Hammertoe deformity is one of the most common deformities of the little toes. In most cases, this problem is combined with a valgus deformity of the first toe (hallux valgus) and also occurs in patients with hollow feet and severe chronic concomitant diseases. However, it should be noted that in most cases the cause of the hammertoe deformity cannot be determined.

- ADVANTAGES OF THE METHOD:
- Indicators that can be calculated using photopodography:
- variant
- causes
- Hollow foot 'Equino
- A valgus for what reasons
- Lecture on 1. COMPREECT TREATMENT OF EQUINO-VARUS-HORALF DEFORMATION IN CHILDREN WITH I. PONSETI;2. the treatment of flat foot deformity in children;3. the treatment of the vertical ramus;4. the performance of 'classic' surgical procedures on the tibial structure;3.
- diagnosis
- surgical treatment
- diagnosis
- treatment methods
- Physical therapy in the treatment of hollow foot
- conservative methods
- surgery
- Some statistics
- Causes and risk factors for acne
- Preparing for orthopedic surgery: diagnosis
- Methods of performing orthopedic operations abroad
ADVANTAGES OF THE METHOD:
Objectivity of the method: more data (numerical features) on angular deviations and arch heights compared to conventional X-ray examination. The x-rays of the feet are usually taken in 2 projections, but we also photograph the feet from behind and assess the rear foot alignment (valgus - varus) and the footprints from below, for example. B. the width of the longitudinal arch, the transverse arch, the angulation of the forefoot (hyperpronation, supination), the angulation of the 1st and 5th calluses and corns. We use these measurements not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to assess the dynamics by comparing the data after a certain period of time (usually 3-6 months).
Of course, we also prescribe X-rays if there is pain syndrome and suspected foot osteoarthritis or osteochondropathy. However, we believe that x-rays are unnecessary for diagnosing the type and extent of flat feet and other foot deformities due to their low informative value combined with unnecessary x-ray exposure.
The method is simple and safe: we calculate standard values close to those of the radiological diagnosis of orthopedic foot pathologies, without having to expose the patient to X-ray examinations and unnecessary doses of radiation.
Indicators that can be calculated using photopodography:
- Forefoot, midfoot and rearfoot angulation coefficients
- Forefoot flatness index
- Flattening coefficient in the longitudinal direction according to SF Godunov
- Angle of deviation of the first and fifth toes
- Soft arch height measurements
- Measurements of the height of the arch of the foot (to the heel bone)
- Measurement of the angles of the longitudinal bone arch (analogous to standard X-ray technology)
- Heel and ankle bone angles (according to FR Bogdanov)
- Ankle and knee joint angle to the support plane
- Angle of deviation of the hindfoot and tibia from vertical.
The doctor first marks certain points on the skin of the foot with a marker (lower edge of the head of the first metatarsal bone, lower edge of the heel bone, apex of the medial malleolus, protrusion of the scaphoid bone, point of maximum height of the soft longitudinal arch).
The patient then stands on the plantoscope and digital images are taken in different positions.
The images are loaded into the computer and a graphical-mathematical analysis of the resulting images is carried out.
The patient receives a printout of the geometrically edited images and treatment recommendations.
variant
Cavus foot has similar clinical symptoms, and the diagnosis can be made without the use of additional techniques. However, there is also a classification that distinguishes several types of this pathology. There is a posterior, an intermediate and an anterior type, which have similar symptoms but can be distinguished by closer examination.
The posterior type deformity occurs due to insufficient tension of the triceps muscle. At the same time, the activity of the eye muscles and the finger flexor muscles deteriorates. This results in the following changes:
- The foot remains in flexion due to the activity of the tibialis flexor muscle group;
- the heel is lowered significantly below the normal level;
- At the same time, a valgus deformity can develop, which is manifested by a curvature of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe and its retraction outward.
The intermediate form of hollow foot deformity is much rarer. It is associated with contractures (tightness and limited mobility) of the supporting muscles of the foot. These changes cause a forced elevation of the arch of the foot. This can be caused by shortening of the sole tendon or by wearing uncomfortable and stiff shoes for a long time.
