When the wound has healed to the point where the non-absorbable sutures are no longer needed, they are removed. The procedure is carried out under sterile conditions. At the first stage, the wound is treated with an antiseptic, and the crust is removed with hydrogen peroxide. The thread is cut with surgical forceps where it penetrates the skin. Gently pull the thread out on the opposite side.

- pain in the ankle
- causes
- Types of foot fissures
- Causes of cracked feet
- First aid
- treatment tactics
- Pharmacological treatment
- Main causes of ankle pain
- Treatment of ankle pain with osteopathy
- How to properly care for seams
- suture healing after childbirth
- Healing of the sutures after a cesarean section
- Healing of the suture after a laparoscopy
- Possible complications
- What to do if the seams become loose?
- What should I do if my sutures hurt?
- treatment tactics
- Classification of foot fissures
- Areas where fractures occur
- Dry patches with scales
- Atopic dermatitis and the difference from psoriasis
- An individual approach
- Main stages of rehabilitation massage:
pain in the ankle
The ankle is a mobile joint made up of several bones: the talus, tibia, and fibula. Ankle pain can be caused by many factors and have different symptoms. Often the pain is an indication of a serious abnormality in the bone, cartilage, or tendon. To avoid permanent damage, it is important that the problem is diagnosed and treated in a timely manner.
Depending on the cause of the pain in the ankle, it can be stabbing, dull, achy, stiff, pulling, burning or throbbing.
causes
Several factors can cause this pain syndrome:
– Contusion – caused by a fall and a violent impact and can be complicated by bleeding into the joint;
- ligament strains and tears - usually caused by a sudden twisting of the foot;
– Achilles tendon injury – with rapid swelling;
– broken bones and dislocations;
Degenerative and dystrophic diseases:
- osteoarthritis;
– osteochondropathies;
- synovitis;
– Achilles tendinitis;
- bursitis;
– Arthritis: viral, tuberculous, gonococcal, purulent, brucellosis;
- Arthritis: rheumatoid, psoriatic, reactive;
– Bechterew's disease;
– rheumatic fever;
- inflammatory bowel disease;
– collagenosis;
Types of foot fissures
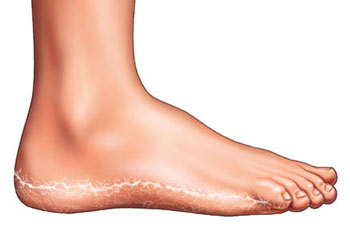
Sometimes the tears on the feet are small and painless, but sometimes they develop deep, bleeding wounds (lacerations) on the feet that make walking and normal life difficult. Superficial (epidermal) cracks are located within the epidermis and heal without a trace. Deep (epidermal) tears also affect the dermis, often leaving scars after healing. Cracks can also be dry or wet, that is, cracks appear on very dry or very wet skin.
Causes of cracked feet
The causes that lead to cracked feet can be endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external).
- Metabolic and hormonal disorders: diabetes, obesity;
- Avitaminosis – lack of vitamins A, E, B;
- allergies;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- Foot and toe deformities, e.g. B. flat feet;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- skin diseases including eczema, psoriasis and ichthyosis;
- taking certain medications;
- Severe restriction of fats in the diet.
External factors for cracked feet include:
- wearing uncomfortable footwear, including waterproof shoes and synthetic socks;
- Climate and environment – hot weather swells feet, makes shoes uncomfortable and affects blood circulation;
- poor personal hygiene;
- improperly performed pedicure – e.g. B. sloppy cutting of the skin and use of coarse saws and pumice stones;
- chlorinated water, heat in baths and saunas;
- Walking barefoot on hard ground.
Cracked heels are inherently recurring. That is why in my practice I always look for the cause of this pathology.
Cracked skin is rarely an isolated condition - more often it is a symptom on the skin that indicates a malfunction throughout the body. In some cases they are a 'marker' for neuroendocrine and immunological disorders, vitamin and mineral balance, fungal infections and orthopedic pathologies.

