Fractures of the heel bone are serious but rare injuries; they account for only 1-2 % of all fractures. However, if not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, they can lead to long-term disabilities. Up to 10 % of these fractures are missed during initial evaluation in the emergency department.

- Severe's disease
- Epidemiology/Etiology
- Heel osteotomy
- Double calcaneal osteotomy.
- Treatment of heel bone fractures
- Main Points
- Important points
- Rehabilitation and physical therapy
- prevention of injuries
- surgical treatment
- Improving blood circulation
- therapeutic exercises
- causes
- Treatment
- symptoms
- diagnosis
- Surgical technique
- Osteosynthesis of the heel bone in the SM-Clinic Surgical Center
Severe's disease
Severe's disease is an abusive syndrome that occurs most often in young athletes who compete in jumping and running events. Other names are calcaneal inflammation or Osgood-Schlatter foot syndrome. The disease was first described by James Warren North in 1912. The problem is related to the constant occurrence of microtrauma caused by pulling on the Achilles tendon. The pull on the tendon occurs at the secondary ossification center of the calcaneus, resulting in damage to the apophysis. The cause of this traction apophysitis is repeated microtrauma or overuse of the heel by young athletes.
The heel bone is located in the back plantar side of the foot. The Achilles tendon attaches below, behind and approximately in the middle of the heel bone. The plantar fascia begins at the medial tuberosity in the plantar area of the heel bone. Closer to the epiphysis is the apophysis, around which the Achilles tendon actually wraps. The growth area of the heel bone and its apophysis are heavily loaded by the plantar fascia and the Achilles tendon. In addition, the different growth rates of muscle and bone can lead to a shortening of the tibialis triceps muscle, which can result in less cushioning between the foot and the ground. In addition, the Achilles tendon has a relatively wide insertion area that is anatomically connected to the plantar aponeurosis. It helps prevent traumatic tears in the ossification center.
Epidemiology/Etiology
Sever's disease is an osteochondrosis caused by excessive stress on the attachment area of the Achilles tendon to the heel bone and the growth plate of the epicondyle. This growth area is C-shaped and can become inflamed from repeated tensile stress on the Achilles tendon. Inflammation of the heel epiphysis often affects young athletes and is thought to be caused by running and jumping.
Friends, Olga Glamazdina's webinar 'Feet: Practice' is coming up. Learn more…
Serious foot diseases occur most often in active children and adolescents aged 7-15 years. It is particularly common during the pubertal growth spurt or at the beginning of the sports season in gymnasts, basketball and soccer players. The disease usually occurs at the beginning of the growth period. Boys are more commonly affected (ratio 2-3:1).
None of these etiological factors have been studied prospectively. In addition, the available studies have not been conducted systematically, so the reliability or validity of the measurements has not been adequately examined.
Heel osteotomy
The indication for heel osteotomy is a flat valgus deformity of the foot and a clubfoot.
The aim of the operation is to eliminate longitudinal flatfoot and valgus deviation of the foot with subsequent fixation of the fused fragments in an anatomically correct position using plates and step screws.
Double calcaneal osteotomy.
Combines the two methods above.
Latest news
'Excellent center. Special thanks to Oleg Ivanovich Dulub – a very attentive and responsible doctor. Many thanks to Svetlana Kucherina for her attention and professionalism. You got me back on my feet and gave me back my will to live! '
'This is a wonderful center whose doctors perform miracles. I had knee surgery and can now work and walk again. Thank you! '
,1. Neurosurgery – thank you very much and thank you again to everyone! The entire team works together and the entire process - from recording to solving the problems - is handled expertly. Not once have I encountered rudeness or shouting, impatience or impoliteness. If you need something, the RNPC will always support you to the best of its knowledge and belief.
