Inserted into the soles of high heels to stabilize the heel (I had to work in a shoe factory).
Centering rings - they will never be worse than these, although I have driven without them for many years on various discs, including those with a larger center tube - without any problems. I still haven't gotten around to buying one.

- How to Choose Supinators for Disc Wheels.
- Hubcaps for light alloy wheels
- Centering rings
- Changing insoles in men's shoes
- The reporter's son Khatab talks about his father
- Installation instructions for the DRM system separators
- Installation instructions for DRA system spacers
- Track widening
- Nuts
- Why are wheel insoles needed?
- Which spacers should be installed on the hub?
- How are the spacers installed?
- When are wheel spacers needed?
- Special features when selecting wheel spacers
- Bykov insoles - a unique remedy for flat feet
- Insoles for the back – materials, composition, function
- Video about supinating insoles:
How to Choose Supinators for Disc Wheels.
If you are not from Saint-Petersburg, we can send you the disc rings by mail to any location in Russia, +200-250 p to the cost of the rings. International delivery companies are also available.
Vibration in the steering wheel when accelerating of the vehicle above 80-90 km/h occurs when rims are used whose center bore diameter is larger than the diameter of the vehicle hub. The maximum allowable difference between these diameters is 0.3-0.35 mm. The standard recommended by vehicle manufacturers is 0.1mm (e.g. Volkswagen hubs are D57mm and their rims are D57.1mm). It is assumed that the rims are centered by the tapers of the bolts/nuts. This is correct, except that bolts or screws cannot actually prevent the vertical movement of the wheel. Your task is to pull the wheel into the plane of the vehicle connection. The holes for them in the disks are 1-1.5 mm larger than their diameter (for M12x1.5 holes – D13-13.5 mm). Under the influence of a dynamic load - impact on bumps, rails, holes in the road - the wheel shifts in relation to the axis of rotation. A displacement of 0.2 mm relative to the wheel hub journal is enough to cause vibration. The car owner goes to tire fitting, the wheels are removed, balanced and mounted. Everything is OK. After a while everything repeats itself. Hundreds of car owners have contacted us because they were tired of wasting time and money fighting the problem. Because, in addition to the inconvenience of driving, the vibrations 'kill' the wheel bearings, the stabilizer struts, the tie rod ends and all the suspension elements 10 times faster. About a year ago we had a man with a new Opel Astra (mileage just over 30 km) who, after a season of occasional vibrations (several times in the tire fitting shop for balancing), replaced all the hubs of the 4 wheels (the bearings are complete on the Astra replaced).
In the meantime, he solved the vibration problem by installing alignment rings (supinators). The cheapest option, plastic rings, is better not even considered. They have low manufacturing accuracy (the best samples come from Japan and have a total clearance of 0.3-0.4 mm, ie they are at the limit of tolerance), and China and our 'cooperation partners' extrude what they can. Nothing can be said about durability and thermal stability - the products simply melt when the hub is heated. Such rings need to be replaced several times per season. Our company initially manufactured aluminum alloy rings. They were sturdier than plastic rings and our equipment ensured high dimensional accuracy. But these rings also had serious disadvantages - the hardness is still not good enough and they have to be replaced after a season or two. In addition, they often stick to the hub and the disc. Today we only manufacture centering rings from stainless steel, an ideal material that has high strength and does not react chemically with iron, aluminum alloys or chemicals. The rings are manufactured on Japanese CNC machines, with an accuracy of 0.01 mm, without concentricity on all surfaces. Guaranteed retention of all parameters for 15 years. Install and forget.
Hubcaps for light alloy wheels
They are small parts called hubcaps that add to the aesthetics of your vehicle. Without hubcaps, your alloy wheels will lose their style.
Before purchasing, pay particular attention to the available dimensions of the fittings. Only the exact dimensions confirm the right choice. The dimensions must be measured:
A minimum error of 1 mm is usually permitted in these measurements. The dimensions of the foot are not very important. If it is larger, it will fit into the free space on the disk.
Centering rings
It is very important that the wheel on the hub is aligned with the axle around which the disc rotates. If this is not the case, the wheel begins to 'rattle' and the suspension is subjected to additional stress at this point. Such inaccuracy can lead to an accident and the driver can no longer feel safe.
