PS To avoid speculation: only editing in Lightroom (Photoshop only noise reduction, sharpening and cropping)!

- Fracture of a toe in a child
- Symptoms of a broken finger in a child
- Symptoms and signs of fractures of the terminal phalanges
- Diagnosis of fractures of the terminal phalanges
- Injury to the nail bed
- diagnosis
- First aid
- tactics
- rehabilitation period
- Symptoms of nail exostosis
- causes for the emergence
- Further treatment
- preventive measures
- 0 Cross-sectional view of the phalanx in the area of the nail:
- 0 Schematic representation of the nail phalanx with the main elements of the finger:
- Interactions with other medicines
- Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
- We are the ones who create a world you want to return to
- Mriya in people
Fracture of a toe in a child
A broken toe is an injury in which one or more of the bones that make up the phalanges of the toes are broken. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, tissue swelling and subcutaneous hematomas. The doctors of the children's department of the SM Clinic in Moscow are engaged in the diagnosis and conservative treatment of toe fractures in children of different age groups. If the injury requires surgical treatment, the young patient is referred to a specialized hospital.
Finger fractures account for approximately 2 % of all injuries in children. Serious injuries are extremely rare in young children due to the structure and function of bones: the younger the child, the less likely a serious injury will occur.


Symptoms of a broken finger in a child
The main symptom of a bone injury is severe, immediate pain. The feeling increases when you try to stand on your foot, feel the injured area, or move your toe. Swellings and hematomas gradually form, often spreading to the foot. A displaced fracture is often accompanied by a visible deformation of the toe, while an open fracture involves injury to the skin. Bone splinters are then visible in the wound.
Visual clues that indicate a broken toe are helpful, such as: E.g.:
- Visible deformation, sometimes shortening of the toe bones compared to a healthy hand;
- Significant swelling;
- Subungual and subcutaneous bruising at the injury site;
- Redness, sometimes blue discoloration of the skin.
A child who injures himself in this way complains of severe pain and inability or limitation of movement of the injured fingers. Fractures of the fingers are almost always accompanied by bruising, and additional symptoms in children may include numbness and reduced sensation in the area of impact.
Skin injuries result in abrasions and scratches that can cause minor bleeding.
Open fractures result in wounds with jagged, bruised edges in which bone and soft tissue fragments are visible.
Symptoms and signs of fractures of the terminal phalanges
The terminal phalanx is swollen and painful. A fracture with significant soft tissue damage can lead to the development of hyperesthesia, which often persists long after the fracture has healed.
As a rule, blood becomes trapped between the nail plate and the nail bed (subungual hematoma), which can cause the nail to turn completely or partially blue-black and bulge. Rupture of the nail bed most commonly results in a subungual hematoma.
Severe damage to the nail bed can lead to permanent deformity of the nail.
Diagnosis of fractures of the terminal phalanges
A finger fracture is diagnosed using an x-ray in anteroposterior, oblique and lateral views. In the lateral view, the injured finger is separated from the other fingers.
In most cases, the fractures are treated symptomatically with a protective covering of the finger (e.g. commercially available aluminum or plastic protectors) for 2 weeks. In rare cases, the fractures prove to be displaced, requiring surgical intervention.
Persistent hyperesthesia may resolve with desensitization therapy.
Subungual hematomas can be drained to relieve pain by puncture (trepanation) of the nail, usually with an electrosurgical device (if the nail is not painted) or with a needle with a diameter of 18 mm inserted in a twisting motion; For both methods, the pressure on the tip of the device should be adjusted as soon as a feeling of absence (indicative of a punctured nail) occurs. If trephination is performed carefully and quickly, anesthesia is not required. Otherwise, a finger nerve block (injection of a local anesthetic into the root of the finger) can be performed.
Injury to the nail bed
In the past, removal of the nail was recommended in all cases of finger break wounds (with or without a fracture) to assess the extent of the nail bed injury and determine whether repair is necessary. Today it is considered that removal of the nail is not necessary if the nail itself is not significantly injured or deformed. In such cases, the crack in the nail bed, if present, usually heals well on its own after splinting; if it is necessary to relieve the pain caused by a subungual hematoma, trephination is performed.
