Step 5 A plication of the lateral ligament complex with augmentation by an Arthrex synthetic internal graft is performed. The high-strength band is fixed inside the thigh and fibula with special SwiveLock knotless anchors. Anterior tissue (anterior talar ligament remnants, extensor retention) is also stretched and sutured to further strengthen the structure.

- athlete's foot
- causes
- Unresolved bony pathology of the foot:
- Constantly wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes with high heels, which shifts the center of gravity and overloads the forefoot
- Diagnosis of pes cavus.
- Surgical treatment of pes cavus.
- Solution
- Footwear for hyperpronation
- Exercises and stretches for hyperpronators
- Short footstand
- duck husbandry
- Calf stretch with closed chain
- Open chain calf stretch
- Stiff or floating foot?
- causes and symptoms
- How to determine your type: hyperpronation test
- Treatment of pronation disorders and flat foot deformity
- How to avoid the disruption
- Choosing the right running shoes for your pronation
- Is it possible to run in minimalist shoes with overweight people? Big, heavy people? With flat feet and hyperpronation?
- What do you think of the Newton running shoes, which are positioned as natural running shoes by the manufacturer?
- Recent Entries.
- Warning!!!
- Criteria for hypermobility syndrome of the joints
- heavy criteria
- Minor Criteria
athlete's foot
Athlete's foot can occur not only in athletes, but also in all other people. The name of this disease comes from the fact that athletes are more susceptible to it, as the infection usually occurs in locker rooms and shower rooms, and physical exertion also makes feet warmer and wetter. Tight-fitting sneakers can also promote the disease.
It is a relatively common fungal disease. In most cases, this type of ringworm is barely noticeable. Many people don't notice cracked heels, hard skin, or corns. Only when the skin begins to peel severely, purulent blisters appear between the toes and an unpleasant odor emanates from the feet does it become clear that a doctor needs to be consulted.
Qualified specialists with a great deal of experience work at the Kurska Health Clinic. They are able to determine the presence of a pathology in the early stages and prescribe a treatment that will soon lead to recovery. The clinic has its own diagnostic facilities, so patients can do all the necessary tests and make a doctor's appointment without leaving the clinic.
causes
Ringworm is caused by a fungal infection that develops in the top layer of skin. Fungal infections thrive best in a vital and warm environment and therefore most commonly affect the area between the toes.
Fungal infections are quite easily transmitted and transmission can occur in the following ways
– Touching the affected person’s toes;
– walking barefoot on dirty surfaces – swimming pools, changing rooms, shower stalls;
– wearing tight-fitting shoes – mushrooms are actively growing without access to air;
– irregular changing of socks;
– fungal infections in the past;
– weakened immune system;
– Living in a humid, warm climate;
- high age;
– prolonged contact of feet with moisture;
– Carrying out an occupation that requires prolonged contact with water.
If you are immune you may not show any symptoms, but in this case you become a carrier of the fungus. It's also important to remember that ringworm doesn't guarantee you won't get the disease again, but rather increases your risk.
Unresolved bony pathology of the foot:
Foot deformity (congenital or acquired): Flatfoot, particularly transverse flatfoot, clubfoot, a valgus deformity of the first toe that contributes to an abnormal distribution of body weight on the toes when walking.
The most important biomechanical cause of forefoot overload is overpronation – a constant accompaniment of flatfoot and pseudostopia. This is a condition where the edge of the nail plate gets pinched between the hammer toe (sole of the foot) and the anvil (shoe), causing permanent injury to the soft tissues of the toenail, leading to the development of an ingrown toenail.
Constantly wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes with high heels, which shifts the center of gravity and overloads the forefoot
Standard: Maximum heel height of 4 centimetres, so that 40 % of the load is on the heel and 60 % of the load on the forefoot. 1 cm heel height corresponds to 10 % the load on the forefoot.
The 8 cm high heel puts 80 % pressure on the forefoot, which leads to transverse flat feet, toe deformations and, in most cases, to the development of an ingrown toenail.
The way out: Refrain from constantly wearing high-heeled model shoes.
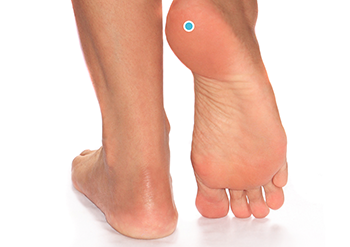
Diagnosis of pes cavus.
The diagnosis of a pes cavus always begins with a thorough medical history. An examination of the foot should be performed by a specialist in foot and ankle surgery and a qualified neurologist. The examination looks for changes in the arch of the foot, corns in unusual places, hammer toes and claw toe deformities. The strength of all muscle groups of the lower limbs and foot, gait and coordination are then assessed. In some cases, X-rays of the foot, a complete neurological examination, an EMG and consultation with a geneticist are required.