Therefore, the demands on the accuracy of the wheel alignment are extremely high. Any deviation is strictly prohibited. The rotation of the wheel must necessarily correspond to the rotation of the hub axle!
To ensure this accuracy, car manufacturers use an additional accessory and the hub is equipped with a special cylinder. Its outer diameter corresponds to the inner dimension of the centering hole in the disc. This ensures that the wheel sits snugly on the hub.
Wheel alignment rings are used to mount the various rims on the vehicle. The centering hole on these special rims usually does not match the hole on the original rim. This makes the centering rings unnecessary.
Changing insoles in men's shoes


insole – Is the inner part of the shoe sole. It is the rigid element that holds the shape of the sole, the base for the heel attachment and the support for the arch of the foot. It is available in wood, plastic, metal, etc.
In women's models, it is quite easy to determine that the insole needs to be replaced. Youtube video about recognizing shoe repairs, a post about supinators. They are also easy enough to change. How do you change the insole in a sandal? In men's shoes, the insole needs to be replaced much less frequently. This is mainly because sales are lower. But from time to time it is still necessary. Has the heel receded and the foot is slipping? Can the heel of men's shoes move backwards and the foot slips? Yes, that happens! Namely with the couple in question.

So we take out the insole. To do this, you need to disassemble the insole - take out the main sole and half the insole. Hmm, the whole thing. However, upon closer inspection, the latter is damaged.
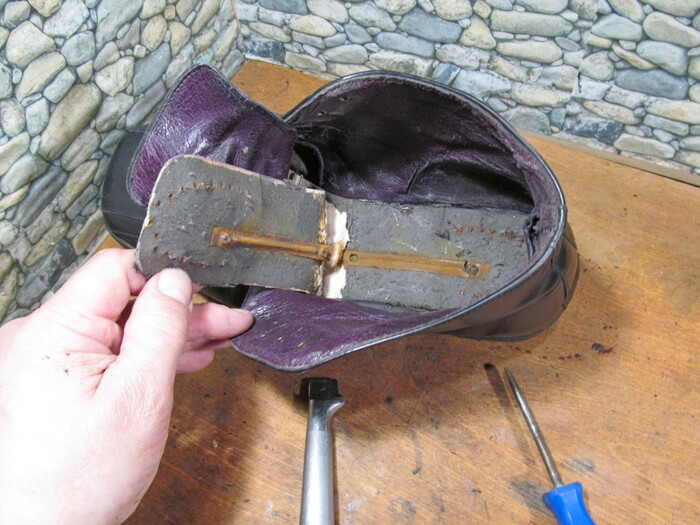

There are a whole range of insoles.

Let's choose the right one. We bend the foot, in this case we straighten it.

The reporter's son Khatab talks about his father
The late Radik 'Xatab' Nizamov's son has told how much money his father received from the website where he posted his repacks.
'The money wasn't much, 30,000, maybe 40,000, not millions, not hundreds of thousands. He did it more for himself, to keep himself busy. Maybe some people thought he made a lot of money from it - he didn't.
He didn't need it at all. I asked him, 'Why do you want to do this? You sit at the computer all day, sometimes at night," and he said, "Well, not everyone has money to buy games. There are children and poor families'. – Ufa1.ru quotes his son.
This story happened about 15 years ago. His future wife and I were just starting our life together. They are both students and unemployed. Money was tight, so I didn't turn down any offer.
And then my future mother-in-law calls. Sergei says that a friend of mine bought an apartment in Kazan (she herself lives in Almetivsk, about 250 km from Kazan!); It is being renovated and is almost finished, and tomorrow the building materials, a few bags of mix and a box of tiles are due to be delivered. She will give you some money.
I'm always ready, a penny won't hurt, and my mother-in-law will give me a plus.
The next day, after taking the last penny for the toll (I would have some money on the way back!), I dressed badly and arrived at the right address at the right time. And the address wasn't easy! It was on Fedoseyevskaya Street! This is one of the most expensive districts of Kazan, the center, just a step away from the Kremlin. I thought I could buy a beer and a bar of chocolate for my wife.
