However, a valgus deformity of the big toe is not just a cosmetic problem. The need for surgical treatment depends on the presence of pain and limitation of activities of daily living.

- Hallux valgus (painful bones) versus other foot problems
- Hallux Hallux Valgus (valgus deformity of the first toe)
- Degrees of severity of hallux valgus
- Hallux valgus treatment
- The surgical treatment of hallux valgus is free of charge within the framework of the HMP.
- Surgical treatment of lateral nail phalanx deformity
- Causes of flat feet
- Treatment of flat feet
- Causes of hallux valgus
- severity of the disease
- WHAT OPERATIONS ARE PERFORMED IN OUR CLINIC AND WHAT ARE THEIR ADVANTAGES?
- SCARF OSTEOTOMY
- prevention
- What is hallux valgus?
- Causes of valgus toe deformity
- What should be examined?
- Surgical treatment of flat feet
Hallux valgus (painful bones) versus other foot problems
The most common foot problem is a flat transverse arch with a deviation of the metatarsal bones at the toe joints - known as hallux valgus. Hallux valgus (painful bones).
The arch of the foot in the area of the metatarsal bones becomes increasingly flattened, the fatty tissue thins out more and more due to the increasing pressure when walking, which leads to increased pressure on the bones and pain (metatarsalgia).
Orthopedic clinics in Germany and Switzerland Clinics in Germany and Switzerland offer a number of proven surgical methods for treating hallux valgus and other foot diseases.
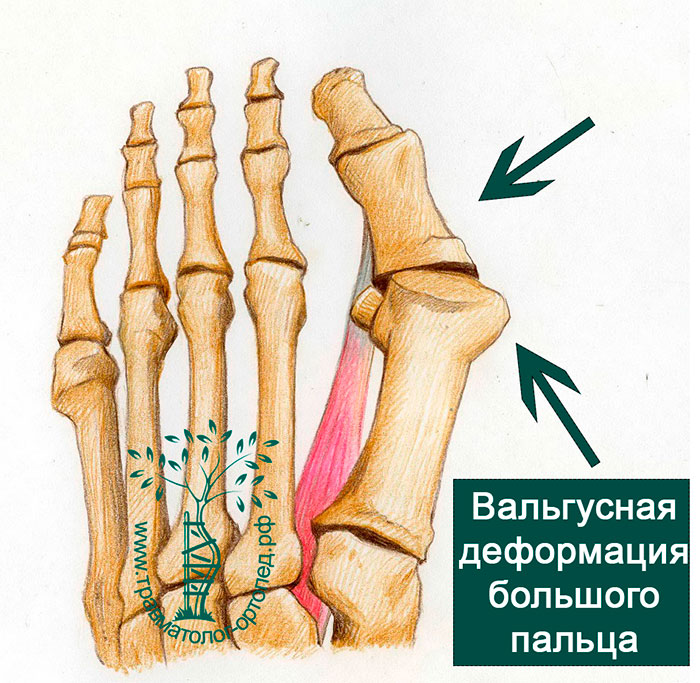
hallux Hallux valgus (valgus deformity of the first toe)
Hallux valgus is an outward deviation of the big toe when the angle between the first metatarsal and the big toe is more than 25 degrees. The development of a valgus deformity can be caused by weakened connective tissue and muscles and by wearing tight, high-heeled shoes.
The misalignment of the first metatarsal causes the skin and soft tissue to bulge towards the inside of the big toe, which becomes visible over time. Under the pressure of tight shoes, the skin can become red and a synovial sac can form, as well as skin abrasions. If the big toe is misaligned, the position of the neighboring toes is disturbed, which leads to the formation of the so-called hammer toe (digitus malleus).