If the nail is severely damaged or deformed, it should be removed and the nail bed restored with thin absorbable sutures (e.g., 6-0 or 7-0 polyglactin-coated sutures). The fingertip is then wrapped with a non-adhesive bandage (e.g. Xerophorm gauze); the wound should be monitored for 24 hours to prevent painful adhesion of the nail bed to the bandage. Experience has shown that, despite the open mechanism of injury, it is not necessary to prescribe antibiotics after nail bed repair for fragmentary fractures with bone separation.
diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on interviewing the patient, visual examination and X-ray examination in various projections.
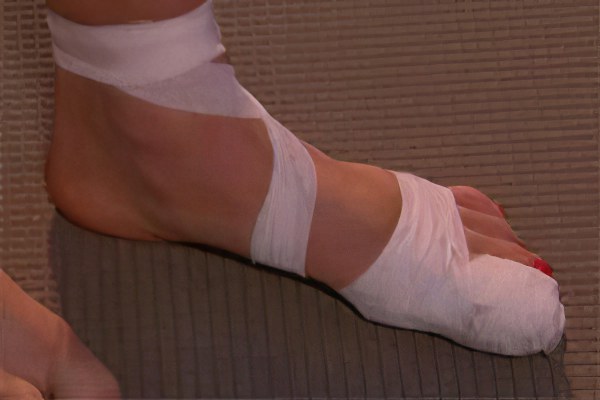
First aid
The foot and toe should be protected by applying a splint (hard object) and a bandage. In the case of an open fracture, make sure that the dressing is sterile.
tactics
Treatment depends on the location and type of injury.
- For open fractures, antibiotics are given to prevent infection and a tetanus shot may be given;
- In the case of phalangeal fractures, the nail is perforated, the blood is removed from below and the fracture site is cut open with other phalanges and neighboring fingers;
- In the case of fractures without displacement of the middle and basal phalanges, these are also immobilized with a plaster for up to two weeks;
- For fractures with displacement, the injured finger is stretched axially or the fragments are reduced manually and then fixed with plaster shoes;
- If there are multiple fractures, a plaster cast is also applied;
- In closed fractures with displacement, as well as in comminuted fractures, a closed repositioning (insertion) of the bone fragments is carried out; this must be very precise and accurate to avoid abnormal bone fusion and possible subsequent deformities;
- For fractures of 2-5 fingers, a plaster cast is applied;
- For fractures of the big toe, a plaster cast is applied from the toe to the knee. Painkillers are given to relieve pain. An intra-articular fracture usually requires surgery to repair the joint using special spokes. The plaster cast is worn for 6-8 weeks.
rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation measures include massages, physiotherapy and physiotherapy. A long-term cast is uncomfortable, but necessary to allow the bones to grow together properly. If the bones do not heal properly, this leads to improper weight distribution on the foot and further problems with walking.
It is recommended to walk as little as possible during rehabilitation, to wear comfortable, spacious shoes without high heels and to elevate the affected leg when resting, for example on a pillow. Cold compresses can be applied for the first 2 to 3 days to reduce swelling, but should not be used excessively.
Maintain a sensible diet, eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, and pay special attention to foods rich in calcium: cheese, cottage cheese, etc. At the same time, you should limit or avoid the consumption of strong coffee, carbonated drinks and alcoholic drinks, as they add calcium to the body revoke. It is also recommended to take multivitamins C, D and B12.
