Effective solutions to health problems in physical education are possible on the basis of joint activities between teachers and parents. In order to involve parents in active participation in preventive and corrective work, we use various forms of communication with families: parent meetings, thematic consultations, educational discussions, open days, open sports lessons, stands (corners) for parents, portfolio displays, etc In this way, the continuity of the child's development and upbringing in the preschool and in the family can be ensured and parents can be made aware of corrective and preventive measures in the upbringing of their children.

- Prevention and correction of flat feet in preschool children
- Similar articles
- Prevention of valgus deformities
- Treatment of valgus deformities
- Basic concepts of hallux valgus deformity of the first toe
- Symptoms of transverse flatfoot
- Symptoms and causes of flat feet
- types of flat feet
- Diagnosis and treatment of foot deformities
- Surgery for valgus deformity of the toes 1.
- Flat foot in a child
- Symptoms of illness
- causes
- Classification of flat feet in children
- Causes of flat feet in children
- Causes of valgus deformity
- Classification of valgus deformities
- Symptoms of valgus deformity
- Diagnosis of valgus deformity
- What are the risks of flat feet?
- Causes of flat feet
- types of flat feet
- flat feet
- preventive treatment
- Choosing the right footwear
- Video review.
Prevention and correction of flat feet in preschool children
Raskova GV, Vlasova TA Prevention and correction of valgus flat feet in preschool children / GV Raskova, TA Vlasova. – Text : immediately // Pedagogy : Traditions and Innovations : Materials of the 6th International Scientific Conference (Chelyabinsk, February 2015). – Chelyabinsk: Dva komsomoltsa, 2015 – С. 92-95 – URL: https://moluch.ru/conf/ped/archive/147/7153/ (date of reference: 03/22/2023).
Health is a great value. Raising a child to be strong, strong, healthy, smart - that is the goal of every parent and one of the main tasks of doctors and teachers.
Today the problem of prevention and correction of deviations in health among preschool children is particularly relevant. This is primarily due to the large number of preschool children with various health problems. This increases the importance of preventive and corrective work directly in preschool institutions, where the child is present on a daily basis and where timely and regular interventions can be ensured.
When organizing health-promoting work in our kindergarten, special attention is paid to the prevention and correction of disorders of the musculoskeletal system (postural disorders and flat feet). The annual examination by the specialists of the city children's polyclinic shows that the majority of preschool children have flat feet.
'Flat feet - valgus position of the feet'. – this is the diagnosis we often hear from a pediatric orthopedist. While the word 'flat foot' is clear, the second part of the diagnosis needs clarification. To put it simply, valgus is an X-shaped position of the foot. Everyone knows what 'X feet' are. – The same applies to the feet. The feet are flattened and 'curved' inwards - these are flat feet.
When your child is born, he or she has no posture or arches. With the appearance of the first independent footrest and the first independent steps under the influence of physical activity, the process of arch formation begins.
Similar articles
engine Task, kindergarten OldDevelopment, child, health work, Movement, kindergarten kindergarten, kindergarten Oldearly Old, Motor skills activities.
physical activity Education, correction flat feet, child, exercises, Foot, toes toes, Musculoskeletal system–Musculoskeletal system apparatus, kindergarten Old, motorcycle Task, kindergarten kindergarten.
Prevention of valgus deformities
- Parents should watch their child's feet. Attention should be focused on the child's gait;
- A preventive visit to the orthopedist prevents the further development of orthopedic pathologies: flat feet, hip dysplasia and torticollis;
- In order to properly train the feet, the muscles and ligaments of the foot must be constantly trained. Weak ligaments cannot support the weight of the body;
- Carrying out a set of physiotherapy exercises for flat feet;
- Perform therapeutic massage at least twice a year;
- Proper, comfortable footwear is an important prerequisite for preventing flat feet. Don't skimp on this part of your child's wardrobe;
- Allow your child to walk on hard grass, stones and sand. Walking on uneven surfaces stimulates the foot's receptors and forces the muscles and ligaments to work;
- An orthopedic massage mat and balancing cushion should be purchased to massage the child's feet and train the muscles.