Degrees of severity of hallux valgus
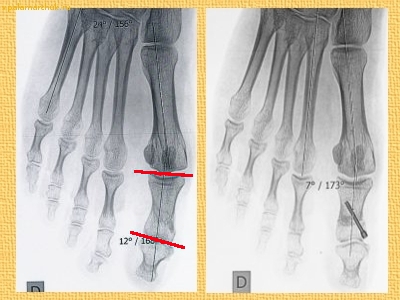
There are different degrees of hallux valgus. The degree of valgus is determined by the change in the angle between the first toe and the first metatarsal – the hallux valgus angle. Important An important value for assessing the degree of hallux valgus is the so-called intermetatarsal angle (metatarsal angle). (Intermetatarsal Angle), meaning the angle between the first and second metatarsal bones. Depending on the size of this angle, a distinction is made between. 3 degrees of hallux valgus of the first toe
The table shows the angle values and the respective degrees of valgus deformity of the first toe:
Every The severity of hallux valgus has its own clinical symptoms.. The main symptom of hallux valgus is a deviation of the first toe outwards - the hallux valgus. Patients also have pain in the area of the metatarsophalangeal joint, where they notice enlargement of the bone, swelling of the joint and reddening of the skin around this joint. This leads to a condition called bursitis. A transversely flattened foot that cannot support the weight of the body. A permanent pathological forefoot deformity develops.
The extent of the deformity and the clinical manifestations of the deformity determine the tactics and approach to the treatment of hallux valgus.
Hallux valgus treatment
Video – Hallux Valgus Surgery, 1:49 min, 3 MB.
In most cases, in the early stages of the disease, The first option in the treatment of hallux valgus is conservative treatment.This includes:
- Lifestyle correction (weight loss, exercise, etc.)
- the use of orthopedic shoes to eliminate interaction in the area of the first metatarsophalangeal joint – the 'painful knot',
- Use of interdigital spacers
- Use of first toe orthotics.
- Using insoles to correct the arch of the foot.
Pharmacological treatment often includes taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and physical therapy.
If several conservative treatments are ineffective or the disease is in an advanced stage, surgical treatment of the hallux valgus deviation of the first toe is performed.
The surgical treatment of hallux valgus is free of charge within the framework of the HMP.
If medically indicated and approved by referral, the operation will be performed at our center under the High-Tech Medical Assistance (HTM) program.
Read more about our High-Tech Care program
Surgical treatment of lateral nail phalanx deformity
The principles of the operation are very simple: the plane of the base and head of the proximal phalanx must be kept parallel. This inevitably requires an osteotomy and removal of the sphenoid bone defect to restore the axis of the finger. After the correction, the bone fragments must be fused together. This is usually a metal screw that allows the fragments to be securely and permanently joined together before being fused.
Restoring the parallelism of the articular planes of the proximal phalanx by wedge resection of the phalanx diaphysis with screw fixation
Minimally invasive surgery is a particularly suitable method for this intervention. Bone resection and screwing are possible through small incisions of a few millimeters and the fingernail phalanx is correctly repositioned. After the procedure, you can walk in normal shoes again almost immediately.
If you find a typo in the text, please let me know. Please highlight the text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Causes of flat feet
– Very variable – heredity, overwork, uncomfortable shoes, high heels, overweight, etc.
– The most common 2nd toe deformity is hammer toe, where the 1st toe is arched under the 2nd toe, the 2nd toe is raised, the toe bones are kinked at the joints, and the protruding parts of the toe become stuck due to friction form non-healing blisters on footwear. Another common complication is. Metacarpophalangeal arthritis (Caused by the heavy stress on the metatarsophalangeal joints due to the flattening of the arch of the foot, it causes fairly severe pain in the metatarsophalangeal joints, often accompanied by swelling and redness of the skin over the metatarsophalangeal joints.
Treatment of flat feet
– supinators, exercises, massage, interphalangeal corrections, in severe cases – surgery. The following exercises can be recommended:
1. Alternate and simultaneous pulling of the toes.
2. Slide the foot of one leg over the shin of the other leg and hug it.
- The feet are placed parallel and the legs are bent. Simultaneously and alternately lift your heels.
- Do the same but lift your toes up.
- Put the foot on top of the other foot. Rotating foot movements.
- Use the toes to grasp, lift, and carry small objects such as pencils, buttons, bones, etc.
- Roll a small rubber ball with your feet.
- Pinch a rubber ball between your feet, raise and lower.
- Pick up a small light mat with your toes and try to crease it.
- Squeeze and relax your feet.
- Roll the sticks with your feet.