ES Azarova, podiatrist, mycologist, dermatocosmetologist, orthopedist and traumatologist.
Which doctor should you see for nail and foot diseases? All about podiatry.
First aid
To avoid serious complications, it is enough to provide first aid to the victim immediately after the injury. This also significantly reduces the intensity of the clinical symptoms (pain, swelling, bruising). The victim should lie down, be anesthetized and raise the injured leg 30-40 cm above the surface. This can be done with a simple pillow or roller.
Now it's time for the cold compresses. A plastic bag filled with ice cubes and wrapped in a thick cloth is placed on the bruised area. If there is no ice in the refrigerator, you can replace it with frozen meat, fish or mixed vegetables. The compress is applied for 15 minutes, then a half-hour break is necessary to avoid frostbite of the epidermis. Under the influence of cold, the swelling that presses on the sensitive nerve endings decreases, and the pain disappears. What else should be done to minimize the negative effects?
- Immobilization of the lower leg by wearing an elastic bandage. It should not be too tight, otherwise the severity of the hematoma and swelling from the compression of blood vessels will increase;
- to prevent severe swelling of the leg. This can be aided by the use of antihistamines in addition to the compresses. If there are no contraindications, give the affected person 0.5-1 tablet of Claritin, Cetrin, Loratadine. The proven Suprastin and Tavegil are also well suited. However, be aware that taking them can cause drowsiness and reduced alertness and concentration.
treatment tactics
In order to quickly restore the function of the injured joint, an integrated approach to the treatment of contusions is taken. The patient is treated with systemic and topical medications and visits the physical therapy office for treatments. Exercise or gymnastics under the supervision of the LFK doctor is recommended from around the 3rd to 5th day of treatment. Regular exercise improves blood flow to the ankle, promotes tissue regeneration and helps with swelling and bruising.
Pharmacological treatment
Long-term treatment with NSAIDs in tablet or capsule form is not necessary. Treating an ankle bruise with cold compresses for 2-3 days will help relieve pain. The discomfort is numb and dull, but increases markedly with walking due to the displacement of the soft tissues. In this case, Naise, Ketorol, Nimulid, Ibuprofen can be taken, but no more than 3 tablets per day. NSAIDs should be combined with proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole is the cheapest and most affordable), otherwise such treatment of bruises can lead to erosive gastritis. Comprehensive treatment of the injury involves the use of such external means:
- NSAIDS. Fastum, Voltaren, Finalgel, Diclofenac ointment and gel, Arthrosilen, Dolgit with pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects. They are applied thinly to the bruised area 2-3 times a day and gently rubbed in. They develop their pain-relieving effect within 15-30 minutes for 4-8 hours. Topical NSAIDs are not indicated for pregnant and lactating women and for children under 6-12 years of age (depending on the active substance);
- Warming ointments. Finalgon, Capsicam, Apisartron are prescribed to patients on day 3-4 of treatment, after the acute inflammatory process has subsided. The preparations contain ingredients with a local irritating, analgesic and distracting effect. They compensate for the lack of nutrients and bioactive compounds, stimulate regenerative processes. Dosing regimen – 2-3 times a day for a week. The drugs have an extensive list of contraindications, sometimes provoking the development of local allergic reactions;
Main causes of ankle pain
- Arthritis of the ankle is an inflammatory process that occurs against the background of trauma, infection, degenerative and destructive changes in other joints. The main symptom is arthralgia – joint pain caused by irritation of the nerve receptors in the synovial membrane.
- An ankle fracture is a hard and soft tissue injury that occurs when the foot suddenly turns outward or inward. When the injury occurs, the sufferer experiences severe pain. Swelling occurs, the soft tissues of the ankle become hyperemic and hot to the touch, and movement of the injured leg is severely limited.
- Achilles tendonitis is an inflammatory condition caused by regular exercise, microtrauma of tendon tissue, and arthritis. There is persistent ankle pain, localized fever, and moderate swelling. Tendonitis is most common in athletes and people who constantly overload the ankle, especially if their job involves repetitive movements.
- Tunnel syndrome is damage to the blood vessels and nerves in the ankle as a result of excessive compression. Causes include tendinitis, ankle injuries, osteoarthritis and diabetes.
- Subluxations and dislocations are often the cause of ankle pain and limited mobility. If these injuries are suspected, it is important to see a specialist, take an X-ray and start treatment as soon as possible.
- Deforming osteoarthritis is a degenerative lesion of the articular structures of the ankle. This systemic pathology leads to deformation, destruction of the joint and severe pain.
- Gout is a chronic disease characterized by the deposition of uric acid salts in joint tissues, leading to deformities and the formation of characteristic gouty nodules. Diagnosis is confirmed by X-rays and examination of synovial fluid.
Treatment of ankle pain with osteopathy
Modern osteopathy has great potential in the treatment of ankle pain, as it not only acts on the symptoms of the disease, but also on its cause. The osteopath activates protective mechanisms aimed at the patient's self-healing and recovery. Blood begins to circulate through tissues more actively, and nutrition of all damaged structures improves, which helps to reduce acute symptoms and normalize the patient's well-being.

