MOBIS classification system
This system is based on 4 activity levels:
– indoors only with mobility aid
– Indoor and outdoor mobility (limited) with mobility aid
– Unrestricted outdoor mobility with increased safety requirements
– Unrestricted mobility on the road with high prosthetic requirements.

- PROSTHETIC FOOT IN ISRAEL
- Heart Surgery in Israel – Prof. Bitran
- Features of the prosthesis
- treatment program
- 1.What is the cost of making a carbon fiber foot?
- 2.How is an individual prosthetic foot made?
- useful information
- Anesthesia in bunion surgery
- How to properly take a loaded foot x-ray
- How you can benefit from a personal consultation with me
- Advantages of the Triton feet
- Silicone foot prostheses have the following properties:
- How soon can I start fitting a prosthesis after an amputation?
- How do I properly attach the liner?
- PROSTHESIS AFTER AMPUTATION IN GERMANY
- Physiological changes
- implementation technique
- What do I have to consider after the surgical treatment of Morton's neuroma?
- What is the cost of foot surgery?
- Techniques for creating different types of stoma
- Principles of rehabilitation of patients with an intestinal ostomy
PROSTHETIC FOOT IN ISRAEL
Thanks to the latest advances in prosthetic orthopedics, the toes and arch of the prosthetic foot can be shaped in such a way that they can hardly be distinguished from healthy feet.
Both patients and the public know that the midfoot is more prominent than the heel when sitting or standing. It is therefore important to create a prosthetic foot that resembles a normal, healthy foot not only from a physiological but also from a psychological point of view. This allows the patient to feel comfortable and natural in it.
The production of artificial toes from so-called toeless prostheses is not only the most individualized approach, but also a very time-consuming process, which involves first removing the cast from the metatarsal of the healthy foot. Then a one millimeter thick layer of special foam is applied, rolled out and the desired shape of the prosthetic foot is reproduced by eye. The toes are not marked as a continuation of the foot axis, but in the valgus position. The length and position of the toes is also taken into account. For some people, the second toe is slightly longer than the first toe, for others it is the other way around. These two toes are made in their natural size, while the third and fourth toes are shorter because in most cases the prosthetic foot is slightly narrower than its model.
All the details are drawn on the surface of the prosthesis with a pencil, and then the individual fingers are formed by separating them, rounding them off and shaping the nail bed like a healthy limb. First, a large block of soft acrylic about 0.2mm thick is poured, then nails are cut from it, and finally each nail is glued to the prepared nail bed. The nail surface must be about half a millimeter deeper than the surrounding material. If necessary, such artificial nails are covered with nail polish.
Heart Surgery in Israel – Prof. Bitran

Professor Daniel Bitran is one of the leading cardiac surgeons in Israel. For the past 12 years, his name has been at the top of the list of the top five cardiac surgeons in the country. He has performed more than 10,000 complex heart and vascular surgeries. The results of the Department of Cardiac Surgery headed by prof. Bitran's results are superior to those of leading cardiac surgery centers in Western Europe, which is reflected in lower mortality rates and the development of postoperative complications.
Features of the prosthesis
Modern prosthetic foot Modern prosthetic feet are extremely comfortable, hygienic and aesthetically pleasing. They are often made from silicone rubber. The cost of a foot prosthesis is calculated individually in Israeli clinics, depending on the degree of amputation.
In any case, the foot prostheses in Israel offer patients the opportunity to regain a safe gait. You get a very realistic looking prosthesis that does not require any complicated care. Israeli hospitals in particular usually use prosthesis materials from the well-known German brand Otto Bock. Among the undoubted advantages of Otto Bock silicone prostheses – high flexibility, comfortable fit, easy care, even pressure distribution, individual choice of color and structure.
In addition to the practical, everyday silicone prostheses, other types of prosthetic feet can also be fitted. Israel is one of the few countries that offers its patients a wide range of non-traditional prosthetic techniques. For example, the following options are available for patients who want to do recreational sports Carbon alloy C-Sprint and Sprinter. With these, the patient can perform sprints or even jumps.