If foot pathology is suspected, you should consult a podiatrist or trauma surgeon. A visual examination is sufficient for an initial diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis and determine the degree of flatfoot, a series of hardware tests are performed:
1. Podometry is a diagnostic method used to determine the presence or absence of flat feet and in which a
Using a protractor to calculate the podometric index (ratio of foot length to height; 31-29 is a normal foot, 29-25 is a flat foot, >25 is a flat/valgus foot).
(2) Plantoscopy (podoscopy) is a method for diagnosing foot pathologies using the Dia-Scan software. In-depth study of foot function, determination of the degree of flat foot, creation of a data archive to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, creation of a photo matrix for the manufacture of individual insoles.
Treatment of valgus deformities
In the early stages of the disease, non-surgical correction of the foot deformity is possible. The aim of such treatment is to strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the foot and restore its correct position in relation to the axis of the lower limbs.
To achieve this effect, the doctor prescribes the following treatments:
- LFK. A set of physiotherapeutic exercises designed to improve joint mobility, muscle strength and ligament strength;
- Therapeutic massage. The massage regulates the muscle tone of the lower leg and foot, relieves excessive tension and makes the muscles stronger, more flexible and elastic, and improves their blood circulation. The effectiveness of massage is greater when performed by a medical massage therapist;
- Wearing orthoses. The insoles should be made individually under the supervision of an orthopedist and according to the existing changes in the foot;
- Use of orthopedic footwear. The product should have an insole and a rigid bar to keep the heel in the correct position.
- Physical therapy. Electrical stimulation of the foot and lower leg muscles aims to restore muscle activity and improve the elastic function of the foot.
If the chosen methods are ineffective, surgical treatment of foot pathology is carried out in orthopedic centers.
Basic concepts of hallux valgus deformity of the first toe
The main cause of hallux valgus is an external deviation of the big toe, which causes additional and unwanted pressure on the other toes. This phenomenon can eventually lead to ankle deformity of the toe.
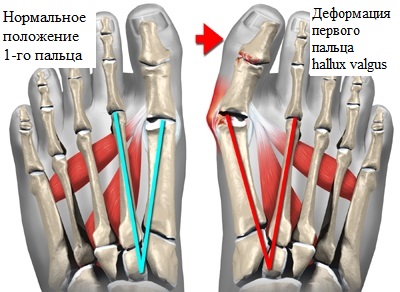
When wearing tight shoes that put excessive pressure on the first metatarsal bone, a pronounced inflammatory process is observed in this area of the foot. If the inflammatory tendency continues, there is a risk of the formation of a so-called 'bunion', which ultimately leads to the formation of exostoses and osteophytes, which are accompanied by pain and contribute to the increased development of deformity changes.
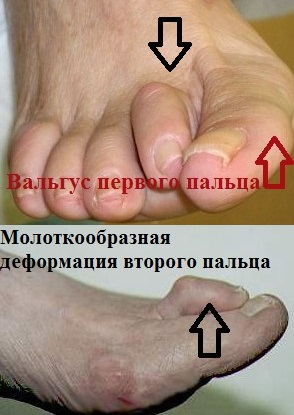
The most common deformity associated with the big toe is transverse flatfoot, which is caused by flattening of the arch of the foot and flattening of the forefoot. This phenomenon is accompanied by the development of corns and calluses, as well as pain syndromes. However, it is important to know that wearing loose footwear significantly reduces the risk of transverse flatfoot and hallux valgus.
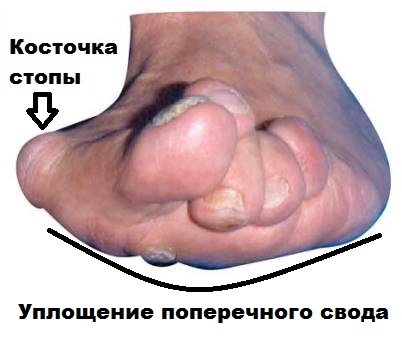
Symptoms of transverse flatfoot
Most often, patients complain of metatarsalgia (pain) in the forefoot, which is caused not only by misalignment of the first toe, but also by hammertoes and flat feet.
The decisive factors for the vast majority of patients are cosmetic defects and problems with the selection and subsequent use of optimally fitting footwear. Often there is deformation not only of the first toe, but also of all other toes, foot deformity and a pronounced pain syndrome.
