Remember: physical activity is very important during rehabilitation, but exercises appropriate to the recovery period should be performed.
- MRI scan in case of platibasis
- MRI examination of the atlanto-dental joint
- symptoms of the disease
- Treatment methods for broken foot bones
- Symptoms of an alveolar fracture
- diagnosis
- symptoms
- Treatment of a fracture
- Costs
- Clinical manifestations
- Rehabilitation and treatment
- Traditional treatment
- Consequences of an elbow fracture with displacement
- classification
- complications
- What are the possible causes?
- Symptoms of a broken bone
- recovery period
- Possible complications
MRI scan in case of platibasis
The craniovertebral junction is the boundary between the base of the skull and the upper cervical spine. The correct alignment of these bony structures ensures adequate space containing the lower parts of the brainstem and the cranial portion of the cervical spinal cord. There are a number of acquired and congenital anomalies that contribute to narrowing of this space, causing temporary or persistent compression of brain structures. One of these abnormalities that is commonly seen on MRI scans is platibasy, a flattening of the skull base and posterior cranial fossa. Platybasia can be congenital (in Down's disease, in combination with Arnold-Chiari anomaly, etc.) or acquired (in fibrous dysplasia, osteomalacia or as a result of long-standing intracranial hypertension in childhood); Clinically, this dysplasia is usually asymptomatic. Platybasia rarely occurs in isolation.
The craniovertebral junction is the boundary between the base of the skull and the upper cervical spine. The correct alignment of these bony structures provides adequate space for the lower parts of the brainstem and the cranial portion of the cervical spinal cord.
There are a number of acquired and congenital anomalies that contribute to the narrowing of this space, causing temporary or permanent compression of brain structures.
One such anomaly that is not uncommon in MRI studies is platybasia.
This is a flattening of the base of the skull, which lies further back in the cranial fossa. Platybasia can be congenital (Down syndrome, combined with Arnold-Chiari anomaly, etc.) or acquired (fibrous dysplasia, osteomalacia or as a result of long-standing intracranial hypertension in childhood).
Clinically, this dysplasia is usually asymptomatic.
MRI examination of the atlanto-dental joint
The atlanto-dental joint is a tight connection between the first two cervical vertebrae, the atlantoaxial and the axis. Together with a strong ligamentous apparatus, they form a strong ligamentous and bony joint that prevents excessive movement of the atlanto-dental joint.
However, damage to this joint caused by various diseases and pathological processes can weaken its strength and lead to pathological mobility.
Fusion of the ossification points of the axis and dentition occurs at the age of 4-6 years, and complete tooth accommodation occurs at the age of 8-10 years. However, cases of incomplete appendicular fusion – a developmental anomaly – are not uncommon. This situation contributes to pathological displacement of the atlas along with the dentition during minor mechanical shocks.
Variant of incomplete dentition fusion.
Traumatic failure of the atlanto-dental connection with displacement, subluxation or fracture of the dentition is possible. Fractures are most commonly caused by falls to the head from a height, whiplash, and blows to the bowed head.
Restricted movement (patients hold their head with their hands) and pain in the neck and back of the head are clinically typical.
Neurological abnormalities are noted in dislocation fractures: tetraparesis, numbness of the limbs, difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath.
Transligamentous dislocation of the dentition.
symptoms of the disease
A fracture of the ankle bone can be manifested by the following symptoms.
- Pain in the back of the foot.
- Limited mobility of the foot. The movement is accompanied by increased pain, the patient has difficulty putting weight on the foot.
- Swelling of the tissue. The more damaged the blood vessels, the greater the swelling and possibly a hematoma with a bluish tint to the skin.
- In an open fracture, there is a wound in the foot and bone fragments may be visible.
- The fracture is often associated with joint dislocations and fractures of other bones of the foot.
- When inflammation occurs, there is a temperature reaction, increased local pain, and a throbbing character.
The most common cause of the disease is trauma to the foot. The mechanism of injury is a sprain or impact on the sole. Often, such injuries occur to drivers during an accident, especially motorcyclists, due to the foot resting on the pedal. Also as a result of falls in icy areas.
Treatment methods for broken foot bones
Treatment for a fracture of the talus depends on the type of fracture. Diagnosis is made by x-rays and sometimes CT scans of the foot. An open fracture requires wound care and regular dressing with antibacterial and antiseptic agents.
The main feature of the treatment is the early start of movement of the foot. The talus is mostly located inside the joint and is covered by cartilage. It is nourished by the synovial fluid. Exercise is essential for blood flow to the tarsal bones and joints. For this reason, a plaster cast is not applied or is only applied for a short time. Instead, the broken parts of the bone are immobilized.
