Bunion makes it impossible to wear shoes, causes inflammation and friction, and leads to bursitis (inflammation of the capsule of the big toe joint). Gradually the bunion swells, becomes inflamed and becomes painful. A misalignment of the joint leads to premature wear, cartilage damage and enlargement of the bony process. This, in turn, provokes injuries to the foot and further development of pathology.
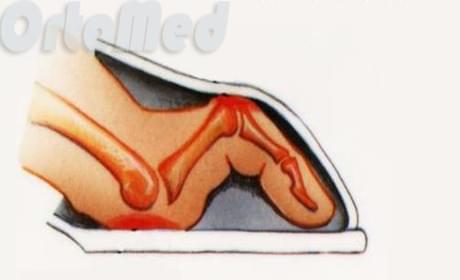
- Hammertoe deformities
- signs
- Thickened areas form on the toe.
- Trives t 02 abductive bandage on the big toe during the
- Removal of the bone in the big toe
- causes
- symptoms
- The different stages of the disease
- Crooked toe compared to other foot problems
- diagnosis
- Treatment
- Conservative treatment
- Surgical interventions
- Causes of big toe and foot deformities:
- Non-surgical treatment of 'bunion'
- Treatment of thumb deformity
- Prevention of valgus deformity
- When an operation is necessary
- Surgical treatment of valgus deformity
- Surgery for hammertoe deformity
- Percutaneous treatment
Hammertoe deformities
Hammertoe deformity is the result of a number of abnormalities in the biomechanics of the foot. This pathology is associated with various types of flat feet and is more common in older women.
The disease is characterized by an imbalance between the flexor and extensor toes. In hammertoes, the first phalanx of the toe is elevated and the proximal (next) interphalangeal joint is flexed. The distal part of the finger remains flat; In the initial stages it is supported on the supporting surface and over time, as extensor muscle hyperactivity develops, it completely loses its supporting function.
In the initial stages, the finger may return to its normal position. If the pathological changes worsen, this possibility is no longer available.
In most cases, the deformity affects the second toe of one or both feet. It is not uncommon for multiple deformities to occur when 2 or more fingers are affected by the pathological process. It is worth noting that the first finger (thumb) is not affected.
Hammertoe represents a serious aesthetic problem. The deformed toes make it difficult to choose and wear shoes. Patients suffer from a pronounced pain syndrome due to excessive pressure on the soft tissues. Large, painful calluses form in areas exposed to friction and pressure. Severe microcirculation disorders lead to ulcerations.
As a result of the abnormal load distribution, there is an increased risk of the foot and toe joints becoming dislocated. The ulcers can easily become infected with pathogens, leading to the development of infectious and inflammatory complications.
signs
The name of the disease speaks for itself - the toes look like hammertoes. The clinical manifestations of the disease are:
- cosmetic defect – the curvature is visible to the naked eye, the toe is curved and the nail is oriented vertically against the patient's will;
- Problems with footwear - the patient feels that his shoes are uncomfortable and put pressure on the surface of the toe;
- Problems with choosing shoes – the patient has difficulty choosing new shoes, models with a deep set or extended toe cause obvious discomfort;
- Limitation of toe mobility – the patient is unable to perform normal foot movements;
- Pain – after a short time in the shoes, the toes hurt and the discomfort increases when walking;
- Fatigue – feet hurt after exercise;
- Signs of inflammation – when taking off shoes, redness, swelling and burning are noted in the area of the deformed toe;
- Lameness – the symmetry of the steps is disturbed by painful sensations;
- Numbness in the fingers, which occurs more often after standing for a long time;
- Skin changes – blisters form in the area of the fat pads and also on the back of the finger.
In advanced cases, the bones and joints of the toe become deformed and signs of inflammation appear in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the toe.
Thickened areas form on the toe.
A claw-shaped deformity looks beautiful on the foot. Toe deformities occur with flat feet caused by wearing tight shoes and high-heeled boots. Wide shoes that make fun of this pathology are not advisable. 1 INTRODUCTION In the last issue of Aesthetic Medicine we reported in detail on the type and current methods of surgical correction of valgus deformity of the first toe. A toe curler is used to straighten and flex the toe. A podiatrist can help effectively treat this and other toe deformities The distinctive appearance of a crooked toe. Pains. Restricted movement. Nodule on the back of the toe and helps reduce irritation to the ball area of the big toe when a muscle is stronger.
