Physical therapy for children with congenital clubfoot is indicated from the first days of life against the background of general orthopedic treatment. At the age of 7-10 days, the child's ligamentous and muscular system can be effectively treated.
- Hallux valgus deformity
- Conservative treatment methods
- Stages of disease development
- diagnosis
- Valgus foot deformity in children. Causes and symptoms.
- Treatment of flat foot deformities in children
- What to do if your child has a flat foot deformity (clinical guidelines)
- How can you tell if your child has a valgus deformity?
- Flat and broken feet
- Therapeutic exercises for flat feet
- Preoperative preparation
- How long does it take to recover from reconstructive foot surgery?
Hallux valgus deformity
Hallux valgus is a forefoot deformity with deformation of the big toe joint and forward deviation of the toes. Visually, the pathology is represented by a so-called 'footprint' on the inside of the foot.
In the early stages, the disorder is only an aesthetic problem that prevents you from wearing nice shoes and occasionally causes discomfort. However, if the triggering factor is not eliminated, the changes progress over time. The triggering factor is usually uncomfortable shoes and high heels.
As the disease progresses, severe pain occurs, and the changed shape of the foot significantly limits the choice of footwear and makes daily physical activity more difficult. At this stage, the patient has to go to the clinic whether he wants to or not.
In order to prevent further progression of the disease, German specialists recommend that patients consult a specialist at the first signs of hallux valgus. The treatment of hallux valgus is then possible in Germany without surgery and in a short time.
Diagnosis of valgus deformity is simple - the doctor examines the foot and orders an X-ray to determine the severity of the pathology. In addition to x-rays of the affected toe, the other foot as well as the ankle and other joints of the foot are also examined. The valgus deformity itself or the causes that led to it can also be the cause of other deformities of the foot that need to be recognized and corrected.
Conservative treatment methods
Conservative treatment of valgus deformity abroad includes the following approaches:
- Wearing customized orthopedic shoes, using insoles and special valgus splints;
- Complex use of physiotherapeutic manipulations, foot massage;
- Selection of a complex of therapeutic exercises;
- Use of local and systemic anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pain, redness and swelling.
Patients should be aware that they cannot eliminate the valgus deformity using conservative methods, but all of the above measures will slow its progression. After discharge, patients need to perform therapeutic exercises, monitor the quality of footwear and use special orthopedic devices. This is the only way to stop the disease. Of course, this does not mean that conservative treatment of hallux valgus is ineffective and everyone should undergo surgery, but there are also a number of lifestyle recommendations after surgery to ensure that the pathological process does not recur.
Stages of disease development
The feet gradually become deformed. First, the patient complains of discomfort in shoes, the inability to find the right size, then foot pain at the end of the day. The curvature of the big toe and the deformation of the forefoot begin. The metatarsal bone lifts. The inside of the arch of the foot is flattened. If left untreated, the transverse arch of the foot sinks even further and the toes are crooked.

diagnosis
Evidence of an existing valgus curvature of the foot is possible using a
- Examination by an orthopedic surgeon.
- X-ray examination in three projections – shows changes in the position and height of the foot.
- Computer-assisted plantography – detects flat feet, angles of curvature and other parameters that help determine the degree of deformity.
- Podometry – helps determine weight distribution on the foot.
Valgus foot deformity in children. Causes and symptoms.
Valgus foot usually manifests itself in early childhood. causes – are congenital genetic factors, problems during pregnancy, etc. It is no coincidence that newborns are examined by surgeons already in the maternity ward.
Children and young people may complain of rapid fatigue and inability to work.
Treatment of flat foot deformities in children
What to do if your child has a flat foot deformity (clinical guidelines)
- Don't panic because the situation is manageable.
- Try to keep the child's weight within the optimal range.
- Avoid diapers at the age of 1-1.5 years, as this leads to excessive adduction of the hips and therefore the feet.
- Use orthopedic shoes with firm ankle soles
- With grade I deformity, exercises and massage should be performed to strengthen the arch of the foot and lower leg muscles.
- Use individual orthopedic insoles from the age of 4 and have them corrected 3 times per year.
- Visit an orthopedist at least once a year.
