At the GlavMedCentre, treatment of elbow joint arthrosis is successfully carried out using modern, non-surgical methods.

Ultrasound examination of the joints
Ultrasound examination of the joint is a non-invasive and safe examination of the musculoskeletal system that can detect any disease characterized by joint pain. This procedure can be carried out as often as required. It is suitable for patients of all ages (including infants) and pregnant women. If necessary, functional tests and stress tests are carried out (much depends on the specific diagnosis). Our center has everything you need to get complete and reliable information: expert equipment and competent doctors/diagnostics.
| Type of service | Price |
| joint ultrasound | |
| knee ultrasound | 600 |
| Ultrasound of the ankle | 600 |
| Hip ultrasound | 600 |
| shoulder ultrasound | 600 |
| Ultrasound of the elbow | 600 |
Indications for ultrasound examination of the joints
There are several indications for this examination:

inflammation of joint tissues;

cartilage and tendon problems;

Trauma to the joint (fractures of adjacent bones, ligament injuries, hematomas, tears, etc.).

hip dysplasia;

The need to determine the amount of synovial fluid;

Before performing a joint puncture;

need for confirmation/confirmation of ligamentous hemorrhages;

Certain diseases of the internal organs.
Experts recommend conducting the examination at the age of 45-50.
causes
Like osteoarthritis of other local joints, elbow osteoarthritis can be divided into the following categories
- Arthritis as an independent form
- Rheumatoid arthritis, which is caused by autoimmune, systemic damage to connective tissue in the body;
- rheumatoid polyarthritis (the elbow joint is affected at the same time as other joints);
- specifically infectious (e.g. tubercular, viral, etc.).
- infectious-allergic;
- Psoriasis;
- juvenile (chronic inflammatory joint disease in children and adolescents), etc.
- allergies;
- metabolic disorders (e.g. gout);
- bronchopulmonary diseases;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- cancers;
- Bone inflammation (osteomyelitis);
- Infections of the gastrointestinal tract or genitourinary tract (reactive arthritis), etc.
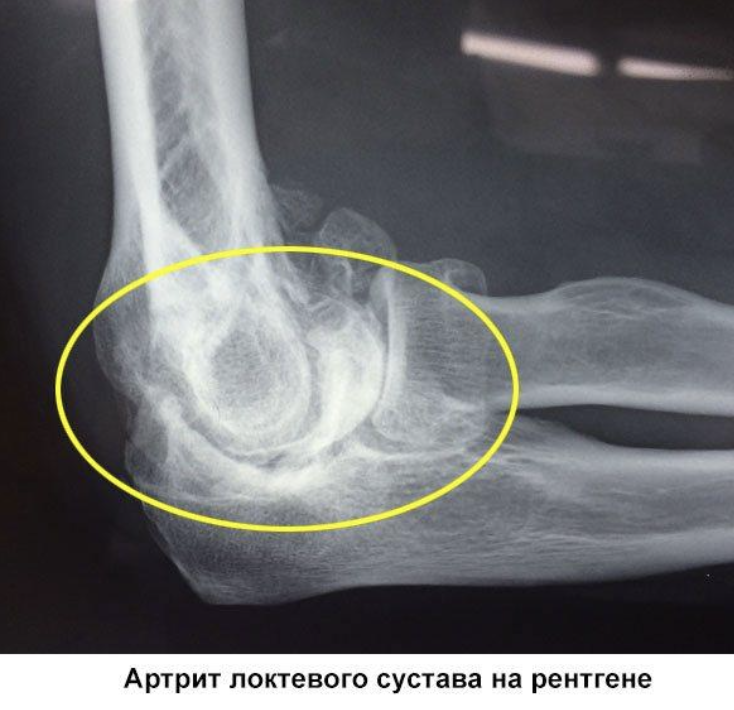
Symptoms and complications
Elbow arthritis is accompanied by persistent, dull pain that periodically increases or decreases. Some patients notice an increase in pain in the early morning hours. The intensity of the pain can range from barely noticeable to excruciating, making it difficult to sleep.
The area around the joint is swollen due to inflammatory exudate (serous or purulent fluid) in the joint cavity and the skin is red. The mobility of the joint is severely impaired.
If the inflammation is caused by the penetration of an infectious agent into the joint, fever, chills, increased fatigue, weakness and other general symptoms also occur. The pain becomes throbbing and twitching.
Inflammation of the elbow joint can be acute (in this case all symptoms are more pronounced), chronic with milder symptoms and subacute.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the joints are affected symmetrically in three or more joint zones. In addition to the elbow, the interphalangeal, metacarpophalangeal, metatarsophalangeal, ankle, wrist and knee joints can also be affected. Dense subcutaneous nodules appear on the volar surface of the elbow. In the early stages of rheumatoid arthritis, the elbow joint is affected without obvious discomfort or loss of function, but as the disease progresses, serious changes develop that limit the patient's ability to care for themselves.
Inflammation of the elbow joint can be complicated by the spread of the inflammatory process to the periarticular tissue, the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joint (arthrosis), muscle hypotrophy, etc. If not treated appropriately, the disease can lead to total disability and disability.