Symptoms of nail exostosis
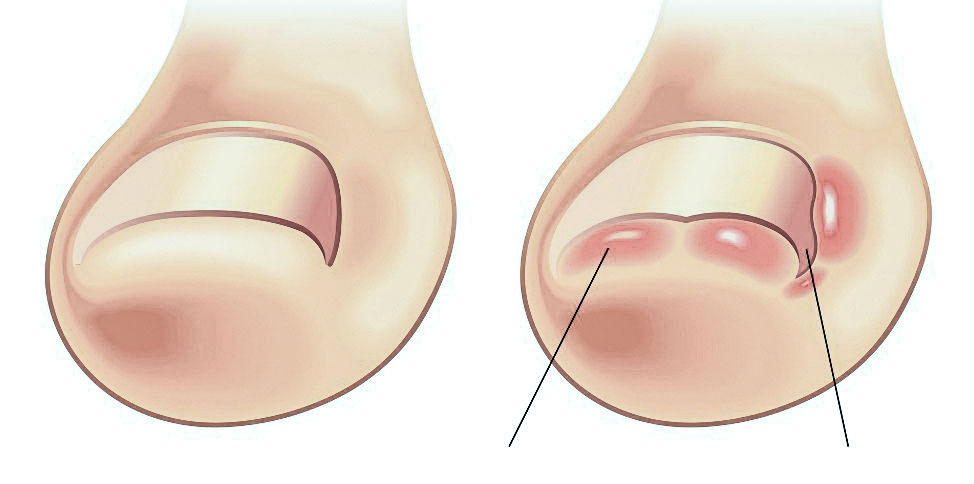
Nail bed exostosis can develop in different ways. In some cases, the osteochondral protrusion is small and may not be noticed for years. It is diagnosed by chance when looking at x-rays taken for other diseases. More commonly, however, exostosis of the lower foot causes discomfort and pain and limits motor function of the affected toe. The patient notices an enlargement of the anterior perineal fold where the ingrown nail lies. This is sometimes accompanied by redness and swelling of the periungual area. The symptoms worsen with any physical activity - especially when running or walking, but also when wearing tight shoes or even with slight pressure on the end of the big toe. The main symptoms of exostosis of the toe bone are.
- Spontaneous peeling of the nail;
- deformation of the nail plate;
- Enlargement of the periungual nail bed;
- Ingrowth of the nail edges.
The formation of a cartilaginous neoplasm under the nail bed leads to an elevation of the free edge of the nail plate and the central part of the nail plate, as well as various deformations. Gradually, the nail of the affected toe begins to deform. In some cases, onychocryptosis may also occur.
Subungual exostosis shares similarities with various types of onychodystrophy, ringworm, and ingrown toenails. Therefore, it is advisable to consult an experienced podiatrist to diagnose the causes of the changes in the shape and condition of the nail plate.
As the disease progresses, subungual exostosis worsens the appearance of the nail and causes the patient unpleasant and frankly painful sensations. Without qualified and timely treatment, this pathology leads to complete loss of the nail!
causes for the emergence
The main cause of subungual exostosis is long-term, frequent trauma to the fingertip. This is often the case when wearing tight, cramped shoes for a long time, jogging for long periods or walking frequently. The condition is common in athletes, cyclists (especially those who use toe braces), ballerinas, and people with an active lifestyle. However, the trigger for cartilage overgrowth is the loss of the natural protection of the fingertip, the nail.
Traumatic exostosis of the nail is a consequence of:
- Hit on the finger – trauma to the finger bone when the nail breaks or falls off spontaneously;
- Surgical nail removal – in the treatment of ingrown nail plates;
- Reducing nail thickness – in the treatment of fungal infections.
Injury to the nail plate or loss of the nail causes increased stress on the toe - especially if the foot tips over while walking or running. This leads to mechanical irritation of the tissue, which is expressed in a compensatory reaction of the body - the formation of a new robust defense, cartilage exostosis.
Further treatment
If the numbness affects the fingers – thumb, index finger, ring finger, middle finger, or all of them – physical therapy treatments can help. They are an excellent complement to drug treatment and help relieve muscle spasms, eliminate swelling and restore normal range of motion in the joints.
- Massages are indicated both directly on the affected area (gentle kneading with the palm of the hand) and in the collar area and all over the body. Massage tones the body, eliminates vascular and neurological pathologies.
- Manual therapy – restores the integrity and flexibility of tendons and increases blood flow to the limbs. The treatment improves the nutrition of the tissues of the hands, eliminates thickening, restores the muscle strength of the hands.
- Gymnastics – improves blood circulation in the upper limbs and body and helps peripheral blood vessels to function properly. Simply turning the head and upper body to the right and left, bending forward and backward and rotating the arms significantly improve the patient's condition.
- Physiotherapy – laser therapy, magnetic therapy, hirudotherapy and other treatments help restore normal blood circulation to the affected area, reduce its temperature, activate cell regeneration and improve metabolism.

preventive measures
To prevent numbness in the fingers, the following recommendations should be followed
- balanced diet – food should be healthy; spicy, salty and hot foods should be avoided;
- Drink – around 40 ml of liquid (water, mineral water, green tea, dried fruit compote) per kg of body weight should be drunk daily;
- Loose clothing for every day - clothing should not restrict freedom of movement or constrict any parts of the body;
- Wearing gloves made of natural materials in winter – the limbs should not be exposed to the cold;
- Sleeping on orthopedic bedding – keep the body in a comfortable position at night;
- Taking hourly breaks to stretch your legs – especially if your arms are heavily strained (office workers, seamstresses, etc.);
- avoiding smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Go for checkups twice a year.