I walk up to the door and panic a little when I see a pallet with three rows of bulk (15 bags) and two rows of porcelain stoneware on it. No, I think there is a mistake, they are probably not my things, mine should be fine, they haven't arrived yet.
I go up to the floor (guess which floor). My aunt opens the door. Oh, Sergei, she says, it's good that you volunteered to help! Thank you very much, you can start now, I'll leave the door open. Anyway, that's my load on the ground floor.
Well, what else can I do but run away (although in retrospect I don't see anything shameful about it).
Installation instructions for the DRM system separators
1. Carefully clean the hub and the mounting surface on the hub of the car from dirt and rust with a wire brush.
2. Place the spacer in the rim and check whether the spacer with its outer chamfer and centering tab rests firmly and without play on the respective rim surfaces.
3. Place the spacer on the vehicle hub and check whether the spacer is flush and free of gaps and whether the inner chamfer and the inner part of the centering tab rest on the corresponding surfaces of the vehicle hub.
4. If necessary, remove any dowel pins, clips and/or protruding brake disc mounting screws.
5. Attach the spacer to the vehicle hub using the nuts provided. When screwing in, pay attention to the minimum number of full turns:
| M12x1.25 | min. 8 turns | 10mm thread length |
| M12x1.5 | min. 6.5 turns | 10mm thread length |
| M12x1.75 | min. 6.5 turns | 12mm thread length |
| M14x1.25 | min. 9 turns | 12mm thread length |
| M14x1.5 | min. 7.5 turns | 11mm thread length |
| 1/2" UNF | min. 8 turns | 11mm thread length |
6. The actual tightening torques for attaching the wheel spacers to the vehicle correspond to the vehicle manufacturer's specifications for wheel attachment.
7. After installing the spacer on the hub, check that the original bolts do not protrude above the plane of the surface of the spacer. If this is the case, only rims that have a corresponding recess on the mounting surface between the mounting holes may be used. These recesses must be deep enough to accommodate the bolts and/or nuts that protrude above the surface of the spacer. Otherwise, the fasteners may break and the rim may come off.
Installation instructions for DRA system spacers
Thoroughly clean the hub end and surface of the vehicle hub from dirt and rust using a wire brush. 2.
2. Insert the spacer into the rim and check whether the spacer with the outer chamfer and the centering tab sits firmly and without play on the respective rim surfaces.
3. Place the spacer on the hub of the vehicle and check whether the spacer is flush and free of gaps and whether the inner chamfer and the inner part of the centering tab rest on the corresponding surfaces of the vehicle hub.
4. If necessary, remove any dowel pins, calipers and/or protruding brake disc mounting bolts.
5. Attach the spacer to the vehicle hub using the included screws. Make sure that the screws are screwed in to the minimum depth:
| M12x1.25 | min. 8 rpm. | 10mm thread length |
| M12x1.5 | min. 6.5 turns | 10mm thread length |
| M12x1.75 | min. 6.5 turns | 12mm thread length |
| M14x1.25 | min. 9 turns | 12mm thread length |
| M14x1.5 | min. 7.5 turns | 11mm thread length |
| 1/2" UNF | min. 8 turns | 11mm thread length |
6. The actual tightening torques for attaching the spacers to the vehicle correspond to the vehicle manufacturer's specifications for wheel attachment.
7. The heads of the spacer mounting screws must not protrude above the surface plane of the spacer.
8. After installing the spacer on the vehicle hub, ensure that the mounting screws do not rub against internal components of the vehicle. 9.
9. Insert the wheel bolt into the rim and check whether the length of the bolt protruding from the rim is less than the thickness of the installed spacer. If this is not the case, replace or shorten the wheel bolt.
Track widening
This term is most often associated with shoes. On a wheel rim, a spacer is a special ring that aligns the seating position of the hub with the center hole.
Drivers who install non-original rims on their car need this ring. Conventionally, these designs always have a slightly larger center hole diameter to allow for a wider range of vehicle applications.
The disadvantage of installing it is that the car can 'roll' at high speeds. To eliminate this phenomenon, supinating pillows are installed. These are available in different materials:
Before purchasing the rail, measure the center hole of the disc and the seat of the hub. The measurements obtained allow you to correctly select the right shoe.
