Obesity, which increases the pressure on the articular surfaces, which can lead to their displacement.
- Plantar deformity of the foot
- Causes of valgus deformities
- etiology
- Forms of hollow foot syndrome
- signs
- Causes of foot deformities
- About the disease
- species
- Symptoms of a foot fracture
- causes of injuries
- Which doctor should I see?
- Different types
- symptoms
- causes of dislocation
- Treatment methods for a dislocation
- What to do if a dislocation occurs
- Prevention of ankle injuries
- Sprained foot: which ointment will help?
- bruises and sprains
- fractures
- Free consultation and diagnosis by a doctor
- symptoms
- diagnosis
- Treatment
Plantar deformity of the foot
The clinic for minimally invasive neurosurgery offers you modern surgical treatment of valgus foot deformity. The procedure is so simple that you will be back on your feet in just a few hours. During the operation, a small surgical access is made, which then heals almost undamaged. After the operation, you will recover quickly and will soon no longer have any problems walking. The convenience and speed of the procedure allows it to be performed on both feet at the same time.
Bunion (Hallux valgus) – Bunion (Hallux valgus) is an external deviation of the big toe and is the most common deformity faced by podiatrists in foot pathology. Bunion (Hallux valgus) is a change in the relationship of the metatarsophalangeal joint in which there is deviation and valgus rotation of the big toe, combined with adduction of the first metatarsal and the formation of a cartilaginous exophyte (growth) on the inside of the head of the first metatarsal bones.
Causes of valgus deformities
Valgus deformities of the foot are in most cases genetic. Short and tight footwear can be a trigger for the deformity (especially in women). The degree of deformity can range from a slight deviation of the toe alone to a significant displacement of the entire metatarsophalangeal joint.
The origin and development of the valgus deformity is due to a forefoot deformity that is accompanied by changes in the midfoot and hindfoot.
When the arch of the foot is lowered and the heel points inward (pronation), the metatarsal bones, particularly the talus and scaphoid, move inward and lengthen by overstretching the ligaments. There is increased pressure from these bones on the cuneiform bones, which in turn act on the I-IV metatarsals at the Lisfranc joint (a joint between the tarsal bones – three cuneiform bones and a navicular bone – and the metatarsal bones). The bases of the I-IV metatarsals are displaced and thrown outwards, causing them to pronate, with the heads of these bones being fulcrums. The metatarsal bones I-IV are brought distally, pivoted outwards in the proximal part and pronated.
The V metatarsal feels less pressure from the metatarsal because it participates in the formation of the external arch and carries the load itself. Its base is connected to the elbow bone, which is medial to the base of the V metatarsal bone. The 5th metatarsal is connected to the elbow bone by a strong metatarsophalangeal ligament. The 5th metatarsal tends to move outwardly along its length relative to the medial portion. Thumb adductor tension causes outward displacement of the sesamoids and first toe, and there is a correlation between sesamoid subluxation and the degree of outward displacement of the fifth metatarsal. Contraction of the adductor muscle of the first toe contributes to supination of the fifth metatarsal.
etiology
The occurrence of a pes cavus can be due to pathological processes in the brain and spinal cord, in the peripheral nerves or to structural problems in the foot. If there is a muscular imbalance in the foot before the final formation of the skeleton, significant changes in the morphology of the bones that make up the foot can be observed. If the deformity occurs after skeletal maturity, the morphology usually remains the same or changes little. Two-thirds of adult patients develop pes cavus on the background of neurological disorders such as periosteal muscle amiotrophy (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease), spinal dysraphism, polyneuritis, intraspinal tumors, polio, syringomyelia, Friedreich's familial ataxia, cerebral palsy, and spinal tumors that can cause muscle imbalances that lead to a widening of the arch of the foot. A patient with a newly diagnosed unilateral foot deformity with no history of trauma should be evaluated for spinal tumors.
The causes and mechanism of the deformity inherent in pes cavus foot syndrome are not fully understood. Factors responsible for the development of pes cavus include muscle weakness and associated neuromuscular disorders, residual sequelae of congenital clubfoot, post-traumatic bone deformities, plantar fascia contractures, and Achilles tendon shortening.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMD), also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy, is a genetically heterogeneous disorder that occurs primarily in the first decade of life and is characterized by delayed motor development, distal muscle weakness, clumsiness, and frequent falls. In adulthood, SBMT can cause painful foot deformities, particularly pes cavus foot. Despite the relative prevalence of this condition, little is known about the mechanism by which muscle imbalance is distributed, the severity of orthopedic deformities, or the nature of the pain that occurs. There is currently no effective treatment to prevent the development of any form of pes cavus foot syndrome.