Symptoms and causes of flat feet
First of all, people with flat feet feel tired when they stand or walk quickly. After a day of hard work the pain gets worse. This is already a reason to think about how to treat flat feet in adults. Note that pain may occur in the feet and into the lower back. To diagnose flat feet, it is necessary to analyze how the patient feels throughout the day.
It is not uncommon for flat feet to be caused by high body weight. In addition, diseases of the spine (scoliosis, osteochondrosis) can lead to a sharp increase in the load on the foot and its deformation. The disease can also be caused by wearing uncomfortable footwear. Therefore, the prevention of flat feet primarily consists in wearing comfortable shoes. Standing for long periods of time has a detrimental effect on the condition of the foot. Additionally, a person may have a genetic predisposition to this condition.
types of flat feet
Orthopedists distinguish between several types of this condition:
- Longitudinal flatfoot – the most common variant of the disease. In this case the foot is in absolute contact with the ground. This causes the person to develop clubfoot. In addition, the shoes of a person with this form of the disease wear out quickly;
- Transverse flatfoot is a deformation of the big toe and also the middle toe. This causes those affected to experience pain when walking. Treating flat feet in adults is quite labor-intensive and time-consuming. He should be treated as soon as the first symptoms appear;
- Longitudinal-transverse flatfoot is a combination of the first two forms of the disease. In this case, more complex treatment is required.
Only when the patient has received the most accurate diagnosis possible can we talk about 'flat feet: prevention and treatment'.
The patient complained of severe pain in the first toe of her right foot, enlargement of the bunion in the foot, and deformity of the toe that prevented her from wearing shoes.
She complained of back pain and the inability to stand, walk, or sit for long periods of time. She also suffered from headaches. The child has been in this condition for three years.
Many people struggle with a condition called hallux valgus. This is a deformation of the bone of the big toe. It leads to a growth on the big toe bone that protrudes from even the most well-fitting shoe.
The disease develops quite slowly. Initially, the patient only experiences mild discomfort when walking. Then problems arise when choosing shoes because shoes of the right size become too small in the toe area.
Over time, the deformation of the big toe bone increases. The patient feels severe pain when walking. His feet also get very tired. It is very important not to give in to this condition and to start treatment immediately at the first signs of hallux valgus.
Diagnosis and treatment of foot deformities
Treatment takes place in the trauma surgery and orthopedics departments. An x-ray image of the affected foot is taken. Based on the x-ray, the doctor recommends further treatment. In the initial phase this can consist of physiotherapy, physical therapy and orthoses. However, if the deformity and pain are severe, the operation should not be postponed: flat feet vary in severity, and the higher the degree, the more difficult the operation and rehabilitation are.
We cannot completely eliminate the disease because it affects the entire foot. But we can eliminate the deformity: straighten the toes, form an acceptable arch so that the person can walk normally, play sports and wear the shoes he likes.

Surgery for valgus deformity of the toes 1.
During the operation, the doctor saws off the bones using a special device and fixes the parts of the foot in the correct position. The arch of the foot is shaped and then the bones are fixed with screws. The operation on a foot takes 1-1.5 hours and is carried out under spinal anesthesia, rarely under general anesthesia. The patient is then admitted to the hospital ward and can walk on crutches the next day. Rehabilitation lasts 5-8 weeks.
An alternative to crutches are orthopedic rehabilitation shoes, which reduce pressure on the front arch of the foot. They can be worn from the second day after surgery and remain in use until the end of rehabilitation. In warm weather, you can even walk around the city or go to work in these shoes.
It's not possible to say, 'You have third-degree flat feet, so you need surgery'. The initiative usually comes from the patient, who can say on admission: 'I feel so uncomfortable that I can't live like this anymore - do the operation! Doctors call it 'tie syndrome': When a patient comes to the doctor, he takes them by the tie and says, 'Unless you fix this, I'm not leaving here'.

- – Gymnastics and therapeutic exercises: strengthen the lower leg muscles and help maintain the elasticity of the foot.
- – Physiotherapy: relieves pain and swelling.
- – Orthoses and shoes: Distribute the load on the feet, improve the spring function and reduce discomfort.
Yes
- – Special shoes for toe straightening.
- – Splints for overnight use.