- Customized orthotics can effectively redistribute the load on the foot and significantly increase stability to prevent injury and reduce pain associated with sports.
– Change of footwear. High, chunky cuffs and low heels with a reduced heel allow for additional ankle and foot stabilization.
– Wearing an AFO (corset, brace) brace can effectively stabilize the ankle and reduce clubfoot symptoms.
When conservative measures are insufficient to manage the pain and instability of a pes cavus, surgical correction of the deformity should be considered. A specialist in foot and ankle surgery will select the necessary interventions on a case-by-case basis. If the pes cavus occurs against the background of neurological disorders, then there is a high probability of repeated interventions.
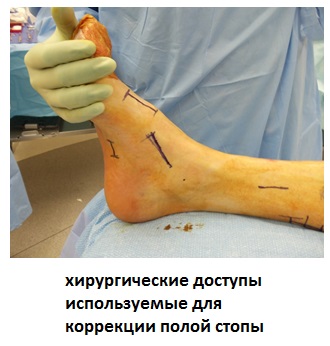
Surgical treatment of pes cavus.
The primary goal of surgery is to eliminate pain and improve gait and function through several possible procedures, including tendon transposition, tendon grafting, corrective osteotomy, and in some cases, arthrodesis.
Surgery is done only when the deformity causes pain, muscle weakness, and muscle contractures, and disrupts the normal biomechanics of gait. If you find a patient with a pes cavus who is not experiencing any symptoms, there is no reason to rush into surgery.
Solution
Relief can be obtained by choosing different shoes or by inserting insoles. These insoles are called orthotics. They are available over the counter or by prescription, and in some cases health insurance will even cover part of the cost. Orthotics support the arch of the foot and can improve the foot's grip on the ground. They can relieve the pain felt and reduce pronation during exercise.
Orthoses are individually made for you based on the information from the gait analysis. Over-the-counter insoles are made in more general sizes and shapes. These insoles are placed in your shoes before you begin walking or other activities.
Orthotics are a passive form of arch support and motion correction. Your doctor may also suggest physical therapy or even chiropractic care to actively change your gait over time.
Footwear for hyperpronation
Finding good shoes can also help:
- Before you buy a shoe, you should consult a podiatrist or a running store that offers a gait analysis. By watching your foot strike in slow motion, you can make the best choice that is tailored to your individual trajectory.
- Measure both feet to ensure you choose the best size that fits both feet. Pay attention to the width and length of your foot.
- Consider going to the store later in the day if possible. Your feet swell throughout the day. Shoes that are perfect in the morning may not feel as good in the evening.
- When trying on shoes, take the socks you usually wear with you. Some people wear thinner socks, others wear thicker socks. This can help you find the most comfortable fit.
- Don't rely on your shoes to stretch or wear out over time. If they feel tight, go up one size.
Exercises and stretches for hyperpronators
Some exercises and stretches can help relieve pain and discomfort or change gait by raising and strengthening the arch of the foot and correcting the position of the ankles and knees.
Short footstand
- Take off your shoes and stand shoulder-width apart.
- Stand with your toes on the floor and distribute your body weight on the outside edges of your feet by arching the arches of your feet.
- Hold the position for a few seconds and then return to the starting position.
- Over time, you should learn to maintain this posture throughout daily activities.
duck husbandry
The standing duck can also help you 'wake up' your glutes. These muscles play a role in how hard you pronate.
- Stand with heels together and feet rotated as in duck pose.
- Try to move your legs outward by engaging your glutes and tilting your pelvis under your body. You may notice your arches lifting and coming out of pronation as your feet rotate.
- You can hold this position for 30 seconds.
Calf stretch with closed chain
This stretching is sometimes referred to as wall stretching. You can do this stretch in pads to make sure you're not stretching the wrong muscles or tendons.
- Stand a few feet away from the wall.
- Bend your front knee and step one foot behind you to stretch your calf muscle.
- Support yourself with your hands on the wall in front of you.
- If you haven't already, try slowly lowering your back heel to the floor.
- Hold this position for up to 20 seconds, then repeat on the other side.
Open chain calf stretch
The open calf chain is a seated stretch.
- Sit on the floor and stretch your legs out in front of you.
- Keep your feet in as neutral a position as possible.
- Lean forward slightly and grasp the toes of your feet to extend them backwards, stretching your calves.
- Hold the position for 10-20 seconds and release. Repeat this stretch several times.
Stiff or floating foot?
'The webbed foot – needs a stable platform for the shoe, cushioning is low, and you may need a built-in device to limit excessive rotation.
Stiff foot – Requires a flexible, shock-absorbing platform.