1. Feet parallel, hands at waist.
2. Crouch and tiptoe forward and backward.
3. Walk on the toes, heels and outside of the foot.
Causes of hallux valgus
With this deformity, the bones of the foot gradually shift and the angle between the metatarsal bones changes. There can be several reasons for this:
- Inherited predisposition. Close relatives are also affected by this condition. Genetic metabolic diseases that affect the entire musculoskeletal system are also affected.
- Inflammatory processes, arthritis, arthrosis and synovitis often lead to various bony deformities.
- clubfoot. Can be congenital or acquired.
- overweight. Due to the high load on the joints of the lower limbs, there is deformation of the joints.
- Individual characteristics of the foot structure. For example, long metatarsal bones or bones in the big toe.
- Wearing tight, high-heeled shoes.
- Lower limb injuries.
Valgus lesions of the foot are more common in older people. Because multiple triggers can be present at the same time.
severity of the disease
In medical practice, a total of four degrees of severity of the disease are distinguished. These are determined by the angle of displacement of the bones of the big toe in relation to the other bones.
- First degree. Shift of up to 15 degrees. There are still no symptoms, no complaints. You may only see a slight enlargement of the bone at the root of the finger.
- Second step. Angle up to 20 degrees. The big toe is slightly deviated from the midline of the foot. Painful sensations appear even with prolonged walking in uncomfortable footwear.
- Third stage. Deviation up to 30 degrees. The joints already hurt constantly when walking. The remaining toes begin to twist. The bump is visible and uncomfortable. Wearing normal shoes becomes very uncomfortable. Blisters and corns may appear.
- Stage 4 The angle of the big toe is more than 30 degrees. The pain is constant, even at rest. Mobility is severely impaired. All the bones of the toe are crooked. Urgent advice from an orthopedic surgeon is required. Surgical treatment is indicated.
WHAT OPERATIONS ARE PERFORMED IN OUR CLINIC AND WHAT ARE THEIR ADVANTAGES?
There are a number of different surgical procedures used for valgus deformities of the first toe. The patient needs to understand that surgery is not just about removing the 'bone' from the foot. The main goal of hallux valgus surgery is to correct the transverse arch of the foot and restore the normal angles between the bones that form it.
The type of surgery depends on the degree and size of the deformity. Operations can be performed on both soft tissue and bone. The surgical procedure on the bones is called an osteotomy. During an osteotomy, the bone is filed down in a special way, further displacing the bone fragments and fixing them in their new normal position.
At various times, pins, screws and staples have been used for fixation, which either remain permanently in the leg or are removed some time after the operation.
In our daily practice, we use innovative, specially shaped screws that securely fix the bones in the correct position until they are fully healed.
In our clinic we use a combination of bone and soft tissue surgery, which leads to better results. Based on studies by foreign colleagues and in our opinion, the most effective surgeries for valgus deformity of the first toe are SCARF, Akin and Chevron osteotomies.
You can read more about it here.
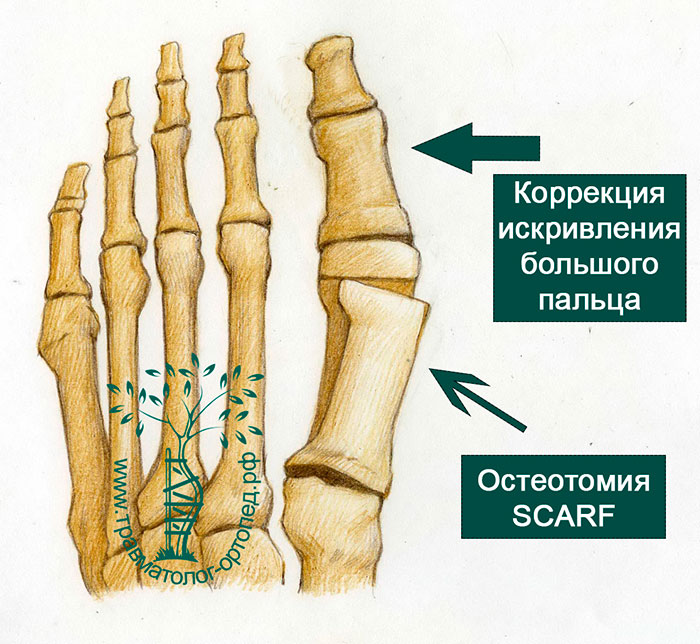
SCARF OSTEOTOMY
In the SCARF osteotomy, surgical access to the first metatarsophalangeal joint is primarily created and the bone is removed.