Nuts
Wheel fastening nuts are mainly used on vehicles from the USA. Meanwhile, Japanese manufacturers have also started using this attachment.
The nuts are made from different materials. The best of these materials is titanium. Usually titanium nuts are used in tuning. It is not commonly used because it is very expensive.
There are also forged aluminum alloy nuts made from silicon and magnesium. Their main advantage is that they are light. The disadvantage, however, is their low strength. Closed steel nuts are considered the strongest type. They reliably protect the bike from dirt and water.
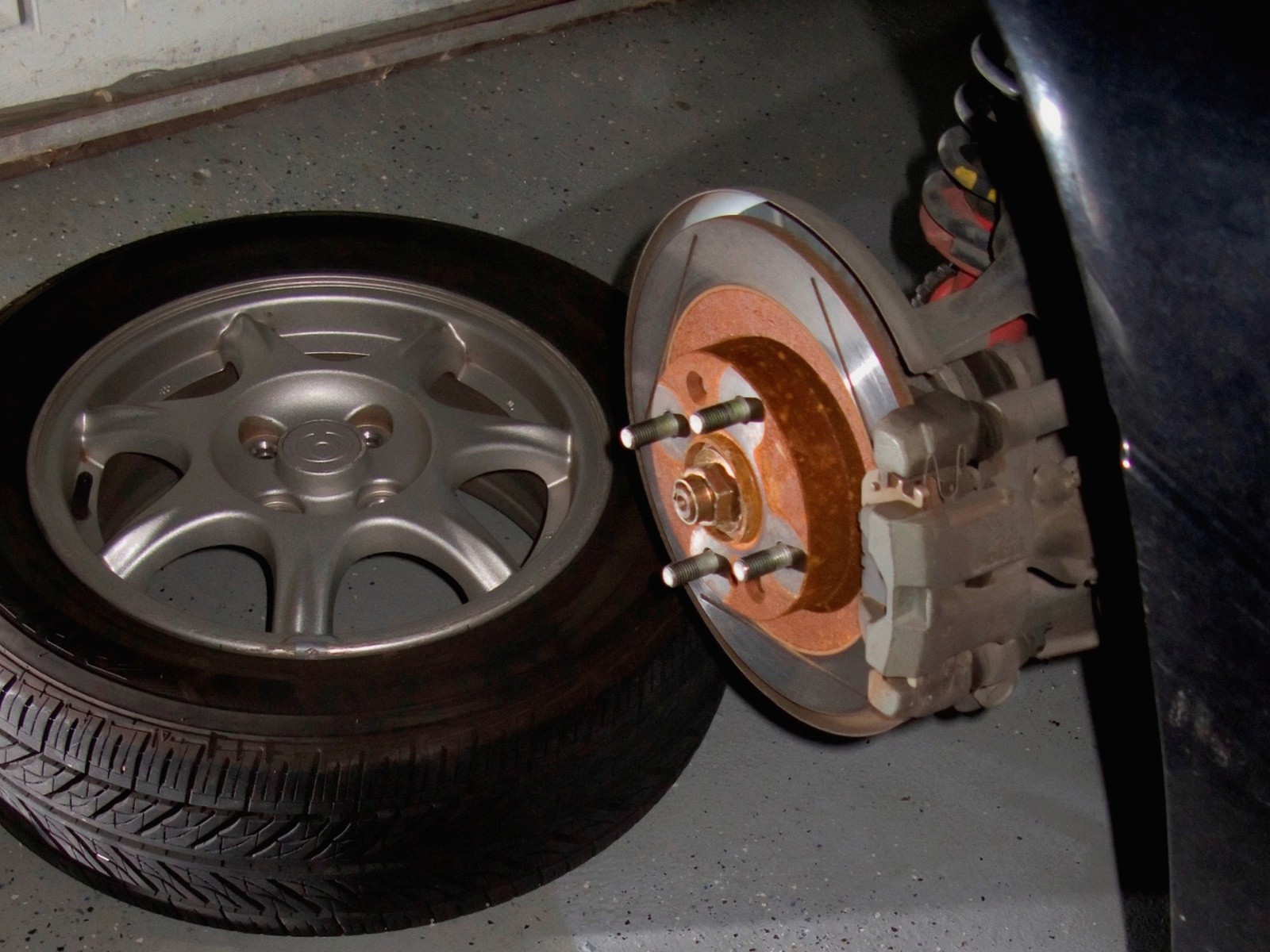

It is not uncommon for non-original rims to be installed on a car, but instead universal rims or rims that fit other makes and models. However, it happens that the parameters of the mounting holes, offset, width, etc. are the same, while the central hole is larger than necessary. Many people are convinced that the diameter of the hub and the 'hole' in the rim must match exactly, and buy so-called centering rings - an absolutely pointless accessory.