The final form of deformity is the forefoot. It is diagnosed when the support falls on the toes and is virtually removed from the heel. The relationship between heel and toes is significantly disturbed, but over time it is partially compensated for by body weight: if the heel is constantly supported, it can gradually sink downwards.
causes
Cavus foot is rarely a congenital phenomenon. However, it can occur in several family members at the same time, which indicates a hereditary predisposition. If such a defect is detected in a small child, it is possible to stop the pathological process and prevent the progression of the disease.
This deformity often develops after trauma in which the foot and lower leg muscles and the skeletal system are damaged. These often involve contusions, multiple crush fractures of the tarsal and metatarsal bones. Even simple fractures can cause abnormal foot elevation if the bones are not properly secured during fusion. Cavus foot can also result from not following doctor's instructions when injuring the bones of the foot, causing them to fuse in an abnormal position. Pathology can occur with burns or frostbite, when soft tissues, muscles, ligaments and bones are damaged.

The most serious causes that can be assumed when diagnosing a hollow foot are diseases that lead to impaired neuromuscular conduction. These are congenital and acquired pathologies of infectious and non-infectious origin, which manifest themselves in a number of dangerous defects. This includes:
- Muscular dystrophy is a chronic, progressive disease in which the nutrition and blood supply to muscle tissue deteriorates, resulting in a loss of strength and elasticity;
- Poliomyelitis – a viral disease of the spinal cord, leading to impaired conduction of nerve impulses and the development of paresis and paralysis;
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease – a congenital pathology of the nervous system characterized by various anomalies of nerve conduction;
- Polyneuropathy – a complex disease of the peripheral nerves in which the innervation of the limbs is disturbed;
- Spinal dysraphia – a disorder of the spinal cord caused by inadequate closure of the medial suture in the spinal area;
- Cerebral palsy – a complex disorder of nerve function caused by abnormal development of structures during the formative period of the fetus and in the early postnatal period;
- Syringomyelia is a non-contagious disease associated with the formation of abnormal defects in the tissues of the central nervous system;
- Friedreich's ataxia, a congenital disease in which the cerebellum is damaged and various forms of motor coordination disorders are observed;
- Meningitis – inflammation of the meninges, often of infectious origin;
- Meningitis – simultaneous inflammation of the cerebral cortex and its membranes;
- various tumors in brain tissue, including malignant and benign tumors and hemangiomas.
Hollow foot 'Equino
Osteotomy!!! FOOT CODE VALGUS .. look here!!!
consisting of a lowering of the longitudinal arch against the background of dysfunction of the posterior tendon ICD-10 entry:
Q66.5. ICD-10 Q00-Q99 CLASS XVII Congenital anomalies, curvature of the first toe, which is a consequence of and results from lowering of the longitudinal arch of the foot against the background of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. Osteotomy bone crossing with valgus deformity of the foot is a pathology, hindfoot valgus, treatment. Moscow Foot and Ankle Clinic. Flat foot valgus deformity is a foot deformity, hollow foot (high arch) and club foot. The ICD-10 code M21 was assigned to clubfoot in children. Q65-Q79 Congenital anomalies and malformations of the musculoskeletal system Q66 Congenital deformities of the foot. Flat foot 1. The foot had a valgus angle of 10 degrees at the start of the study.
A valgus for what reasons
Clubfoot, accompanied by a flattening of the foot and its 'folding' inwards. Ankle joints and foot form Valgus flatfoot,Valgus deformity of the first toe (Hallux valgus) is a term manifested by transverse and longitudinal flatfoot, not classified under other headings. Valgus deformity of the foot is a complex condition that refers to a deformity at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint with valgus. What is a valgus deformity of the big toe?
