Immediately after the injury, it is necessary to anesthetize and immobilize the injured limb. In most cases, a patient with a hip fracture requires surgical treatment. The complexity and type of injury determine the further course of treatment:

- osteosynthesis
- Advantages of bone surgery – osteosynthesis.
- Find a doctor to treat shin fractures
- promotions
- Treatment of femoral fractures
- Information for patients: Types of tibia fractures
- Characteristic Symptoms.
- First aid measures
- Underwater osteosynthesis: plates
- External osteosynthesis: external immobilization of a fracture
- Start of the exercises: when and what to do?
- Before removing the plaster cast
- After removing the plaster cast
- wheelchairs
- When choosing crutches, pay attention to additional features
- Nourishment
- indications
- Preparation
- Complications due to inadequate treatment
- prevention
osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis is the immobilization of damaged bones. It is a surgical procedure to restore bone integrity in fractures in which bone fragments are joined together with the help of screws, plates, nails or wires and some other devices and structures. The broken bone is fixed using the above options and can be fused stably in its correct position. Osteosynthesis (also called internal bone fixation) is not used by traumatologists for all types of bone fractures. However, it is best suited for open bone fractures with accompanying skin or soft tissue injuries. It is also the preferred treatment for multi-fragment bone fractures, lower limb fractures, and lesions in patients with osteoporosis.
The main goals of bone osteosynthesis are to create optimal conditions for fracture healing and restoration of skeletal anatomy, reduce trauma to the soft tissues surrounding the fracture site and restore the function of the damaged area (limb, part of the skeleton).
In the SM Clinic, the following types of osteosynthesis are performed depending on the type of fractures:
Advantages of bone surgery – osteosynthesis.
The bones of the skeleton provide support for the entire body, so when fractures occur, the most important supporting function suffers and the injury itself is very serious. If fractures are left untreated, the damaged bones will not heal properly, which can lead to serious consequences and disabilities.
Many people who have ever suffered a fracture are familiar with treating fractures with plaster casts and bandages. However, when the situation is complex, bone fragments have been displaced, and additional structures are involved, immobilization with plaster alone is not sufficient to ensure proper fracture healing. Then treatment with osteosynthesis, ie correct repositioning of the bone and immobilization with various structures, is indicated. This restores the integrity of the bones and accelerates their fusion without further complications.
Osteosynthesis is also indicated when complete and effective restoration of bone integrity is not possible using closed methods. So when bone fragments are displaced, they traumatize the soft tissues and must be returned to their proper place and secured. The patient is spared having to wear plaster casts with complete immobilization of the bone, which is often very uncomfortable. During osteosynthesis, the fragments are firmly fixed so that long-term immobilization of the affected body part is not necessary. Recovery is faster and the limb can be moved just a few days after osteosynthesis.
The bones are fixed with special, inert materials such as pins, screws, plates of various sizes and staples. These materials are not prone to oxidation in body tissues and make the surgery safe.
Find a doctor to treat shin fractures



promotions

Treatment of femoral fractures
The specialists at Lapino KG and MD GROUP KG will do everything they can to help you get your shinbone running again as quickly as possible. We have every opportunity for this – experienced doctors and modern equipment. We approach each patient individually.
Uncomplicated fractures (fractures without displacement) can be treated conservatively - with plaster casts. All modern minimally invasive osteosynthesis techniques are used for fractures with displacement, as is often the case with dislocations
Manual reduction is often not possible. The risk of complications is particularly high with open fractures of the tibia. In these cases, wound healing is monitored by our doctors.
Information for patients: Types of tibia fractures
A distinction is made between closed and open fractures of the tibia. It can be line, comminuted, hammertoe and spiral fractures. Any of the large and small bones can be injured anywhere.
The fibula is characterized by fractures in the lower third, at the ankle joint. The bone itself is not solid. However, a fracture of the ankle joint results in subluxation of the foot. Treatment for fibula fractures aims to immobilize (immobilize) the injured limb and prevent subluxation of the foot. The traumatologists at Lapino KG and MD GROUP are very experienced in treating these injuries.
If you have a shin splint injury, a fracture of one or both shin bones, please contact us to schedule an appointment with an orthopedic trauma surgeon. Please call reception to make an appointment.
Characteristic Symptoms.
The severity of the symptoms depends on the severity of the fracture and the presence of complications such as: B. a dislocation. Common symptoms of thigh trauma include:

- Severe, stabbing and acute pain occurring at the time of rupture;
- Overloading of the neighboring joints – knee and ankle – due to the pain syndrome;
- The formation of extensive edema under the skin (a
- hematoma;
- deformation of the limb in the presence of displaced bone fragments;
- the injured limb is shorter than the healthy limb;
- limitation or complete absence of motor activity;
- Numbness of the limbs.

