7. Tighten your feet with an elastic band: pull the band towards you while supporting yourself with your foot.

- 9 EXERCISES FOR THE LOWER LEG MUSCLES
- anatomy
- Aerobic shin training
- bench press
- French bench press
- An effective workout
- crouch jumps
- block jump
- jump rope
- jump rope
- swing up
- Chapter 32 Structure of the lower leg muscles
- Articles to read:
- The best exercises for the triceps
- Combined training for the triceps
- Option 1: French bench press plus California bench press or narrow grip.
- Variant 2: French upper body press plus bench press.
- Variation 3: Barbell top squat with bottom grip plus bottom squat with top grip
- choice of exercise
- 1. top - bottom
- Muscle regeneration between training sessions
- Trapezius Muscle Anatomy
- Functions of the trapezius muscle
- diagnosis
- Treatment
9 EXERCISES FOR THE LOWER LEG MUSCLES
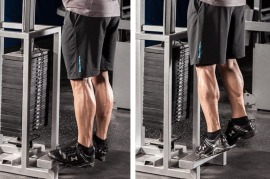
Muscle Shin Splints: 9 Daily Simple Exercises.
1. Lean your shoulders against a wall, plant your heels a foot away from it, slowly lift your toes 10-15 times, and without touching the floor, step down.
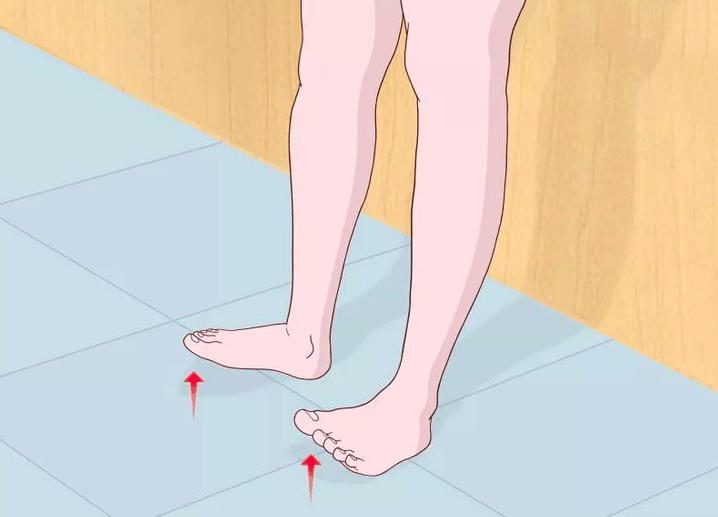
2. now qualitatively work on the toe raises of each leg separately. Stand against a wall, lean one foot against it and raise the toes of the other foot 10-15 times, descending without touching the floor.
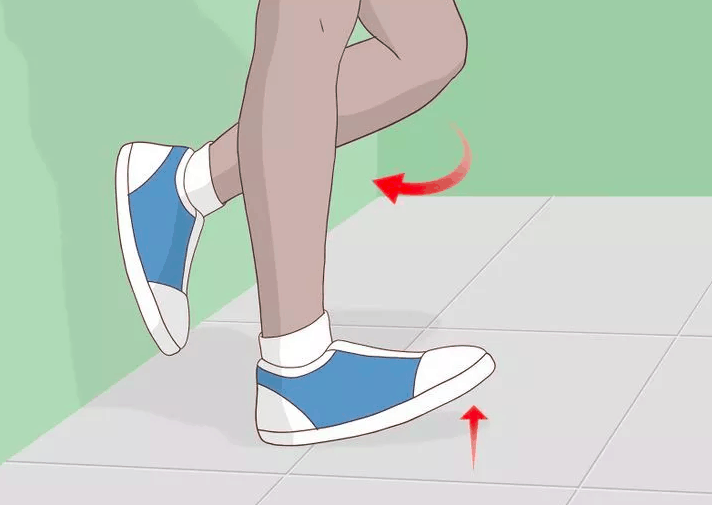
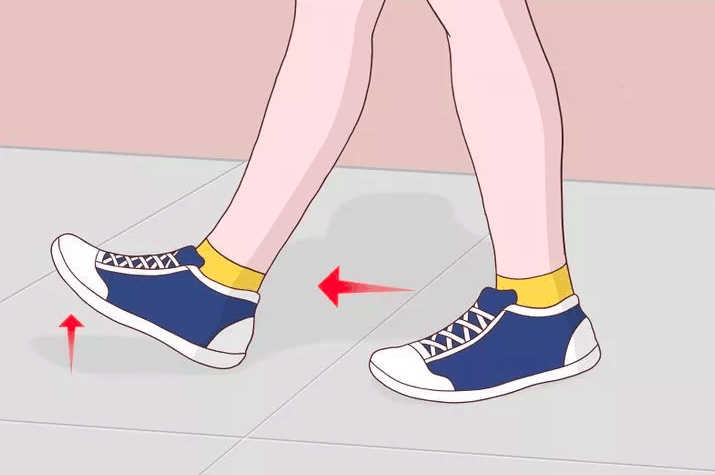
(3) This exercise can also be done while walking: just walk on your heels. Make sure your foot lands on the heel and the toe is raised, do not drop, walk 10-15 steps. You can repeat this exercise several times throughout the day.
