At the stage of intermittent flatfoot, in addition to the above measures, the recommendation is to change the work environment in order to reduce the static load on the foot. With flat feet, orthopedists recommend wearing orthopedic shoes and special orthoses as part of the complex of therapeutic measures. If the flatfoot progresses further, surgical treatment is indicated. At the stage of flatfoot, conservative methods are ineffective. Various plastic surgeries: resection of bone parts, tendon transplant, etc.

- Clubfoot: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
- Symptoms of Flat Feet
- Orthopedic foot treatment
- The most common operations to correct foot deformities
- Diabetic foot symptoms
- Pathogenesis of the diabetic foot
- complications
- Treatment feedback
- vascular disease
- myositis
- Symptoms of Flat Feet
- Transverse flatfoot
- diagnosis
- Causes of pain syndrome
- Which diseases are manifested by pain?
- Why do the feet hurt?
- complications
- Pain in foot and swelling
- diagnosis
Clubfoot: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Clubfoot is a condition in which the arch of the foot flattens out. As a result, the foot almost completely loses its cushioning properties. The feet of those affected hurt a lot after walking for a long time. Women are four times more likely to suffer from this condition than men. In the advanced stage, flat feet lead to arthritis, arthrosis, back and calf pain and a curvature of the spine.
The human foot is unique: due to its structure, it is elastic. The foot has two arches: the transverse arch, which lies between the balls of the toes, and the longitudinal arch, which runs along the inside edge of the foot. The arch of the foot is supported by a system of ligaments and muscles. No animal, not even a kangaroo, has a springy foot.
A healthy foot helps people keep their balance and reduces tremors when walking. When the foot's musculoskeletal mechanism is weakened, the foot becomes flat and unable to support the load. This leads to the development of flat feet.
Symptoms of Flat Feet
The disease develops gradually and is often not noticed by those affected. First, the affected person feels a slight pain in the legs and feet. Feet tire more quickly after walking or standing work. At the end of the day, feet swell and feel heavy. Symptoms subside after rest or massage.
With flat feet, the shoes wear out faster, especially on the inside. The foot increases in length or width and one has to buy bigger shoes. Women find it difficult to walk in high heels.
Orthopedic foot treatment
The term 'foot orthopedics' takes on a whole new meaning in modern medicine, which differs markedly from the dominant doctrine in Soviet medicine. For many decades, there was virtually no systematic approach to the comprehensive management of diseases associated with deformities of the osteoarticular skeleton of the foot. There was a small list of surgeries performed according to standard indications, without thorough enough diagnostics. As a result, there were few positive outcomes, and there was a negative perception among the medical community and patients about the severity and painfulness of the postoperative period and the low number of successful procedures. All this was due in large part to underdeveloped diagnostic capabilities, lack of knowledge of new data on the pathogenesis of the process and outdated surgical techniques.
Today, the orthopedic care of foot deformities is dealt with comprehensively, among other things, on the basis of multi-centre studies:
In modern orthopedics, on the basis of a large amount of collected material, new principles of surgical treatment of the foot have emerged, which are presented below:
- Maximum correction of osteoarticular deformities
- Stable bone anchoring through special techniques
- Complete correction of the entire arch of the foot
The principle of maximum correction means a one-time correction of all elements of the foot deformity with restoration of the normal arch of the foot and the ability to wear normal footwear in the postoperative period without removing the internal fixation structures.
The most common operations to correct foot deformities
The approach to the choice of surgical intervention is always individual to each patient, but there are several universal approaches.
- Elimination of the 'thickening' itself
- Restoration of the anatomical structures at the base of the 1st finger (correction of the ligaments)
- Alignment of the axis of the 1st finger.
The main surgical intervention is osteotomy (splitting of the bone) and fixation (anchoring of the newly formed bone in the right direction, removal of connective tissue due to inflammation). During the osteotomy, the orthopedist/traumatologist correctly aligns the axis of the first finger. The osteotomy process itself is the secret of a successful operation.