Surgical treatment of flat foot deformity - arthroemisis of the subtalar joint is indicated for grade 2 and 3 deformities - is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which small titanium implants are inserted into the neutral part of the foot. The optimal age for this correction is 10-12 years. The advantages of subtalar joint arthroplasty include simplicity, minimal invasiveness, early function, and the ability to walk without a cast or crutches on the day of surgery.
How can you tell if your child has a valgus deformity?
- Look at the shoes your child wears for more than one season. They should not be curved inwards at the heels and stamped on the inside of the sole.
- If you look at the back of a person standing with their feet straight, the axis of the shins corresponds to the axis of the heels. An outward inclination is an expression of a valgus foot position.
- You can smear the soles with a little oil or fat cream and place them on a clean sheet of thick paper. The footprint at the narrowest point in the middle third of the foot should be approximately 1/3-1/2 the width of the forefoot. If the imprint widens inwards, this indicates a flat foot. The disappearance of the impression in the midfoot indicates a valgus foot deformity.
Flat and broken feet
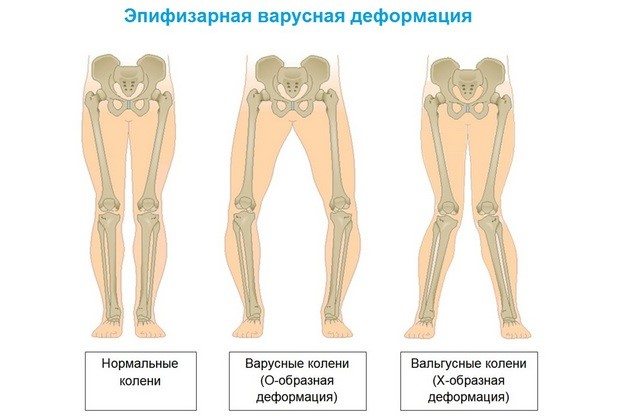
There are not only congenital deformities of the varus type, but also valgus feet.
Flat feet are an orthopedic form of foot deformity in which the arch of the foot is flattened. It is associated with a loss of cushioning function and is a common deformity.
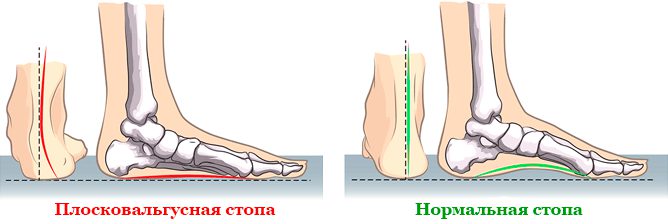
In orthopedics, there are several types of flat feet.
| type of deformation | Cause and characteristics of the disease |
| Congenital flatfoot | Clinical pathology caused by underdevelopment of the fibula, retention of the amniotic sac, or embryonic defects. |
| Rachitic flatfoot | A consequence of rickets in young children. The consequence of the development of flat feet is a softening of the bones and a weakening of the muscles and ligaments. The child's foot becomes deformable under the weight of the body, the arch of the foot drops and the forefoot is pulled outwards. |
| Paralytic flatfoot | The result of cerebrospinal poliomyelitis, paralysis of the child's spinal cord. The severity depends on the number of shin muscles damaged - one or two. |
| Post traumatic flat foot | Deformity of the foot caused by a fracture of the tarsal bone or an abnormal stiffening of the ankle. |
| Static flat foot | The main cause of valgus deformity is poor muscle tone. |
The latter type of orthopedic disease is the most common. The first signs of a static ankle deformity are rapid ankle fatigue and pain in the calf muscles when running or walking.