4. When stretching, don't forget to stretch your shin muscles. This is best done while sitting and using your own body weight. Sit on your feet, arch your back slightly, and transfer the pressure to your feet by pressing lightly and contracting your calf muscles for 30 seconds.
anatomy
The lower leg muscles are located on the tibia and fibula. They involve several muscles, but the most important muscles we need to look at are the anterior tibialis muscle and the triceps brachii muscle.
The anterior tibialis muscle is located on the outside of the tibia and can be easily felt. It is involved in the extension and supination of the foot.
The triceps muscle is located on the posterior surface of the tibia. As its name suggests, it consists of three heads, two of which form the superficial part of the muscle, the calf muscle. The deep bundle of the triceps muscle is quite extensive. It forms the massive form of the lower leg and resembles a fish in shape. Hence the name: flounder muscle.
In the calf and camel muscles, the slow (oxidative) fiber type predominates. They are predisposed to prolonged aerobic work. They are also characterized by a very high explosive power. All weightlifting movements are predominantly performed with a strong extension of the foot.
In order to hypertrophy a muscle, stress must be generated. So how do you create them for the explosive and endurance muscles of the lower limbs?
Aerobic shin training
The shin muscles get a good workout during prolonged aerobic activities like walking, running, and cycling. When training on a stationary bike, use proper pedal position and range of motion. The main support should be on the fingertips of the feet, and the distance between the seat and the pedals should be chosen individually. The range of motion should allow almost full extension of the foot. You should choose a workout where you can do 80-85 rpm for at least 30 minutes. You can train your lower leg muscles perfectly on the elliptical trainer and the stepper. Modern cardio equipment also includes the jump rope, which engages the target muscles.
In addition to cycling, the lower leg is also good for strength training in the gym. You can work with both free weights and machines.
Include the following exercises in your exercise routine:
- leg press foot extension;
- lifting of toes in the gae ;
- foot stretches sitting on a bench or a special trainer;
- Raise dumbbells (barbells) while standing on tiptoe.

Since the lower leg muscles are endurance muscles, they should be engaged for at least a minute per attempt. The working weight should be chosen depending on your training plan. You can e.g. B. Do 15 reps slowly with a short pause at the point of maximum resistance, or do 30 reps at a faster pace. The most important thing is to keep in mind the duration of the approach. When doing this type of training, let the burning sensation in the working muscles guide you.
Shin training is often combined with hamstring work. Many athletes alternate between bicep, hamstring, and lower leg exercises. This technique was widely used by Tom Platz, the legendary bodybuilder of the 20th century. He very often added supersets for these muscle groups.
bench press
The bench press is performed on a bench (Smith bench or power frame), and when it's at a negative incline (legs overhead), the effect is even better.
Lie on your back on the bench and rest your shoulder blades and glutes on it. The feet are pressed to the ground. Take the barbell off the backrest and hold it at chest height with your arms outstretched. Keep the grip shoulder-width apart. Inhale and lower the dumbbell under your pecs. Then lift them up and exhale. Three or four sets of 6-12 reps is the norm.
When you spread your elbows wide, you're engaging the outer part of your triceps. Pressing them against the body puts the most stress on the long arm. Pay attention to the width of the handle. If it's too wide, your pecs will get bigger. If it is too tight, you can easily hurt your wrists.
French bench press
Used exclusively to 'pump up' the triceps. It is not a bench press in the classic form. The focus here is on stretching the arms. Relatively light weights are used. It is recommended to do this exercise at the beginning of the workout, but not at first. Do close-grip barbell bench presses or push-ups beforehand.