Historically, a transverse osteotomy was performed, followed by precarious fixation with thin spokes or a solid metal structure. After such a procedure, the load on the foot is eliminated for 3-3.5 months. During this period, the ligaments and muscles of the foot atrophy, the foot becomes unsightly, rehabilitation is delayed, and the ability to wear normal footwear is severely reduced (the presence of a massive metal structure on the bone). The metalloplasty is then removed in a second operation. This is extremely annoying, painful and uncomfortable, especially for the elderly. The results are usually very unpredictable. After that, it is difficult to wear shoes and scars form on the foot. The whole recovery process takes up to 6-7 months.
A completely different result is obtained with the modern technique of longitudinal or horizontal osteotomy, the so-called Chevron or SCARF. This type of surgery is performed at ANDROMEDA Clinic by leading orthopedic and trauma surgeons using a minimally invasive oscillating saw that is only used in our clinic. After using special Baruca screws to fix the bone fragments, the result of the operation exceeded all expectations.
Diabetic foot symptoms
The starting point for the development of DFS is not the date of diagnosing diabetes, but the time when the first symptoms of DFS (isolated spikes in blood sugar, dry mouth and others) are noticed.
- numbness, chills, burning, swelling of the feet and other discomfort;
- hair loss on the feet and lower legs, sweating on the feet;
- skin discoloration (hyperpigmentation, hyperpigmentation, cyanosis);
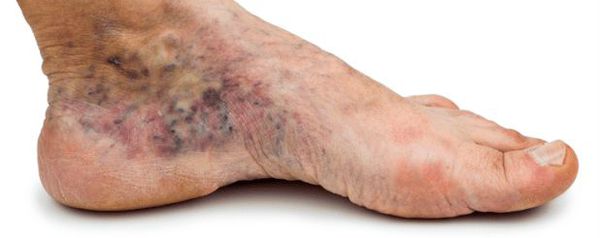
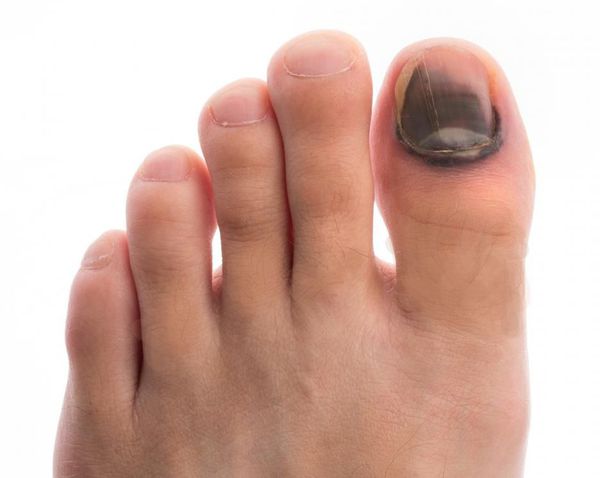
- foot deformity;
- decreased sensitivity of feet - vibration, temperature, pain and touch;
- Foot pain and ulceration, which occurs both at rest and at night and when walking certain distances;
- thinning of the skin, peeling;
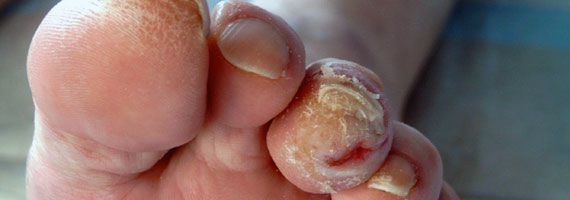
- Decreased or increased temperature in the foot and lower leg;
- Protracted epithelialization (healing) of micro-injuries - up to two months, after which brown scars remain;
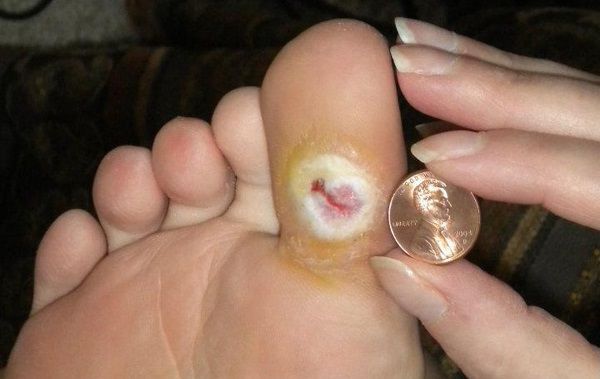
The distal parts of the limbs are most often affected: the toes and the plantar surface at the projection of the metatarsal heads. The area of \u200b\u200bthe trophic ulcers depends on the cause of their formation.
