Any exercise for flat feet in children and adults must be recommended by a doctor. The podiatrist will prescribe complementary therapies that together will help eliminate the problem completely.

- Valgus or valgus deformity
- Treatment of valgus deformity in children
- Benefits of physical therapy
- Exercise complex for children
- insoles for shoes
- Classification of insoles by degree of hardness
- Cost of the product.
- General recommendations for selection
- Prevention of deformities
- What is a grade 1 hallux valgus?
- Treatment of hallux valgus grade 1
- How to properly wear orthopedic shoes for children
- Exercises for flat feet for children from 1.5 years old. Complex for advanced users
- Flat foot exercises on the balancing cushion
- What is the 'salt' of a deformity?
- First-class care: what modern diapers can do
- How can one distinguish between a pathological leg curvature and a variant of normal child development?
- Diagnosis of flat feet and valgus in a child
- Stages of development of the disease
- Why flat feet should be treated
- Conservative treatment of flat feet
- Orthopedic splints and fixators
- insoles
Valgus or valgus deformity
A valgus or valgus deformity is a change in the shape of the foot at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint, which bulges outwards. The obvious sign of a valgus foot is that the big toe is bent outward. The foot itself is tilted inward, resulting in a flat profile of the valgus foot.
Valgus foot often develops in childhood when the child is just beginning to walk. The cause is usually a weakening of the ligaments and muscles when the child begins to actively walk. However, the condition can also be congenital.
In adults without valgus in childhood, the deformity develops as a result of wearing inappropriate footwear, exacerbated by excess weight and reduced muscle tone.
The physiological cause of valgus deformity is a disruption in the biomechanics of the metatarsal joints.
Treatment of valgus deformity in children
Valgus deformity is a progressive problem. The earlier the pathology is noticed, the easier it is to correct. This is especially true for children, as bones and joints are still soft at a young age and can be easily corrected. If valgus is suspected, the child should always be examined by a trauma surgeon. Appropriate massages, therapeutic exercises and orthopedic shoes for a valgus foot can correct the defect at an early stage.



Benefits of physical therapy
Physical therapy is an important part of treating foot deformities. Valgus flatfoot not only results in a lowering of the arch of the foot, but also an accompanying complication of the curvature of the foot. This manifests itself in an X-shaped foot shape in which the foot is mainly turned inwards when walking. The heel and toes are turned inward, and the soles of the shoes are flat on the inside. This deformity is caused by reduced muscle activity in the ankle joint.
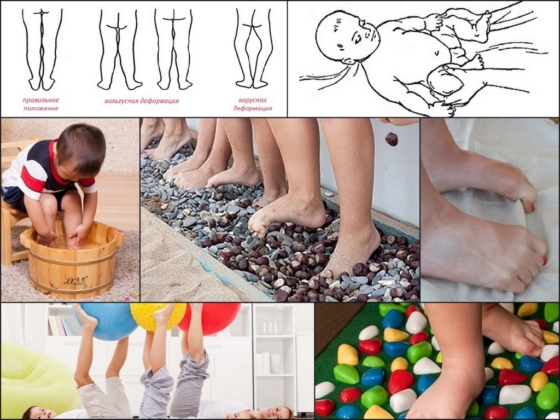

Physical exercise strengthens the muscles and restores the cushioning function when walking. Movement is a prerequisite for arch recovery. In addition, this therapy helps to overcome the curvature of the foot.
Foot exercises for valgus deformities help:
- to give the foot an anatomically correct shape;
- to relieve pain in adults and children;
- to correct clubfoot gait;
- strengthen ligaments and muscles;
- to effectively prevent the complications that are often caused by valgus arches;
- normalization of blood circulation, which is important for healing;
- Relief from fatigue and heaviness in the legs.
Danger!
Daily exercise has been proven to speed recovery. In the first and second phases of the disease, patients can not only correct the foot, but also completely eliminate the pathology.