- Rapid relief from the attack of pain;
- restoration of nutrition and blood flow to joint structures;
- increase in amplitude of movement;
- acceleration of regeneration of damaged soft and hard tissues;
- reducing swelling, congestion and discomfort;
- restoration of innervation, return of sensation;
- Suppression of joint deformations caused by systemic diseases.
We recommend that patients with joint pain seek help as early as possible. An osteopathic treatment will restore your normal life, restore disturbed needs and give you the joy of movement without pain, discomfort and anxiety.

Osteopathic doctor, orthopedic surgeon. Specialization: problems of the musculoskeletal system in children, headaches, neuroses in children, treatment of stuttering.
How to properly care for seams
When hospitalized, wound care is performed by a doctor or nurse. At home, the patient should follow the doctor's instructions for wound care. Keep the wound clean and treat it daily with an antiseptic: iodine, manganese solution or brilliant green. If a bandage has been applied, consult your doctor before removing it. Special medication can speed up the healing process. One such product is Kontraktubex gel, which contains onion extract, allantoin and heparin. It can be used after the wound has healed.
suture healing after childbirth
Good hygiene is important for rapid healing of the birth sutures:
- Thorough hand washing before going to the toilet;
- Frequent changing of sanitary napkins;
- Daily change of bed linen and towels;
- During the month, bathing should be replaced with a hygienic shower.
With external perineal sutures, in addition to proper hygiene, care must be taken to keep the wound dry, not to sit on hard surfaces for the first 2 weeks, and to avoid constipation. It is advisable to lie on your side, on your knees or sit on a pillow. Your doctor may prescribe specific exercises to improve tissue circulation and wound healing.
Healing of the sutures after a cesarean section
After discharge, you should take a shower and wash the skin in the area of \u200b\u200bthe seam with soap and water twice a day. At the end of the second week, special ointments can be applied to regenerate the skin.
Healing of the suture after a laparoscopy
Complications after laparoscopy are rare. To be on the safe side, you should stay in bed for a day after the procedure. In the beginning it is advisable to stick to the diet and avoid alcohol. You should shower for personal hygiene and apply an antiseptic to the sutures. Physical activity is limited in the first 3 weeks.
Possible complications
The main complications of wound healing are pain, pus and suture incompetence (detachment). Sclerosis can be caused by bacterial, fungal or viral invasion of the wound. Infection is most commonly caused by bacteria. Therefore, it is not uncommon for the surgeon to prescribe a course of antibiotics after surgery as a preventive measure. Postoperative suppression requires identification of the pathogen and determination of its antibiotic susceptibility. In addition to prescribing antibiotics, the wound may need to be opened and drained.
What to do if the seams become loose?
Suture loosening is more common in elderly and debilitated patients. The likelihood of this complication occurring is between five and 12 days after surgery. In such a situation, a doctor should be consulted immediately. The doctor will decide whether to leave the wound open or sew it up again. In case of evisceration, that is, when the loop of intestine pierces the wound, urgent surgical intervention is required. This can be caused by abdominal bloating, severe coughing, or vomiting.
What should I do if my sutures hurt?
Pain around the sutures is normal for a week after surgery. Your surgeon may recommend taking pain medication for the first few days. Pain will be relieved if you follow your doctor's instructions: limiting physical activity, wound care, and wound hygiene. If the pain is severe or lasts a long time, you should consult your doctor, since the pain may be a symptom of a complication: inflammation, infection, adhesions, fractures.
treatment tactics