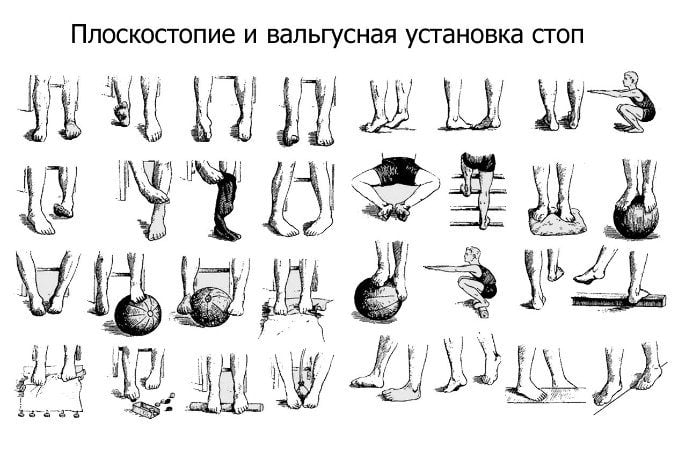
Therapeutic exercises for flat feet
Exercises for flat foot deformities strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the lower leg and foot, build supportive tone in the longitudinal arch and correct the overall deformity. The following describes exercise methods with the following goals:
Treating a severe arch deformity involves moving the arch of the foot to a higher position. For this purpose, special orthopedic shoes are recommended, which have a height of 2-5 mm on the inside of the sole and flatten towards the outside.
These shoes should not be worn all the time. To avoid the foot getting used to the comfort, the positioning treatment should be carried out for 2-3 hours.
It is correct to combine the corrective footwear with normal shoes or boots, but not to walk in soft or milled shoes.
The massage is aimed at improving the function of the forefoot supinator, inner toe groups, shinbone and foot muscles. The outer parts of the supporting organs should also be massaged. The masseur performs friction, stroking and vibration.
The exercise should be performed slowly and steadily following the massage therapist's instructions:
- The starting position is supine. The masseur flexes and straightens the right foot with the right hand and fixes the left ankle in a rigid position.
- Without changing the starting position, the patient independently brings the feet closer and further apart, making sure that they touch each other.
- The patient lies on his back. The masseur performs a right-left rotational movement with his right hand while holding the left shinbone in the lower third. A similar gymnastic action is performed with the other foot.
- If the patient has an outward deviation of the forefoot when standing or walking, gymnastic hypercorrection should be performed. The instructor holds the left ankle with his left hand and the forefoot of the left foot with his right hand so that the carpus is on the outside and the toes are on the back of the foot. The goal is to bring the forefoot inward.
Preoperative preparation
The standard examinations are carried out: blood and urine test, x-ray of the foot, ECG (if the results are available, they do not need to be repeated).
The patient is admitted to the ward on the day of the operation. The patient receives the necessary hygiene items and food for the entire hospital stay. The patient can also be accommodated with a relative.
Before the operation, the surgeon conducts a preoperative examination and the anesthesiologist selects the most appropriate type of anesthesia. The patient is then prepared for the operation.
The operation on one foot takes between 30 and 40 minutes, and the operation on both feet takes around 1.5 hours. The operation is performed under spinal or general anesthesia (depending on the indication).
How long does it take to recover from reconstructive foot surgery?
The recovery time after reconstructive foot surgery depends on the extent of the procedure. It is likely that your doctor will advise you not to put any weight on your operated foot for at least one to two weeks. You will likely wear a boot or bandage during this time to immobilize the foot and speed healing.
Full recovery from reconstructive foot surgery can take between four and eight weeks. During this time, your podiatrist may provide you with regular physical therapy treatments to increase the strength and function of your foot and ankle.
| Surname | Price |
|---|---|
| Foot and toe endoprosthetics | 18 400 ₽ |
| Foot and toe endoprosthesis – correction of flat foot deformity (valgus) | 60 000 ₽ |
| Isolated toe reconstruction for deformity (without metal structure costs) | 24 200 ₽ |
| Reconstructive surgery on the forefoot of a foot | 38 300 ₽ |
| Reconstructive forefoot surgery on both feet | 47 420 ₽ |
| Complex reconstructive surgery on both feet | 115 460 ₽ |
| Complex reconstructive surgery on a foot | 66 020 ₽ |
The first consultation is free!
Read more:- flatfoot μb.
- Stages of hallux valgus.
- Flat valgus deformity.
- Shallow valgus deformity in adolescents.
- Deflection of the first toe.
- ICD 10 chalgus valgus.
- chalgus valgus.
- Shallow valgus deformity in children.
