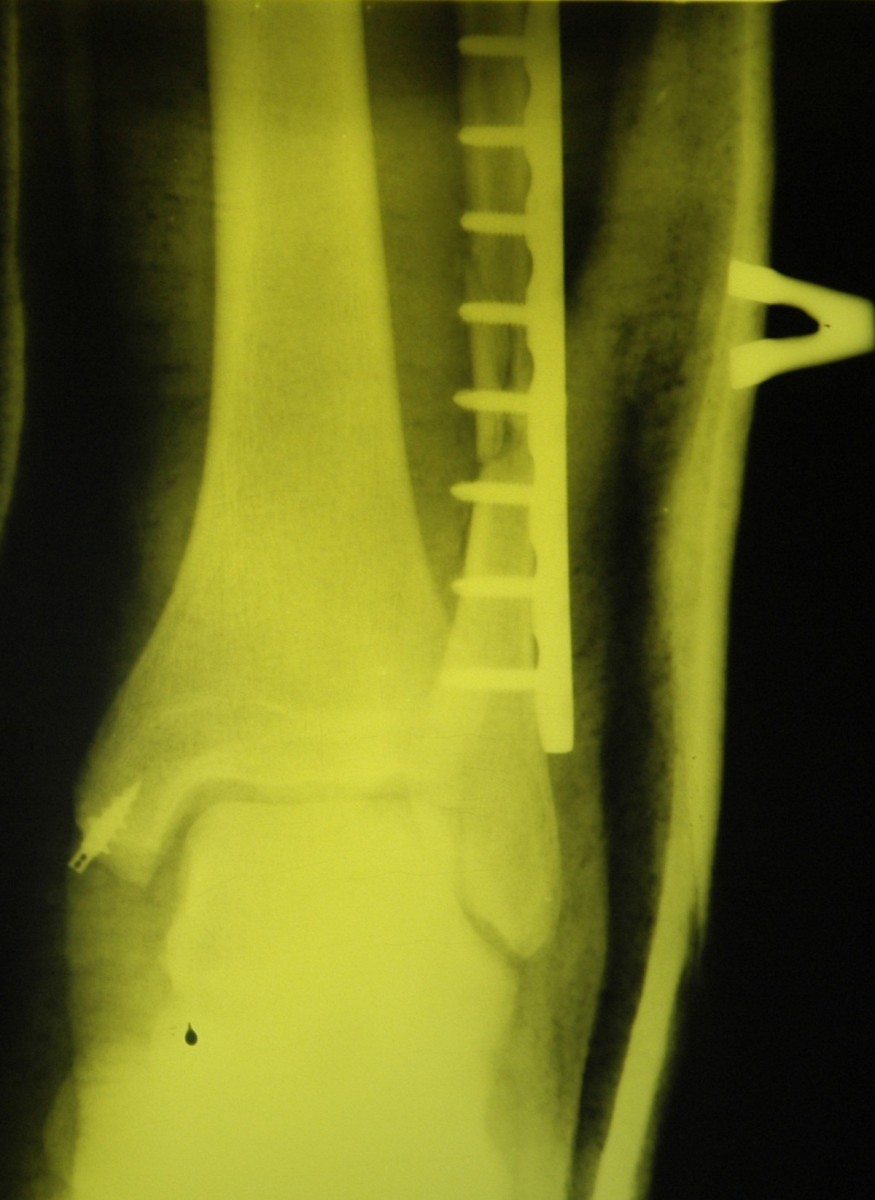
In such cases, surgical treatment is indicated. Surgery should be performed as soon as possible if the general condition of the patient and the condition of the soft tissues around the fracture allow it.
 |  |
Very often, ankle fractures are complicated by poor perfusion of the periarticular tissues, leading to the formation of blisters and sometimes necrosis. Such manifestations on the skin require special treatment, so the operation may be delayed.
Special metal constructions, usually plates, screws and spokes, are used to surgically assemble the bone fragments into their correct position and correct the subluxation of the foot.
- Photo: Outer malleolus fracture.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
- Fracture of the heel bone.
- Closed fracture of the ankle.
- tibia and fibula.
- Fracture of the 5th metatarsal.
- Bones of the human ankle.
- Fracture of the calcaneus of the foot.