'Hello, I would like to say a few nice things about the 2nd orthopedic clinic. I was treated in this department from April 15th to April 22nd and it was one of the most pleasant hospital stays! Thank you for the highly professional team of doctors, nurses and carers. Special thanks to my attending physician Roman Sirotkin! In the summer of 2018 he provided medical care for my son after his injury and now for me. He is a dedicated and caring doctor. None of my questions went unanswered. Thanks again! '
'I would like to thank Svetlana Viktorovna Kutscherovna, the head of the physiotherapy department, and the therapists: Voronyuk Tatiana Ivanovna and Danilenko Natalia Anatolievna, for their professionalism, support and care for our son Ivan Andreyevich Dubogria during his treatment in the newest kinesitherapy department ' Exarta'. Despite the difficulty of the exercises, our son works diligently on the therapy and enjoys the doctors' well-being. '
, Good morning!!! I have been being treated at the RNPC since April and had surgery (lumbosacral spine) in May. I would like to thank the 1st neurosurgical department, namely the head of the department Makarevich Sergey Valentinov, the operating surgeon Pustovoytov Kirill Vasilievich, the attending and operating doctor Krivorot Kirill Anatolievich. For all your help with my health and your attentive and caring attitude! I want to wish you good health! Sucess at work! Prosperity for your family! And only grateful patients! '
Treatment of heel bone fractures
The question of whether a treatment of intra-articular fractures of the heel bone There is controversy about whether it should be treated surgically or non-surgically.
An extra-articular fracture of the heel bone is treated symptomatically with protection, rest (avoiding heavy lifting), a pressure bandage (which also provides protection), ice, and elevation of the limbs (treatment regimen [ PRICE A fracture is a break in the integrity of the bone. Most fractures result from a single significant Force applied to a normal bone. In addition to fractures, there are also injuries to the musculoskeletal system. Read more information ]). Once the swelling has subsided, a plaster cast is applied.
Main Points
If fractures of the heel bone are not diagnosed and treated promptly, they can lead to long-term disabilities.
Because these fractures are typically caused by high-energy axial loading of the feet, other injuries (e.g., compression fractures of the thoracic spine) are also common; Other complications include compartment syndrome (in up to 10 % cases).
It is controversial whether intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus should be treated surgically or non-surgically.
When diagnosing a heel bone fracture, it should always be checked whether a lumbar vertebra fracture is present.
Extra-articular fractures of the heel bone are treated symptomatically with PRICE and a cast.
Copyright © 2023 Merck & Co, Inc, Rahway, NJ, USA and its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Important points
If heel bone fractures are not diagnosed and treated promptly, they can lead to long-term disabilities.
Because these fractures are typically caused by high axial loading on the feet, other injuries are also common (e.g., compression fracture of the thoracic spine); Further complications include compartment syndromes (in up to 10 % cases).
Whether intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus should be treated surgically or nonsurgically is controversial.
When diagnosing a heel bone fracture, it should always be checked for a lumbar spine fracture.
Extra-articular fractures of the heel bone are treated symptomatically with PRICE and a cast.
Copyright © 2023 Merck & Co, Inc, Rahway, NJ, USA and its subsidiaries. All rights reserved.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy

Rehabilitation is one of the most important phases of therapy. After two months, the patient can gradually put weight on the affected limb: it is recommended to initially walk on a flat surface for 5-15 minutes, and then gradually abandon crutches, walkers and canes. Physical therapy is also recommended:
Physiotherapeutic treatments and massages are also very helpful. They improve blood and lymph circulation, restore limb function and prevent contractures and deformities. The patient is recommended to start with exercises under the guidance of a specialist, after which simple exercises and self-massage can be performed at home.
prevention of injuries
Recovering from a fracture is a long and arduous process. With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable: the function of the limbs is restored within a few months. However, if the fracture is complicated by an infection or contracture, this period may last more than a year. It is therefore much easier to take care of your health in advance by following a few simple rules:
- Follow safety regulations when engaging in dangerous sports;
- Wear comfortable shoes with a thick sole and good cushioning;
- avoid jumps with straight legs;
- pay attention to a healthy diet, do not give up dairy and meat products;
- Regular physical activity helps to strengthen the body and make it more resistant to external influences.
surgical treatment
- Surgical treatment is used only for severe deformities: all bony and cartilaginous overgrowths are removed;
- a wedge resection of the tuberosity is performed;
- Sometimes (in case of severe pain) the nerves supplying the heel area are cut (neurotomy), but this method is undesirable and not at all acceptable for diabetics and people suffering from neuropathy, as it leads to loss of sensitivity in the heel leads.