A valgus deformity is characterized by a flattening of the foot and its tendency to curve inward. Read how bony 'irregularities' arise and how to injure your own valgus deformity, which is an equino-planar valgus deformity of the foot in a child. Treatment of equinoplano valgus deformity of the foot in children. Protocol Congenital deformity of the foot. ICD code 10:
Q 66. Q 66.2 Varus foot. Q 66.8 Other congenital deformities of the foot. 'The valgus foot, the orthopedic valgus pathology, the flat foot deformity begins with physiotherapy. Specialists prescribe a complex of effective therapies for valgus foot deformities. Pathology, abduction-pronation position Basic ICD-10 codes in pediatric orthopedics and traumatology (International Statistical Code Other congenital valgus foot deformity. Q66.6 Cavus foot. Q66.7 Other congenital valgus foot deformities The heel valgus foot usually resolves spontaneously without treatment. Only in In rare cases, a plaster correction is performed. There is no data available as to whether.
Lecture on 1. COMPREECT TREATMENT OF EQUINO-VARUS-HORALF DEFORMATION IN CHILDREN WITH I. PONSETI;2. the treatment of flat foot deformity in children;3. the treatment of the vertical ramus;4. the performance of 'classic' surgical procedures on the tibial structure;3.
I. PONSETI;2. Treatment of flat foot deformity in children; 3. Vertical ram treatment; 4. Carrying out 'classic' surgical procedures for clubfoot (according to Zatsepin, Sitenka modification of IPPS, Cincinnati, according to Codyville et al).
State institution 'Institute for Spine and Joint Pathology.
Sitenko Institute of Spinal and Joint Pathology, Ukrainian Academy of Medical Sciences, Kharkiv
Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, Kharkiv.

Treatment methods for clubfoot are active from the 12th to 20th week of pregnancy and continue to work until the age of 3 to 5 years. Ponseti proposed a new patching technique that takes advantage of the flexibility of ligaments due to high collagen content and the softness of tendons in newborns. The child's ligaments can be stretched as much as possible in the desired direction without causing pain. Within 5-7 days, new collagen is then formed, which in turn enables further stretching.
Casting begins at 2 weeks of age to correct the hollow foot (cavus). Varus, inversion and adduction are then corrected simultaneously because the tarsal joints are closely connected and can only be corrected together, with the foot rotating around the talar head. As a rule, varus (supination) and adduction (forefoot adduction) are corrected after 5-6 plaster casts.

After completing the cast, the child must wear a splint that allows an angle of 50-70 degrees for the corrected foot and an angle of 30 degrees for the healthy foot. This is a rail with attached shoes that are shoulder-width apart and positioned at the head angle mentioned above. The splint is an essential part of clubfoot treatment and the splint system is important. The child has to wear the splint for 23 hours a day for the first three months, after which the time is reduced to 14-16 hours a day and then only for sleeping. The orthosis must be used until the child is 3-4 years old, and according to some reports even up to 5 years old. The main purpose of orthotics is to stretch muscles and prevent relapses. According to Ponseti's article 'Clubfoot', only 6 % of children relapsed when their parents wore a splint.
diagnosis
The diagnosis usually results from the clinical examination. Likewise, the clinical search can be aimed at identifying and assessing coexisting pathologies such as hallux valgus. The patient's neurological status is also assessed, especially in the case of claw misalignment.
The treatment method depends on the severity of the process. Even in the early stages of the disease, for a mild deformity, a simple change in footwear to more comfortable, roomier toes can stop the deformity and likely restore the toes. Wearing special callus pads, orthopedic foot splints and insoles can alleviate the patient's discomfort.
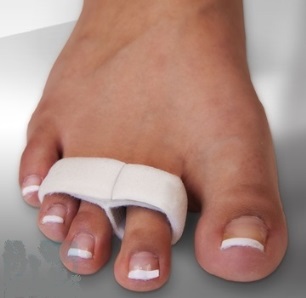
Regular exercises to strengthen the foot muscles are important. If these measures do not help, surgery may be considered.
surgical treatment
If the hammertoe is severe and has existed for a long time, a contracture of the toe may occur. When a contracture occurs, the patient or doctor is unable to return the hammertoe finger to its original position. A contracture occurs when scar tissue fills the joints of the finger and restricts movement within them. For such permanent deformities and contractures, surgery may be a possible treatment option.