Hold a barbell (such as an EZ dumbbell) with a wide, straight grip. Raise them above your head. Inhale and lower the barbell behind your head (if you want to 'work' the long bar) or towards your forehead (if you want to 'work' the outside of the triceps). The elbows must be close together. In this case, the load rests on the long beam. Breathe in and out at the top point. Don't stop at the bottom. The norm is 3-4 sets of 6-12 repetitions. Do not hold the device in an inverted grip: the rod could slip out. Do not use heavy weights as the back muscles are strained. Always keep your feet on the ground for balance.
The exercise can be performed not only while lying down, but also while sitting. However, in this case, you need to take care of your technique. Losing your balance can cause injury.
An effective workout
crouch jumps
Place your feet shoulder-width apart, arms at your sides. Then squat down, but keep your body weight on your toes. Then, in an explosive move, jump up and land on your toes. Repeat this action several times.
block jump
Place a low block (bench, dresser) in front of you. Explosively jump onto a block and land on the balls of your feet. Return to the starting position and repeat the jump a few times.
jump rope
Get a skipping rope and jump on it for three to ten minutes. Get fast and beautiful calves with this classic exercise.
jump rope
Get ready to squat, but not on two legs, but on one. The other must be stretched out in front of you. Beginners can hold on to a chair or a wall. Do three sets of 10-15 repetitions for each leg.
swing up
Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Sit up and hop up. Gently return to the starting position and repeat the exercise several times. For maximum effect, grab a pair of dumbbells.
Chapter 32 Structure of the lower leg muscles

The tibial muscles, like the muscles of the thigh and pelvic girdle, are relatively highly developed, as are their ancillary apparatus, as determined by their loading associated with upright posture and lower limb motor function. The tibial muscles, which originate in the bones, intermuscular septa, and fascia of the tibia, affect the knee, ankle, and ankle joints. There are anterior, posterior, and lateral muscle groups in the tibia. The anterior group includes the anterior tibialis muscle, long toe extensor muscle, and long toe extensor muscle; the posterior group includes the triceps muscle (consisting of the calf muscle and the camel muscle), the popliteus muscle, the biceps muscle of the thigh, the flexor longus muscle of the toes, and the posterior tibialis muscle; the lateral group includes the musculus tibialis short and longus and the musculus fibularis.
The muscles of the rear group – especially the M. triceps surae – ensure the characteristic rounding of the lower leg. The triceps surae muscle is made up of two muscles: the calf muscle, which lies superficially, and the corset muscle, which is hidden beneath the calf muscle. The calf muscle is a two-jointed muscle that extends through the knee and ankle, while the trochanter is a single-jointed muscle that extends through the ankle only.
The calf muscle, the gastrocnemius muscle, has two heads: one medial and one lateral, the superficial layers of which are represented by powerful bundles of tendons. The lateral head begins on the outside of the femoral epicondyle above the inferior condyle; the medial head begins at the medial condyle of the thigh.
The lambdanoid muscle, the soleus muscle, is thick, flat, and lies in front of the calf muscle. The tubercle muscle has an extensive origin on the posterior surface of the tibia and on the tendon arch that overlaps the tibia and fibula. It is a feathered muscle and merges into a flat tendon that is involved in the formation of the heel tendon.
Articles to read:
- Chapter 33 Development of the abdominal muscles The abdominal muscles form the muscular basis of the lateral, anterior and posterior abdominal wall. Depending on the topography and the location of origin and insertion, the muscles are…
- Chapter 35 Muscle development of the arm The muscles of the free upper extremity are divided into the upper arm and forearm muscles. The muscles of the arm are in turn divided into two groups – the anterior (flexors) and…
The best exercises for the triceps
There are many different exercises for the triceps, but not all are equally effective. Here are the best exercises that will produce noticeable results in increasing the volume of your triceps.
It's one of the most effective exercises for the triceps that's easy to perform and doesn't require complicated training equipment. The bench press also trains the chest muscles and harmonizes the development of the arms and chest. Depending on the incline of the bench, you can specifically train the front or rear muscles when bench pressing. The bench press is recommended for both beginners and professionals.
This tricep exercise trains all three muscle heads. The French bench press is suitable for both professionals and beginners. There are several variants of the French press, but they are all about as effective and train the same muscle groups as the classic French triceps push.