If the pain worsens, the surface of the heel can be rubbed with ointments based on diclofenac, indomethacin, ibuprofen, Fastum gel or quinoa ointment.
- Warm baths with sea salt, decoction of pine needles or eucalyptus;
- penetrating warming compresses with dimethoxide partially diluted with water;
- Pharmacy bile compresses.
Improving blood circulation
- To improve blood circulation in the heels, they should be rubbed and kneaded daily, massaging the muscles that form the arches of the feet.
- Massage with ointments (Viprosal, Apisartron, Heparin) enhances the effect.
- The use of needle massage balls is also useful.
therapeutic exercises
Physical therapy for Schinz disease helps slow the process of osteochondropathy, as exercise can improve bone nutrition and prevent aseptic necrosis.
However, the exercises should be chosen so as not to put too much strain on the heel, and in the event of exacerbations, the strain should be omitted altogether. Therefore, sitting (lying down) on the floor or on a chair without putting any strain on the heel is recommended during this time.
- Sitting on a chair, move your foot by flexing and extending it.
- Raise and lower your toes, keeping your heels on the floor.
- Tuck your toes and relax them again.
- While sitting, stand on your toes and lower yourself down.
- Rotate your ankles while sitting.
causes
Stroke fractures in the neck area caused by a fall on the abducted leg. This pushes the head into the neck and creates a valgus deformity. Valgus deformity – The head is shifted outwards and upwards and the angle between the shaft of the femur and the neck increases. The injury does not affect the blood supply to the femoral head and does not cause necrosis or destruction of the hip joint.
- Severe pain when moving the sore leg and trying to lean on the heel.
- Bruising or swelling in the groin and hips.
- Shortening of the lower limbs by 1-4 cm.
- When lying on your back, the foot of the injured leg protrudes.
- When tapping on the heel, increased pain occurs at the site of the injury.
- Inability to remove the foot from the bed and keep it upright (heel pinch syndrome).
In older people with little physical activity, the fracture splits more slowly. After the injury, it is necessary to go to a trauma center for a ROENTGEN. This examination allows the fracture to be identified and treated in a timely manner. If the fracture ruptures, treatment tactics become much more complicated, the rehabilitation period increases and the risk of complications increases.
Treatment
As with other hip fractures, embedded injuries can be treated conservatively or surgically. Conservative treatment involves placing a Bellaire splint around the injured leg. Conservative treatment uses the Bellaire splint and skeletal traction..
During surgical treatment, the broken bones are fixed with screws, spokes or plates.
Surgical treatment is recommended for elderly patients unless contraindications exist. Surgical intervention allows for shorter bed rest and prevents complications such as: B.. Bedsores, thromboembolic diseases, congestive pneumonia, exacerbation of chronic diseases. Two weeks after surgery, patients can use crutches without putting too much strain on the affected leg.
In the first few days after skeletal traction or surgery, patients should therapeutic exercises. In the first phase, turning in bed, moving your toes and raising your pelvis are recommended. After that, it is allowed to sit up in bed, bend the knee joint and tense and relax the muscles of the affected limb. Restoration of mobility is carried out by walking on crutches, overcoming obstacles and prescription Massage and physical therapy.
The prognosis after an injury is favorable in young people and older people until the fracture ruptures. Broken bone fragments increase mortality in patients over 60 years of age in the first few years after a hip injury.
symptoms
Different people may experience different symptoms, both acute and gradual.
- Increasing pain in the heel during or after movement;
- Acute pain in the heel when touching the affected area;
- difficulty flexing/extending the foot;
- swelling in the affected joint area;
- Redness of the skin and increased body temperature at the problem area;
- Inability to stand on the affected leg without using additional support (crutches or cane);
- limping when walking ;
- Pain in the area of the Achilles tendon insertion;
- When you stand horizontally, the pain diminishes or disappears;
- The patient unconsciously tries to lean on the forefoot while walking to relieve the pain.