Not
Flat foot in a child
This diagnosis can be made in a child from 3 years old. Until then, all children will have flat feet. However, after the age of 3, the feet should align and assume a normal position. During this period you may notice a change in the shape of your feet. If it is too flat or too wide, problems may arise in the future. Experts distinguish between these types of flat feet in children:
In children, the most common cause of this condition is heredity. Very often the child is born with ligament problems and muscle weakness. Talus problems or abnormal talus formation in the mother's abdomen also occur. Acquired flat feet are not uncommon during puberty. It occurs as a result of the above factors:
The latter is rare, but it still happens. When choosing children's shoes, you should always keep in mind that the body is 'soft' during the growth phase and can easily be influenced by external factors.
Symptoms of illness
When a child begins to walk, he puts his foot in one direction or the other. Over time, the child grows, the foot takes on its normal shape and moves as it should. If this is not the case, these are the first signs of valgus flatfoot. The development of pathology has tragic consequences that will affect the child's entire life. In order to detect the disease in time, parents need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- pain when wearing shoes;
- problems choosing shoes;
- changes in the toes;
- Blow;
- pain in feet at the end of the day;
- Development of osteoarthritis.
Over time, the foot develops an X-shape. The child has an awkward gait. He gets tired quickly and often complains of pain in his feet. It is important not to overlook these symptoms and seek medical attention in a timely manner. Valgus deformity often leads to the development of such complications:
There is no need to panic if such symptoms occur. It takes many years for serious complications to develop. However, if you take care of your child in a timely manner, he can quickly recover and forget about possible flat feet.
causes
The disease in a child can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, possible abnormal development of the fetus in the womb is a factor. In the second case, the occurrence of this pathology is associated with the abnormal development of the child's tendon apparatus after birth. If one does not classify the causes, they generally look like this
- Congenital bone weakness;
- genetic predisposition;
- obesity at a young age;
- trauma to the feet;
- thyroid disease;
- Wearing unsuitable shoes.
In some cases, the child develops valgus foot after injuries to the ligaments, muscles and bones of the lower limbs. Sometimes a child's lower limbs need to be cast due to problems at birth. This is also a common reason for the development of a valgus foot. In addition, this pathology can occur against the background of neuromuscular disease:
Classification of flat feet in children
Depending on the time of occurrence, two forms are distinguished: congenital and acquired. The congenital form is rare, no more than 5 % cases, in combination with other musculoskeletal anomalies. The acquired form is not diagnosed before the age of 5-6 years. The newborn has a flat foot, which is the norm. The arches of the feet begin to form from 8 months of age when the child stands and tries to walk. By the age of 5-6 years, the formation of the arches of the feet is complete. If the foot remains flat up to this age, damage to the knee and hip joints, the spine and internal organs can occur.
Depending on the leading damage to the anatomical structures of the foot, the following types of flat feet in children are distinguished:
Longitudinal flatfoot – this is the most common form. In this case, the length of the foot increases and the sole touches the ground with its entire surface. In transverse flatfoot, however, the length of the foot decreases and the foot rests on the heads of the metatarsal bones.
Causes of flat feet in children
Scientists believe that the main cause is a hereditary factor - the presence of the disease in relatives. The prerequisite is connective tissue dysplasia or a congenital weakness of the connective tissue. In addition to heredity, other factors also play a role:
- Rickets – bones and muscles in particular are affected;
- Fractures of the bones that make up the foot – metatarsals, ankle, heel, etc;
- Poliomyelitis – causes muscle weakness in the lower leg and foot;
- Encephalopathy – changes muscle tone;
- Flat feet in which the toes and heel point outward.
If the connective tissue is weak, unfavorable factors cause the changes: standing for a long time, walking without a break and unsuitable footwear (thick, non-curved soles, incorrect size), excess weight, which increases the load on the foot.
Causes of valgus deformity
A valgus deformity can be congenital or acquired. A congenital deformity has the following causes:
- Connective tissue hypoplasia, a condition in which the strong fibrous bands that support bones and joints, including the foot, are underdeveloped. Weak ligaments in the arch, sole, and ankle cause the foot to drop and turn inward;
- vertical talus or congenital vertical ramus, usually associated with connective tissue dysplasia and other musculoskeletal disorders;
- short Achilles tendon.