Forms of hollow foot syndrome
Three main forms of pescavus syndrome are described in the literature: 'pescavovarus', 'pescalcaneocavus' and 'true' pescavus. These three types can be distinguished based on their etiology, clinical features, and radiological findings.
- Pes cavovarus or pes cavus, the most common form of pes cavus, occurs mainly in neuromuscular disorders such as BSMT and is usually referred to as 'idiopathic' in cases where no etiology can be established. Pes cavovarus is characterized by an outwardly rotated heel, a plantarly flexed first metatarsal, and twisted toes. Radiographic examination of the pes cavovarus usually shows that the toe is plantarly curved relative to the heel.
- A pes calcaneocavus, or heel foot, usually occurs with polio-related paralysis of the triceps brachii muscle. This case is characterized by a posteriorly flexed heel bone and a plantarly flexed toe. The radiological images show a large talonavicular angle.
- A 'true' pes cavus is characterized by a lack of dorsiflexion or an outward flexion of the heel bone and an excessively high longitudinal arch caused by plantar flexion of the toe relative to the heel. The combination of these features leads to the so-called 'combined' pes cavus, which then retains or loses its mobility.
Depending on the location of the highest point of the longitudinal arch, there are four types of pes cavus: anterior (toes), metatarsal, posterior and combined.
signs
The main clinical signs of the deformity can be:
- Visually perceptible curvature of the foot;
- pain when walking;
- difficulty adjusting footwear;
- Restriction of mobility in the ankle and in the mobile joints of the foot;
- rapid fatigue when walking and exercising;
- secondary postural curvature.
The doctor can make an initial diagnosis based on the appearance of the foot:
- Excessive plantar flexion where it is difficult or impractical to flex the foot to the other side, indicating clubfoot;
- backward flexion of the distal part of the foot (closer to the shinbone) is indicative of a heel foot;
- A foot that is twisted so that it rests only on the tubers of the heel bone and the heads of the metatarsal bones is called pes cavus;
- a foot that does not have a physiological arch is called flatfoot (transverse or longitudinal);
- In clubfoot, the foot is shortened and protrudes.
Causes of foot deformities
Foot deformities can be caused by the following factors:
- Congenital, including hereditary, anomalies of the musculoskeletal compartment of the distal foot;
- Post-traumatic changes resulting from abnormal healing of bone fractures;
- Post-burn lesions – an acquired deformity of the foot resulting from 3rd or 4th burns;
- Deformative arthrosis of the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints, leading to gradual erosion of the cartilaginous layer and exposure of bony tissue with the formation of persistent adhesions;
- neurological disorders leading to paresis (partial loss of innervation) or paralysis (complete blockade of neuromuscular conduction) - these can result from stroke, multiple sclerosis and other pathologies.
About the disease
Dislocations at this point account for about 2 %. When the left or right foot is dislocated, the ankle bone is usually displaced and the entire foot is affected (the biomechanics are disturbed). This injury is always characterized by damage to the retaining straps. Multi-traumatic dislocations can be combined with fractures in the back or front of the foot.
The disruption of bone connections in the foot is accompanied by severe pain, swelling and changes in the normal shape of the organ. The anatomical abnormalities lead to functional disorders - passive and active movements of the foot are no longer possible, as is supporting the foot in general.
How can a foot dislocation be diagnosed? The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints, evidence of injury, and the results of objective examination (examination and palpation of the foot). The final diagnosis is made on the basis of an X-ray examination. In most cases, the x-ray can rule out/confirm a possible bone fracture.
Foot dislocations are usually treated conservatively. Under anesthesia, the doctor returns the dislocated bones to their physiological position, after which a cast is applied (later replaced with a cast). Treatment concludes with an appropriate rehabilitation program.
species
Sprains of the foot can come in the following forms
- robe
- subtalar;
- Lateral tarsal and metatarsal – the dislocated bone deviates outward;
- Metatarsal and metatarsal bones – the dislocated bone deviates inward;
- Interphalangeal Dislocations.
