The ICD-10 code for foot mucus is L03.0, and its immediate cause is infection of the foot tissue with bacteria that cause purulent inflammation. These infiltrate the tissue:
- A stiff first toe (Hallux rigidus
- diagnosis
- classification
- diagnosis
- lifestyle
- Alcohol abuse
- diagnosis
- treatment methods
- Treatment of hammertoe deformities:
- Surgical Treatment of Hammertoe Deformity:
- Hammertoe Deformity Care:
- Prevention of hammertoe curvature:
- Types of deformation
- symptoms
- The back: treatment with herpes simplex
- Gontine: treatment, medications and therapies
- Findings and discussion
- Conclusions.
A stiff first toe (Hallux rigidus
Hallux rigidus or the stiff metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is a form of osteoarthritis. It is characterized by varying degrees of defects on the articular surfaces. The exact cause of the condition is not known, but it is thought to be caused by overuse of the joint as a result of excessive stress on the foot and wearing uncomfortable footwear.
The big toe joint is one of the most heavily stressed areas of the foot. Therefore, as the pathology progresses, the pain and discomfort when walking and gait change. All of these symptoms mean that the patient should be gentle with the affected area when moving around. This changes the load on the entire limb and promotes the development or progression of degenerative changes in the knee and hip joints.
Treatment of a stiffened first toe abroad is aimed at correcting the pathological changes through conservative methods or, if the process is neglected, through surgery.
diagnosis
Orthopedic clinics offer a minimum level of examinations to diagnose the pathology. By taking x-rays of the affected foot in anterior and lateral projection, one can get a complete picture of the extent of the pathology. In clinics abroad, digital computer tomographs are used, which can be used to take X-rays with minimal strain on the body. The images obtained can be stored and processed in a database so that they can be re-examined at any time in different modes.
classification
Clinical classification:
Classification of the International Society of Lymphology (ISL).
Table 1. Classification by disease stage [7].
| stage | definition |
| 0 (or Ia) | Latent or subclinical, when edema is not clinically present although lymphatic transport is impaired, characterized by subtle changes in the ratio of tissue fluid and composition and changes in subjective symptoms |
| Stage 1 (easy) | Systemic, transient, mild edema in the evening, which in most cases subsides in the morning or after rest. The swelling increases with strenuous exercise or prolonged immobility. Clinical picture: The texture is pasty, pressure leaves an indentation. The skin is unchanged, easily shifted and pale. |
| Stage 2 (moderate severity) | It is characterized by persistent swelling that continues even after a night's sleep. The clinical picture is characterized by connective tissue hypertrophy, skin tension, thickening, poor mobility, no fossa under pressure and a pain syndrome. |
| Stage 3 (severe) | Lymphatic drainage may become irreversible, fibrous cystic lesions appear in the affected tissue, and elephantiasis develops. The affected limb loses its contours and proportions. Hyperkeratosis, papillomas and tissue hypertrophy in the form of misshapen nodules ('cushions') separated by deep folds occur. Concomitant diseases and complications may develop: deforming osteoarthritis, contractures, eczema, lymphadenopathy in skin trauma (the swelling may decrease), trophic ulcers, possible development of purulent-septic infection. |
diagnosis
List of basic and additional diagnostic measures:
Basic (mandatory) diagnostic tests performed on an outpatient basis[7]:
– USAS.
Additional diagnostic examinations carried out on an outpatient basis.[7]:
– MRI/lymphangiography;
– Computed tomography/angiography;
– Genetic testing for hereditary syndromes.
Minimum list of tests to be performed upon referral for planned hospitalization:According to the internal regulations of the hospital, taking into account the current regulation of the competent health authority.
Basic (mandatory) diagnostic examinations upon inpatient admission: none.
Additional diagnostic examinations in the inpatient area: none.
Diagnostic measures in the emergency phase: none.
Diagnostic criteria for making the diagnosis:
Complaints about:
– swelling;
– skin changes;
– trophic disorders.
Anamnese:
– Hereditary and family-related;
– surgical interventions and trauma;
– Presence of oncological diseases;
– inflammatory processes;
– venous and artery diseases;
– trips abroad;
– Immobilization due to orthopedic or neurological processes;
– Administration of medication.
Anamnese:
– Duration of the illness;
– time of onset of edema;
– Duration of the reversible phase;
– factors favoring the process (pregnancy, significant pressure on the limb over a certain period of time, minor trauma, sometimes minor skin injuries (insect bites, scratches);
– Starting site of peripheral edema (distal or central);
– soreness;
– Presence of infectious complications.
lifestyle
Among these aspects we find other influencing factors: for example, lack of exercise and sedentary work, which lead to poor blood circulation and swelling Swelling in the legscaused by excess weight. Sometimes, especially with women, it happens that feet swelling due to tight shoes, e.g. B. with pumps or soft ballerina shoes with flat soles. In such cases, the problem disappears and only resurfaces when the shoes are put back on. Pay attention to the poor composition of your diet: daily consumption of fast food with too much salt is not good for your general health, among other things, it puts a strain on your health Kidneys and causes water retention in the body.