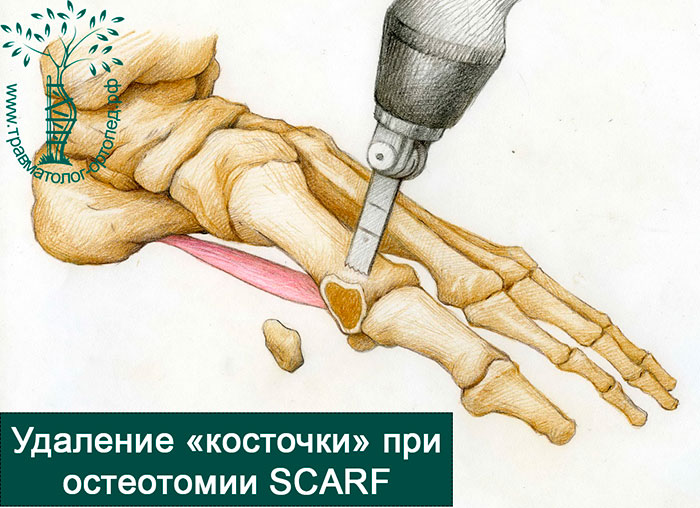
During the operation, one long horizontal and two short transverse incisions are made in the first metatarsal.
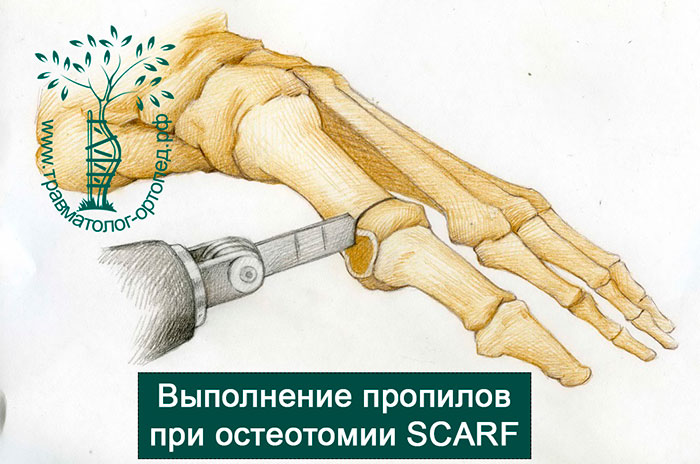
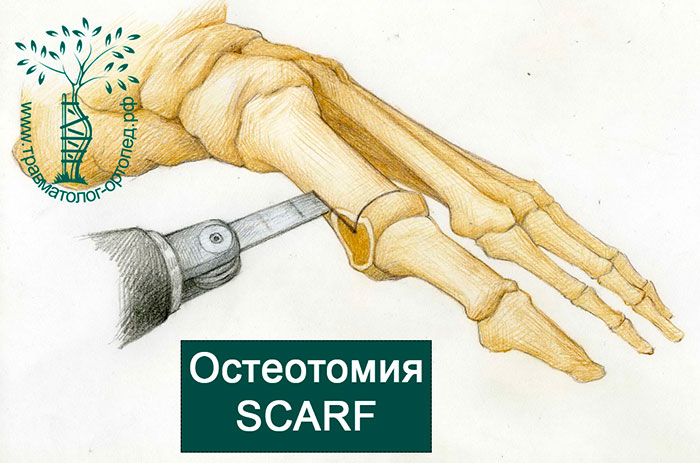
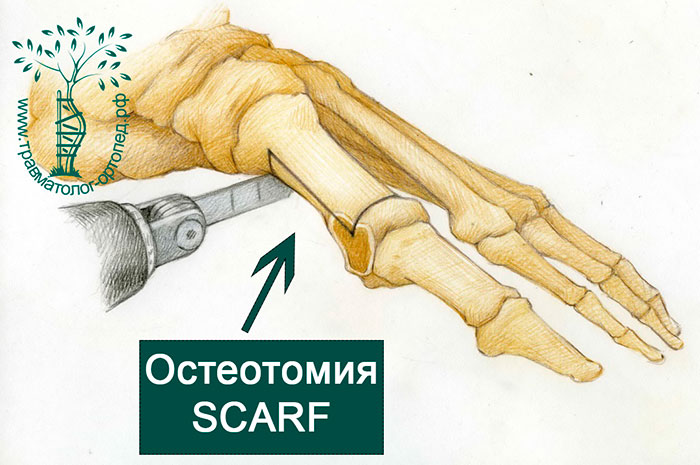
Depending on the direction and angle of the incisions, the surgeon can move the bony fragments of the first metatarsal over a wide range.