A distinction is also made between complete dislocations, where the bones are no longer in contact with each other, and partial dislocations, where only part of the bones are in contact with each other.
Symptoms of a foot fracture
The severity of symptoms depends on how badly an area of the leg has been damaged. It is not uncommon for a low level of discomfort related to an injury to result in victims not even visiting a hospital. This leads to complications such as severe pain, inflammation and unhealed fractures. Also, without a radiological diagnosis, the injury is mistaken for a soft tissue injury such as a contusion or dislocation. In order to identify the nature of the problem and seek help in a timely manner, it is important to know the main symptoms of a fracture:
- acute pain in the foot, inability to take a step;
- swelling, redness, bruising;
- increase in local temperature;
- inability to move toes;
- Deformation of the foot, hard thickening under the skin;
- In severe cases of fractures: abnormal mobility of the bones.
Symptoms of a foot fracture can vary in severity and location. This depends on how severe the injury is and what part of the foot is affected. The overall condition is also affected by possible damage to other connective tissues - cartilage, tendons, ligaments. Injuries to these bones are most common:
In severe cases, the injury can be aggravated by displacement, which can lead to an open fracture. This is a dangerous condition in which bone fragments break through soft tissues.
causes of injuries
Injuries can occur regardless of occupation and lifestyle. The fragility of the foot bones means that even minor mechanical impacts can compromise their integrity. Professional athletes and the elderly are particularly at risk. Causes of foot fractures include:
- Vertical or side impact;
- twisting and bending;
- bow; bending over a stiff rib;
- twist;
- Crushing Impact.
A foot fracture is not uncommon as a result of a fall in which the foot is twisted or struck by a heavy object. Foot injuries are a typical feature of soccer players and athletes. In children, on the other hand, these fractures occur much less frequently due to the high flexibility of the bones. In older people, injuries are often associated with osteoporosis or osteomyelitis.
Which doctor should I see?
Timely medical treatment will help control the symptoms – pain, swelling, inflammation – and significantly speed up the healing process. Therefore, do not hesitate to visit a hospital if you suspect a fracture. A doctor is responsible for treating these types of injuries:
Different types
Foot dislocation is a general term that refers to a dislocation of one of the joints of the foot, and there are several known to exist. It is not uncommon for this condition to occur in conjunction with a ligament injury or even a broken bone. The human foot is very complex, made up of 26 bones that form three main sections:
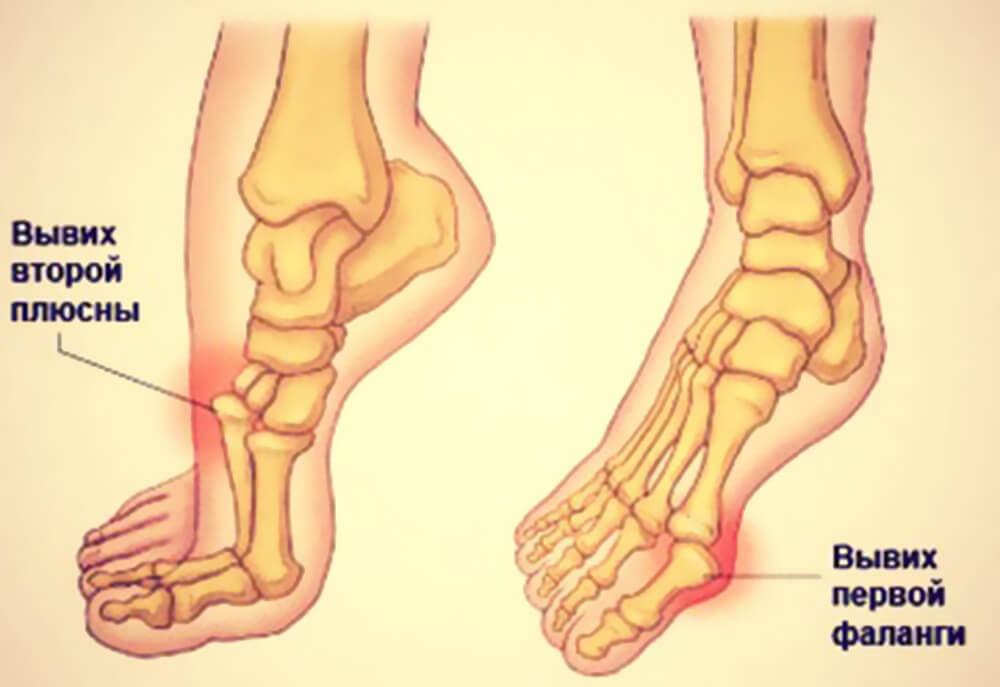
The tarsal region (foot root) consists of seven bones.The tarsal region consists of seven bones: the tibia, talus, scaphoid, calcaneus, and three sphenoid bones. These elements join with the metatarsal bones, of which there are five, and meet the phalanges. The phalanges are made up of fourteen bones that form the toes. The flexible ankle is where the foot meets the shin. It consists of the fibula, the tibia and the ankle bone.