In children without musculoskeletal anomalies, the deformity can be caused by incorrect or premature formation of the child's ability to walk - early walking in a walker before the foot is ready for such a load, wearing shoes with stiff soles that do not support the development of the arch of the foot allow.
Acquired valgus deformities in adults can occur for the following reasons:
- aggravation of flat feet;
- Compensation after trauma – ligament tears, fractures and dislocations of the lower limbs;
- endocrine disorders leading to osteoporosis, including after rickets and after menopause;
- Neurological causes – resulting from muscle paralysis or hypertension;
- clubfoot overcorrection;
- postural abnormalities;
- A sudden increase in stress on the foot due to significant weight gain or pregnancy.
Classification of valgus deformities
Valgus deformities of the foot vary in cause and severity. Depending on the cause, a distinction is made between:
- Congenital valgus deformities – dysplastic, structural or compensatory;
- Acquired valgus deformity – static, traumatic, rickets and postmenopausal, paralytic and spastic, hypercorrection.
Symptoms of valgus deformity
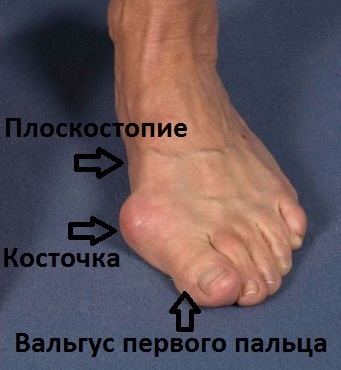
In the initial stages of valgus deformity, valgus feet may be clinically inconspicuous, and the presence of lesions is detected only by the podiatrist during examination and using instrumental diagnostic methods. Gradually, the curvature of the foot and lower limbs becomes more noticeable - the foot tilts inward and the heel rotates and rests on its inner edge. When the feet are close together and the ankles meet, the distance between the heel bones is established. The outer malleolus is flattened, the inner malleolus is more convex, and one or two bony protrusions form underneath - the head of the talus and the horn of the navicular bone are pronounced. The rotation of the foot causes an X-shaped bend in the shinbone and a change in gait. A hallux valgus develops - a deformity of the first metatarsophalangeal joint with outward bending of the thumb.
In addition to the external changes, the deformity is noticeable through pain. Initially, after prolonged walking or static stress, discomfort, fatigue and aching pain occur, which then become permanent. The pain syndrome affects not only the foot and ankle, but also the knee, hip and back. The lack of cushioning on the part of the foot leads to overloading and chronic joint injuries throughout the entire kinetic chain. Patients with a neglected valgus foot deformity develop osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints, and the increased pressure on the spine leads to intervertebral fractures.
Diagnosis of valgus deformity
The diagnosis is made based on the following criteria, among others
- Patient's complaints about deformation of the lower limbs, pain, increased fatigue, changed gait;
- Medical history – at what age did the first symptoms appear, how did the disease develop;
- Patient's medical history – any illnesses or injuries that predispose to the development of clubfoot;
- objective examination by an orthopedist/traumatologist – shows changes in the configuration of the foot, pain points along the arch of the foot, in the area of the instep and in the projection of the excessively tense muscles of the lower leg;
- X-ray of the foot - shows reduced arch height and abnormal spatial relationships of the bones in the foot, as well as signs of osteoarthritis in the foot;
- Podometry – assesses the distribution of loads on the foot;
- Computer-assisted plantography – used to calculate arch angles, heel inclination and indices that provide a picture of the spatial organization of the foot.
What are the risks of flat feet?
If we look closely at a healthy foot, we see two arches: a transverse and a longitudinal arch. These arches keep us balanced while walking and allow us to walk long distances without tiring.
If the arches are deformed, the diagnosis of flatfoot is made. Some patients receive intensive treatment after learning about the disease, while others do nothing. Both approaches are wrong because it is important to see a podiatrist to determine the extent and form of the pathology before treating the foot disease. However, if flat feet are left untreated, they progress quickly and treatment becomes more difficult.
Currently, between 40 and 60 people worldwide live with flat feet. The disease can lead to complications such as spinal curvature, radiculitis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral fractures, as well as pelvic bone diseases, knee joint diseases and toe curvature.