Straight – When a curved trainer presses on the outside of the foot and creates excessive space on the inside.
Crooked – when a simple trainer presses on the big toe and its ankle.
causes and symptoms
There are several causes of the development of this pathology:
- Excessive pronation of the foot is often related to the sufferer's occupation. Ligaments and tendons are torn in athletes. The musculoskeletal system suffers, cushioning and other functions are impaired. The weakening of ligaments, muscles and tendons leads to the development of hyperpronation.
- The structures of the musculoskeletal system can wear out. Elderly people suffer from flat feet.
- A sedentary lifestyle leads to bad atrophic changes in muscles and ligaments. The result is hypo/hyperpronation.
- High heels do not provide sufficient cushioning. By the age of 40, most women will develop flat feet.
- Excess weight puts stress on the lower limbs.
- Poor foot position is hereditary. If the mother or father has a pronation of the foot, children can suffer from this disorder from a young age.
The pathological condition is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Patients often complain of pain in the arch of the foot. These occur as a result of inflammation or a strained ligament.
- Patients notice a loss of stability.
- Walking on the inner surfaces of the feet occurs. Pathological changes lead to pain in the heels, ankles, knees and lower back.
- Women are more likely to complain of a cosmetic defect, ie an outward curvature of the foot. Over time, the lowered arch of the foot puts additional strain on the bony structures and tendons. Plantar fasciitis - heel spurs develop.

How to determine your type: hyperpronation test
You can determine the presence of a foot deformity at home. The simple method takes no more than 5 minutes. To get the result you need a bowl of water and ordinary paper. Soak the soles of your feet in the water. Place them on the prepared paper. Look closely at the footprints. The test can show one of three results:
- The width of the footprint is equal to half the foot. This result indicates a physiological foot structure.
- The indented arch takes up the entire width of the foot. Such a pattern is characteristic of flat feet.
- If only the toe and heel prints are visible on the paper, the person is suffering from hyperpronation.
Pronation can be detected without special tests. A worn shoe reveals more about its wearer. If there is excessive pronation on the side of the liner, a clear deviation and deformation will be noted. Another sign of impairment is excessive wear on the inner edge of the heel area.
For the lazy there is a simple test. Stand up straight and ask a friend to tuck a toe under the arch of your foot. A normal overhang corresponds to a normal foot structure. A strong overhang indicates anomalies. The absence of an overhang indicates hypopronation.
Treatment of pronation disorders and flat foot deformity

The first step in treating pronation disorders is to relieve the patient of painful sensations caused by various forms of physical activity and to prevent them from worsening. For this purpose, the doctor will prescribe individually selected orthopedic insoles and shoes.
If you have severe pain after a day on your feet and if you have swelling, foot baths and massages can improve the condition.
Exercise is also important in treating pronation disorders. Regular exercise strengthens the muscles and ligaments involved in maintaining normal foot arches.
How to avoid the disruption

Regardless of what type of foot pronation disorder is present, it is not life-threatening. However, that does not mean that the issue should be ignored as the consequences can be quite devastating.
Modern medicine offers special computer-based tests to find out what caused the pronation disorder.
To avoid the appearance of these disorders, it is enough to choose shoes carefully. – They should be neither too loose nor too tight and have an insole (especially for children's shoes). It is best to choose orthopedic insoles to reduce the load when you are on your feet for a long time.
Choosing the right running shoes for your pronation

When choosing running shoes, you must first know what distance you plan to run, and then determine your pronation.
- Normal pronation – In this case, you should choose running shoes from the category 'Support'. Because with normal pronation, the natural cushioning of the human being works well and the foot does not need any additional support.
- people with flat feet, should pay attention to shoes of class 'Control'. They prevent excessive 'twisting' of the foot and ensure that excessive pronation is properly controlled. A lack of this class of running shoes can lead to various running injuries.
- hyperpronators, so people with a high arch should choose running shoes with neutral cushioning so they can take full advantage of the cushioning. This class of running shoe is referred to as 'Neutral'.
Treatment of pronation disorders does not take much time, nor does it require complex treatments. However, one should not allow the condition of the foot to deteriorate to the point where qualified orthopedic treatment becomes necessary.
Follow the advice in this article, pay attention to the quality of the shoes you buy and there will be no problems. My ladies!!! High heels have a negative impact on the health of your feet. This should not be forgotten.
Is it possible to run in minimalist shoes with overweight people? Big, heavy people? With flat feet and hyperpronation?
There are no uniform recommendations for overweight runners, because every case is different. If you're more than 20 percent overweight, don't wear minimalist shoes. Being overweight puts too much strain on your ankles. In this case, the most important thing is to shorten the stride length. This reduces the kinetic energy of the impact upon landing. The sole of the shoe in this case should have a certain thickness, but with a slight difference in height.