Sometimes it is enough to take your daily medication, for example for your blood pressure. Blood pressure or diabetes. However, these medications are the most common cause of swelling foot. If you see a connection between medication and swellingyou should yourself to your doctor talk about these side effects. Other medications that cause these problems include estrogen-based medications, testosterone supplements, blood pressure medications Blood pressureCorticosteroids and non-steroidal drugs such as Ibalgin and others.
Alcohol abuse
Do you like wine? We are sure that even a good glass of wine every Friday won't hurt you. But if you drink alcohol every day, and it doesn't matter whether it's wine or liquor, it leads to water retention in your body, which is your Legsas well as your face or hands may swell.
After the winter season, everyone is looking forward to the welcome warmth of barbecue evenings with family and friends. Here’s to long weekend trips and swimming in the water. However, what can make summer uncomfortable is the heat, which causes, among other things, the following swelling feet. This leads to reduced blood flow in in the veinswhich then begins to collect in the legs legs and causes... swelling or even a feeling of heaviness. These sensations can often be confused with inflammation. In this case, too feet Swelling and pain, but with the difference that one leg is usually affected, which can also become red.
diagnosis
Visual inspection of the injured limb usually reveals signs of inflammation: swollen and edematous tissue, flattening of the arch of the sole, redness, overheating, etc. Most of these signs are characteristic of various types of inflammation, so an instrumental diagnosis of phlegmon of the foot, which also includes examinations, is required:
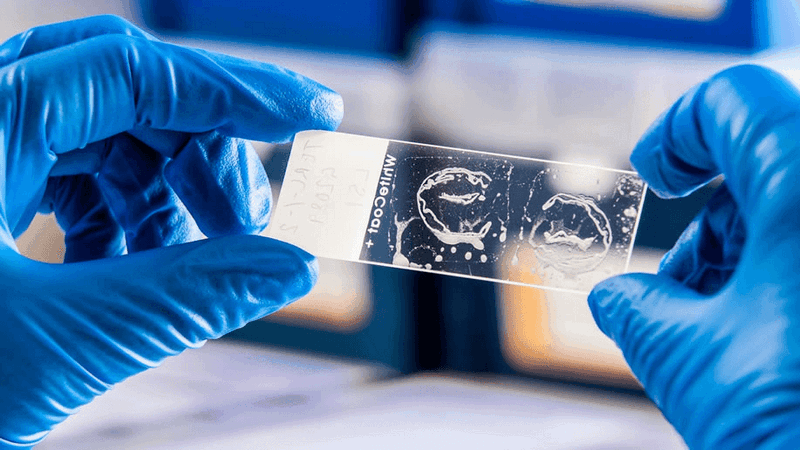
- Blood – general laboratory analysis;
- Puncture of the contents of the inflammatory focus with bacteriological examination and identification of the pathogen;
- Bacteriological culture of the puncture in laboratory media to detect the infectious agent and determine antibiotic resistance.
X-rays of the foot may also be required to determine the depth of tissue damage, as well as differential diagnosis to clarify the nature of the purulent process.
treatment methods
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the foot, the purulent-inflammatory process rapidly spreads to the entire lower extremity and progresses. Therefore, any form of pathology requires immediate hospitalization of the patient. Outpatient treatment of the abscessed foot is excluded because the patient must be under constant medical supervision. The operation and subsequent conservative treatment are carried out in a medical facility.
The operation consists in opening the inflammation, removing pus and necrotic tissue, washing and draining the resulting cavity. After the operation, an aseptic bandage is placed on the wound. Further treatment consists of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and general measures. If the phlegm is of anaerobic origin, the patient receives a serum against gangrene. In cases of severe poisoning, infusion therapy is indicated.
Since purulent tissue inflammation is a serious clinical picture, preventative measures against foot phlegmon are extremely important, including
- Prevention of foot injuries, even minor ones;
- Use of sturdy shoes and soles in traumatic situations;
- timely antiseptic treatment of the injured areas;
- timely detection of inflammation and referral to a medical institution;
- timely treatment of inflammations such as carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis, etc;
- Strengthening immunity, treating immunocompromised conditions.
Treatment of hammertoe deformities:
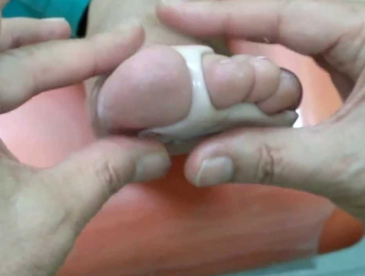
Conservative treatment. In the initial stages, it is advisable to wear loose shoes and put a bandage on the rear foot.