When you delve deeply into attaching the wheel to the hub with tapered bolts (or tapered or half-round nuts - whatever), almost every technician understands that alignment rings are a pointless accessory. But it can't always be explained in words without a 'visual demonstration'. So let's take a look at some simple but quite understandable schematic images.
Since the center hole of the original OEM disc is usually the same diameter as the hub boss, many think that the equality of these diameters is a necessary and mandatory factor. However, this is not the case! The center hole and diameter play absolutely no role in aligning and locking the wheel. The wheel is centered and secured only by the tapered part of the bolts, and nothing else.
Why are wheel insoles needed?
There are many different rims on the market today. However, some rims are only suitable for certain brands. For example Audi, Mercedes, Volkswagen.
If such a rim is installed on another model, there may be problems with the dimensions of the holes, that is, the seat and the disc do not fit together. To quickly solve this problem, specially developed spacer rings are used.
What are spacer rings?
Before buying rims for a car, it is important to pay attention to a few important parameters.
An important parameter of the rim is the diameter of the main hole. If it matches the parameters of the hub cylinder, the fit is tight. The suspension will function correctly and the dynamics of the vehicle will not be affected.
If this parameter does not match, the wheels will wobble. The suspension is stressed and the parts begin to wear and break more.
In such cases, it is essential to use locking rings to prevent accidental loosening of the screws. They protect the disc bore from cracking. If the rings are not installed, the tires will wear unevenly, which will have a negative impact on the vehicle's handling.
Advantages of centering rings
Firstly, correctly mounted rims ensure safe driving.
Secondly, the screws are not subjected to additional stress and arbitrary loosening is prevented.
Thirdly, suspension vibrations are eliminated and tire wear becomes even.
Which spacers should be installed on the hub?
The main functions of these parts are as follows:
- Increasing the pitch and track width.
- Possibility to mount non-standard wheels.
- Increased vehicle stability when cornering.
- Tuning: sporty appearance of the vehicle.
Consider the types of spacers depending on various factors: purpose, design features, brands.
- Universal. The parts do not require any change in fastening, their thickness can range from 3 to 6 mm.
- Spacer (with through hole). They are 7 to 20 mm thick and can be mounted on long bolts.
- Spacers allow the installation of discs up to 60 mm thick.
- Spacers are used on vehicles where the wheels are secured with nuts rather than bolts.
- Conversion plates are used to mount wheels with a different axle size than the factory one.
- Center bore modification, stamped or cast wheels: used when wheel diameter is increased;
- Metal-corrected wheels: have the disadvantage that the concentricity is increased;
- mixed: include both of the above functions.
According to well-known brands:
- 'PROMA'. Russian company that produces high-quality spare parts and accessories and competes with foreign manufacturers.
- 'Hofmann'. This German company produces tuning parts for European and American cars. The products are reliable and have a reinforced design.
- 'Bimecc'. The manufacturer from Italy is a leader in the production of wheel accessories for various car models in Europe. A lightweight magnesium and aluminum alloy is used that meets European quality standards.
- Up to 10mm. The small thickness of the component is used to mount discs with unusual dimensions in such a way that there is no contact with the brake caliper;
- 12 to 25 mm – for wheelbase extensions and tuning;
- 25 to 50 mm - for mounting with bolts or studs.
How are the spacers installed?
There are various recommendations and schemes for installing wheel spacers. Below you will find a basic, accepted procedure.
- Use a metal brush to carefully remove dirt and corrosion from the hub surface.
- Attach the part to the rim and check that it is flush with the centering tab and chamfer.
- Check whether the inner chamfer and the centering shoulder rest against the hub surface.