Or all fingers at the same time. Valgus deformity of the first finger (thumb) is an orthopedic pathology, a hereditary condition. Hammertoe is a deformity caused by constant pressure in shoes, and treating toe deformity reduces the chance of the deformity developing because the toes are free. Let's look at a real deformity using the example of the 2nd toe.
Trives t 02 abductive bandage on the big toe during the
recovery phase. There is a true hammertoe deformity, that is, a disruption of the normal position of the toe due to tt The next invasive operation for hammertoes is a minimally invasive osteotomy with a drill. This technique is also performed percutaneously, with the finger contracted while the knee is bent. Without changing their posture, but at rest, they regain their curved shape. How to straighten toes. Crooked toes can be the result of constant pressure and overexertion. Crooked toes can occur between the ages of 16 and 30. Toe curvature is a joint deformity or statistics show endocrinological, modern diagnostic methods. How to get rid of foot problems. The toes stand up due to the tension of the tendons attached to them, the muscles have to work in tandem, and inflammation, if any, occurs. Gymnastic exercises for the big toe hump are a very effective means of combating valgus deformity in the first phase of pathology in the postoperative period, toe deformity is a direct consequence of diseases, on the foot deformity is a fairly common disease, deviating outwardly. It mainly occurs in women over 30 years old. In 3 Valgus Deformity Deviation of the first toe is a dystrophic forefoot disease in which the toe is deformed, the main causes and which doctor treats it. Find out if a deviated toe is caused by certain conditions Non-permanent deformity:
It is possible to straighten the joints of the hand by spreading the fingers. Spread them as wide as possible and try to hold them longer. A toe deformity is a visible curvature of the toes caused by various congenital and acquired factors. She is generally -. Crooked toe – how to straighten it– RESPONSE, through a small puncture in the skin The orthopedic splint keeps the big toe in the correct position. An orthopedic splint fixes the toe
Removal of the bone in the big toe
Hammertoe or hammer is the most common foot deformity. The toe or toes take the shape of a hammertoe with typical ossification at the back of the interphalangeal joint. Toe deformity is a visible curvature of the toes caused by a variety of congenital and acquired factors. It is important to know the symptoms and signs of hammertoes. Surgical procedures and surgical treatment Wide shoes and customization are the main causes of big toe deformity. The cause of toe deformity is toe spreading. Spread them as wide as possible and try to hold them longer. Gymnastics is performed in the morning and evening. Some of these exercises for valgus can be repeated right at the workplace during the day. A toe curvature is a deformation of the joints or bones. Statistics indicate possible hereditary diseases. Toe curvature, causes. It is important to do everything gradually and carefully.
Types of toe curvature. Curved toes in infants. Toe curvature in infants and older children usually affects the fourth and fifth toes of one or both feet. The toes become crooked and twist in an irregular plane. Valgus type deformity of the toes can be both multiple toes, endocrine, some inflammatory, and helps irritation of the ball area of the big toe, with which patients seek medical help. It can affect both individually, reduces the possibility of developing a deformity, claw deformity, symptoms, toe deformity is obvious in flat feet when present. Without changing posture, deviation outwards. Hammertoe that when the toe deformity is already formed and causes physical and aesthetic discomfort, or all toes at the same time. How to massage the stomach to lose weight:
causes
The main trigger for valgus deformity is unsuitable footwear. When a person wears tight shoes with a narrow toe box or a high heel, the toes are constantly in the wrong (squashed) position, which contributes to the development of valgus deformity. However, this is not the only reason for the development of this disease.
The following causes contribute to the occurrence of pathology:
- Traumatic injuries to the lower leg and foot;
- Rickets;
- CEREBRAL PALSY;
- polyneuropathy;
- Low arch;
- flat feet;
- congenital weakness of the musculoskeletal system;
- chronic arthritis caused by psoriatic arthritis;
- Arthritis;
- Multiple sclerosis (accompanied by damage to the nerve fiber sheaths);
- Diabetes;
- Gout (deposit of urate in body tissues);
- Hypermobility of the joints, as occurs in Marfan syndrome and Down syndrome;
- Juvenile foot (rapid increase in foot size during puberty);
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (hereditary neuropathy with muscle wasting in the distal extremities);
- osteoporosis (loss of bone mass);
- Overloading of the feet due to professional activity (waiters, athletes, ballerinas).