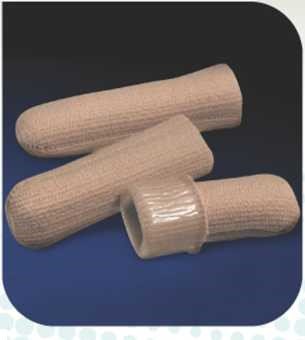
In addition, conservative treatment of hammertoe deformity includes the use of special orthopedic aids, such as: B. a scapula or hammer toe splint. The use of such orthopedic devices helps to gradually straighten the deformed toe and relieve pain. It is also possible to use protective caps or a gel bandage to prevent the toe from rubbing against the shoe.
Surgical treatment consists in eliminating the pronounced flexion contracture of the interphalangeal joints.
Surgical Treatment of Hammertoe Deformity:
- Symptomatic. This procedure removes all bony growths and protrusions. With this surgical procedure, excellent treatment results can be achieved in a short time. However, there are cases where the toe deformity recurs after a few years.
- radical. During this procedure, the bones and ligaments are deeply plastically deformed. The operation is designed to shape the transverse arch of the foot and eliminate flat feet (one of the main causes of hammertoe deformity). This treatment requires a longer rehabilitation period than symptomatic treatment, but is significantly more effective.

If surgery on the patient's foot is contraindicated, custom-made orthopedic shoes should be made, and in case of hammertoe deformities, the shoes should also be provided with a soft upper.
Hammertoe Deformity Care:
Typically, the patient does not require additional care and is able to care for themselves.
Prevention of hammertoe curvature:
The most important prevention strategy is early detection and treatment of transverse flatfoot and valgus deformity of the foot (toe bone). Comfortable, loose footwear should also be preferred over tight and uncomfortable shoes.
Types of deformation
The Hamilton test indicates 4 degrees of hammertoe deformity:
- Degree zero – the joint has no instability;
- Grade one – mild instability in which less than half of the articular surface area ratio is reduced;
- Grade two - moderate instability (more than 50 % of the articular surfaces are unsupported)
- Grade three – pronounced instability (the finger is dislocated during diagnostic examination);
- Grade four – dislocation that cannot be corrected by passive methods.
It is assumed that the more pronounced the instability of the joint, the more severely the sole ligament is affected.
symptoms
The main symptoms of hammertoe are:
- Pain, the intensity of which increases as the pathological process progresses;
- A visible deformity that disrupts the aesthetics of the foot and prevents the wearing of fashionable footwear.
During objective examination, the traumatologist detects abnormal flexion in the first interphalangeal joint and hyperextension in the second interphalangeal joint. The big toe joint is in a similar position. In most cases, the affected toe has deviated towards the back of the foot.
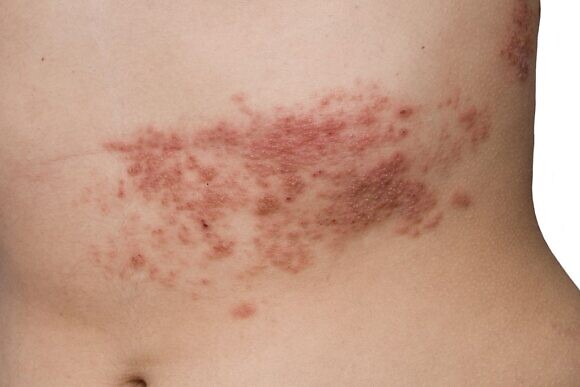
The back: treatment with herpes simplex
Don't blindly trust the advice of family and friends who don't have medical training. Any tinctures, baths, rubs, or applications to the skin can cause damage, increasing itching and increasing the area where the rash occurs. In many cases, folk medicine not only cannot eliminate the disease, but can also be dangerous.
The danger is that when experimenting with self-medication, the disease progresses, those affected feel worse, and complications may arise that complicate the healing process when there is a desire to see a doctor. Remember that the argument 'even if it doesn't help, it doesn't hurt' doesn't apply in this case. If you suspect shingles, see your doctor immediately and start treatment with proven medications.
Gontine: treatment, medications and therapies
Currently, all pharmacological measures for the treatment and prevention of shingles can be divided into three main groups: chemotherapy (acyclic nucleosides), immunotherapy and a combination of both, in which the patient simultaneously takes chemotherapy and immunomodulating drugs.
Vitamins B1, B6 and B12, ascorbic acid, rutin and, if necessary, antihistamines are also used. If the pain is severe, the patient can be given NSAIDs and analgesics.