If you regularly experience numbness in your fingertips, you should see your doctor to protect yourself from future complications.
0 Cross-sectional view of the phalanx in the area of the nail:
1.1 Lunula
1.2 nail plate
1.3 lateral ridge
1.4 Hyponychium
1.5 dermis
1.6 Bony phalanx
1.7 Lateral flap
2.1 Proximal fold (posterior ramus)
2.2 Eponychium
2.3 Real epidermis
2.4 Pterygium
2.5 Nail fold
2.6 nail plate
2.7 Distal part of the nail plate (free edge)
2.8 nail bed
2.9 Hyponychium
2.10 Anchoring elements
2.11 Bony phalanx
2.12 matrix
The nail bed is a An important anatomical element of every nail. It is responsible for the blood supply and innervation of the nail bed. Damage to this area slows the growth of the nail, significantly changing its appearance.
The nail has several anatomical units. One of them is the root. It is partially covered by the skin fold (cuticle). This part affects how the length of the nail plate will grow.
0 Schematic representation of the nail phalanx with the main elements of the finger:
3.1 Skin of the finger.
3.2 Posterior nail fold (proximal fold)
3.3 Lunula
3.4 Free edge of the nail
3.5 nail plate
3.6 Lateral (lateral) nail fold
The free edge is the distal part of each nail plate. When doing a manicure or pedicure, this is the area where most of the work is focused. There are no nerve endings or blood vessels on the free edge of the nail plate. Therefore, there is no bleeding or discomfort when this area is processed with a file.
Another part of the nail that is sometimes forgotten are the Sine. This is the area where the nail plate meets the shaft of the skin. During a manicure or pedicure, the treatment of the maxillary sinuses should be done carefully. Careless treatment of this area can be dangerous as it can lead to infection. The sinuses should only be treated with an instrument that has been previously disinfected.
Interactions with other medicines
Only alcohol interaction studies have been conducted. Animal studies have shown that there is no interaction between mebeverine-SZ and ethanol.
Before taking Mebeverin-SZ, ask your doctor if.
- if you experience symptoms for the first time;
– unwanted and unexplained weight loss;
- rectal bleeding or blood in the stool;
- if anyone in your family has been diagnosed with bowel cancer, celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease;
- if you are over 50 years old and the symptoms appear for the first time;
Consult your doctor if your condition worsens or your symptoms do not improve after 2 weeks of use.
Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
No studies have been conducted on the effects of the drug on the ability to drive and other mechanisms. The pharmacological properties of the drug and the experience with its use do not indicate an adverse effect of mebverine on the ability to drive and use machines.
Foil-coated tablets, 135 mg.
Pack of 10 tablets in polyvinyl chloride film and painted aluminum foil or heat-sealed aluminum foil.
All 30 tablets in low pressure polymer polyethylene jars with HDPE closures or in low pressure polymer polyethylene vials with HDPE closures or imported low pressure polyethylene bottles with HDPE closures.
The cardboard packaging contains each jar, bottle, 3-pack, 4-pack, 5-pack and 6-pack with instructions for use.
We are the ones who create a world,
to which you would like to return
back
The Mriya team has prepared a special route suitable for both your own arrival and a transfer with our chauffeur from any city in Russia. If you choose public transportation, let the concierge service think about the logistics and find the most convenient solution for you.
Mriya in people
There was a time when I thought: What's the point of organizing a wedding?
But what could be better than investing in magical moments.
We can imagine how we will show the pictures with Mriya to our children and they will say that we were beautiful and not always old
As you can see by our faces in these photos.
We absolutely love our stay at @mriya_resort @mriya.winepark
We almost merge with the landscape.
#mriyalovesyou #mriyareporter #steaming bridge #mriyaresort#blacksea#crimea
It probably would have been more of a Luhari photo in the @mriya_resort dressing gown, but so far so good.
Read more:- lower leg prosthetics.
- name of the fingers.
- How to amputate a leg.
- foot bone in Latin.
- Why are the big toes crooked?.
- Why the socks tear at the big toe.
- Growth zones of the foot bones.
- Why are a teenager's toes crooked?.