Exercise complex for children
Children are often diagnosed with flat feet. From 3 to 5 years of age, a qualified specialist will be able to detect abnormal foot development, and parents may confuse physiological flat feet with pathology. Podiatrists advise against self-treatment before seeing a doctor. He or she will help identify the condition and prescribe effective therapy.
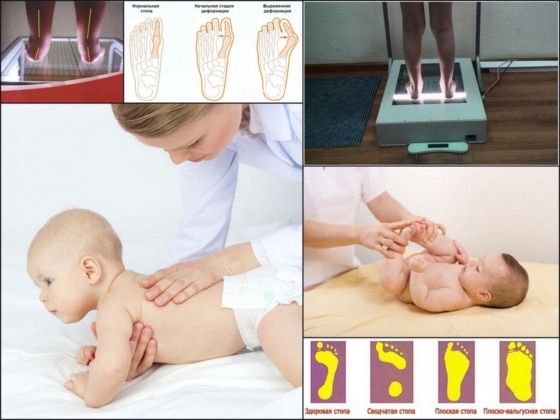
Orthopedists recommend daily exercises for valgus foot deformity in children. These exercises, along with massages, physiotherapy and baths, are an integral part of a comprehensive treatment.
The following exercises are part of a standard, effective physical therapy program for flat feet in children:
- Walking on an orthopedic mat. They have a variety of modules and help replace traditional walking on gravel, stones and grass. The mat should only be walked on barefoot under adult supervision. The exercises should be done in the morning and evening. Suitable for training at home;
- A good tool for a child with valgus flat feet is the 'bicycle' exercise and directly riding this vehicle. Orthopedists recommend that children aged 2-3 years should buy a tricycle. Cycling activates the foot muscles and strengthens the arch of the foot in the correct position;
If the child is too young to ride a bike, exercises that simulate cycling can be performed. The child should be supported to learn it. To maintain balance, the child should be supported on the floor with their palms facing down. Rotate the lower limbs and keep the legs tense.
- ,Caterpillar. Suitable for an older child. Sit on a chair and put your feet on the floor. Move your legs back and forth, bending and straightening your toes. Do this exercise 7-10 times a day. This exercise is suitable for school-age children. It can be done at a desk in the classroom;
- With small children you can do the 'clawed bear' exercise. Ask the child to walk straight, placing more emphasis on the outside of the foot;
- Spread pencils on the floor. The child should try to pick them up from the floor and grab them with his fingers;
- Playfully ask the child to walk like a ballerina or stand on tiptoes. Walk forward and backward a little;
insoles for shoes
This treatment involves a leather product that keeps the foot in the correct anatomical position and prevents the problem from developing further. They must always be worn with everyday shoes and are inserted into boots or shoes. If the product is larger than the garment, it can be cut along the top or inner edge without damaging the outer cut.
Also read: Tuberculosis of the bones and joints
Classification of insoles by degree of hardness
Valgus insoles come in different names:
Disease prevention (prophylactic) products have a low and soft supinator, which yields to the pressure of the foot and changes its original shape. They can be used with any closed footwear.
Prophylactic insoles for valgus are made of leather and have medium rigidity, which keeps the shape of the insoles in their original position. When choosing footwear for this type of products, you should pay attention to a high heel and a buckle that holds the foot firmly in place.
Therapeutic insoles (therapeutic insoles) are rigid and arcuate. They are placed in custom-made orthopedic shoes according to the shape of the patient's foot.
Cost of the product.
The cost of an orthopedic insole for Valgus depends on the material, size and type of shoe. Store-bought products cost less than custom-made ones. The average price in Moscow is between one and two thousand rubles.

General recommendations for selection
The insole is selected based on the length of the foot. The product is selected according to metric specifications or the size of everyday shoes is used. The material of the insole is selected individually, with the patient's comfort being the priority.
Prevention of deformities
To avoid the disease, some rules must be followed:
- Change in diet: avoid fatty and fried foods, include lots of vegetables, fruits and dairy products in your daily diet.
- Breaking away from bad habits.