Pathogenesis of the diabetic foot
The mechanism for the development of SD involves the following sequence of disorders:
- Production of the hormone insulin decreases.
- The blood sugar concentration rises – hyperglycaemia develops.
- Blood flow in the small vessels is blocked, and oxygen and other micronutrients no longer flow through the vessel wall.
- Nerve fibers and receptors are destroyed.
- Micro- and macro-ischemia of the foot tissue occurs.
- Tropic ulcers form.
In AS, all tissues of the foot are damaged.
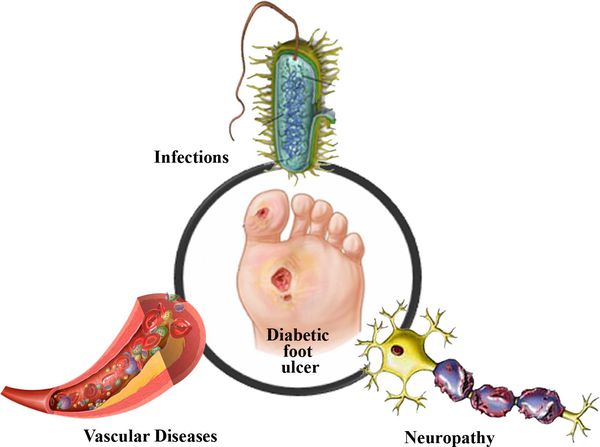
As a result of the lack of insulin in the diabetic's body, the amount of glucose in the blood increases. This in turn affects the function of the small and large vessels:
As a result of these changes, blood circulation is impaired and small blood clots form. These changes in the body prevent enough micronutrients and oxygen from reaching the cells, leading to metabolic disorders. The lack of oxygen in the tissues slows down cell division and leads to cell death.
Elevated blood sugar levels also damage nerve fibers – sensitivity is reduced.
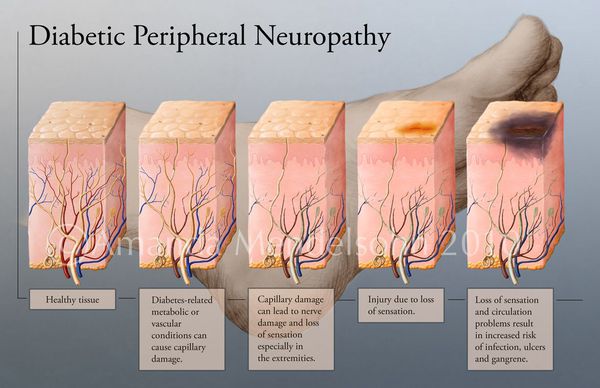
All these destructive processes in the tissues of the foot mean that damage to the skin heals easily and only slowly. The condition of the foot can be aggravated by infections that can lead to gangrene - a tissue necrosis. [9]
complications
As the disease progresses, symptoms worsen and complications arise. Muscle strength in the patient's legs decreases.
Left untreated, equine foot complications can lead to foot deformities. Getting your foot in the right position is easy at first, but over time this becomes increasingly difficult without fixation. To prevent foot deformity, it is important to identify the cause of the defect as early as possible: it could be a spinal disease or a muscle injury.