- Remove grub screws, clamps and locating pins (if any).
- Check the grub screws by comparing them with the factory set grub screws. The thread length must be greater by the thickness of the spacer. The conical seat surface must exactly match the counter surface. If the factory wheel bolts have a movable spherical or conical surface, the extended bolts must also have this.
- Attach the spacer to the hub with long screws and align the mounting holes beforehand.
- After installation, check that the mounting screws do not rub against the inside of the hub or caliper.
- The tightening torque for the fastening screws is 100 N*m.
Carry out the assembly carefully so as not to damage the parts and not to damage the threads of the vehicle mounts. First tighten the two screws opposite the wheel and then the remaining screws.
Caution! Tighten the screws with a dynamic wrench, an impact wrench will not provide the correct torque.
After assembly, rotate the wheels in the suspended position and check that the wheels do not rub against the body panels. It is recommended to check the tightness of the screws after 100 km and tighten them if necessary. Self-adjustment of the parts is not permitted.
Wheel spacers are a way to tune and mount unusual rims, lengthen the track and give the vehicle a sporty look. It is important to select these parts carefully, taking into account our recommendations.
When are wheel spacers needed?
Wheel spacers are often used in car tuning. These are metal components that are mounted between the hub and the rim. They are installed when:
- when installing rims whose distance between the wheel bolts deviates from the norm. In this case, the part is attached to the hub using standard screws. The rim is then attached to the spacer itself using the screws included in the kit.
- Mount the discs with an offset that differs from the standard setting. Wider rims give the vehicle a more aggressive look. In this case, special spacers 'distance' the wheel from the vehicle's suspension.
- Installation of brake discs that are larger compared to the standard brake discs. In this case, using spacers will prevent wider wheels from damaging other suspension components and the body.
- Increasing the vehicle's track width.
Special features when selecting wheel spacers
When choosing spacers, it should be noted that they are available in many versions:
- Thin, i.e. between 3 and 10 millimeters thick. They are used when caliper discs or tires easily penetrate suspension components.
- Medium, i.e. between 12 and 20 millimeters thick. They are used when wheel arch extensions are fitted; they eliminate the 'dimpled' effect of the wheels.
- Thick, that is, between 20 and 30 millimeters thick. They are used for mounting wheels with negative offset as well as tires larger than standard size. They are first mounted on the hub and then the rim is mounted on the spacer itself.
- Extra thick, i.e. 30-40 millimeters thick. They are indispensable when tuning jeeps or off-road vehicles. The installation procedure is exactly the same as for the thick spacers.

When choosing the right spacers, pay attention to the quality of the product itself, not the price. Inconsistencies in dimensions or differences in materials are unacceptable. You also need to check that the mounting holes are 'in place'. If even one of these parameters is incorrect, the spacers will rub against the suspension and cause deformation of the suspension components. Caution: Installing 'handmade' spacers can have serious consequences, including traffic accidents.
Bykov insoles - a unique remedy for flat feet
Supinator insoles restore and support flat feet to their normal state.