Well suited for patients with a high level of physical activity Triton prostheses. They have a number of innovative features that allow the patient to engage in all types of active activities. Learn more…
Some of the most popular cosmetic foot prosthetics today are. Products from the SACH and Dynamic brands. These products are also used in foot replacement centers in Israel. The SACH and Dynamic foot prostheses are characterized by their realistic appearance, the smooth surface and the detailed reproduction of the toes. A space is provided between the first and second toes to allow the wearer to wear flip flops.
treatment program
- Diagnostic examinations (computed tomography, laboratory tests, X-rays, electromyography).
- Consultation of an orthopedic surgeon.
- Preparation for fitting the prosthesis.
- Adjustment and conversion to the prosthesis.
- Dynamic Monitoring.
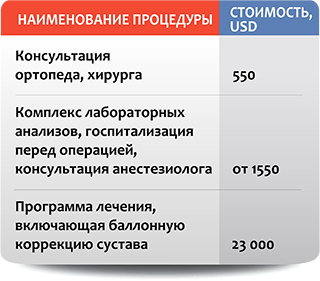
1. What is the cost of making a carbon fiber foot?
When ordering carbon fiber prostheses, the same principles apply as for silicone prostheses. First of all, the individual parameters are taken into account. In addition, the condition of the residual limb, the patient's age, their activity level and the sport they wish to practice are all taken into account. Therefore, the approximate cost of making a prosthetic foot in Israel with a so-called sports prosthesis can only be given after an assessment of the patient's needs.
2. How is an individual prosthetic foot made?
Making a custom prosthetic foot with toes is quite a time-consuming process. In the first step, a plaster cast is taken from the healthy foot. Then a 1 mm thick layer of special foam is applied. When making a custom prosthesis, the relative position and length of the toes must be considered. For example, in some people, the second toe is longer than the first toe (thumb). With a modern prosthetic foot, it is possible to wear open-toe shoes and even walk barefoot on a sandy beach.
useful information
I explain how the treatment process works. What to look out for.
How to get the best possible results.
How you can make your feet healthy and beautiful again and maintain your quality of life for many years to come.
Anesthesia in bunion surgery
I am often asked two questions: - What anesthesia is used for bunion removal - Can I choose general anesthesia to be unconscious during the operation.
In this video, I give in-depth answers to these two must-watch questions
How to properly take a loaded foot x-ray
In order to be able to correctly assess a forefoot deformity (hallux valgus), a stress X-ray is necessary, ie the patient must be standing at the time of the recording.
We recommend the First Diagnostic Center at Calle Siqueirosa 10.
How you can benefit from a personal consultation with me
I am often asked why it is better to come for a consultation before the operation. Finally, you can send in your scans, chat on social media, and then head straight to the operating table. I've been performing surgeries for 18 years and I've noticed a few things
Advantages of the Triton feet
- Particularly harmonious rolling behavior thanks to an interactive spring system with 3 spring elements connected to one another
- Noticeable sole flexion
- Split forefoot provides more security, stability and control when walking and standing
- Excellent dynamics, energy storage and conservation
- Easy and individual fit through attached heel wedges
- A wide range of possible uses in different environments – from home use to leisure sports
- Suitable for patients weighing up to 150 kg
Sime surgery already means the amputation of the lower limbs. The principle here is to preserve as much limb length as possible, because the greater the amputation, the smaller the contact surface of the residual limb. With the amputation, the surgeon wants to obtain a support surface on which loads are possible and the proprioceptive sensitivity can be used.
Plastics, mainly silicone rubber, are used for functional and cosmetic prostheses in the foot area. Thanks to the use of precise measuring technology, it is now possible to produce prostheses for Lisfranc and Chopar amputations with open ankles and ankles.
Silicone foot prostheses have the following properties:
- Optimum fixation of the residual limb;
- Even pressure distribution;
- high flexibility;
- adaptability in color and shape;
- Easy maintenance and care.
These prostheses are usually worn with normal footwear and are also used when walking barefoot.