Before treating a dislocation, it is important to determine the type of dislocation as subsequent treatment will depend on it. Types of foot dislocations include. the following designations:
- - Dislocation of the toes.
- – Dislocation of the subtalar joint.
- - Dislocation of the ankle.
- - Dislocation of the tarsal bones.
- - Dislocation of the tarsal bones.
A dislocated foot can occur in combination with a ligament injury or even a broken bone.
Each of these variants requires special treatment, which is why it is so important to immediately visit a medical facility, where a specialist will determine the nature of the injury. He will also rule out the possibility of a fracture, which is not uncommon with this type of injury. The doctor will then tell you what to do in the event of a foot sprain and it is important that you follow all of their recommendations.
Traumatologists point out that there is a type, called an incomplete dislocation, in which there is a gradual displacement of the articular surface, but the ligaments are only partially, ie not completely, torn. There are several types of incomplete ankle dislocations, These include the following.:
symptoms
Very often people suffer from sprained ankles that can only be treated at home Only after consultation with a qualified medical specialist.. The clinical signs of a sprained foot directly depend on the location of the injury, the type of joint and the presence of concomitant injuries. A twisted tibia is rarely diagnosed; According to statistics, it occurs in 1.5-2 % of dislocations. A total ankle sprain is caused by separation of the articular surfaces, resulting in damage to the ligaments and bones of the foot.
There are a number of characteristics with a dislocated foot, what to do at home is determined only after the diagnosis is made. First, the specialist takes an anamnesis, that is, he talks to the patient and notes his symptoms, as a rule, the list of complaints with such an injury is the same for everyone, it includes, among others the following appearances:
- – Excruciating pain that makes it difficult for the patient to sit or walk;
- – Swelling of soft tissues with bruising and congestion;
- – Even visible inward or outward displacement of the joint can be noted;
- – skin damage associated with an open dislocation or fracture of the arch of the heel, foot or toe;
- - Damage to nerve tissue, which manifests itself as a sensory disturbance;
- – convulsions in the lower limbs;
- – total or partial loss of the ability to walk;
- – swelling and bruising of the toes;
- - lack of blood supply, which can lead to sensory disturbances and in rare cases even to gangrene;
- – changes in the configuration of the distal limbs;
- - Pain associated with a Lisfranc-type dislocation;
- – Symptoms of muscle sprain, ankle fracture and rupture of ligaments associated with ankle injury.
causes of dislocation
A dislocation can occur in any joint. A typical dislocation can be caused by trauma. For example, a dislocation can occur when the joint is moved excessively (outside the normal range of motion). As a rule, this is a forced movement (e.g. as a result of a fall: a person falls on the back of the shoulder and suffers a shoulder dislocation). A blow to the joint area can also cause a dislocation. Dislocations resulting from trauma are called traumatic dislocations.

However, a dislocation can also have a non-traumatic origin. In this case, it is caused by the destruction of the articulating ends of the bones as a result of such diseases as polio, osteoarthritis, arthrosis and tuberculosis. Such dislocations are called pathological dislocations.
There are also congenital dislocations. This pathology occurs in the fetus during fetal development.
Particular attention is paid to so-called habitual dislocations. A habitual dislocation is a dislocation that also occurs with minor trauma to the same joint. It is caused by a weakness of the articular apparatus (capsule, ligaments, muscles) or a change in the configuration of the articular surfaces. In most cases, habitual dislocation occurs when a joint regains mobility too soon after repair of a traumatic dislocation.