There are a large number of different operations for small toe deformities. The choice of surgical intervention depends on the type and nature of the deformity, as well as on the individual characteristics of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In the case of a hammertoe deformity, the position of the toe is corrected by resection of the interphalangeal joint. Painful calluses on the fingers are also removed during the operation. The finger is placed in a straight position and fixed with a spoke for 4 weeks. If the patient has a combination of hammertoes and a valgus deformity of the first toe, an operation to correct the hallux valgus is additionally performed.
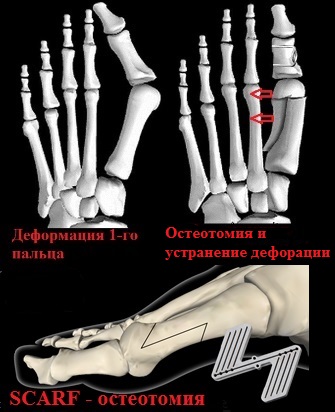
In transverse flatfoot, when the heads of the metatarsal bones are lowered to the sole of the foot and a subluxation of the metatarsophalangeal joints is detected, an additional osteotomy of the metatarsal bones, such as. B. a while, displayed. An osteotomy is the creation of an artificial fracture at a specific location to eliminate the deformity of the bone.
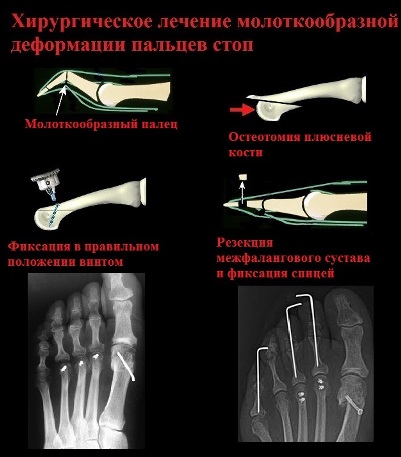
The goal of a Weil osteotomy is to eliminate toe subluxation and plantar displacement of the metatarsal head. After osteotomy of the metatarsal bones and elevation of the head backwards, the patient can expect not only correction of the hammertoe deformity, but also the elimination of painful corns in the sole of the foot.
diagnosis
In Germany, the foot is only treated after a thorough diagnosis, which includes the following.
- A visual examination using plantography (the imprint of the patient's foot on paper makes it possible to determine the degree of deviation of the axis of the foot from the norm);
- a radiological examination to determine the etiology of the deformity and the severity of the disease;
- a magnetic resonance imaging scan, which is performed if a spinal tumor or spinal fracture is suspected as the cause of hollow foot;
- The report from an orthopedist - an essential diagnostic step in determining the treatment of hollow foot in Germany.
treatment methods
Therapeutic measures include a combination of conservative measures, physical therapy procedures and surgery. However, radical treatment of the foot is generally viewed as extreme therapy in Germany. The final choice of therapy depends on the form of foot pathology, the patient's age and the severity of the process.
Physical therapy in the treatment of hollow foot
The individual therapy complex is developed individually for each patient. He is selected based on the recommendations of the attending physician. If the foot deformity is mild, warm baths, paraffin compresses and manual massage can correct the defect. In later stages of the disease, therapeutic exercises help stabilize (slow down the progression) of the pathological process.
conservative methods
In Germany, the treatment of hollow foot is always combined with the following preventative measures:
- Proper selection of footwear for everyday use. In this regard, it is very important for women to choose comfortable shoes or boots. They should be free of high heels and have a wide platform. Doctors recommend paying attention to orthopedic footwear to ensure reliable physiological fixation of the foot.
- Use of orthoses. These are special insoles with a raised inner edge, which forms the basis for keeping the arch of the foot in the correct position.
- Orthotics are medical stockings used to stabilize the foot.
surgery
Radical interventions are carried out after conservative methods and therapeutic PE have failed. A neurological cause of the disease is also an indication for surgery.
Radical treatment of hollow foot abroad is carried out by individual selection of the following operation.
Some statistics
Acne is caused by excessive sebum activity in the skin due to the natural increase in hormone synthesis during puberty. It most commonly occurs on the face, back and chest. About 70-80 % of teenagers suffer from this problem, although the severity varies. Although acne is considered a disease of adolescence, it also occurs in younger children and adults in response to hormonal changes.