The rehabilitation process after an amputation takes up to six months on average. The main task during this period is to prepare the residual limb for fitting the prosthesis. It should be borne in mind that the suitability of the residual limb for a particular prosthesis design is largely determined by the postoperative musculoskeletal status, which in turn is highly dependent on the surgical technique and the underlying or concomitant disease. This should be discussed with your doctor.
If you wish to undergo diagnosis or treatment in clinics in Germany, please send your inquiry or email to [email protected] or call us in Moscow: +7 965 337-40-66 or +7 495 755- 70-12
How soon can I start fitting a prosthesis after an amputation?
It all depends on the condition of the stump. For a young, active person without comorbidities, 7-8 weeks are usually sufficient.
The pad should be washed daily under warm running water with pH neutral soap. Never clean the insoles with chemicals (petrol, benzine, etc.), as these leach out the bioactive substances contained in the silicone and destroy the silicone itself. Before inserting the insole, do not apply any ointments or creams to the rest of the residual limb, with the exception of Otto Bock special products (derma clean, derma prevent and derma repair). In winter, when the stump gets too dry, silicone creams (or silicone-glycerin cream) are a good idea.
How do I properly attach the liner?
Turn the liner over so the silicone is facing out as much as possible, then roll the liner firmly over the residual limb, avoiding air pockets between the skin and the inside of the liner. Never roll the liner into a 'bagel' before rolling it up. Never slip the liner over the residual limb like a shoe while holding the edges.




How long after the amputation can I start with the prosthesis?
It depends on the condition of the stump. Seven to eight weeks is usually sufficient if it is an active young person without underlying diseases.
Why do I need a training prosthesis?
How do I properly care for an insole?
Wash the insert daily under warm running water with pH-neutral soap. Never clean the insert with chemicals (gasoline, petroleum ether, etc.) as these wash out the bioactive substances contained in the silicone and destroy the silicone itself. Before inserting the liner, do not apply any ointments or creams to the remaining limbs, with the exception of Otto Bock special products (derma clean, derma prevent and derma repair). In winter, when the skin of the stump is too dry, silicone creams (or silicone glycerin cream) are a good help.
How do I apply the liner correctly?
Turn the liner with the silicone outwards as far as possible and roll the liner tightly over the rest of the limb, avoiding air gaps between the skin and the inside of the liner. Never roll the liner into a 'bagel' before rolling it up. Never slip the liner over the rest of the limb like a shoe, holding the edges.
PROSTHESIS AFTER AMPUTATION IN GERMANY
Today, foot amputations are performed at more than a dozen different levels, from the removal of a single toe to the resection of a metatarsal. This is why there are so many different models of prosthetic feet today.
Anyone who has had an operation according to Lisfranc or Chopar can also manage at home without a prosthesis, ie they can stand and walk without outside help, which e.g. B. is very practical when showering. They can also move around with a prosthesis, giving them more confidence.
In Syme and Chopar amputations, the stump stem begins just below the knee. This may require special footwear that has extra padding under the sole of the sound leg, as the artificial leg is sometimes shorter than the leg in these situations. In recent years, thanks to precise measurement technology, it has become possible to produce prostheses for Chopar and Lisfranc amputations with open ankles and ankles.
In the case of short residual limbs that are in good condition at the level of the tarsus, experts recommend a shinbone-supported prosthesis, while a capsular prosthesis makes more sense in the case of poor residual limb conditions. The modified Teufel prosthesis is offered as a lighter variant for a better ventilated intermediate prosthesis.
Various types of plastic are common today for cosmetic and functional prosthetics in the foot area, but highly elastic silicone rubber is most commonly used, which ensures even pressure distribution and optimal adhesion to the residual limb. Silicone prosthetic feet are easy to care for and low-maintenance, individually adjustable in color and size. They are worn with standard footwear and can even be worn 'barefoot'.
Physiological changes
The low anastomosis created with the EWR stapler ensures adequate blood supply to the organs. This is associated with less tissue trauma and sets the stage for a reduced likelihood of anastomotic leaks. Therefore, it is considered the anastomosis of choice in every possible case, especially in cases where the intestinal wall is damaged and ischemic after radiation.