If there is no dislocation, the bone is fixed with small punctures through the skin. Many fractures, dislocations and broken bones require open access surgery. During surgery, the bone is returned to its normal position and repaired, fragments that could cause inflammation are removed, and the wound is stitched up.
Symptoms of an alveolar fracture
A fracture of the alveolar process can be diagnosed by the presence of a
- acute, cramp-like pain in the jaw when chewing or swallowing saliva,
- swelling of the mucous membranes,
- Damage to the gums (with or without bleeding),
- painful closing of the jaw,
During palpation, the injured part can be moved or the separated area can be felt. Externally, the fracture is characterized by bruises, bruises on the face in the area of the fracture. External examination and x-rays show an alveolar fracture or complete separation of the bone from the main skull bone.
Depending on the angle at which the impact occurred, the broken part may move sideways, inward, or into the mouth. If the impact occurs in the lower jaw, the impact occurs from the lower jaw to the upper jaw and the broken part shifts upwards.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of the fracture is made by the oral surgeon. An x-ray can show different degrees of damage:
- Partial fracture – part of the bone is damaged but not completely detached;
- non-displaced fracture – all parts of the bone are damaged;
- Complete fracture – the x-ray shows a gap between the detached part and the skull;
- Fracture in different places – damage to the alveolar process in different places, fragmentation of the bone;
- Fracture with deformation – completely separated part displaced at different angles.
symptoms
Since this bone is located in the middle part of the foot. The symptoms of a fracture are similar to other injuries. The following symptoms are characteristic of a fracture of the talus bone of the foot:
- severe swelling in the area of the back of the foot,
- Blue discoloration of the skin at the injury site,
- enlargement of the foot,
- extensive hematomas,
- abnormal change in the shape of the foot,
- severe pain in the foot and the entire ankle,
- limited mobility.
Symptoms largely depend on the location of the fracture:
- With marginal injuries, they are involuntary and not characterized by severe pain syndrome, which is often confused with a simple bruise,
- A severe deformation of the ankle joint can be seen in the neck,
- Severe pain in the Achilles tendon is characteristic of fractures of the posterior tendon process and increases on palpation.
Warning. An accurate diagnosis of a fracture or simple bruise can only be made by a doctor after the necessary X-ray examination. If you experience these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Treatment of a fracture
Surgical treatment of heel bone fractures is necessary in any case, as serious complications can occur if not treated in a timely manner. The treatment itself depends on the type of injury. There are essentially three methods of stiffening:
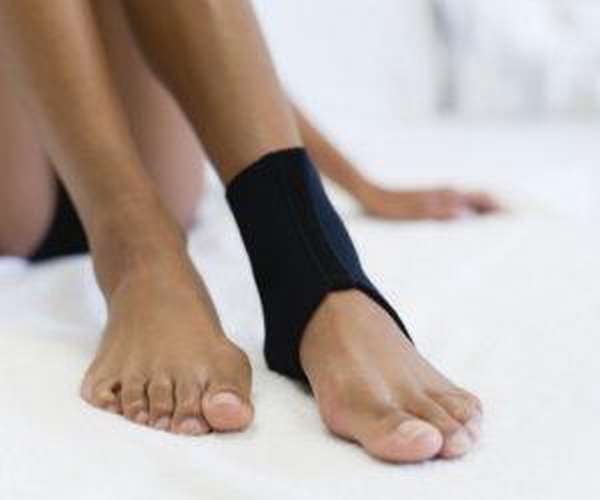

Treatment of a fracture of the posterior process of the talus usually involves immobilization. It consists of. Placing a plaster or plastic splint over the fracture site..
This procedure is performed when the injury is simple and there are no complications. A metal rail is attached to the underside of the plaster. This keeps the foot in a fixed position.
The patient must elevate the injured leg using the immobilization bandage. In this way, unwanted swelling is avoided. Painkillers are recommended to relieve the pain associated with the injury.
Treatment for a displaced talus fracture includes closed reduction. A bandage is applied before reduction and the following procedure is followed:
- Anesthesia is administered
- Position the patient on his stomach and bend the leg at the knee
- pulling the heel and flexing the foot one degree,
- reattachment of bone fragments,
- and putting on an immobilization shoe.
After 7 weeks, the bandage is changed, but the patient can flex the foot 900 degrees.
How do you treat a patellar fracture?
Learn how to provide first aid for various fractures.
In severe cases, open reduction or osteosynthesis is performed:
- A non-consolidated ankle bone fracture in which healing is significantly impaired,
- In the case of irreversible dislocations,
- injuries with risk of necrosis,
- Presence of displacement of more than 1 cm,
- Closed fracture with soft tissue damage,
- Open fracture.
Costs
- Examination of the teeth and fixation of the dentures.
- Examination of the mucous membranes.
- Examination of the gums.