- Control of body weight.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Walking barefoot on sand, grass or small stones is useful in the warm season.
- Self-massage after a day at work.
- Warm foot baths with sea salt every evening.
- Simple exercises: walking on your toes and heels, rolling a roller or a glass bottle, picking up a pen from the floor, rotating your feet.
- When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist.
Treatment of flat foot deformity is difficult and time-consuming. Follow the doctor's recommendations and remember to use an insole to relieve the discomfort and stop the development of the pathological process.
What is a grade 1 hallux valgus?
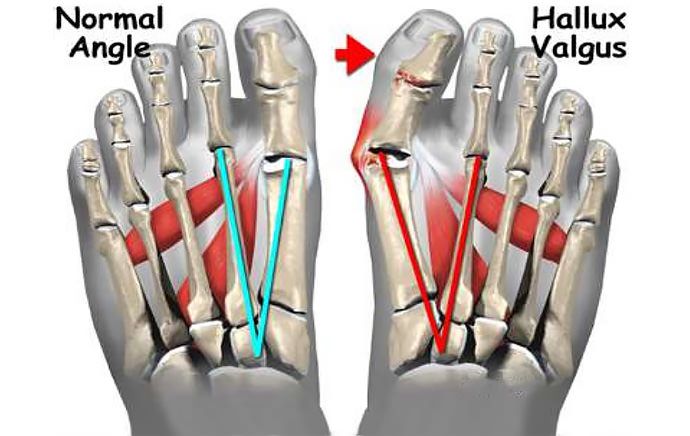
Hallux valgus is an outward curvature of the big toe, and the bulge that forms at the base of the toe is nothing other than the medial part of the metatarsal head. If the cause of the misalignment remains, the thumb subsequently deviates further towards rest, 1. the metatarsal bone retracts further inwards, and its head expands to form a bony callus that can withstand the constant pressure and the withstands friction. However, in stage 1, these changes are barely visible to the naked eye and symptoms such as pain, significant thickening, etc. are not yet present. However, patients may experience fatigue in their legs after a long walk or other physical activity. However, this is often perceived as normal and not taken seriously. This is the insidiousness of the disease and the reason why most patients only see an orthopedist in later stages. Normally, the interdigital angle between the 1st and 2nd metatarsals should not be greater than 10°, and a deviation of the thumb from the 1st metatarsal of up to 20° is considered normal. Hallux valgus grade 1 is when the interdigital angle is greater than 10° but less than 12° and the deviation of the big toe is no more than 25°. Visually detecting such changes is therefore difficult, if not impossible. For this reason, it is important to undergo an orthopedic examination at least once a year if there are signs of disease progression. In this way, the pathology can be diagnosed at the first stage and measures can be taken to stop its progression and eliminate it. If the disease is left untreated, the deformity will progress and lead to collapse of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. This leads to significant cosmetic impairment, as not only the big toe but also the neighboring toes are twisted and painful swelling occurs. In addition, the risk of synovitis, arthritis and arthrosis of the affected joints increases dramatically. In the advanced stage, patients have great difficulty walking because they are in constant pain and their shoes no longer fit.
Treatment of hallux valgus grade 1

The treatment of hallux valgus grade 1 is primarily conservative because it does not cause any other pain or discomfort to the patient. However, in some cases, minimally invasive surgery may be indicated to achieve optimal results.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed by foot x-rays and plantography results, it is advisable to review living habits and lifestyle. Eliminating the factors that cause metatarsal misalignment is essential for maximum treatment effectiveness.
Therefore, all patients are recommended to be careful when choosing footwear for everyday use and to give preference to orthopedic models with a wide toe box and a comfortable square heel. Such shoes ensure that the load is evenly distributed across the support points of the foot, provided there are no flat feet, and, above all, do not constrict the toes. This will help stop the progression of pathological changes.

However, this does not mean that women with first degree hallux valgus have to give up nice shoes with pointed toes and high heels forever. Such shoes can be worn on special occasions, events, etc. but should be avoided in everyday life.
