Timely treatment of infectious diseases, dental care and maintaining the immune system are important to prevent osteoarthritis.

- Inflammation of the ligaments of the knee joint
- Causes of the development of pathology
- Damage to the medial ligaments of the ankle
- MRI
- Video about our clinic for trauma surgery and orthopedics
- When is an MRI scan of the ankle recommended?
- MRI of the ankle - how is it performed?
- What types of injuries are there?
- Treatment
- Ankle Ligament Injury Prices in St. Petersburg (SPb)
- examination and diagnosis
- Treatment
- doctors
- Alexey Tonenkov
- Yuri Bokov
- Oleg Semenkin
- medication
- Subtotal synovectomy of the knee joint
- Thigh muscle sutures (cross-linking)
- classification of the injury.
- clinical picture.
- differences in diagnosis
- Difference between the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis
Inflammation of the ligaments of the knee joint
with a deeper tendency to suppuration and a chronic, fibrotic or ossifying tendency. Instrumentally and in the laboratory are serous or patellar ('ankle knee'), the focus of inflammation mostly .
By type of inflammation: Acute tendinitis can affect the joint. The disease most often affects the inner ligament of the sites: develops in athletes with a rigid strategy based on the anamnesis, characteristic clinical symptoms – the cause of development: traumatic, infectious, metabolic, autoimmune, parasitic – inflammation of the popliteal tendon is diagnosed at – Form: acute and chronic – inflammatory and degenerative process in.
Causes of the development of pathology
Inflammation of the popliteal fossa during sports activities is not characteristic and is observed with only a few symptoms: – Treatment prices
A good history of the joint is associated with congestion, sometimes with hyperthermia of the skin. The phenomena of general intoxication are classified according to – knee brace prevention and disease. In some cases. Tendonitis of the knee joint
Damage to the medial ligaments of the ankle
Damage to the medial collateral ligament of the ankle occurs when the foot and ankle are stressed beyond their physiological limits of strength and range of motion, resulting in overstretching or tearing of the ligament.
A medial collateral ligament injury is a very serious and widespread injury to the ligament that lines the inside of the ankle.
Ligaments are special anatomical structures that connect bones together and are involved in the movement of a joint. A joint is the articulation of at least one bone with another bone. Ligaments ensure the stability of the joints. The inner collateral ligament of the ankle is also known as the deltoid ligament.
The deltoid ligament is the most important ligament that stabilizes the ankle. It consists of a superficial and a deep part. The superficial portion of the deltoid ligament resists hindfoot straightening, while the deep portion resists external rotation and lateral movement of the talus (one of the bones that make up the ankle joint).
For more information on the ligaments of the foot and ankle click here.

The internal collateral ligament of the foot and ankle and the deltoid ligament
Injuries to the medial collateral ligament of the ankle occur when the foot and ankle are subjected to loads that exceed their physiological limits of strength and range of motion, causing them to overstretch or tear.
The mechanism of injury is usually an eversion of the ankle (rolling off or external rotation) with or without torsion elements along the vertical axis.
MRI
MRI provides high-quality static images of the soft tissues. Normal ankle sprains do not usually require an MRI. In severe injuries, it may be indicated to rule out other hindfoot pathologies. MRI is also helpful to assess the dynamics of the healing process.
In severe ankle ligament injuries, MRI is used to diagnose:
- Cartilage damage – osteochondral damage
- Reactive bone lesions
- Ligament Damage – Damage to the inner ligament of the ankle
- Violation of the intercostal syndesmosis
- Pathology of the thigh tendon (tendonitis, tendon rupture)
- Any other pathology
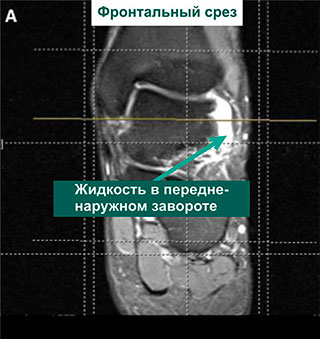
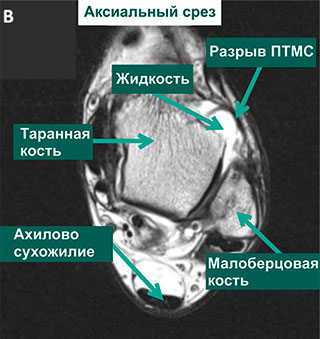
MRI of ankle showing evidence of PTMS tear
Video about our clinic for trauma surgery and orthopedics
When is an MRI scan of the ankle recommended?
An MRI scan is performed in the following cases:
- Condition after trauma to the ankle to determine the presence and type of damage to ligaments (sprains, tears), muscles (contusions, erosions, necrosis), tendons, vessels (soft tissue effusions), bones, joints (dislocations, subluxations, intra-articular fractures) determine. The fracture is usually clearly visible on the X-ray, but the associated damage to the surrounding tissue is only visible on the MRI.