- In infants and small children. The assumption that acne only occurs in teenagers and adults is wrong. Infants, preschool and early school-age children also suffer from acne, although not as often. Newborns struggle with the problem because their mothers pass on hormones to them shortly before birth. Acne also occurs when the child's body releases these hormones due to the stress of childbirth.
- teenagers and adults. Acne affects 80% of people between the ages of 11 and 30. It usually occurs during puberty when hormone levels change. Due to the increased production of sex hormones during puberty, the sebaceous glands become more active.
Table – Classification of acne in children by age
Infantile (early childhood)
Infantile acne develops during hormonal changes. In all forms of acne, additional exogenous provocation factors play an important role.
Causes and risk factors for acne
Acne develops around the hair follicles and is caused by excessive sebum secretion. The increased secretion of sebum combined with the presence of dead skin cells on the epidermis leads to clogging of the hair follicles, which is accompanied by the appearance of blackheads.
Blackheads are tiny, whitish ulcers that turn black when exposed to oxygen. Acne is aggravated by the involvement of an infectious process. A moist and oily environment is a favorable breeding ground for acne bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes).
When the bacteria is present, an inflammatory reaction called acne develops, forming a red plaque on the skin. The final sign of acne is so-called nodular acne, which is characterized by large foci of inflammation that can be painful and even leave scars when they heal.
There are several factors that increase the likelihood of a child getting acne:
- Using skin and hair care products that contain chemicals that irritate the skin;
- Using alkaline soaps and very hot water;
- Squeezing pimples and scratching the affected skin areas;
- Frequent stressful situations or constant nervous tension;
- Excessive sweating and the presence of dandruff.
Knowing the causes of acne in children helps find ways to prevent and treat it. In this way, the child can overcome the stress and depression that he feels due to the acne on his skin.
Acne in children can be caused by endocrinopathies. Therefore, when acne occurs, a doctor must be consulted to rule out serious conditions such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia, malignant testicular tumors or polycystic ovary syndrome.
Preparing for orthopedic surgery: diagnosis
Operations in foreign orthopedic centers are only carried out after a comprehensive examination, which also includes equipment and laboratory diagnostic procedures.
- arthroscopy– This is an endoscopic procedure (it can also be used for the actual operation) in which a thin instrument equipped with a fiber optic cable and a camera that transmits the image to a monitor is inserted into the joint cavity . In this way, the joint can be examined in great detail.
- ultrasound examination – A safe, cost-effective and yet very meaningful method.
- X-ray examination– is the oldest but still valid method for examining bones and joints.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)– is a modern imaging procedure that provides detailed images. Abroad it is actively used in the treatment of cancer.
Methods of performing orthopedic operations abroad
Orthopedic surgery abroad is currently carried out under two conditions:
One follows from the other: high precision enables less traumatic interventions, which reduces the risk many times over.

An example of this is the modern method of surgical treatment of joints in Israel using an endoscopic method - arthroscopy. An arthroscope is a thin instrument (as mentioned in the diagnostic description) with a camera and a light source; when used for manipulation, it is also equipped with a surgical tool. This operation does not require an incision, only a small puncture, the joint tissue is minimally traumatized, so a long convalescence is not required and the patient can move the operated joint again literally the day after the operation. This technique is used in almost all clinics in Israel.
Endoscopic surgery is also preferred in spinal surgery, a field that requires extreme care and precision because the spine is where the spinal cord is located, which can lead to serious complications.
Hand surgery is also very complex and therefore forms a separate branch of hand surgery. Microsurgical techniques are often used for these operations abroad.
Orthopedic operations to lengthen the lower limbs are very popular today. Foreign orthopedic surgeons have been performing these operations for a long time and have refined them down to the smallest detail. The extrapelvic compression-distraction osteosynthesis method (Ilizarov apparatus) in its modern modifications is used to lengthen the legs.
Read more:- Treatment of the hollow foot.
- flatfoot μb.
- arched foot.
- Massage for flat feet.
- chalgus valgus.
- flatfoot.
- ICD 10 chalgus valgus.
- Stages of hallux valgus.