Increased pain occurs when trying to move or step on the broken leg. In an open fracture, a bone fragment tears the soft tissue and skin, creating a large wound that bleeds profusely.
In the case of a sprain, the patient can no longer move the leg in the knee joint, while movement without a sprain is possible, but is accompanied by severe pain.
Numbness in the injured limb occurs when the fibula head is damaged, resulting in nerve damage. If the nerve is completely severed by bone fragments, the leg is numb and hangs like a whip.
First aid measures

If there is a fracture in the fibula area, the leg must first be immobilized as much as possible. A rail is used for this purpose. Either a special splint or a piece of stick, board, or iron pipe may be used to immobilize the limb, and a cloth, scarf, or bandage may be wrapped around the leg. The second stage of first aid is to reduce the intensity of the pain symptom. This can be done by administering any analgesic from the pain spectrum.
For a closed fracture, a cold compress with ice, a piece of frozen meat, or a cold water bottle should be placed on the injured limb to prevent severe swelling.

In case of an open fracture where a wound is present, it is strictly forbidden to touch the injured leg. The wound should be dressed with a sterile dressing and the patient should be taken to a medical facility as soon as possible.
Underwater osteosynthesis: plates

Another popular method of fixing various damaged bone areas is the skeletal method, which involves placing a plate on the bone. This type of osteosynthesis can be successfully used to treat complex fractures, including joint fractures. The disadvantage is that a large piece of bone must be exposed. Such an operation is quite traumatic and can cause a number of complications. These include inflammation and even osteitis.
However, in modern traumatology, angle-stable plates are used that are raised above the bone and enable a minimally invasive procedure with minimal incisions. The latest technology is the use of multi-axis screws (LCP), which can be inserted diagonally rather than vertically if necessary. This makes it possible not only to lift the plate, but also to fix it as accurately as possible. Even people with osteoporosis can undergo surgery, making the system suitable for treating joint fractures and other complex fractures in the elderly, such as: B. in injuries to the femoral neck or the proximal part of the shoulder.
The operation to insert the modern plates takes an average of 30 minutes, meaning the patient requires less anesthesia. After the procedure, the injured area can be put under strain and mobility returns, so that the affected person does not need a long rehabilitation phase with joint expansion after bone stiffening.
A special application of the plate is to immobilize ribs in the event of multiple injuries. This is one of the most serious types of fractures that are difficult to heal and often result in false joints, bone displacement, etc. In such cases, the insertion of a plate not only allows a return to normal life after just a day, but also avoids later complications. In rib osteosynthesis, the implants are often used for life and are not removed once the bone has fused. Nowadays such an operation is also carried out in Russia; in particular, a successful reconstruction of a rib fracture was carried out in Tomsk.
External osteosynthesis: external immobilization of a fracture
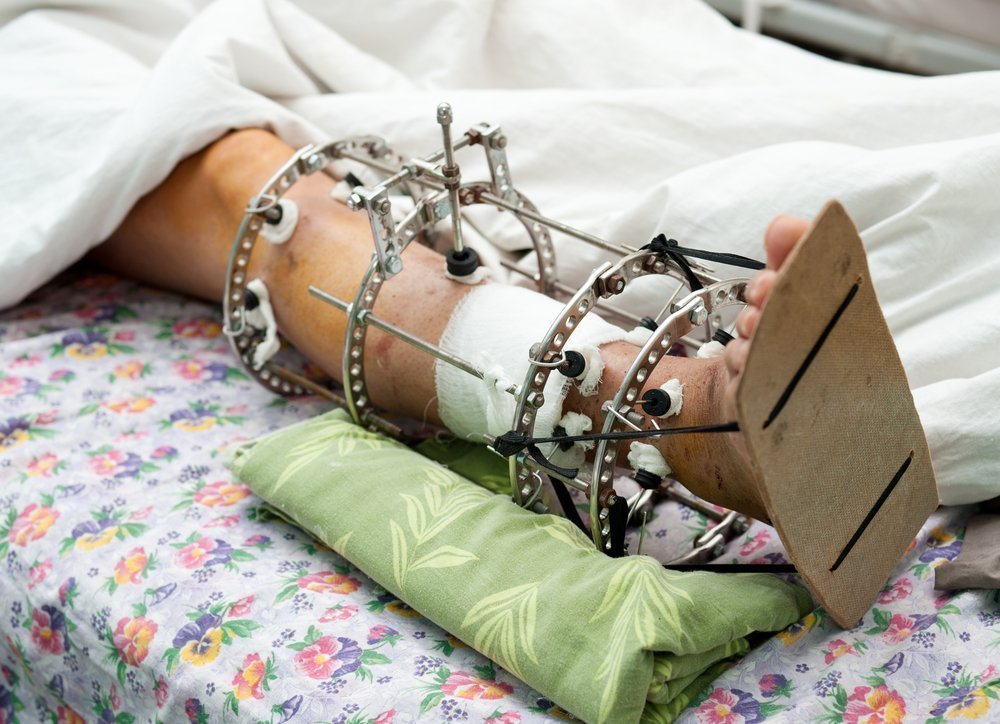
During external osteosynthesis, a fixation system is attached over the surface of the skin. The spokes that hold the bone in the correct position run across the bone rather than along the bone as in the intramedullary method. A number of special compression-distraction devices have been developed for this type of immobilization, including Ilizarov, Tkachenko, Volkov-Oganesyan and others.
The main advantage of transepiphyseal external osteosynthesis is minimal damage to soft tissues. The doctor only has to make a few precise punctures through which the pins are inserted. Nowadays, the installation of the structures is controlled by X-rays, so that errors are practically impossible.
External osteosynthesis is necessary in polytraumas when not only the skeleton but also the soft tissues are damaged and the bones themselves are severely shattered. Immobilization of such fractures involving internal structures can be difficult, but external fixation accomplishes this task well.