Sufficient mobilization of the descending colon must be ensured. Frequently, the splenofemoral ligament must be divided and the transverse colon mobilized sufficiently to ensure that the anastomotic sutures are not under tension. If complete mobilization requires sacrificing the inferior mesenteric artery, care must be taken not to damage the blood supply through the median colonic artery along with the marginal colonic artery.
Care should be taken when placing pressure sutures. They must not be placed more than 0.5 cm from the edge of the intestine. Otherwise, too much tissue will accumulate in the anvil, causing it to become wedged in the EAE stapler's suture mechanism. This leads to failure of the anastomosis. The size of the EAE stapler must be carefully matched to the diameter of the colon and rectum. Using a clip that is too large can crush the intestinal tacini, leading to ischemia and necrosis.
After removing the EOG stapler and prior to removing the stapler, it is very effective to place intermittent Lembert sutures with synthetic absorbable material north, south, and west around the stapled bowel to reduce the tension at the suture line and the improve wound healing.
In the final phase of the surgery, three tests are performed: inspection of the anastomosis, observation of the stapler O-rings, and the 'bladder test'. The last of these tests, the 'bladder test', is of the utmost importance. Most anastomotic leaks can be diagnosed during surgery, so the surgeon should not wait until the fifth or seventh postoperative day for the leak to become visible.
implementation technique

1 – The vaginal cuffs formed after an anterior colorectal resection and total pelvic hysterectomy and can be sutured with absorbable sutures. The rectal stump is visible at the level of the rectus lift muscle. The descending colon is sutured with an automated surgical stapler.

2 – In this sagittal section of the female pelvis after removal of the uterus and inferior rectal colon, it can be seen that the vaginal vault has been reattached with interrupted absorbable sutures. An EOG clip can be inserted through the anus. The rectal stump is sutured with a 2-0 Nylon Pursuit suture. The descending colon is marked on the pool edge. B' marks the urinary bladder and the pubic conjunctiva.

3 – The figure shows the mobilization of the descending colon. The peritoneum in the left lateral cortex has been resected up to the spleno-oesophageal ligament. The spleno-oesophageal ligament was clamped and transected. If the colon can be placed in the pelvis next to the rectal stump without tension, the mobilization is considered complete. Attention must be paid to the convexity of the left ureter, which must be visible at all times. At the top, the EOG clamp is placed over the rectal stump. The chain suture was tied around the central rod and the anvil stapler opened. Allis clamps are used to pass the descending colon through the anvil.

4 – The pelvic view shows the vaginal cuff covered with a synthetic catgut suture. The chain suture is placed in the rectal stump and tied around the center rod of the EOG stapler. The anvil of the stapler is pushed forward and the descending colon is mobilized from above. At this point, there are two rows of surgical staples in the descending colon to prevent intestinal contents from leaking into the wound.
What do I have to consider after the surgical treatment of Morton's neuroma?
Immediately after the operation, the foot should be elevated. A cooling compress should be placed on the foot to prevent pain and swelling. The stitches are removed after about 10 days. You can then shower again.
You will also receive special shoes that relieve your forefoot and shift your body weight to your heel. If you are planning a longer walk, you should also take elbow braces with you. Thrombosis prophylaxis is essential during the time when you cannot put full weight on your foot. This prevents the formation of dangerous blood clots. Physiotherapy and lymphatic drainage can prevent muscle atrophy and forefoot edema. The duration of forefoot edema often depends on the age of the patient.
What is the cost of foot surgery?
In addition to the costs for the surgical treatment of Morton's neuroma, the additional costs for diagnostics, doctor's appointments and aids (e.g. elbow crutches) amount to around 1,500 to 2,000 euros. If you are planning outpatient physiotherapy after the operation, we will be happy to provide you with a cost estimate. Information on the cost of hotel accommodation and possible additional treatment in a rehabilitation center can be found on the relevant website.
In order to determine the size of the Morton's neuroma and to diagnose any other diseases, foot specialists in Germany need a current MRI scan of the foot and the results of an X-ray examination. Once we have all the required documentation, we will email you patient information and a preliminary estimate for Morton's neuroma treatment within 1-2 business days.