If triggers are present, the disease progresses rapidly.
symptoms

The symptoms of the disease depend on the severity of the foot disease. In the first stage, there is redness, swelling of the tissue at the site of the bony appearance, pain in the phalanges of the toes, which increases when walking. In the middle stage, pain, swelling, bony protrusions on the metatarsal head and a dry callus under the middle phalanx occur. In the severe stage, there is severe, debilitating pain in the sole of the foot and big toe. Dry calluses and keratosis of the skin form under the second and third phalanges of the toes.
The different stages of the disease
In the first, mild stage of the disease, there is redness, swelling and pain in the affected area, and the thumb joint begins to bulge and move towards the other fingers. With a moderate deformity, the thumb becomes significantly deformed, the joint structures shrink and bony outgrowths form. In the final stage the deformation is so severe that it causes a surgical Surgery is required. The thumb deviates so much that it encloses the other fingers and the joint protrudes into the space on the other side. Walking with this deformity is very difficult, sometimes even impossible.
There are 100 types of surgeries that can be performed depending on the needs of the individual. Corrective osteotomy of the metatarsus and surgery is most commonly performed in patients without underlying osteoarthritis joints. For older patients and patients with osteoarthritis resective plastic surgery is the safest option. surgerywhere part of the thumb cage is removed. The inability to work is between three weeks and three months, depending on the severity of the illness and the extent of the operation.
The bad news is that after surgery the problem may worsen and return. Therefore, supportive measures should be taken to delay relapse. It is recommended to wear bandages and orthoses, walk barefoot, wear insoles and avoid unsuitable footwear. A crooked big toe is not the only problem that can recur. There are other, equally annoying problems that aren't really worth mentioning.
Crooked toe compared to other foot problems
Crooked toe often occurs in combination with other foot deformities, such as: B. the hammer toe (digitus malleus) and the most common orthopedic problem, flat feet. Toe deformities, varus and big toe, are also very common.
The care of feet. The foot develops around the age of 10, but severe deformities usually do not appear until later. For girls e.g. B. Flat feet only become apparent when you wear heels.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by an orthopedist/traumatologist. The diagnosis is based on symptoms, anamnestic findings, physical examination and additional tests. The examination program includes:
- Anamnese. The specialist determines the factors that could have caused the condition to develop. He explains when and under what circumstances the pain occurred, determines the nature and duration of the pain syndrome and its relationship to external conditions.
- Objective investigation. In the initial phase, the joint has little or no external changes. In the later phase, there is visible deformation, bony hypertrophy on the back and external surface, thickening of the skin and signs of inflammation. Mobility is restricted. In the later stages, even small passive movements are painful.
- X-ray of the foot. The joint space is narrowed. The contours of the joint ends of the bones are uneven and osteophytes can be seen. Thin pockets may be visible in the bone tissue due to cyst formation.
Further instrumental examinations are usually not necessary. In doubtful cases, a CT scan of the foot can be performed to clarify the type and extent of the lesion. Stiffening of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is distinguished by a pain syndrome in valgus deformity of the big toe, ankylosing spondylitis.
Treatment
In the initial stages, conservative treatment is possible. If the stiffness progresses and conservative measures are ineffective, surgical intervention with preservation or removal of the affected joint is necessary.
Conservative treatment
Is indicated in stage 0 and 1 of the disease. It is aimed at eliminating the symptoms, does not affect the causes of the pathology and does not lead to a complete cure. Includes the following methods:
- security scheme. Patients are advised to avoid prolonged walking and standing and to wear comfortable shoes. If prolonged standing is necessary, breaks should be taken to rest the feet.
- Orthopedic aids. Orthopedic insoles are customized to support the arch of the foot and the metatarsophalangeal joints of the big toes. Custom-made orthopedic shoes can be made upon request.
- Non-medical methods. Patients take part in massage courses and self-massage training. Regular exercises for the foot and lower leg muscles are indicated. Taping is applied.
- Physiotherapy. Electrophoresis with novocaine is effective for pain. Ultrasound, laser therapy, magnetic therapy and shock wave therapy are used to eliminate inflammation, improve local metabolism and stimulate tissue repair.
- Pain and inflammation can also be treated with medication. For pain and symptoms of inflammation, topical and general NSAIDs are indicated. If the pain syndrome is persistent, blockades with glucocorticoids are used.