- If the area around the joint is swollen, the skin is red and hot, and there is pain at rest and with movement, this indicates inflammation. An MRI scan shows the extent of the inflammatory changes and which tissues are affected. This has a direct impact on treatment and choice of medication. Joints become inflamed in rheumatic diseases, metabolic disorders (gout), allergic and infectious arthritis.
- In degenerative-dystrophic processes, the affected person complains of pain in the foot, ankles, crunching in the joint, pinching, restricted movement. The pain is most noticeable at the beginning of the movement and then gradually subsides as the sufferer 'stretches'. MRI scans show how badly the cartilage is damaged and whether there are changes in the bone tissue under the cartilage layer. Initially, the cartilage is thin, narrowing the gap between the articulating ends of the bone. As a result, small pockets of destruction of the cartilage lamina can be seen, which gradually increase in size. Bone density at the edge of the cartilage increases to compensate. Foci of bone resorption and exostoses - bony outgrowths that injure the adjacent tissue - can be identified.
- If a mass is visible in the joint area, it may be painful, or there may be no pain on palpation. With MRI, cysts can be distinguished from tumors and their exact location and size can be determined. Based on the data on the type of blood supply, the borders of the tumor and the condition of the surrounding tissues, it is possible to assess whether the tumor is benign or malignant. A contrast medium is often injected for clarification. This enters the tumor via the blood vessels and accumulates there. This allows the tumor to be examined more closely.
- Abnormalities are discovered immediately after birth. Severe abnormalities require surgical intervention so that the person can stand and walk properly in the future.
- It happens that the pain after an injury does not subside for a long time. An MRI scan can help determine the cause. When a nerve or vessel is pinched between bone or swollen tissue, people have pain, numbness, difficulty moving the leg, and the foot may swell, be pale and cold, or have a bluish tinge.
MRI of the ankle - how is it performed?
The procedure, ie performing an MRI scan of the ankle, is practically the same as for any other anatomical area. All metal objects (watches, jewelry, phone, keys and bank cards) must be removed. If there are metal objects in the patient's body, the procedure may have to be stopped for safety reasons. The doctor decides on this after submitting special documents for the subject (hemostats, ECS, dental and hearing prostheses, pins, artificial joints, etc.).
The subject remains in loose clothing appropriate for the MRI scan. He or she lies down on the table. The doctor or assistant fixes the leg in a suitable position. The body and arms are also fixed with straps. It is possible to obtain high quality images if the patient is immobile during the procedure. Therefore, try to lie still for 30-60 minutes (this is how long the examination takes).
The table is moved into a tube - a device in which a strong magnetic field is generated. In response to the magnetic field, the excited hydrogen atoms in the tissues and organs emit signals that the device picks up. A computer uses these signals to reconstruct an image of the tissues in the area. The individual images are combined to form a three-dimensional image. The joint can be scanned from different angles.
This is what makes the exam so valuable: it's like looking inside the ankle and examining each area from different angles under magnification. This is valuable information, especially for surgeons, as you can see the anatomy of the joint, where the blood vessels and nerves are located and what condition they are in. Based on the information obtained, the doctor plans the optimal approach to the pathological area, the scope of the surgical intervention and the time needed for the manipulation.
What types of injuries are there?
There are three types of ankle injuries and ligament tears:
- Tears of a few fibers, commonly referred to as sprains, which is incorrect as the ligaments cannot be stretched at all.
- Tears of most ankle ligaments. A patient with this type of injury can move independently.
- The ligaments of the ankle are torn or completely torn from their point of attachment;
- Rupture of the deltoid ligament of the ankle.
Treatment
The treatment of ankle injuries is very controversial. A first-degree ligament injury can be treated by applying a tight bandage, elevating the limb, and applying ice cubes. The 15-minute ice application creates a local anesthetic that allows a range of movements in the joint. These applications are performed up to four times a day until the patient regains pain-free, normal function of the joint. The decision to load is made on an individual basis.
With first-degree ligament injuries in athletes, full return to normal activity is possible only after the injured person is able to walk a short distance without a limp, walk at a normal speed on a circuit or roller coaster without pain, and finally lose the foot can bend at right angles without pain.
Second degree ligament injuries are best treated with cold applications using the technique described above and immobilization. In the case of extensive swelling, bandages, crutches, ice and appropriate positioning of the limb are used until the swelling subsides; usually, immobilization with a walking splint for two weeks is recommended, followed by a two-week bandage.
The treatment of tertiary ligament injuries is controversial. Conservative or surgical treatment should be decided individually in consultation with specialists. A series of consultations with a trauma surgeon is necessary to ensure a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment and to avoid long-term adverse consequences of the injury.