In severe cases, the patient suffers paralysis of the foot and is no longer able to walk independently. With the paralytic form of the disease, it is important to timely fix the foot in the correct position so as not to spoil its shape. For this purpose, orthopedic shoes and other aids are used.
If the patient visits the doctor in time and starts treatment of the sagging feet, he can move freely again.
Treatment feedback
i want dr Thank Marina Koreshkova for her professional approach which was very helpful and caring. I had a herniated disc in my neck and my shoulder was very weak. Marina Kimovna suggested me a suitable method of treatment. I felt much better after the first treatment. Nice clinic and caring staff. I would like to thank everyone who was involved in my treatment. I HIGHLY RECOMMEND YOU.
If you cannot move the front part of your foot and it is making it difficult to walk, you should see a specialist. The doctor at Master's Health in St. Petersburg will conduct a comprehensive examination and determine what is the cause of your foot paresis. You can help the doctor by remembering when you first felt weakness in your foot. We use the following diagnostic methods:

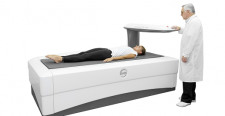



vascular disease
One of the most serious causes of foot pain is atherosclerosis of the lower limbs, which affects the supply of oxygen and nutrients to foot tissues. The main causes of this disease are diabetes and smoking.
Diabetes leads to the development of the so-called diabetic foot, which is characterized by a number of pathological changes. In the early stages, symptoms such as decreased skin sensitivity, numbness, deformed nails, swelling, itching, dryness, skin discoloration, and sole pain when walking can occur. In later stages, non-healing ulcers develop, invading progressively deeper layers of tissue down to the bone, leading to gangrene requiring immediate amputation of the feet above the affected tissue.
myositis
Muscle pain in the foot can occur after strenuous exercise due to the accumulation of lactic acid in muscle tissue. This type of pain requires no treatment and goes away within a few days.
Inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the foot, caused by inflammation, can cause great discomfort:
They make walking difficult and cause distress, but of all the causes of foot pain, they are the most harmless. If you consult a doctor in time, these diseases can be easily treated and do not lead to complications.
It is important to properly diagnose soft tissue infections in the feet so that they are not confused with the symptoms of much more serious conditions such as lower extremity atherosclerosis or diabetic foot.
Symptoms of Flat Feet
Transverse flatfoot

Normally, the transverse arch of the foot, formed by the heads of the metatarsal bones, has an arch shape. The heads of the V and I metatarsal bones provide the main support for standing and walking. The development of flat feet weakens the supporting structures of the arch of the foot: the plantar fascia, which bears the brunt of supporting the arch, the intercondylar fascia, and the muscles of the foot.
There is a redistribution of support force to the heads of all metatarsals, with the load on the head of the first metatarsal decreasing and the loading on the heads of the second through fourth metatarsals dramatically increasing. The I toe deviates outward and the heads of the I metatarsal bone and I toe form an angle. Osteoarthritis develops in the I metatarsophalangeal joint. There is pain and restricted movement in the joint.
The increased pressure on the heads of the metatarsal bones leads to a thinning of the subcutaneous fat tissue on the plantar surface, further reducing the cushioning function of the foot. Corns form on the soles of the feet in the area of the metatarsal heads.
Depending on the extent of the angle between the 1st toe and the 1st metatarsal bone, the following degrees of transverse flatfoot are distinguished:
- Grade I (weak). The angle is less than 20 degrees.
- Grade II (moderately pronounced). The angle is between 20 and 35 degrees.
- Grade III (strongly pronounced). An angle greater than 35 degrees.
Patients visit the doctor most often because of a cosmetic defect in the foot, less often because of pain when walking, corns on the sole of the foot, rough skin growths or inflammation in the area of the 1st
As a rule, the patient reports a history of a longer-lasting, more or less severe burning sensation or pain in the foot when walking. On examination, a deformity of the foot is found: flattening of the transverse arch, characteristic deformity of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe and hammer toes in severe flat feet.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by orthopedic surgeons. To determine the type and severity of flatfoot, the following methods are used:
- anamnese. The specialist notes the presence of discomfort such as pain and heaviness in the legs, swelling at the end of the day, increased fatigue when standing and walking. The orthopedist explains the patient's relationship to static loads, weight gain and shoe size over the past few years.