In some cases, atrophy and hyperesthesia of the heel skin and even atrophy of the lower leg muscles may occur. The above symptoms usually persist for a long period of time.
diagnosis
The podiatrist makes the diagnosis taking into account the clinical picture, the anamnesis and the x-rays.
1. X-ray diagnosis. The x-ray image is taken from the side view - this angle is the most informative.
In stage 1 disease, the image shows thickening of the tuberosity and an enlargement of the gap between the tuberosity and the heel bone. In addition, patchy and irregular ossification as well as bone and cortical loosening can be seen.
In the later stages of the disease, fragments of the tuberosity and signs of newly formed bone substance can be seen on the x-ray. A healthy calcaneal tuberosity can have up to four ossification nuclei, which often makes diagnosis difficult.
2 MRI and CT examination. In case of doubt, a comparative examination of the heel bones of both feet is carried out and patients are sent for an MRI or CT scan of the heel bone.
3 Differential diagnosis. In addition, a differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude diseases such as osteitis, synovitis, bursitis, tuberculosis of the calcaneus or malignant neoplasms and to ensure that the diagnosis is made correctly.
A healthy skin color in the affected area and the absence of certain blood changes (normal sediment, no leukocytosis) can rule out inflammation. In the case of a malignant tumor or bone tuberculosis, the patient exhibits symptoms such as irritability and lethargy, as well as increased fatigue. The above symptoms do not occur in Schinz disease.
Conditions such as periostitis and calcaneal tuberosity are most common in adults who experience acute pain in the morning, the first activity after a short break, after which the patient gets used to it and the pain subsides.
If in doubt, a consultation with an oncologist or phthesiologist may be necessary.
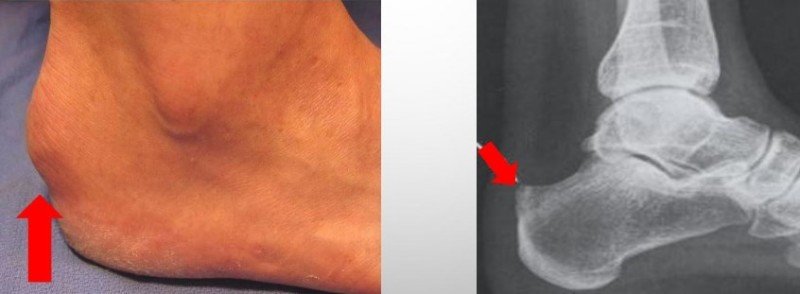
Surgical technique
Osteosynthesis is an open procedure that is performed under anesthesia. After applying antiseptics, the surgeon makes an incision in the tissue to gain access to the bone. The bone fragments are then repositioned and fixed with a metal orthosis. After the procedure is completed, the wound is stitched up and the leg is fitted with a cast or a rigid orthosis.
Take advantage of this unique opportunity for a free consultation on elective surgery. Read more.

Osteosynthesis of the heel bone in the SM-Clinic Surgical Center
Osteosynthesis allows the patient to recover more quickly and restore limb function after a long-term bone fracture. Thanks to the fixation, the patient can perform therapeutic exercises earlier, thus avoiding muscle atrophy and joint contractures.
For the first 1-3 days, the patient remains in the clinic under medical supervision. If tissue healing is normal, the patient is discharged home and given detailed instructions on drug treatment and postoperative wound care. Before removing the stitches, all heat treatments (hot baths, baths or saunas), swimming in open or public waters and physical activities are prohibited. The stitches are removed after 2 weeks and the plaster cast after 4-6 weeks. After this time, the patient begins physiotherapy, physiotherapy and massage courses. Full standing on the leg is only possible when the fractures have completely healed, that is, after 4-6 months. Until then, crutches should be used.
On the SM-Clinic Surgery Center website you can find up-to-date information about all operations, find out prices and make appointments with the surgeon. Employees will also answer all your questions in the service's contact center.
Read more:- heel bone injury.
- Anatomy of the heel bone x-ray.
- Anatomy of the heel bone.
- Fracture of the heel bone.
- Displacement fracture of the heel bone.
- Fracture of the calcaneus of the foot.
- Osteophyte of the heel bone.
- Fracture of the articular process of the heel bone.