With contractures, conservative and surgical treatments are used. Myorelaxants (Mydocalm, Sirdalud) are prescribed to eliminate muscle spasms, and if this does not succeed, botulinum toxin is injected into the affected muscles. Pain is relieved by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, dexalgin, ibuprofen), first by injections and then by tablets. In the case of severe pain, novocaine/lidocaine blockades are used in the joint area.
Massage, physical therapy, and therapeutic exercises are used to improve muscle tone and improve blood flow to the joints. Relatives caring for a bedridden patient must be familiar with the massage technique. This treatment is necessary daily to restore normal motor activity of the limbs.
Regular paraffin therapies, mud packs and galvanizations are helpful electrophoresis. Therapeutic exercises help to develop joint mobility faster and increase resilience.
Plaster casts or splints for a contracted limb can prevent the development of irreversible changes. A splint is placed around the arm or foot to hold the limb in a physiological position. The bandage is not too tight so as not to disturb blood circulation. The splint is removed daily for massage and physical therapy.
In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed to remove skin scars, adhesions of tendons and fascia, and to replace the affected joint with an artificial joint implant if ankylosis has developed.
Classification of foot fissures
Superficial (epidermal) fissures – They are localized in the epidermis and heal (dissolve) without leaving traces (see Figure 1).
Deep (epidermal) cracksFissures are very painful and often bleed (see Fig. 2) and are located within the epidermis and dermis (cuticle). Deep fissures are very painful and often bleed (see Figure 2).
Bleeding cracks are called cracks.
In this course, the most common problems on the customer's foot are practiced using various techniques and tools. 'Practitioner' course for podiatrists. Learn more >>
Areas where fractures occur
- heel area;
- midfoot area;
- thumb joint;
- Toe spacing and natural creases;
- in the spaces between the toes;
- in areas of skin extending over the joints;
- hyperkeratosis (increased keratosis resulting in thickening of the stratum corneum without structural changes in skin cells);
- Drying out of the protective structural layer of fat on the soles of the feet also leads to cracking.
The causes of these skin changes can be endogenous (internal) i exogenous (external).
- climate and environmental conditions
After a stay at the beach, when the skin is exposed to heat, seawater and sand, it becomes very dry and cracked. The UV rays cause all the skin, including that on the heels, to suffer and become thinner;
- Personal hygiene
If you only care about washing your feet, the skin will become rough and cracked over time. Proper foot care includes treatments such as foot baths, exfoliation, hydration and conditioning;
- Improper foot care
Excessive skin removal with a razor and use of inappropriate foot care products;
- Harsh outdoor conditions
walking barefoot on sand, dirt or asphalt;
- Wearing the wrong type of footwear
Flip-flops, slippers, close-fitting footwear;
- Contact with chlorinated water
visit to a swimming pool;
- influence of temperature
Heat and dry air, city dust and sand also injure and damage the skin of the heels;
- therapeutic measures
medication and radiation.
 |  |  |
Dry patches with scales
Pink, raised, dry patches on the body and head can be a sign of psoriasis. With this dermatological pathology, raised plaques - psoriatic papules - appear on the skin of the affected person. They protrude above the surface of the skin, cause severe itching and scaling, and tend to spread and grow together.

Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that most commonly affects the elbows, head, knees and groin. Dry, pink patches covered with white scales are foci of chronic inflammation. Under the influence of internal autoimmune processes, the epidermal cells divide several times faster than necessary. As a result, tiny scales of dead skin cells constantly break off.
Atopic dermatitis and the difference from psoriasis
Atopic dermatitis can also cause dry patches on the body. As with psoriasis, these patches can cause itching. Due to the skin's increased sensitivity to environmental factors, its self-regulatory mechanisms, including the barrier function, are disrupted. Atopic dermatitis is triggered by allergies, but the predisposition to this skin reaction is genetic.

Atopic dermatitis is most common in children. The disease has a chronic course, in which relapses alternate with phases of remission. Here are the typical symptoms of atopic dermatitis:
- Dry skin;
- flaking and redness of the eyelids;
- dry, flesh-colored plaques on trunk and limbs;
- cracking.
It is difficult for a non-medical professional to differentiate between psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, but a doctor can easily make a differential diagnosis. There are several differences that speak in favor of one pathology or another. Atopic dermatitis is more likely to occur in children, while psoriasis may not appear until adulthood. Psoriatic plaques are raised above the skin and scales are visible on them. Dry patches in atopic dermatitis are flat. It is also important to consider the typical localization.
An individual approach
'A lot depends on the condition of a person's ligaments and muscles,' says Maria Istifeeva. – says Maria Istifeeva. – In children, for example, the ligaments are more flexible, so with proper treatment of the injury, the rehabilitation time is shorter than in most adults. The same applies to people who play sports and are physically fit. As a rule, 15 sessions are sufficient, in some cases 20 to a maximum of 25 sessions.
The number of massage sessions and their duration are determined individually, depending on the patient's age, the duration of the immobilization of the limbs and, of course, the type of injury.
Main stages of rehabilitation massage:
- Step 1: Drainage massage to reduce swelling is carried out for 2-3 days.
- Stage 2: Massage to eliminate muscle tension and improve blood circulation.
- Level 3: Ligament irradiation to improve ligament flexibility, both through massage and exercise.
CNMT provides rehabilitation for arm, forearm, finger, wrist and elbow fractures, rotator cuff tears, ligament and muscle tears, hip, tibia and foot fractures.
Read more:- Outer malleolus of the right tibia.
- Ankle ligament strain, ICD.
- ankle-shin.
- How do you treat a sprained ankle?.
- ankle where.
- Take off the ankles.
- What a torn ankle ligament looks like.
- ankle and ankle.