- Determination of the type of occlusion.
- Recommendations.
- Medical advice.
- Panoramic X-ray, computer tomography.
- Anesthesia.
- Taking a print.
- Creation of a computer model of the future occlusion.
- Manufacture of prosthetic constructions.
- Adjusting prostheses.
- Adjust.
- Corrections.
- Replacing temporary restorations with permanent ones.
- Recommendations from specialists.
- Medical consultations.
- Scanning the jaw.
- Anesthesia.
- Restoration of teeth using the chosen method.
- Specialist medical advice.
- Medical advice.
- Taking x-rays of the jaw.
- Partial filling of the root canal.
- Making an impression.
- Production and adjustment of the microprosthesis.
- Doctor's recommendations.
- Consultation with the doctor.
- Making scans.
- filling the root.
- Impression of the jaw.
- Computer modeling of prosthetic results.
- Making and inserting the crown.
- Advice from the doctor.

Free of charge
Clinical manifestations
Injuries to the lower jaw are often accompanied by other injuries to the jaw and musculoskeletal system, bruises and concussions of internal organs and brain structures [4,6]. In these cases, the patient is unconscious and cannot report any symptoms. External signs of injury are assessed:
- soft tissue swelling;
- bleeding;
- asymmetry of the face;
- occlusion problems;
- protrusion or recession of the mandible;
- bruising on the skin;
- protrusion of tongue;
- Impairment of swallowing and breathing through the mouth.
A conscious jaw fracture is associated with difficulty speaking and chewing and impaired swallowing of saliva (3,17). The patient complains of persistent, severe pain, which increases when attempting to move the lower jaw or apply pressure to the soft tissues adjacent to the injury site. In cases of mucosal injury, oral bleeding and blood clots may be observed [1,9]. Nerve damage is manifested by reduced pain and touch sensitivity and numbness.
Rehabilitation and treatment

If the ulnar fracture is closed, the patient does not require repositioning, traction or osteosynthesis. If the injury is a comminuted fracture, the fragments must be reduced. This is done through a surgical procedure. First, skeletal traction is performed on the patient to relax the massive triceps muscle. For this purpose, a marginal puncture of the bone is carried out. Surgical intervention is also necessary if an open fracture is present and primary wound care is required.
After surgical treatment, a plaster cast is applied and the patient is given painkillers, antimicrobial medications and muscle relaxants. During the bone healing process, x-rays are taken to track the progress of healing. Once the bandage has been removed and the fractures have partially healed, the affected person needs a long recovery period. This also includes physiotherapy.
Rehabilitation after an elbow fracture includes activities such as.
- therapeutic baths;
- Acupuncture;
- electrophoresis;
- sludge treatment;
- paraffin compresses;
- Magnetic therapy
- therapeutic massage;
- PHYSICAL THERAPY.
Traditional treatment

The use of medicines in the treatment of elbow fractures is possible after surgery or in the case of an elbow fracture without dislocation. A plaster cast and prolonged rest of the limbs are recommended. Multivitamin and calcium supplements are also recommended. This accelerates the healing process of the bones. If there is severe swelling of the upper limb, local application of an ointment with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory component is recommended.
Consequences of an elbow fracture with displacement
After the operation, the patient needs a long rehabilitation period. This also includes physiotherapy in a sanatorium. Do not put excessive strain on the injured arm as this may lead to a relapse. Injury to the left elbow process has few negative consequences because it does not affect the main working area of the arm.
classification
- 1 type. Minor bone loss is observed. A prosthesis is required to relieve pressure on the appendicular bone and stop bone loss.
- Type 2: Moderate bone loss. Osteoplasty is required.
- Type 3. Severe bone atrophy. This type requires surgical intervention to restore bone volume.
- The patients' faces look older,
- the lower facial area shrinks,
- wrinkles appear around the mouth,
- and a receding lip,
- Speech and chewing are impaired.
complications
Bone loss leads to problems with dentures. This is the most serious complication. Due to bone loss, the adhesion and anchoring of removable dentures is impaired and the fit of implants is completely lost. The lack of prostheses leads to disruption of the digestive system.
The most dangerous is a pathological fracture of the thin part of the jaw. Recovery from such complications is lengthy and requires a long rehabilitation period.