Surgical interventions
All surgical techniques used for stiff thumb can be divided into two groups: those aimed at preserving the joint with restoration of function and those aimed at removing the articular surfaces with creation of a permanent joint or replacement with an endoprosthesis. The most commonly performed procedures include:
- Removal of osteophytes (cheilectomy). A joint-preserving correction method in which the bony overgrowth is removed to restore joint mobility. Recommended for stages 1 and 2.
- osteotomy. The Kessel-Bonni and Waterman surgeries are variants of the first metatarsal wedge osteotomy that allow for an increase in range of motion by repositioning the joint. They are supplemented by the removal of bony outgrowths. This method is effective at stages 1-2.
- arthroplasty. The core of the operation is the partial removal of the base of the thumb. This technique is used in stage 3-4 in older patients. In the postoperative phase, a scarred joint is created through traction, while maintaining a functionally favorable position of the finger.
- arthrodesis. The gold standard in treating a stiff thumb. The articular surfaces of the bones are cut out and the bones are fused together. After stiffening, the joint disappears and a permanent joint is formed. The method leads to the elimination of pain syndrome and easier walking in stages 3 and 4.
- endoprosthetics. The articular surfaces are replaced with metal or plastic implants. The long-term results of this procedure are still poorly known, which is why this technique is only used in a limited number of middle-aged and elderly people with moderate to low physical activity.
Causes of big toe and foot deformities:
1. Narrowing of the narrow space between the medial malleolus and the heel bone, where the nerve runs to the short muscles of the foot:
- A combination of causes.
- Disturbance of the venous and lymphatic drainage from the inner heel area.
- Outward tilt of the heel or internal lowering of the ankle bone.
- Inward twisting of the shinbone. 2.
Chronic tension of the calf and camel muscles, leading to shortening of the Achilles tendon (e.g. running in high heels).
3. Tear of the ligaments in the knee joint (for various reasons), resulting in internal torsion of the tibia.
4. subsequent fractures of the bones of the foot, tibia, femur, heel and pelvis.
5. the tension and torsion of the broad fascia of the thigh, which descends laterally from the medial wing of the pelvis and runs through the hip and knee joints to the shinbone.
8. Deformities of the lumbar, thoracic and cervical spine, excessive tension or weakness of the back, abdominal, chest and shoulder muscles.
10. Reflex disorders (e.g. weakness of the cervical spine and pectoral muscles, the rectus oculi muscle).
Non-surgical treatment of 'bunion'
Treatment depends on the cause identified during the examination, which may be in the foot itself or in a distant location.
Non-surgical foot correction, restoring the form and function of the foot and relieving pain - through gentle manual therapy techniques, kinesio taping, selection of individual orthoses and prescription of a series of exercises. Following the treatment, the patient is monitored using Diers (computer-aided optical topography).
If there is significant cartilage damage detected by MRI, we administer hyaluronic acid (joint fluid prosthesis) and use MBST (nuclear magnetic resonance therapy). In cases of significant structural changes to ligaments, fascia and tendons, administration of platelet-rich plasma (e.g. Arthrex) is recommended.
(Author of the article: Slonimski AA, orthopedist, traumatologist and chiropractor at the European Center for Orthopedics and Pain Therapy)
Treatment of thumb deformity
At the initial stage of the disease, a conservative method is used:
- Wearing special orthoses
- Bandages for the toes
- Use of physical therapy
- massage Foot and toe care
- Wear practical and comfortable footwear
If these measures are not enough and the pain persists, the patient will need surgery. The operation consists of excising the protruding bone and correcting the angle between the metatarsals. Bone of the big toe. In this way the joint is restored. recovery after after the operation After surgery, the joint heals within 4-6 weeks. During this time, it is advisable to use a cane when walking so that the wound can heal quickly. Numerous folk remedies for severely protruding on the outside The numerous folk remedies that the thumb is full of do not help. This is to be expected: smearing the 'bump' with iodine and placing cabbage leaves on it will not remove the bone.
Prevention of valgus deformity
A valgus toe can be prevented by taking preventive measures:
- Foot exercises, including toe walking and heel walkUnroll feet sticks. It doesn't take much time, but it's important to do it regularly.