- Objective investigation. The doctor examines the foot in a free state and under load and assesses the foot's appearance, arch, deformities, and range of motion.
- X-ray examination of the foot. Carried out under load (for functional tests). It is the most important diagnostic method. Allows accurate determination of the longitudinal and transverse arches, physiological and pathological angles between the foot bones, etc.
- other techniques.. Plantography (ineffective in infants and obese people) and podometry are used to determine and assess the severity of flat feet.
Causes of pain syndrome
Many years of research and medical practice point to a variety of factors that lead to foot pain. This can include:
- Trauma;
- muscle insufficiency;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- uncomfortable footwear;
- calcium deficiency;
- hygroma;
- abnormal anatomy.
Do not leave unattended if the foot develops pain, swelling, or fever at the tip or other parts. This can be a sign of a serious abnormality in the body that can lead to disability.
As a rule, the symptoms affect the entire foot, which makes diagnosis difficult and requires great medical skill. You should consult a doctor with your symptoms:
Narrow specialists, of course, only exist in specialist clinics. In polyclinics, a surgeon is responsible for bone, cartilage and joint diseases.
Which diseases are manifested by pain?
In the course of life, the foot is often exposed to trauma. For example, something heavy falls on the foot, the foot is twisted, dislocations, fractures, sprains and torn ligaments occur. The complexity of the injury is determined by x-rays.
In 85 % cases, dislocations are diagnosed by a trauma surgeon. When the ankle moves outward, the cause of pain in the ankle bone and surrounding connective tissue is a sprain, a torn ligament. The affected person feels severe acute pain, and swelling and hematoma appear immediately. Even after the treatment, the patients feel an instability of the joint.
When the ankle is sprained, the small bones in the foot can become dislocated, which medical professionals call ankle syndrome. Symptoms include morning pain, swelling, redness, and pain on the outside of the foot all the way to the toes. Sometimes those affected live with this condition for a long time. However, with proper treatment, it can be cured fairly quickly.
A stress fracture, which is a miniature break in a bone, is associated with mild pain that usually worsens. In practice, it turns out that this type of fracture is characteristic of the calcaneus, metatarsal and scaphoid. Characteristic of the injury is that the foot is swollen and painful at the top.
Acute pain in the foot in the area of the toes is often caused by gout. This disease is a metabolic disorder in which the uric acid salts are not sufficiently eliminated from the body. These accumulate in the joints over the years and form salt deposits that damage the cartilage and make the joints unusable. It occurs in men, but also in women. The aggravation is so severe that the pain is unbearable. Without professional treatment, the joints in the patient's limbs eventually become inoperable.
3 Even simple calluses if they have grown deep into the sole; a nail that has grown into the toe; Warts – can cause pain.
Why do the feet hurt?
Foot pain is a symptom of an injury or disease. There are the following causes of foot pain.