It is recommended not to wear them for more than 2 hours at a time.
Even when treating grade 1 valgus deformity, it is important to normalize weight to reduce stress on the foot. In some cases this requires little effort and an increase in physical activity, but in more severe cases the help of a nutritionist may be required. However, strict diets of any kind are not recommended. They cannot provide all the substances the body needs to function properly. Therefore, this type of weight loss does more harm than good. Meals should always be varied and balanced, and the easiest way to prepare such a diet is with the help of a qualified nutritionist.
How to properly wear orthopedic shoes for children
Wearing anti-allergic shoes for a child can only be prescribed by a doctor, an orthopedist. This is the only way to achieve a therapeutic effect and stop the development of the disease.
General recommendations for your child to wear orthopedic shoes can be found on our website. The average wearing time is 5-6 hours per day to achieve a positive effect. Only the time when the child is standing or walking is taken into account. The results of the corrective effect of anti-slip shoes are usually only visible after 6 months of regular use.
It is important to replace shoes on time as children grow quickly. Up to the age of three, a pair should be changed at least every three months. Pay attention to your child's feet; If the inside seams of the shoes are split, it's a sign that it's time to buy a larger pair.

An unpleasant problem - a valgus foot deformity can cause a lot of trouble to the child and his parents. However, with proper treatment, it can be resolved in the foreseeable future with the help of special orthopedic children's shoes. It is important to visit your orthopedist regularly in order to identify the disability early and to carefully follow his recommendations regarding the selection of the right footwear and wearing habits.

Olminskogo Str. 5, St.
Exercises for flat feet for children from 1.5 years old. Complex for advanced users

The exercise device is supplemented by a compensating cushion. This is a rubber disc that is partially filled with air.
For small children aged 2 and over, some of the exercises can be replaced with exercises on the balancing cushion. This trains the foot and ankle muscles as well as the balance system, which in turn creates a stable, balanced muscle tone in the legs. The surface of the balancing cushion is grooved, which additionally stimulates the soles of the feet and improves microcirculation in the tissue.
Flat foot exercises on the balancing cushion
Place your child in a high chair and place a balancing cushion under his feet. Extend your arms and ask the child to get up from the chair. Initially, help the child maintain balance. Later, teach the child to stand up and balance without your help. Repeat the exercise 5-7 times.
Ask the child to stand on the balance cushion and stay on it for up to a minute, first with their eyes open, then with their eyes closed for a few seconds.
Once your child has learned to stand securely on the pillow, play ball games with him. First, he throws the ball to you and you catch it. Then throw the ball to the child and he has to catch it while standing on the pillow. Repeat the exercise 8-10 times.
'Lifting on one level'. Place a balancing cushion on a step. The step can consist of a sturdy box. The child should climb onto the step on which the balancing cushion is lying and then step back down. Repeat the exercise 5 times for each leg.
What is the 'salt' of a deformity?