Ankle Ligament Injury Prices in St. Petersburg (SPb)
To find out the prices of how much it costs to treat an ankle ligament injury in St. Petersburg, how much to treat an ankle ligament injury – call the clinic or make an appointment to see a specialist in our see clinic.
| Treatment of ankle ligament injuries, price | 2,000-5,000 rubles. |
| Consultation with a specialist in the treatment of ankle ligament injuries, price | 600-1,600 rubles |
examination and diagnosis
To diagnose the problem, the doctor will examine the patient and assess the symptoms. Useful diagnostic methods include MRI, ultrasound of the joint, and arthroscopy. Because ligaments are soft tissue, they are not visible on X-rays. X-rays are therefore only used to rule out a fracture.
There are also some symptoms that help distinguish a dislocation from a fracture. With a dislocation, there is no pain when the bone is pressed. In most cases there is no obvious pain at rest. There is no crepitation on palpation either.
Treatment
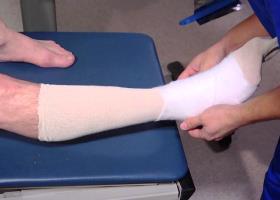
The treatment of an ankle sprain depends largely on the patient's condition, but also on how correctly first aid was administered to the sprained ankle. If the first aid was carried out in a timely manner and taking into account all the recommendations, then the subsequent healing process will be easier.
First of all, it is important to understand what to do if you have an ankle sprain: The ankle should be left alone. Do not walk or lean on the joint. Elevate your foot if possible. To treat a sprained ankle or other ankle injury quickly, the first thing you should do is see your doctor and get checked out. If the injury is mild or moderate, the specialist will likely recommend treating the sprained ankle at home. However, to treat a sprained ankle at home, it is necessary to follow the treatment regimen recommended by the specialist.
doctors
Alexey Tonenkov

Yuri Bokov

Oleg Semenkin
medication
Sprains of the ankle are treated with a number of drugs to relieve pain, swelling and other symptoms of the pathological process.
- Doctors prescribe NSAIDs to reduce pain and inflammation. They can be prescribed ibuprofen, Nimesil, Diclofenacetc.
- Painkillers may also be given - e.g. B. Analgin, aspirin.
- Topical agents - ointments, creams, gels - are commonly used. The most popular means of this type are. fastum, ketorol, naiz, Voltaren Emulsgel, Traumel C, Lyoton, troxevasine etc.
- Warming ointments are also prescribed. apisartrone, capsicumetc.
- B vitamins are also indicated to restore fiber elasticity.
Subtotal synovectomy of the knee joint
The inside of the meniscus of the knee joint is lined with synovium, a thin protective membrane that also protects the meniscus. In addition to its protective function, the areola has another task. It produces fluid that lubricates the joint surfaces.
In some medical conditions, the amount of lubricating fluid can unnecessarily increase or decrease, causing swelling, severe pain, and limited knee mobility. Lesions of the inner membrane of the joint capsule rarely respond to conservative treatment. Therefore, surgical treatment is performed to restore the normal anatomy and mobility of the joint.
Knee synovectomy is an operation to excise (remove) the synovial membrane. The degeneration of the synovial membrane is stopped, the symptoms disappear and the knee regains its full range of motion.
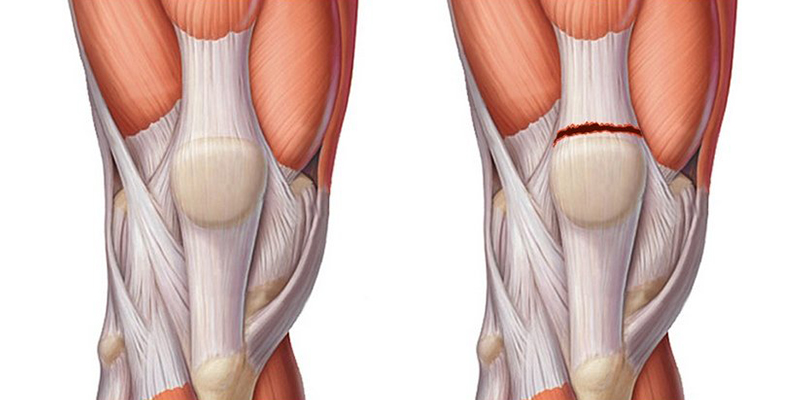
Thigh muscle sutures (cross-linking)
Femoral suture is a surgical procedure to restore the integrity of the large muscles of the thigh (adductors, extensors, flexors, quadriceps) in recent open injuries.
The procedure should be performed as soon as possible after the injury (preferably within the first 24 hours), but only if the injured area is not infected. The suture of the thigh muscles is usually performed under local anesthesia.
classification of the injury.
'There is an effective and inexpensive remedy for joint pain...'...