Treatment methods for a dislocation
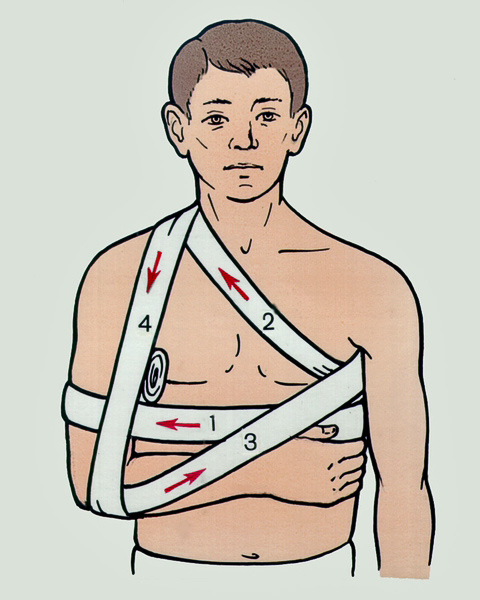
What to do if a dislocation occurs
In the case of a dislocation, the first measure is to immobilize the injured joint (immobilization). Ideally, a splint should be used, but when this is not possible, immobilization should be done with improvised means - a cloth, piece of cloth, etc. Cold compresses are recommended to reduce swelling and relieve pain. You can use crushed ice from the freezer or a cold water bottle. A pain reliever can be taken.
The dislocation needs to be put back in place, and it should be done quickly. If the dislocation is not corrected within 1 to 2 days, the swelling makes correction difficult and surgery (tissue incision) may be needed. Under no circumstances should you try to fix the dislocation yourself! Successful self-treatment is rare and the risk of causing yourself additional pain and making the situation worse is significant.
In the event of a dislocation, contact a trauma center or trauma surgeon as soon as possible. You can get professional help from an accident doctor or surgeon in one of the general practitioner's clinics.
Do not undertake the treatment on your own. Contact our specialists who will make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Prevention of ankle injuries
The tricky thing about ankle injuries is that once an ankle is sprained, it increases your susceptibility to further injury from clumsy movement, improper footwear, fast walking, or exercise.
So if you frequently sprain your ankle while walking and then have a long limp or fall on a 'flat spot', you should consider how you can prevent these conditions. To do this, you should take the following steps:
- Choose and wear good shoes that fit you and are comfortable to walk in. Preferably with a small, stable heel and an orthopedic insole. Women should be aware that wearing high-heeled shoes increases the susceptibility to injury to the feet, so they should not be worn for long periods of time.

Sprains and more serious ankle problems should be avoided as most ankle injuries result from not looking under your feet when walking.
Sprained foot: which ointment will help?
The first task in treating the aftermath of an injury is to relieve the patient's pain. These requirements are met by analgesic ointments, which are successfully used on the advice of a doctor and with individual pain relief. Immediately after the injury, only cooling painkilling ointments can be used. Painkillers with a warming effect are only allowed a few days after the dislocation, when the inflammation is slowly subsiding. Popular ointments with this effect are:
Short list of ointments for sprains:
- Dolgit;
- ketonal;
- voltaren;
- bystromgel;
- emulsifier;
- deep-relief;
- fastum gel;
- Naiz Gel;
- Diclofenac.
The above remedies are easy to find at the pharmacy. They are based on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and are used for bruises. They are safe and hypoallergenic and are even suitable for children of all ages.
Hormone mixtures should be used with great caution in adults. They speed up the recovery process and help when other remedies are ineffective, but can often not only be helpful, but also harmful. It is worth trusting the doctor – if the doctor prescribes hormone mixtures, they should only be used in the amounts indicated on the prescription.
bruises and sprains
Foot bruises are accompanied by severe pain because the skin and muscle layer is very thin and the impact falls on the periosteum, the connective tissue that covers the bone. Swelling occurs quickly and increases over time. Therefore, prehospital care is necessary to reduce swelling and pain. You can cool your foot with ice and try not to put any strain on your foot.
Sprains of the foot are quite rare. Appearance depends on the joint where the injury occurred. The following symptoms can occur with a sprain of the foot in the subtalar joint: The foot is untypically displaced and points inwards with the sole, the lateral malleolus is protruded and tight skin is visible over the ankle. The inner ankle, on the other hand, is pressed in and the skin is drawn in.