Running shoes with a very thin sole of two to three millimeters thick, like the ones I use, are not suitable as permanent shoes and for people who are not overweight but are just learning the right running technique. It would take one to three years of training to fully transition to such running shoes. Nevertheless, to the
However, it makes sense to use minimalist shoes as training shoes and to run certain distances in them. This allows you to get a feel for how your foot works without injuring it, which is very likely when walking barefoot, especially in an urban environment.
The same applies to tall people with a relatively high body weight. The transition to completely minimalist footwear will take longer, and there's no guarantee they'll end up being customized specifically for running. One option is to use such shoes in everyday life, choosing a model with a slightly thicker sole, a wide toe box and a slight drop for running.
In Russia, doctors traditionally consider flat feet as a type of pathology, while in other countries many medical specialists consider them a variant of the normal foot structure.
Hyperpronation is a consequence of this trait. Running in minimalist shoes is absolutely not contraindicated for people with hyperpronation. On the contrary, with specific running exercises and strengthening the feet, hyperpronation will decrease over time. In fact, one of the most common causes of hyperpronation is insufficiently strengthened feet and weak ligaments and stabilizing muscles. Exercise and proper walking make the muscles and ligaments of the feet strong so that movement becomes natural.
What do you think of the Newton running shoes, which are positioned as natural running shoes by the manufacturer?
Newton was probably the first company to notice the lack of natural running shoes on the market and started producing them. The only point of contention is the special fins on the tread. Newton touts them as a technological innovation that allows energy to be stored and released, making running more efficient. But since the beginning of the 21st century, studies from various institutes, from Harvard to Swedish laboratories, have shown that all the super technologies used in running shoes either do nothing for the athlete or only make running difficult. They didn't increase speed or reduce injuries, and they turned out to be just another marketing gimmick. I love the phrase from the book Run Fast and Injury Free by Gordon Peary, the great British runner of the 1950s and 1960s: 'Anything you put your body through will degrade your running technique'.
That said, Newton is a pretty good natural running transition trainer, just don't get too attached to him. If you shop around, you can find a model or two that are suitable for proper running at almost every running shoe manufacturer. It is not only pure sports companies that produce such running shoes. For example, Merell has a line of natural running shoes that work particularly well on rocky terrain. I own one of these shoes myself.
It's important to realize that it's not enough to just buy minimalist running shoes and expect them to improve your running technique. Such shoes will not change much on their own. They don't encourage, but they don't hinder natural running, which, judging by the statistics of injured recreational runners, is certainly the case.
Recent Entries.
Warning!!!
HMS is a common rheumatic syndrome that is not prognostically dangerous but causes serious diagnostic problems in practice. In a patient with suspected HMS, the doctor must pay attention to little-noticed details during the history-taking and examination; knowledge and experience are required to determine whether the nature of the complaint is consistent with the abnormal joint mobility noted. The treatment of HMS syndrome also has its own peculiarities and differs from the traditional treatment of other joint patients
It is important to explain to the patient the cause of their joint problem ('weak ligaments') in a way that they can understand and to reassure them that it is not a serious condition leading to impending disability. With moderate arthralgia, this is sufficient. It is helpful to discourage exercise that causes pain and discomfort in the joints and to minimize the risk of injury, which includes proper career counseling and exclusion from fun sports.
Criteria for hypermobility syndrome of the joints
heavy criteria
Minor Criteria
- Beiton scale 1-3 (for people over 50 years of age)
- Joint pain in one to three joints lasting less than 3 months or lumbodynia, spondylosis, spondylolysis
- Dislocation/subluxation in more than one joint or recurrent in one joint
- Periarticular lesions with more than two locations (epicondylitis, tendinitis, synovitis, synovial bursitis)
- Marfanoid (tall, thin, arm span/height ratio > 1.03, upper/lower body ratio < 0.83, arachnodactyly)
- Abnormal skin: thinness, hypersensitivity, scarring, atrophic scars
- Ocular manifestations: drooping eyelids or myopia or antimongoloid wrinkles
- Varicose veins or hernia or uterine/rectal prolapse.
Two major criteria, one major and two minor criteria, or four minor criteria must be present for the diagnosis of SGMS
Excluded: Marfan syndrome in the absence of lens and ascending aortic lesions; Osteogenesis imperfecta in the absence of multiple fractures and blue sclerosis
Read more:- How to determine the type of pronation.
- Sneakers with hyperpronation.
- pronation.
- What is pronation and supination?.
- pronation and supination.
- What is a neutral pronation?.
- Pronation and supination in anatomy.
- foot muscle pronation.