F-215 ankle brace

You can ask any question about the product or the shop.
Our qualified specialist staff will help you.
Our online shop offers several delivery options:
- Courier delivery in cities where the network operates;
- Self-delivery from a repair pharmacy;
- Delivery by 'Russian Post';
- Delivery by a transport company ('SDEK', 'Boxberry');
- Delivery by a transport company ('SDEC', 'Boxberry') to your door.
Delivery by courier.
In the cities of the presence network 'Vosstanovitelnaya Medina' (Rostov-on-Don, Azov, Stavropol, Nevinnomyssk, Mineralnye Vody, Pyatigorsk, Essentuki, Kislovodsk, Georgievsk, Novopavlovsk, Budyonnovsk) you can order delivery of goods by courier. After receiving the goods at the warehouse, the courier will contact you and offer you a convenient delivery date.
Free delivery on orders from 10,000 rubles (except for goods for which a special price applies).
Collection from the Salon 'Regenerative Medicine'.
You can pick up the paid goods on site at one of the nearest salons. Please note that some discounts are only valid when paying online. Our salons are located in Rostov-on-Don, Azov, Stavropol, Nevinnomyssk, Mineralnye Vody, Pyatigorsk, Essentuki, Kislovodsk, Georgievsk, Novopavlovsk, Budennovsk.
The possibility of self-delivery and the costs of salon delivery are determined by the operator of the online shop. The conversation takes place on weekdays from 9:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m.
Delivery by 'Russian Post'
You can order delivery through 'Russian Post'. The large number of post offices allows you to receive your order almost anywhere in our country. When the goods arrive at your address, you will receive a notification about the package and you can track the shipped order using a tracking number.
Documents
Surgical and conservative treatment of acute injuries and chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system related to professional or amateur sports activities
Minimally traumatic (endoscopic) procedures on the shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee and ankle.
- If the meniscus of the knee joint is torn, it is stitched or resected;
- Tears to the anterior and posterior ligaments as well as the collateral ligaments of the knee joint are repaired using the body's own tendons or artificial transplants;
- Patellar dislocation is treated with medial collateral ligament (MPFL) repair and tibial tuberosity osteotomy;
- If there is damage to the outer ligament group of the ankle joint, a ligament suture is performed, and if the damage has existed for a long time, an open or endoscopic operation according to Brostrom is performed;
- Anterior and posterior endoscopy of the ankle joint with correction of the identified pathology is performed;
- With Achilles tendon pathology associated with Haglund deformity, correction of the deformity is performed with tendon refixation;
- In the event of an Achilles tendon rupture, a minimally invasive suture is performed via a mini-access;
- In sports-related foot injuries, the plantar plate of the metatarsophalangeal joints is sutured;
- Operations to correct complex foot deformities with hallux valgus with curvature of the II-V toes are carried out;
- Operations are performed for Morton's neuromas;
- Habitual shoulder dislocation is treated both endoscopically and openly (Latarger operation). Depending on the indication and clinical situation, the rotator cuff suture can also be performed openly or endoscopically. Tenodesis is usually performed for tendinitis of the long head of the biceps brachii;
- Ligaments of the elbow joint are restored with tendon transplants (own tissue). Endoscopy of the elbow joint with removal of foreign bodies is carried out, as is the treatment of synovial fold syndrome (plica syndrome) and joint stiffening;
- He has experience in wrist endoscopy with reconstruction of the triangular fibrocartilage complex and good results in percutaneous osteosynthesis of scaphoid stress fractures;
- We have experience in the successful surgical and conservative treatment of chronic conditions such as Achilles tendonitis, subacromial impingement syndrome, epicondylitis and heel spur syndrome. Modern techniques of tissue treatment are widely used - for example, PRP therapy (platelet-rich plasma), orthokine therapy and hyaluronic acid injections;