| foot pain | symptoms of an illness |
|---|---|
| Bad feeling in feet | Tired, heavy feet at the end of the day, swollen ankles. Feet tire quickly, women find it difficult to walk in high heels. The foot widens. |
| bruise | The most common foot injury. Causes pain in the foot, swelling, swelling, bruising on the skin. |
| Sprained ligaments | Occurs after exercise or heavy physical labor. Causes severe foot pain and swelling. |
| Torn ligaments | Acute, stabbing pain in foot immediately after injury. The foot hurts when resting and cannot be stepped on. |
| fracture | Severe pain in the foot, swelling and inability to put weight on the foot. |
| arthritis in the foot | Pain in the foot, under the toes, swelling and stiffness in the joint. The skin over the joint turns red and feels hot. |
| Inflammation of the tendon of the posterior tibialis muscle | Aching pain in the arch of the foot that goes away with rest. Without treatment, the pain is chronic, increasing with walking and not decreasing with sleep. |
| Condylar deformity of the big and little toe | The big toe or little toe is offset laterally in relation to the other toes. The part of the joint on the inside or outside of the foot is enlarged. |
| metatarsalgia | pain in the sole of the foot. The foot cannot be supported when walking. |
| plantar fasciitis | Pain in the heel or in the inner part of the sole of the foot. The pain occurs acutely in the morning after getting up. The pain subsides over the course of the day. |
| heel spur | Severe pain in the back of the foot. The sufferer has difficulty walking or even standing. |
| achillotendinitis | Sharp, stabbing pains in back of foot and lower leg. Feet hurt when walking after a long period of rest. |
| osteoporosis | Feet hurt at rest, pain sensations increase with movement. The pain occurs when pressure is applied to the bones in the foot that are close to the skin. |
| varicose veins | This condition begins with a feeling of heaviness in the feet and lower legs. Pain in the foot occurs in the later stages of varicose veins. |
| Obliterative arteritis | Nausea, chronic foot pain, acute foot pain after hypothermia, ulceration, limping. |
| Diabetic foot | A complication associated with diabetes. It is accompanied by pain and swelling of the foot, ulcers form on the skin. There is numbness in the feet and weakness in the legs. |
| ligament inflammation | This is inflammation of the ligaments that causes pain in the foot. The foot can hurt on the side, instep, sole and ankle. |
| gout | Sudden pain in the foot, most severe in the first toe. Swelling and fever occur in the affected joint. |
complications
Left untreated, joint pain in the feet can lead to serious complications.
Flat feet lead to foot deformities, leg pain and spinal pain. As a result, scoliosis can develop.
If varicose veins are left untreated, thrombosis can occur, i.e. a blockage of the venous lumen by blood clots. Another complication of varicose veins is phlebitis, an inflammation of the vein wall. These two complications often occur simultaneously.
In advanced cases, gout leads to the formation of kidney stones. These can lead to kidney failure and death.
With the progression of diabetic foot disease, deep ulcers form on the feet, the affected person no longer feels the touch of the foot or, on the contrary, feels pain in the foot even at rest. Loss of feeling and blockage of blood vessels can lead to amputation of one or both feet.
Pain in foot and swelling
Self-diagnosis of the cause of discomfort in the lower limbs can now be performed using online self-diagnosis. However, only the presumed cause of the complaints is given; the final diagnosis should only be made by a doctor. For example, if you suffer from pain and swelling in the upper part of your foot, your doctor may tell you at the first examination that the discomfort is caused by medication, such as B.
- hormonal oral contraceptives;
- drugs that lower blood pressure;
- adrenal medications;
- antidepressants.
Upper foot pain with swelling around the joints can also be caused by:
- Infectious processes in the lower limbs;
- Impaired outflow of lymphatic fluid;
- fatigue and insomnia;
- kidney disease;
- Obesity;
- insect and animal bites;
- allergic arthritis.
diagnosis
Pain in the upper part of the foot is not always due to an obvious cause: animal bite, fatigue, trauma. During the initial examination by a specialist, the problem is often not recognized immediately. Various tests are carried out to find out what is causing the symptoms. This helps ensure that the diagnosis is as accurate as possible. The doctor can send the patient for examinations, for example:
| diagnostic methods | Time |
|---|---|
| MRI of the foot. | 30 minutes. |
| electromyography | 30 min. |
| X-ray of the ankle | 20 min. |
| X-ray of the foot | 20 minutes |
| Computed tomography of the joints | 15 minutes |
A timely appointment with a specialist can help prevent serious complications. Some of these lead to bone and joint destruction that is very difficult to treat.
Read more:- flat feet (valgus foot).
- The longitudinal arch of the foot is.
- Which doctor treats flat feet?.
- flat foot pronation.
- Which ligaments strengthen the transverse arch of the foot?.
- Longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot.
- The foot of a healthy person.
- Why do feet hurt after running?.