In the case of sprains, the swelling is visible quite quickly. Therefore, it is important that the injured person is taken to a trauma center as soon as possible. Do not repair the dislocation yourself as this is not possible without anesthesia.
During transport, immobilize the injured limb with a splint or other improvised device, place it on a roller and put something cool on it. Under no circumstances should the limb be stepped on or leaned against, as this can increase pain and worsen the dislocation.
Dislocations of the forefoot and midfoot cause swelling and deformity of the foot. The initial treatment should be the same as for this problem in other joints.
A direct blow to the foot, which causes severe pain and increasing swelling, can be either a bruise or a dislocation of the foot. These are difficult to tell apart from the outside. In such a case, the injured person must be taken to a hospital.
fractures
The most common cause of a fracture is an unfortunate jump or fall on your foot. When the bones in the back of the foot break, they can shift and put pressure on the tendons and skin, reducing their blood supply. As a result, necrosis of the foot tissue can occur. The first symptoms of such an injury are severe pain, swelling and bruising under the ankle. When the heel is pushed up, the pain gets worse.
This type of fracture requires urgent medical attention. It's important to get to the hospital before swelling develops. If this is the case, the leg must be immobilized with a splint, elevated and cooled with ice.
With a fracture of the heel bone, the tissues in the heel area swell, the foot flattens, and the tendon flattens out. At the same time, the heel widens optically. Even a light touch on the damaged area causes pain.
When the metatarsal bones that make up the forefoot are broken, the pain on pressure increases and bleeding increases.

A toe injury is more likely to damage the skin. At the site of the injury, there is bleeding under the skin, the toe hurts badly, its axis and mobility are changed.
There are a few things to consider when treating a broken toe bone. A bandage must be applied to immobilize the finger. A wide bandage is used for this, which is wrapped around the finger several times. If several fingers are affected, this should be done for each finger individually.
If the joint and ligaments are bruised, there will be pain and swelling in the ankle area. All movements in the joint are restricted. However, the injured is able to step on the foot. First aid in this case is to apply ice and elevate the limb. In addition, the joint should be protected with a tight bandage.
Free consultation and diagnosis by a doctor
During the consultation we conduct a thorough diagnosis of the entire spine and each of its segments. We determine exactly which segments and nerve roots are affected and which are causing the pain symptoms. As a result of the consultation, we provide detailed treatment recommendations and, if necessary, prescribe additional diagnostics.
We carry out a functional diagnosis of the spine
We perform manipulations that lead to a significant reduction in pain.
We develop an individual treatment program
symptoms
The clinical picture of hip subluxation consists of the following symptoms:
The severity of the clinic depends on the degree of deviation of the femoral head from its physiological position.
Pain syndrome in subluxation:
The pain is localized around the joint and has no tendency to spread. The pain is annoying, moderate in intensity, and increases with movement.
Tissue swelling from subluxation may be subtle in patients with well-developed muscle tissue around the joint.
The range of motion of the hip joint is severely restricted. The patient cannot raise the leg or sit up without support.
Symptoms such as stiffness, discomfort when walking, restricted movement and excruciating pain in the hip joint are reasons to see a specialist.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints, medical history, clinical picture, physical examination findings, and instrumental findings.
X-rays of the affected joint in two projections are sufficient to determine the deviation of the femoral head into the acetabulum and to plan treatment measures.
Additional investigations are needed to detect abnormalities that have caused changes in the connective tissues that lead to ligament weakness and stretching of the joint capsule: MRI, ultrasound, electromyography.
The individual diagnostic plan of measures for each patient is determined by the doctor based on the evaluation of the data from the preliminary examinations.
Treatment
The treatment strategy for hip subluxation depends on the underlying cause of the problem.
If it is a traumatic subluxation, the patient is immediately taken to a doctor after the first aid (immobilisation of the affected joint with improvised means). After reduction, the joint is immobilized with a cast or splint.
Read more:- Subtalar dislocation of the foot.
- Dislocation of a bone in a joint.
- The lateral dislocation is.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- How do you tell if it's an ankle fracture or a dislocation?.
- Lisfranc joint.
- Anatomy of the Lisfranc joint.
- Diagram of a joint with and without a dislocation.