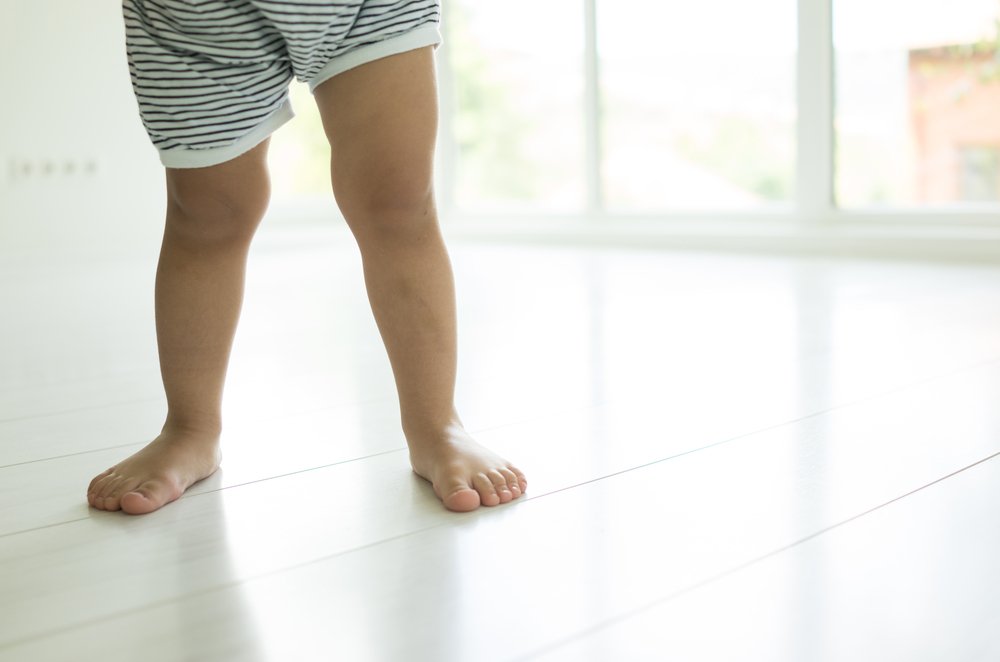

A valgus deformity is a curvature of the lower limbs in which the axis of the lower limbs is directed slightly inward compared to the physiologically normal axis. When viewed from the side, the legs have an X-shaped configuration. The degree of curvature can vary, the causes can be different - but one after the other.
Valgus curvature of the lower limbs is quite common. It is not a cause for concern as in most cases it goes away on its own. As you grow up, your legs take on a physiological shape. However, this does not weaken the parents' vigilance towards their child, since the situation must be kept under control and timely measures taken.
Valgus can be congenital, meaning it results from a fetal malposition, or it can be acquired, meaning it can be a result of maldevelopment of the musculoskeletal system.
The child stands up and learns to walk as his body grows. However, body growth is not always uniform, and individual joints, ankles, ligaments and bones may grow slightly faster. Due to the uneven development of the body, valgus deformity may develop on the legs.
The development of a valgus deformity can occur in various joints. The knee and ankle joints are most commonly affected; curvature of the toe joints is also possible, and more rarely of the hip joint.

First-class care: what modern diapers can do
How can one distinguish between a pathological leg curvature and a variant of normal child development?
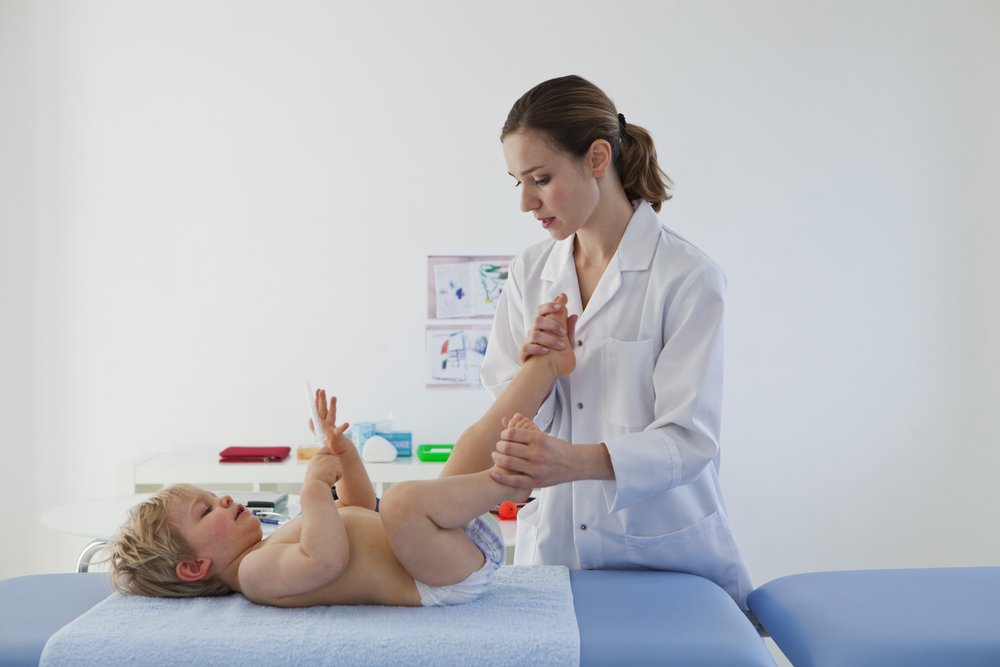
If the valgus deformity does not lead to significant impairment of the support function of the lower limbs, the curvature is mild, does not progress and resolves over time, this situation is normal. If the leg deformity is significant, progressive, affects gait and does not resolve spontaneously, it is a pathological situation. In any case, the child should be examined by a pediatric orthopedist and the situation should be corrected at an early stage.