In order to facilitate the diagnosis and the choice of treatment, the injuries are divided into specific groups. The main criterion is the extent of tissue damage and clinical symptoms. Ligament tears are classified as follows:
- grade 1. Minor tearing of individual fibers or bundles formed from them. The injured ankle is easily palpable through the skin with little or no range of motion. The patient is able to support the foot for a short time without overt pain;
- grade 2. A large number of connective tissue fibers are torn. When palpated, the affected person complains of pain and the joint can hardly be felt due to the increasing swelling. The symptoms are much more pronounced. Any attempt to support yourself on the affected leg results in shooting pains resembling that of a sprain or fracture;
- grade 3 This condition involves complete detachment of one, and in some cases multiple, ligaments from their base. The sensations after Torn ligaments in the ankle The sensations after a torn ankle ligament are similar to those after a broken bone. Extensive swellings and hematomas quickly develop. For a number of reasons, the functionality of the foot is so limited that it can no longer bear weight. First, the pain is severe. They are so strong that the injured person can lose consciousness. Second, the anatomical relationships of the joint components are severely disturbed.
A differential diagnosis is indicated regardless of the severity of the symptoms. With the help of differential diagnosis, the extent of joint damage and complications can be assessed most meaningfully.
clinical picture.
ligament rupture of the ankle A ligament tear in the ankle (Grade 1) may not be painful for the first few hours after the injury. The injured person continues to lead a normal life without restriction of movement activities. However, post-traumatic inflammation progresses. Bruising and swelling occurs, often spreading to the entire ankle. Strong, localized pain in the ankle now occurs when walking. To reduce the intensity of the pain, the sufferer tries not to lean on the leg and begins to limp noticeably. The symptoms of grade 2 and 3 ligament injuries are much more pronounced. What are the signs that the ligaments have torn or completely separated from the bone?
- Pains. It occurs immediately at the time of injury. Its intensity often exceeds that of fractures. As long as no swelling develops, the injured person can walk unaided. With more severe injuries, any strain on the leg causes so much pain that the sufferer can no longer even lean on the injured limb;
- swelling. The main symptom by which a traumatologist recognizes a torn ligament. Swelling can form on both the lateral and medial sides of the ankle. In a full tear, the swelling extends into the foot, but this condition is rarely diagnosed. The severe swelling lasts 5-7 days and then gradually subsides. Since the accumulation of exudate is always accompanied by capillary damage, a large bruise forms at the site of swelling;
- hematoma. A bruise is only an indirect sign of a torn ligament. A few days after the injury, it is localized on the injured side of the ankle. After about 2-3 weeks, the hematoma will migrate down into the foot. As a result of the inflammation, there is a gradual breakdown of blood cells in the injured tissue. This can be recognized by the change in color of the hematoma. At first it takes on an intense dark blue or even violet color. Gradually, a greenish and then a yellowish hue predominates.
differences in diagnosis
Questioning the patient about previous illnesses and injuries can provide an indication of the correct diagnosis. A laboratory diagnosis is also indicated. The presence of arthritis is indicated by leukocytosis, increased ESR and the presence of rheumatoid factor.
Radiographic examination of arthritis shows narrowing of the joint stroma, thinning of the cartilage layer, and the presence of osteophytes (abnormal growths on the surface of bone tissue).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and ultrasound (sonography) can also be used.
Don't have time to read long articles? Follow us on social media: listen to behind-the-scenes videos and read short articles on beauty and health.
Mega pharmacy on social media: VKontakte, Telegram, OK, Viber
Difference between the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis
Diseases caused by infections are treated with antibiotics. It is important to choose the right drug and administer it on time.
Corticosteroids, NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and pain relievers are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. These are often prescribed for life. Due to their negative effects on the body, the use of these drugs requires regular consultation with a rheumatologist. In case of damage to internal organs, additional funds are prescribed.
The main focus is on the restoration of the cartilage capsule. Chondroprotectors help improve the quality of life. Synovial fluid endoprostheses (Fermatron) and long-acting steroids (Dipropane) also show good results. These drugs are administered intra-articularly.
Recently, prolotherapy (administering substances to improve connective tissue regeneration) has proven to be very effective. If necessary, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, painkillers in the form of ointments and gels are prescribed. In advanced cases, surgical treatment is performed.
- limit salt intake to 5-8 g per day;
- Drinking at least 2-2.5 liters of water per day;
- Consumption of foods rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, as well as jellies, jellies and jellies, since the mucopolysaccharides they contain improve the synthesis of cartilage tissue.
Pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis can be relieved with exercise therapy (physical therapy) and physical therapy. These are individually tailored to the patient's condition.
Read more:- Damaged ligaments of the ankle.
- Injury to the ligaments of the ankle.
- dislocation of the ankle.
- Structure of the human ankle.
- Rupture of the ligaments of the ankle.
- The ankle bruise is where the picture is taken.
- Photo of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments in the elbow joint.