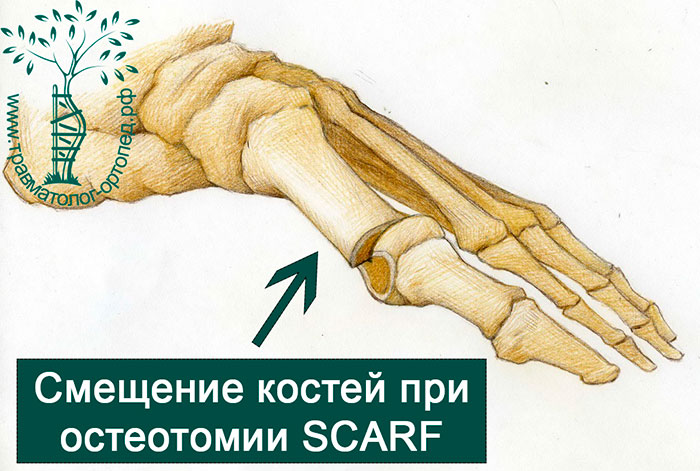
With this type of osteotomy, practically any type of misalignment of the first toe can be corrected.
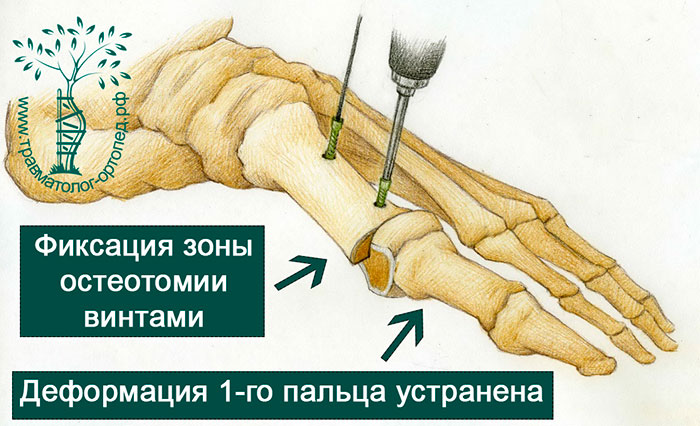
Once the misalignment has been corrected, the displaced bone fragments are fixed with two screws. The titanium screws hold the bones firmly together until they are fully fused.
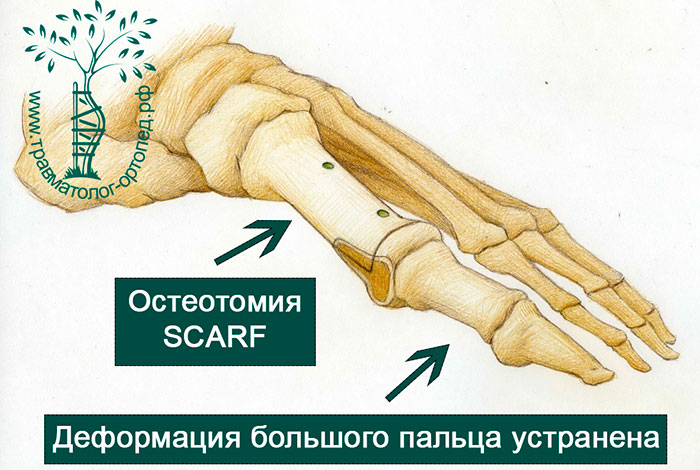
This treatment corrects deformities of the first toe, relieves pain when walking and makes feet beautiful and slim again.
prevention
The most important preventive measure is regular check-ups by the orthopedist, especially if the patient already has other factors. Women should also avoid wearing high heels all the time, as this leads to flat feet and later valgus deformities.