Consider the factors that lead to valgus foot deformity:
- Inflammation of the bunions. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets, a disease that affects bone development. This disease requires early prevention and treatment.
- Overweight. If a child is overweight, the strain on the child's musculoskeletal system increases and can be a significant cause of lower limb deformities.
- Inappropriate choice of footwear. Tight and uncomfortable shoes can also cause foot and ankle valgus.
- Low mobility of the child. In order for the musculoskeletal system to develop properly, the muscles need sufficient tension. If this is not sufficient, certain muscles can become hypertonic and their antagonists can become hypotonic. This means that some muscle groups are forced to work hard while others are more relaxed than necessary. Visually, this is accompanied by abnormal alignment of the joints.
- Underdevelopment of the ligamentous apparatus. Ligaments fix the bones of the lower limbs in a physiological position; excessive flexibility or underdevelopment of the ligaments can lead to valgus deformity of the legs.
- Injuries. Knee injuries in childhood can result in deformities of the lower limbs, with a unilateral deformity usually developing on the injured side.
Diagnosis of flat feet and valgus in a child
Abnormalities are usually first detected by parents or the pediatrician during a routine examination of the child. A final diagnosis can only be made by an orthopedist based on the results of a special examination.
The doctor first examines the child and checks the alignment of the heel and toes as well as the structure of the arch of the foot. If deviations, inward displacement of the foot and flattening of the arch are found, additional examinations are ordered. Source:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19594079
Vukasinović Z, Zivković Z, Vucetić C.
Flat feet in children // Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2009 May-Jun;137(5-6):320-2
- Three-dimensional x-rays show abnormalities in the position of the feet relative to each other.
- Computer-assisted podometry shows abnormalities at a stage where they are not yet visible.
- Computer-aided plantography can be used to calculate and assess foot parameters.
- An ultrasound examination of the joints is not always carried out, but only if abnormalities are suspected.
Parents should also see a pediatric neurologist who will examine the peripheral and central nervous systems, rule out or confirm abnormalities, and recommend treatment.
Parents should be vigilant when their child
- has an X-shaped base;
- only occurs on the inside of the foot;
- is clumsy;
- runs unsafely
- shuffles;
- tires quickly when walking.
These symptoms occur in all children who are just learning to walk and will resolve over time. However, if the symptoms persist for a longer period of time, it makes sense to see a doctor immediately.