Many doctors believe that taking acyclic nucleosides alone as the main treatment is not enough and that this monotherapy is not justified. i These drugs are most effective only in the first 72 hours of the disease and can only suppress the herpes virus in the active replication phase, that is, the phase in which two daughter DNA molecules are created on the basis of the mother DNA molecule. They have no effect on viruses that already exist and are in a latent or 'sleeping' state. In addition, acyclic nucleosides do not contribute to the restoration of immunity.
To treat herpes in the body, patients need immune correction. Therefore, in this case, a strategy of combining acyclic nucleosides and interferon alfa-2b preparations, which is considered reasonable and most effective by clinicians, as reflected in clinical and methodological guidelines, would be appropriate.
Interferons are 'universal' fighters that, in contrast to antibodies, are not directed against specific pathogens, but rather represent a non-specific (innate) immunity and
which are able to fight all viral particles. Interferons are able to stop the reproduction and spread of viral or bacterial particles.
Findings and discussion
At the time of referral, patients complained primarily of pain in the lower limbs due to arterial insufficiency (intermittent claudication; pain that disappears when the limbs are lowered). In 42 % patients, pain or sensory changes were associated with the development of diabetic neuropathy. The examination data of the limbs also corresponded to non-critical (mostly IIB-IIIA) stages of CHD against the background of neuropathic and angiopathic changes (most patients had a mixed form of CHD). Most patients had distal lesions of the main vascular bed with impaired patency of the arteries of the lower extremities and feet, which in many cases precluded reconstructive vascular surgery and was an indication for conservative treatment (Table 1).
/12/1.png)
When analyzing the perfusion indices and amplitude-frequency characteristics of microcirculation using the LDFgram data, we examined: microcirculation index (M), which reflects the level of basal perfusion, tissue perfusion; Standard deviation (σ) - temporal variability, fluctuation of erythrocyte flow (len), amplitude of low frequency fluctuation (ALF) and derived parameters: ALF/M - myogenic activity index (vasomotor) and σ/ALF - neurogenic activity index (microvascular tone).
LDF has reliably established that patients with diabetic foot syndrome with ASD stages I-IIIA have a reduced microvascular index. And this reduction is more pronounced in the first interdigital space on the dorsal surface of the foot than in the medial malleolus region.
The relatively greater blood flow in the ankle area is most likely due to increased tension of the precapillary sphincters and smooth myocytes in the microvascular wall, causing arteriovenous shunts to open and blood to be released into the venous system bypassing the capillary network. This phenomenon, also known as steal syndrome, is a criterion for the specifically diabetic character of the vascular changes that accompany the simultaneous development of diabetic polyneuropathy.
Conclusions.
1. Abnormalities of cutaneous microcirculation in patients with diabetic foot syndrome and chronic arterial insufficiency of Fontein-Pokrovsky stage I-IIIA are evidenced by a decrease in the microcirculation index to 4.1 perfusion units, myogenic tone to 202.9 % and neurogenic vascular tone 15, 7 % in the medial ankle area and a decrease in the microcirculation index to 2.3 perfusion units, a decrease in vasomotor flax to 1.8 perfusion units and neurogenic activity to 18.8 % in the first interdigital interval on the dorsal surface of the foot.
2. Patients with ischemic and mixed forms of diabetic foot syndrome had increased plasma malondialdehyde levels up to 1.62 μmol/l with a simultaneous decrease in catalase activity to 0.48 mmol/mg, increased sialic acid levels of 233-235 units, there was plasma reactive protein determined, indicating a pronounced imbalance in the lipid peroxidation system with a predominant pro-oxidant activity and depletion of the enzymatic antioxidant guard cell, as well as the development of a chronic inflammatory process. These changes are accompanied by a decrease in the microcirculation index in laser Doppler flow measurement, which shows the possible influence of lipid peroxidation disorders and inflammatory processes on the development of microcirculation disorders and ischemic changes in the tissues of the limbs in diabetes.
3. Under the influence of polymagnetotherapy by a pulsed magnetic field, stimulation of microcirculation in the limb occurs, which is characterized by an increase in the microcirculation index by 2-3 times, its coefficient of variation by 1.5 times, the occurrence of high-frequency oscillations and a 1.5-fold increase in the amplitude of the low-frequency oscillations or myogenic activity.
4 The effectiveness of polymagnetotherapy by applying a pulsed magnetic field in the comprehensive conservative treatment of diabetic foot syndrome with chronic arterial insufficiency is evidenced by the improvement in the quality of life of patients after treatment: pain sensations decrease, pain-free walking distance increases, emotional mood, social adjustment and general vital tone improve.
Read more:- Why amputate legs for diabetes?.
- X-ray of Charcot's foot.
- Diabetic foot ulcers.
- Photo: Diabetic heels.
- foot in Latin.
- Metatarsal amputation.
- Foot.
- How much does shoulder dislocation surgery cost?.