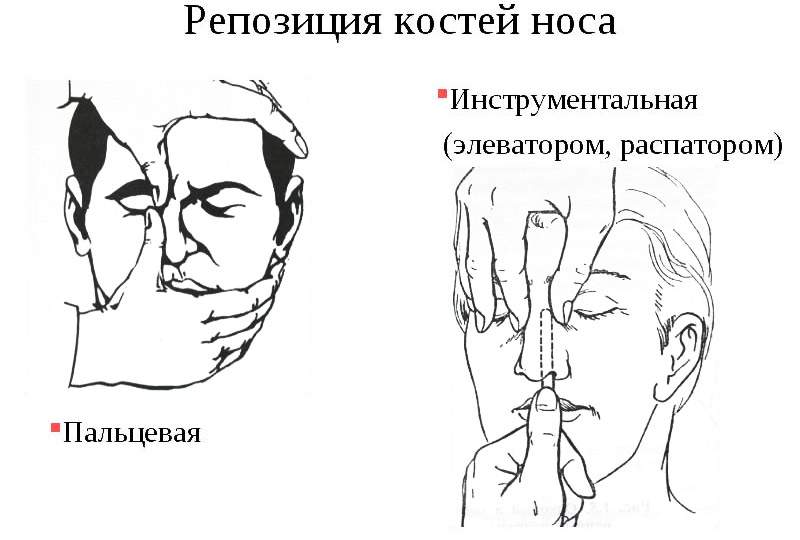
What are the possible causes?
In most cases, a broken nose is the result of a frontal or side impact. Sometimes a fracture can also be the result of a fall on the face. Common causes include:
- Consequences of sporting events, contact sports, boxing, martial arts, wrestling;
- Domestic situations including fights, drunken brawls. For children, this may include playground games, chase games;
- Car accidents in which the victim's nose is broken due to contact with the steering wheel or windshield. In this case, the fracture is usually associated with closed or open head trauma and other fractures;
- Occupational accidents in which safety regulations were violated. These situations are not uncommon among construction workers, agricultural workers and employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations;
- Injuries related to warfare. They are observed in soldiers participating in combat or training activities.
Symptoms of a broken bone
With various fractures of the facial and nasal bones, patients complain of the following symptoms
- strong pain;
- changes in contours;
- problems with breathing, smell;
- discharge of blood;
- Loss of orientation, dizziness and vomiting may occur.
The associated injuries sometimes result in the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the paranasal sinuses. The external examination shows:
Palpation reveals moving bone fragments, distorted bone protrusions, and sharp bone edges. If the swelling is extensive, palpation is difficult.
Extensive hematomas extending into the eyes and temple region may indicate a possible skull base injury. It is therefore important to see a doctor immediately if you have a nose fracture so that a diagnosis can be made to rule out serious brain damage.
recovery period
During rehabilitation, the injured person can take part in sports courses:
Only the doctor can select a set of exercises. When choosing the program, the doctor takes into account the injured person's health status, his age, gender and other important factors.
Remember: exercise is very important during rehabilitation, but exercises should be appropriate to the recovery period.
At the beginning, only the joints that are not covered by the bandage should be trained. When the bandage is loosened, the patient can perform exercises that involve the ankle joint. Perform the exercises gently, gradually increasing the amplitude and muscle tension. At a later stage, the injured person can also practice walking with the ankle:
You can also do half-squat exercises or run stairs. Do not forget that the injured person should be examined and x-rayed by a doctor once a month.

Possible complications
It is important to follow all doctor's recommendations after a talus fracture. Otherwise there may be dangerous consequences. In the injured person:
- Cartilage, fibers and blood vessels are destroyed;
- the risk of bone inflammation, aseptic bone necrosis and deforming arthritis is high;
- the ankle joint will no longer function normally;
- a severe migraine develops.
In addition, such an injury can drastically limit your ability to work, and that is not a particularly pleasant consequence.
Remember: such a leg injury can render even a normal person disabled.
Complications can occur if:
- the patient's operation, osteosynthesis, was not carried out correctly;
- the doctor accidentally injures vital systems or tissues while gaining access to the site of injury;
- the patient has a severe disorder of innervation, blood circulation within the joint; or
- the affected person has performed exercises from the rehabilitation program that are unacceptable for him in terms of the load.
It is possible to avoid complications. For this purpose, the injured person should follow a daily regime and consume appropriate foods. In addition, he should receive vitamins and calcium supplements. However, these are mostly prescribed to people at risk. Calcium-rich foods should also not be excluded from the diet.
In conclusion, a fracture of the talus of the foot is considered very dangerous. However, it is very rare in humans. However, if a victim who has sustained a lower limb injury is in doubt, they should go to the nearest trauma center and be examined. This is the only way a fracture can be confirmed or ruled out. And get help from a qualified specialist. The injured person should then undergo the treatment and rehabilitation prescribed by the doctor. This allows the injured person to regain mobility in the injured limb.
Read more:- Fracture of the calcaneus of the foot.
- Fracture of the heel bone.
- Fracture of the 5th metatarsal.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
- Displacement fracture of the heel bone.
- How to distinguish a fracture from an ankle sprain.
- Closed fracture of the ankle.
- fracture of the lateral malleolus.