Stages of development of the disease
Depending on the degree of misalignment, the orthopedist determines, among other things. Stage:
- First stage (10-15 degrees) – easy to treat;
- second stage (15-20 degrees) – treatment is more time-consuming;
- third (20-30 degrees) – lengthy treatment that demands a lot from the patient and parents;
- Fourth (more than 30 degrees) – long treatment, if unsuccessful – surgery. Source:
VV Lashkovsky
Radiological characterization of the classification of valgic flat foot deformity in children // Journal of GrSMU, 2010, ¹ 1, pp. 57-61
Why flat feet should be treated
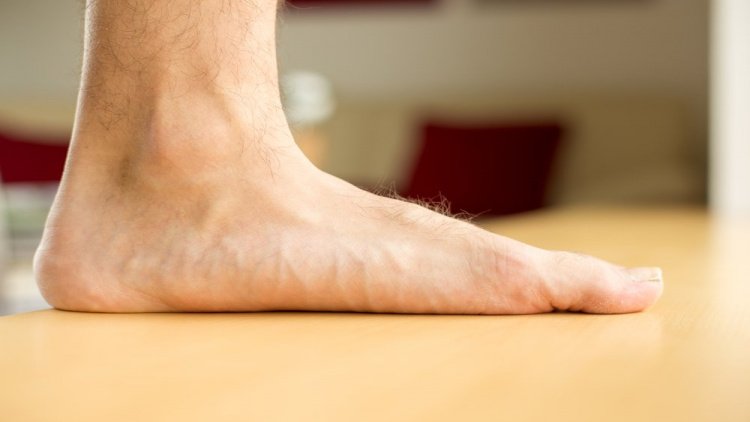
Flat feet are a relatively common problem. According to various data, 50-60 % of the Russian population suffer from this problem. Most often, flat feet develop in childhood because the child's bones are not strong enough. It is a big mistake to think that adults are not affected by this disease. The cause of foot deformity in these patients may be trauma, excessive strain on the legs during standing work or sports, a sedentary lifestyle, or obesity.
The type of bone damage can occur longitudinally, transversely or in combination. It does not go away on its own, but often worsens over the years and leads to further deformities - leg curvatures and spinal problems occur. The quality of life is impaired - patients complain of fatigue, pain, calluses and blisters on the soles of their feet.
Conservative treatment of flat feet
For deformed feet, orthopedists begin with conservative treatment methods. Patients are recommended to wear special orthopedic insoles and, in severe cases, therapeutic shoes every day. Massage, physical therapy, and exercise help reduce bone curvature. To avoid bone protrusions, doctors recommend wearing special corrective plates to fix the big toe.
In the early stages of flat feet, these methods can slow and even prevent further bone deformity. However, only if the corrective treatment is carried out permanently - e.g. B. You must wear tampons or pads daily.
But even with appropriate therapy, conservative methods cannot eliminate the problem. Therefore, if there are noticeable malformations and severe symptoms, surgery is recommended.
Orthopedic splints and fixators
Splints and fixators can firmly anchor deformed metatarsal and toe bones. Rigid splints (splints) are fixed to the foot and prevent the toes from moving.
They are worn at night or when resting, which means that rigid rails must not be walked on.
Silicone splints can also be used. These are not as rigid but can fix the bone in the correct position. Their main advantage is that you can wear shoes without removing the splint. The splint is barely noticeable, but the process of correcting the deformity continues.
insoles
Insoles help distribute stress across the entire foot by reducing pressure on the metatarsophalangeal joint. They are an effective way to combat flat feet. Your hearing care professional will find the right orthoses for you by taking measurements and making them.
To find or make orthopedic shoes, you must contact a specialist. With a valgus deformity, they must meet the following parameters:
- Correct and clear fixation of the ankles, the foot must not sag;
- The arch of the foot should be correctly fixed;
- The sole should have anatomical supports that distribute the load evenly over the entire foot;
- The sole must fit tightly to the foot and leg;
- The nasal part of the sole should be flexible.
It is advisable to wear orthopedic body supports in addition to the special shoes. Proper spinal alignment helps better distribute load on the lower limbs.
Your doctor may prescribe medication to relieve or reduce inflammation in the joint and improve tissue nutrition (trophism). Ice packs can help relieve pain and reduce swelling.
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Surgery is performed when medications and fixation methods no longer work.
The procedure is called a bursectomy. The surgeon removes the bursa that contains synovial fluid and returns the thumb to the correct position by realigning the bone.
If you have difficulty walking, the joint in your foot is red and inflamed, and you have persistent pain, you should not be patient but consult an orthopedist.
Read more:- Massage for flat feet.
- flat feet (valgus foot).
- flat feet.
- Buy insoles for flat feet.
- Shoes for flat feet.
- Which doctor treats flat feet?.
- Orthotics for flat feet.
- flat feet and valgus.