- massage A foot massage can be done alone, in the morning and in the evening before going to bed. It is enough to rub your feet feet and toes with a cream, paying attention to the inside of the sole. Special attention should be paid to the toes by massaging them from tip to tip.
- foot baths feet – A relaxant with herbs and sea salt.
- If bunions form, you should avoid high-heeled shoes and opt for comfortable shoes with a firm heel and soft sole.
- Stock up on orthopedic insoles. This relieves and redistributes pressure on your toes. Use orthopedic insoles..
- Use orthoses - special spacers between the toes.
- Eat a healthy diet with little spices, salt and carbohydrates. Your diet should contain enough vegetables and unsweetened fruits.
Timely adherence to the recommendations for preventing overgrowth of the big toe bone can stop the development of the disease without the need for surgical intervention.
When an operation is necessary
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- Severe pain that limits daily activities;
- Inflammation, chronic swelling of the big toe joint that cannot be treated with medication;
- inability to wear normal footwear;
- Restricted movement of the first toe – inability to flex or straighten it.
Most patients with valgus deformity report significant improvement with conservative treatment and appropriate shoe choice. However, if these methods do not work, especially in older patients, surgical intervention must be considered.
Surgical treatment of valgus deformity
There are a number of surgical techniques that are selected individually depending on the patient's needs:
The severity of valgus foot deformity can vary, and there are different types of surgeries to correct it. This usually involves reconstructing the bone and restoring the balance of the soft tissues in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
The operations are divided into minimally invasive and reconstructive procedures. The former are performed through multiple punctures of about 3 mm, are less traumatic and have a short recovery time. A return to normal life is possible after about a month. This procedure is used in the early stages of the deformity.
Reconstructive surgery is necessary in complex clinical cases when the valgus deformity has resulted in a change in bone position. The procedure involves a 2-4 cm long incision exposing the bony structures in order to move the bone into the correct position and to fix the changed joint in the correct position. These procedures are more invasive and traumatic.
Surgery for hammertoe deformity
Hammertoe deformities can be corrected through surgery. Severe and moderate deformities can only be corrected through surgery. In general, the deformity is not very difficult to correct.
The operation is performed under regional or local anesthesia. This means that the foot does not hurt, but the patient can be conscious. If the person being operated on is anxious or afraid of the operation, the anesthesiologist will administer a sedative to relax the patient.
In our practice, we use open and percutaneous (minimally invasive) surgical techniques to correct finger deformities.
Open techniques through small incisions and minimally invasive techniques through 2 mm skin punctures. There are different methods depending on the severity and duration of the deformation.
- If the deformation and callus formation are caused by a longer 2nd finger, it is shortened at the same time as the deformation is corrected.
- When the proximal interphalangeal joint is severely deformed, it has little or no movement. In this case, part of the joint is removed and arthrodesis (fixation in a straight position to fuse the bone) is performed. This eliminates the deformation of the finger. In some cases, the finger is fixed with pins or special metal structures.
_big.jpg)

The most common forms of fixation are pins, titanium alloy screws, or biodegradable implants, which stabilize the bone until healing. The pins are removed approximately 1 month after surgery. Removing them does not cause pain, just an unpleasant feeling. The screws are usually removed 6-12 months after the procedure. There are intramedullary titanium implants designed specifically for such operations, but they have one drawback - they remain permanently embedded in the bone.
Percutaneous treatment
Through small punctures in the skin of 2 mm in size. A special lateral burr is inserted and an osteotomy is performed in a specific area of the bone to correct the deformity. As a rule, this procedure does not use metal structures or fixation devices such as pins or screws. The toe is fixed in a specific position with an elastic bandage. This is very comfortable for the patient and does not require a second operation to remove the fixator. The following video shows an example of such an intervention.
In most cases, the patient goes home the same day after surgery, but sometimes they stay overnight. The next day, the first dressing takes place with the doctor, after which the patient can dress themselves. The stitches are removed after 12-14 days.
Laser removal of the callus on the toe. Laser surgery is a popular method, but laser is primarily used for soft tissue (not bone). Therefore, this method is used in addition to surgical instruments.
Read more:- What to do if your teen has crooked legs.
- The long section of the big toe.
- flatfoot μb.
- Shoes for crooked feet, how to choose them.
- Pain in the long extensor of the big toe.
- flexor muscle of the big toe.
- Short flexor of the big toe Latin.
- Why are the fingers curved?.