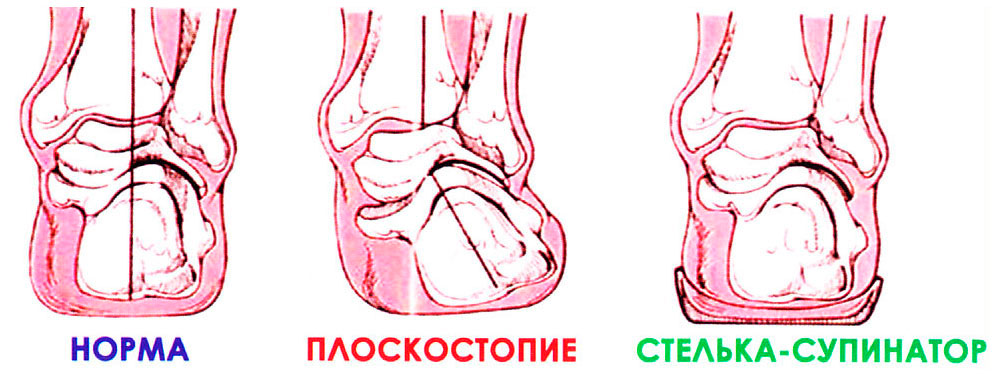
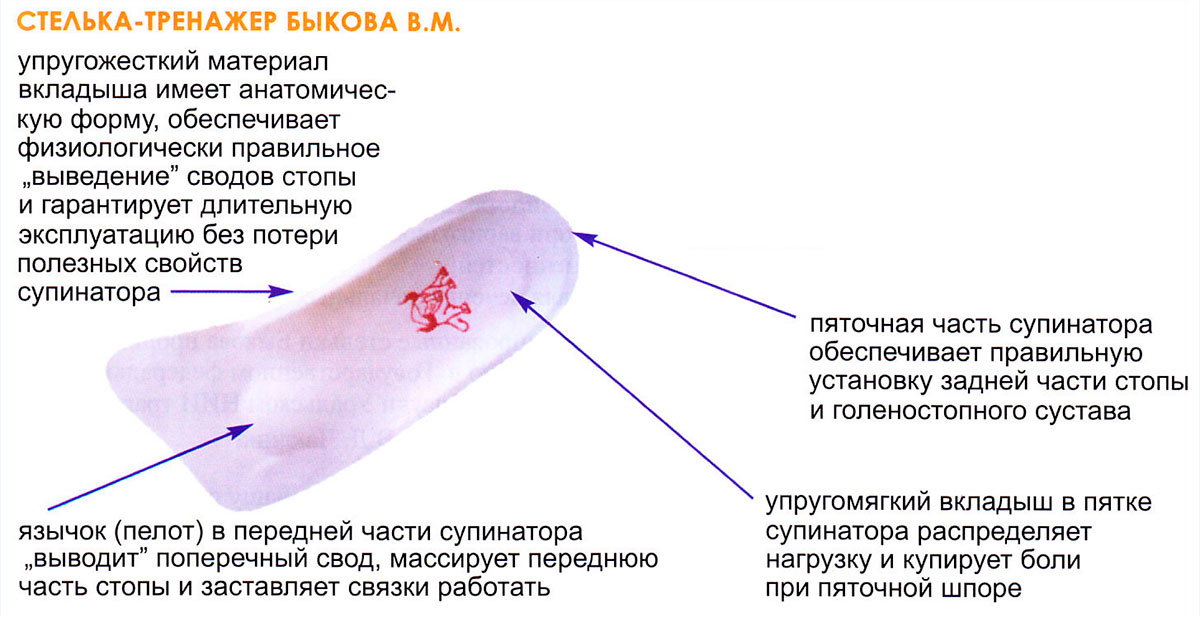
The Bykov supinators made of flexible and rigid material act as a training aid, forcing muscles and ligaments to work hard to regain lost properties. The wave-shaped elastic insole bounces up and down and stresses the muscles and ligaments of the foot. Their activity normalizes blood circulation in the limbs. The insole supports the arch of the foot, promotes the stability of the foot when standing and walking, massages the surface of the sole of the foot, prevents signs of foot fatigue, relieves pain when walking, improves general health and prevents the development of pathological conditions of the musculoskeletal system - the consequences of flat feet. In childhood and adolescence, the condition of the foot improves significantly through comprehensive treatment and targeted exercises, leading to recovery. The unique 'cinch' helps stop the pain of 'heel spurs'.
Insoles for the back – materials, composition, function
The insoles are ideal for preventing and treating the following diseases:
- heel spur
- neuromas
- calluses
- tendovaginitis
- corns
- synovitis
- Toe and forefoot deformities
- Diabetic foot
- osteochondrosis
- disc prolapse
- radiculitis
- contortions
– scoliosis
– kyphosis - sciatica
- Fatigue of the muscles in the back
- back pain
Joint diseases of the knee:
- Deforming arthritis of the knee joint
- inflammation of the meniscus
- Synovitis - Accumulation of fluid in the joint
- Sprained knee ligaments
Video about supinating insoles:
Bykov insoles (Told by the inventor)
Orders can be placed online
24/7
- amputation set.
- insoles for shoes.
- Shoes for the elderly with sore feet.
- Perseus official website.
- Making hooves for shoes.
- Stapa.
- longevity of the shoes.
- What does the insole of a child's shoe look like?.