Foreign patients can register for Morton neuroblastoma surgery at short notice. As soon as the advance payment specified in the cost estimate has reached our account, we will be happy to help you obtain a visa. If the visa is not granted, you will receive a full refund.
Due to the sometimes long travel times, we try to keep the time between the first examination and the operation as short as possible. During the outpatient and inpatient treatment of Morton's neuroblastoma, linguistically qualified medical staff who speak several foreign languages (e.g. English, Russian, Spanish, Portuguese) are available to you. Translators (e.g. for Arabic) are paid separately. We also organize transfers, can make hotel reservations and advise you and your loved ones on how to spend your time in Germany.
Techniques for creating different types of stoma
In a single-hole Brook ileostomy, the surgeon drains the end of the ileum through an opening in the right ileum and sutures the lining to the skin. The resulting 'trunk' protrudes 2 cm over the skin. It can easily be pulled back into the opening of the colostomy bag. A coccyx ileostomy is performed in patients who have undergone a coloproctomy. Once the patient is stabilized after the major surgery, the surgeons perform the second phase of the surgery. A special intestinal reservoir is formed in front of the ileostomy and a muscle cuff is applied to 'squeeze' the ileostomy itself. The reservoir is emptied twice a day via a special catheter. Thornball loop ileostomy is used for severe cancer and inflammation when resection is not possible due to the severity of the patient's condition. In this procedure, a loop of small intestine is removed through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and fixed there. The anterior abdominal wall is then severed and the stoma becomes a double-flush stoma. Split bilateral ileostomies have become quite common in recent years. In this operation, the ends of the small intestine are removed crossed in separate openings. This technique allows the surgeon to easily separate the adductor and diverticulum slings in order to connect them during stoma closure surgery. Multiple stomata (after Thornball) were formerly used in fulminant colitis. Today, this type of stoma is only used in atypical situations. During the operation, the injured intestinal wall is wounded up to the aponeurosis. The goal of surgery is to remove gas from toxic dilatation and decompress the bowel without performing an emergency resection. Three to five ileostomies are made at skin level without decompression. The advantage of this type of surgical stoma is that a risky emergency resection can be avoided. The disadvantage of this procedure is that the diseased bowel remains in situ and a second resection is required.
Principles of rehabilitation of patients with an intestinal ostomy
Many patients undergo reconstructive surgery at Yusupov Hospital after having an intestinal stoma removed. All problems disappear once the stoma is removed. Patients are able to return to natural secretion of intestinal contents through the anus. A permanent stoma is created in patients with colon or rectal cancer. To keep them alive, all or part of the diseased part of the intestine is removed.
Sometimes doctors are unsuccessful in performing reconstructive surgery and closing the stoma. This is the case when the temporary stoma has not fulfilled its protective function and complications have arisen below the stoma which make it impossible to close the opening. Reconstructive surgery to close the stoma is not performed when there is uncompensated comorbidity and any surgical intervention is life-threatening.
The problem is the closure of a stoma with a single opening. If an anatomically short rectal stump remains after stoma removal, reconstructive surgery can be technically difficult. The qualifications of the oncologists in the Yusupov Hospital, the technical equipment of the oncological operating room and the experience of the doctors in reconstructive surgery mean that patients cannot be refused stoma closure for technical reasons. In the presence of comorbidities, general practitioners prescribe individual treatment to compensate for the patient's condition. In complicated cases (cardiac arrhythmias), patients are operated on in partner clinics with the cardiovascular department.
Oncologists are only unable to perform reconstructive surgery if the patient's natural anus was removed in the original surgery. Reconstructive surgery with rectal reconstruction is performed only in young patients free of comorbidities. The decision to carry out the operation is made jointly by the doctors at a Medical Board meeting. Psychologists help patients to live with their stoma. Medical staff also teach patients how to take care of the unnatural anus themselves.
Read more:- stump care.
- prosthetic legs.
- prosthetic foot.
- The reamputation is.
- prosthetic leg.
- Leg prosthesis below the knee.
- Life after a leg amputation.
- A tricky stump.