Causes of flat feet
Flat feet and other foot diseases are often observed in people whose jobs involve constant stress on the feet: couriers, hairdressers, salespeople, etc. Wearing tight shoes or high-heeled boots also aggravates the foot, increases the load on the forefoot and leads to this that the foot bends inwards. Therefore, the optimal heel height for adults is 3 to 4 cm and for children 1 to 1.5 cm.
There are several factors that can lead to this foot condition:
- Pregnancy;
- overweight;
- Diseases that cause bone fragility (flu, rickets, etc.)
- genetic predisposition;
- underdevelopment of the musculoskeletal system;
- various injuries (fracture of the heel bone, fracture of the ankle, injury to the ligaments and muscles that strengthen the arch of the foot).
types of flat feet
According to the time of their appearance, flat feet are divided into two large groups: congenital and acquired.
Congenital flatfoot Congenital flatfoot is the result of a congenital foot defect and is quite rare, with only 3 % cases occurring.
Congenital flatfoot Can occur at any age and includes the following forms:
Flat feet. Treatment of foot deformities and diseases
Flat feet. Treatment of foot deformities and diseases
flat feet
Flat feet is a condition that progresses quite quickly. There are 3 stages of this disease.
grade 1 (Slight flat tire.) is caused by a weakening of the ligaments. The shape of the foot is not changed, but at the end of the day, after a long walk, pain appears in the legs. The pain usually subsides after a period of rest. In this condition, the gait is less springy and the foot swells in the evening.
grade 2 (combined flatfoot (combined flatfoot)). At this stage the flat foot is already noticeable. The foot becomes larger, the gait is difficult and walking becomes difficult. Pain increases, affecting not only the foot and ankle joints, but also the knee.
grade 3 (Extremely pronounced flat feet.). A significant deformation of the foot leads to a change in the position of the toes; the big toe is tilted outwards. There is constant pain in the feet, ankles and knee joints. Various disorders can occur – osteochondrosis, arthrosis, scoliosis, intervertebral fractures. Walking is difficult, even at slow paces and over short distances. The patient can no longer walk in normal shoes.
preventive treatment
To prevent flat feet, the following measures are taken:
- Pay attention to your gait, try to walk straight, place your feet so that the toes of your shoes 'look' forward while moving without deviating;
- Choose the right profession, taking into account physical characteristics and predisposition to flat feet (do not engage in activities that place a lot of stress on the feet);
- Wearing suitable, preferably orthopedic, footwear (avoid high heels and stilettos, choose shoes with well-padded soles, the height of the heel should not exceed 4-5 cm);
- Provision of spastic insoles;
- take more frequent breaks from work, give your feet a break (do short exercises, warm up your feet);
- Relaxing foot baths and self-massage after prolonged exertion;
- Walk more often on the floor, on special mats, on stones, on the inside of the feet, move more;
- Avoid heavy exercises and excessive loads;
- Exercise, gymnastics, sport.
Choosing the right footwear
There are certain criteria when choosing the right footwear for adults and children:
- The sole and shaft of the shoe should be made of high-quality leather;
- a low heel (no higher than 4 cm for women) and a wide toe box (shoes with a pointed toe box are strictly prohibited for patients with flat feet);
- No strong crunching, no crumbling of the outer layer, no discoloration on the feet and socks. Good shoes do not cause allergic rashes, abrasions or blisters;
- flexibility of the sole (avoiding the 'stilt' effect);
- It is best not to wear high heels; Soft shoes without heels are preferable (especially for children), as are shoes with a firm heel.
Warning. Flat feet – a rather insidious condition that accelerates the deterioration of all elements of the musculoskeletal system.
The problem is not easy to solve because patients almost never pay attention to the problem.
Many people consider flat feet to be a minor abnormality that does not have serious effects on the health and function of the musculoskeletal system.
Failure to diagnose and treat in a timely manner leads to progression of the disease, which in turn leads to various complications.
It is better to consult an orthopedist in the early stages of flat feet to prevent further progression of the disease and protect yourself from serious problems.
Video review.
Read more:- Flat valgus foot in a child.
- Which doctor treats flat feet?.
- flat feet.
- Massage for flat feet.
- Flat valgus foot in an adult.
- Shoes for flat feet.
- flat feet.
- Shoes for flat feet for women.