A good compound exercise that aims to increase the volume of the triceps, especially the lower part. The technique for performing push-ups is quite simple. To make them more effective, you can use weights. According to Mike Mentzer, this exercise works best for the triceps. It can also be done outside of the gym as there are bars in stadiums, parks, etc.
An important advantage of push-ups is that they can be performed at home without additional equipment. It's basically a bench press, but in reverse. Push-ups from the floor also work the back, leg and abdominal muscles. Therefore, this exercise is used as a warm-up exercise. Insufficient loading is the negative side of floor push-ups, but having a weighted backpack or a partner creates extra loading.
If the exercise is performed on a lever machine, the advantage lies in the simple execution. The same muscle groups are used as with push-ups on the bar. Tricep push-ups increase tricep capacity in the same way as core exercises.
Combined training for the triceps

Doing more than two consecutive exercises for the same muscle group without rest is a blended approach. There are many exercises for tricep training that use wildly different working weights for the same number of reps. For example, an athlete who does ten reps of the French bench press with 70 kg can easily do ten reps of the narrow-grip bench press with 250-250 lbs. A lifter doing a 70kg French bench press on an overhead bar will easily be able to do 100kg triceps push-ups on the same bar for the same number of reps. This fact is used to create simple sequences for performing two consecutive exercises in tricep pushdown training.
Option 1: French bench press plus California bench press or narrow grip.
After executing z. B. After 10 repetitions of the French bench press (to failure), you should immediately begin the California bench press or the bench press with the same barbell. Your triceps are tired after the French bench press, leaving enough mass to complete the second exercise in the attempt.
Variant 2: French upper body press plus bench press.
After completing the required number of reps on the first exercise, immediately move on to the second exercise on that block and with that weight, without rest.
Variation 3: Barbell top squat with bottom grip plus bottom squat with top grip
After performing the top-grip tricep push-up from below, perform the top-grip tricep push-up on the same block. It is convenient to perform this exercise with each hand separately, since there is no need to grab the handle, only twist it.
The benefit of these combinations is that they can be done with a ball, especially in crowded gyms, and the tricep pumping on these variations is absolutely fantastic due to the lack of rest between the two exercises. However, frequent use of this technique sometimes has the opposite effect. Instead of the triceps growing, they can be overtrained.
choice of exercise
The first thing to think about is what kind of exercises you should be doing at the gym. The range of exercises is indeed wide, from the usual dumbbell and barbell exercises you can do at home, to the many different machines you can use in the gym for a more targeted and safer workout. We won't go into too much detail here and will only look at specific devices. Once you start exercising, you'll quickly find your favorite equipment and exercises. What is much more important is not exactly which exercises you do, but how you do them, how the exercises are distributed over the training days, what should be trained in one training session and what in another, which muscles are trained at the beginning and which at the end of the training session should be.
When dividing the exercises over the training days, three basic principles must be observed. These principles are primarily used to fill the training program with exercises.
1. top - bottom
The legs are the largest muscle group in our body. Therefore, there is an opinion that a separate day of training should be devoted to them. This is also supported by the fact that the biceps femoris and the quadriceps belong to different 'pull-push' groups, so that you can easily train them at the same time. Among other things, there is an opinion that muscles such as the biceps and triceps should not be trained separately at all, since they are already sufficiently stressed in chest and back exercises. Following these principles, we can divide our body into upper back, chest, and lower legs and train these parts alternately. Although it's better for beginners to train two days a week when transitioning from a total body workout to a split system, it can also be used by experienced athletes for an intense four-day training program. An example of this would be dividing muscle groups into training days:
Muscle regeneration between training sessions
Resting your muscles is just as important as making them work hard. Recovery time depends on several factors related to the size of the muscles and the extent to which they were damaged during exercise. The larger the muscle group in question, the more damage it will take from training and the longer it will take to fully recover. Another factor is the intensity of your workout. The amount of time you need to recover determines how much you use your muscles when you exercise. The harder the workout, the longer it takes to recover from it. It should also be noted that a beginner's recovery time is shorter than that of an experienced athlete because their muscle mass is lower.
A good exercise program isn't just a list of exercises and a visit to the gym. Strength training is a way of life. Train to train regularly. Train well without overdoing it. You're not going to build a good body in a month; don't even try. Remember to rest, stick to a program, get enough sleep, and generally lead a healthy lifestyle. You will have to work hard, but the result will be worth the effort. A beautiful, strong body and a sense of satisfaction with the work done will not last long.