It is important for people who work with their feet to take breaks and wear orthopedic shoes or insoles when needed.
In addition, regular barefoot walking is a good preventive measure as it works the muscles and tendons of the lower limbs.
What is hallux valgus?
Hallux valgus (ICD code M20.1) is an external malformation of the big toe. It is popularly known as bunions or bunions on the foot. The pathology consists in a change in the angle between the metatarsal bone and the big toe. As a result of the joint deformity, the bone head protrudes and forms a bulge that is hard to the touch. Over time, the bulge increases in size due to bony changes and soft tissue swelling.
The valgus deformity of the first finger is one of the most common diseases in orthopedics and traumatology. The valgus deformity occurs most frequently in older women; men are affected much less frequently.
This is due to the connective tissue weakness of the female sex and a preference for high-heeled shoes.
Causes of valgus toe deformity
Hallux valgus is an acquired defect that develops throughout life. Most often, the curvature develops against the background of a transverse flatfoot, a shallow valgus deformity, a violation of the biomechanics of the foot.
Big toe deformity is caused by the following conditions:
Weakening of the ligaments, especially in women during a phase of reduced production of female sex hormones;
Contrary to popular belief, uncomfortable high-heeled shoes are not the direct cause of hallux valgus. However, in the presence of a predisposition or in the early stages of the curvature, walking in such shoes accelerates the progression of the pathology. Flat-soled shoes and models with very short toes also contribute to this deformity.
Metabolic causes of big toe valgus deformity include:
Hallux valgus is also often diagnosed with neuromuscular diseases: multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, hereditary motor-sensory neuropathy.
What should be examined?
As a rule, parents complain that their child has flat feet when it starts to walk on its own. It is important to distinguish between a physiological flattening of the arch of the foot in a child under the age of three and a flat valgus deformity, which requires supervision by an orthopedist.
If the axis of the heel bone is in the midline and the arch of the foot in young children is moderately flattened under load, massaging the muscles of the lower limbs and wearing shoes with a firm grip may be sufficient. If the child has hindfoot valgus deviation and flattening of the arch of the foot, comprehensive rehabilitation treatment is required.
Treatment of flatfoot deformity includes massage of internal muscles of lower legs and feet and plantar muscles, 15-20 sessions four times a year, heat treatments (ozokerite, paraffin, fango), corrective exercises to shape the arch of the foot. It is also necessary to incorporate exercises into the child's daily routine to strengthen the muscles that support the arch of the foot. This can be achieved through playful therapeutic exercises, such as B. rolling a cylindrical object, walking on your toes and outsides of your feet, climbing an inclined board, pedaling barefoot on a bicycle or exercise bike, etc. Good results in strengthening muscles can be obtained through active training in the pool can be achieved with a therapeutic swimming instructor. If the child responds sufficiently, electrostimulation of the muscles that support the arch of the foot is recommended as a supportive measure.
In cases where the foot remains in a valgus position even without loading and there is tendon tension in the peroneal and extensor muscles, we recommend a step cast in adduction, varus and supination for 1-2 months until the foot has reached a medial position. The patient then sleeps for another 3-4 months with a cast or splint and is provided with orthopedic shoes.
Surgical treatment of flat feet
Surgical treatment to correct the deformity is rare. The percentage of patients who undergo surgery relative to those who are observed is at most 7 %. If necessary, tendonoplasty is performed on the inside of the foot, supplemented by extra-articular arthrodesis of the subtalar joint according to Grice. In adolescents with painful flatfoot contractures, the foot is reshaped with a tripod arthrodesis.
The optimal age for surgical treatment of severe congenital flatfoot deformity is 5-6 months when conservative treatment is ineffective. Lengthening of the tendons of the contracted muscles, relief of the ankles on the outer, rear, inner and front surface, open reduction of the talus up to the fork of the ankle, restoration of the normal joint conditions in the midfoot, forefoot and hindfoot by creating a duplication of the tibialis posterior tendon.
Read more:- flatfoot μb.
- chalgus valgus.
- Stages of hallux valgus.
- ICD 10 chalgus valgus.
- Metatarsophalangeal joint of toe 1.
- flatfoot.
- First metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot (metatarsophalangeal joint).
- How much does bunion surgery cost?.