- Tailored therapeutic exercise packages are developed for post-surgery recovery.
Our advantages:
- Possibility of combined treatment: surgery and rehabilitation treatment
- Supervision of rehabilitation by a surgeon
- the patient can use the proven recovery methods of the athletes of the Russian national team.
The Department of Sports Traumatology and Sports Medicine (OSTIS) turned one year old in June.
It was a challenging but very successful year.
We have introduced new wrist, knee and elbow surgeries, as well as sternoclavicular joint stabilization surgeries for chronic and acute traumatic instability. The department's employees were involved in the development of recommendations for rehabilitation after operations on the joints of the upper and lower limbs. The recommendations have been published in print and follow a series of similar publications. Currently, as part of scientific activity, intensive work is being carried out on the individualization of conservative and surgical treatment of diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system in athletes.
We now have our own operating room and state-of-the-art rehabilitation equipment.
The doors of the department have opened this year not only to the top athletes of the national team, but also to patients who simply want quality treatment for their illness or injury.
Sports technology is of greatest interest in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Here we often use our know-how in bioorthopedics, a new treatment area. In bioorthopedics, preparations made from the body's own tissue, such as fatty tissue or blood, are used for repairs. We regularly use bioorthopedic technologies such as platelet-enriched plasma or mesenchymal stem cells to treat gonarthrosis, coxarthrosis and osteoarthritis of the ankle and wrist.
It's no secret that injuries to the joint ligaments are very common in sports. Therefore, non-professional athletes often come to us with injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament, posterior cruciate ligament, knee collateral ligament and ankle joint. We use our experience working with professional athletes to operate on and repair these types of injuries.
Diagnosis of laryngitis
The diagnosis of laryngitis is made by the doctor based on an examination of the patient, including laryngoscopy.
In chronic laryngitis, it is important to determine the cause of the disease; The treatment strategy depends on this. Laboratory studies (tests) should clarify the situation.
It is important to remember that voice problems can also have causes other than inflammation, such as: B. trauma, a stroke, age-related vocal cord changes or benign or malignant tumor growths.
If laryngitis is suspected to be due to a bacterial infection, a culture (bacteriological culture) of throat secretions (or tissue) is done.
Make an appointment with a specialist in the primary care network to accurately diagnose the disease.
Treatment methods for laryngitis
Laryngitis is usually treated with home remedies such as inhalations, warm drinking and reducing pressure on the vocal cords (more rest if possible). If treated, laryngitis will clear up within one to two weeks.
Laryngitis should be treated by a doctor if:
If laryngitis occurs in a toddler, a doctor should be consulted at home. An adult with symptoms of laryngitis can see an otolaryngologist, family doctor or general practitioner. The child can be examined by a pediatrician or a pediatric otolaryngologist.
If the sputum is thick and viscous, expectorant and sputum-thinning agents are usually prescribed. If traditional treatment for acute laryngitis fails, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Physiotherapy is used to treat chronic laryngitis. Physiotherapy is carried out on the neck using electrophoresis, UHF or UVB.
Do not treat on your own. Contact our specialists who will make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
- Ligaments of the human leg.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle photo.
- Damaged ligaments of the ankle.
- Damaged ligaments in the ankle.
- Orthopedic shoes in Marin.
- Custom made orthopedic shoes.
- Damaged insoles in shoes - what to do?.
- Fracture of the lateral condyle.