Trapezius Muscle Anatomy
The anatomy of the trapezius muscle shows that it is actually a trapezius. To be precise, we have two trapezius muscles, one left and one right. Separately, they each have a triangular shape, with the apex pointing to the shoulder joint and the base pointing to the spine. When they come together at the spine, they form a trapezium. As a reminder, a trapezoid is a quadrilateral where two sides are parallel and the other two are not. By the way, since it is not one, but two muscles, it can happen that the trapezius muscle hurts on the left, the right or both sides.
The anatomy of the trapezius muscle shows that it is divided into three parts: upper, middle and lower. The upper portion is commonly referred to as the neck trapezius, while the middle and lower portions are referred to as the back trapezius. But we want to make it clear right away that this classification is not official - for the purposes of documents - but colloquial - for ease of speech. In general, the trapezius muscle is one of the largest muscles. It starts at the back of the head, extends to the lower thoracic vertebrae, covers the shoulders and extends to the collarbones.
Functions of the trapezius muscle
The trapezius muscle is the muscle that moves and stabilizes the shoulder, scapula, and neck. We activate the trapezius muscle when we try to straighten our shoulders and neck, when we bring our shoulder blades together and tilt our head back and forward, and when we move our shoulders up and down and back and forward. When we walk we move our shoulders and the muscle works dynamically, while when we sit at the computer it works statically. And even if we just stand with our arms down, the muscle works and provides an anti-gravity effect. By the way, to relieve the trapezius muscle, we tend to cross our arms in front of our chest or put them in our pockets.
Speaking of the anti-gravity function of the trapezius muscle, it becomes clear why when working at a desk it is important to be careful not to strain the elbows, otherwise the weight of the arms will overload them. If this situation is repeated day after day and lasts for many hours, the occurrence of pain is inevitable. This brings us to the question of what causes trapezius muscle pain. The same applies to driving a car - the elbows should not be strained.
The 'cervical' function of the trapezius muscle causes the head to rotate and tilt. Therefore, the monitor and TV screen should be right in front of us. It also prevents the development of pain and pathologies. By the way, the habit of holding the phone to your ear is also a cause of trapezius muscle pain.
diagnosis
The doctor can make a diagnosis based on the symptoms, medical history, and examination. When examining the tendon, the doctor will note swelling or redness in the area of the tendon of the triceps muscle, as well as tenderness on palpation. If necessary, an X-ray examination is ordered to rule out changes in the bone tissue. An MRI can visualize not only the condition of the bone tissue, but also the tendon itself and the extent of its damage. Laboratory tests can also be ordered if systemic, inflammatory diseases or metabolic disorders have to be ruled out.
Most patients with this condition recover with appropriate treatment and can return to normal activity within a few weeks. However, rehabilitation can sometimes take several months, particularly in patients who do not seek immediate medical attention. Appropriate early treatment (physiotherapy, physical therapy) is essential for speedy recovery. Inadequate treatment can lead to irreversible changes in tendon tissue.
Treatment
Tendonitis of the triceps muscleTendonitis of the triceps muscle can usually be treated, but in some cases treatment is ineffective. The first measure of pain relief is to stop all activities that cause pain. Conservative treatments for tendinitis include local cold therapy (20 minutes long, 3-4 times a day), NSAIDs (such as Movalis, Tselebrex, Voltaren), splints and orthotics to reduce stress on the tendon and allow tendon tissue regeneration.
Physiotherapy is very effective in treating tendonitis. Various physiotherapeutic techniques are used (e.g. ultrasound, cryotherapy, electrophoresis). Among the most modern treatment methods HILT therapy .
PHYSICAL THERAPY. An exercise program specially selected by an LFC specialist can restore muscular strength to the triceps muscle as well as mobility and strength to the triceps tendon. LFC begins as soon as the pain and inflammation subside. Intensity and stress are adjusted individually and step by step.
surgical treatment The operation of a tendon tear is the only treatment option and should be carried out no later than 2 weeks after the diagnosis of the tear.
Use of the material is permitted with an active hyperlink to the permanent article page.
Read more:- Anatomy of the triceps muscle.
- abdominal muscle.
- Tibialis posterior muscle.
- The flexor muscles of the foot.
- Lift your heels off the floor during the squat.
- Anterior shin muscle (tibialis anterior).
- Square soleus muscle.
- Which muscle extends the lower leg and flexes the thigh.