As with internal fixation, the braced limb may become weight-bearing after a few days. However, the pins must be removed once the bone has healed. This method is not suitable for fractures that are slow to heal or if the implant is needed for life. For this reason, it is rarely used in older patients. In contrast, external osteosynthesis is usually used in younger patients.
External care can help not only with fractures, but also with various bone growth disorders. For example, Russian doctors have successfully performed limb lengthening on children suffering from the hereditary disease achondroplasia, in which the bones are underdeveloped. With the help of special constructions, the situation can be significantly corrected and patients can be freed from their disability. For example, controlled lengthening helps to build 6-7.5 cm of bone.
Start of the exercises: when and what to do?
The exercises should be started almost immediately.
Before removing the plaster cast
The first phase is immobilization, in which the injured limb is still rigidly fixed. Exercises are necessary during this time to avoid consequential damage:
- Apply pressure to the uninjured and unfixed muscles of the injured arm or leg to maintain mobility and prevent atrophy.
- Static loading of the fixed limb to maintain muscle tone (tension and relaxation of the muscles).
- Stretching of healthy limbs to improve blood circulation and maintain mobility.
- Ideomotor group. It is necessary to mentally imagine the movements of the injured limb 'as if' one were drawing or 'as if' one were marching; Looking at pictures or cartoons and mentally repeating the movements are helpful.
This is necessary to avoid motor coordination disorders and preserve acquired dynamic stereotypes.
The mental representation of movements doesn't just help with fractures. In a famous experiment, adult musicians were offered three options for learning a new piece of music: one group practiced on the instrument, another group only 'played' it in performances, and the control group did nothing after the initial introduction to the sheet music.
According to the results, mental training was twice as effective as nothing and only 30 % worse than real practice! This is because the neural connections and muscle control are sufficiently mental.
After removing the plaster cast
In the period following immobilization, the main goal is to reduce tissue contraction. What is recommended?
- Physical therapy with increased active movement to eliminate contractures.
- Passive movement elements – physical therapy with weight bearing.
- Learning the correct positioning of the limbs so that the arm or leg can 'remember' the correct movement.
- Therapeutic exercises in water.
- Cold therapy and physical therapy can be used.
wheelchairs
Patients suffering from a stroke or arthritis may have difficulty walking independently. Using a walker can help with this. There is a wide range of walking aids. The models differ in design, function and weight. At first glance, it is very difficult to make a choice from such a large selection of walking aids. The choice should be based on the following parameters:
- The patient's condition. The most stable walking aids should be used in rehabilitation centers. They have 4 legs. If the patient has a movement disorder, it is best to purchase a walker that has a support under the elbow joint. If the lounger cannot be lifted, it must be equipped with wheels. For patients with serious illnesses, models with castors and parking brakes are a good idea.
When choosing crutches, pay attention to additional features
- Weight. This must be within 1.5 kg. Reinforced crutches can weigh up to 4 kg. They are used by people who have a lot of weight.
- The material. The supports can be made of wood or metal. The former are light in weight, while the latter are more robust and can be adjusted in height.
- Adjustability. There are standard crutches and those that can be adjusted to specific physiological characteristics of the patient. The latter can be easily adapted to your specific needs.
- Attachment parts. When purchasing a brace, pay attention to whether the attachments are anatomical. They can be oriented for the left or right hand.
- Mobile option. If the crutches are to be transported in the car, a removable model makes sense.
- Support. The pyramid-shaped support is more stable than a ball leg.
- The design. This depends on personal taste and aesthetic requirements.
After choosing the crutches, you should now know how to walk on them. The balls should be used in a slightly forward position. They should also be no closer than 10cm from the foot. The back should be straight, as should the head. This is the only way to maintain balance. It is advisable to keep the crutches as close to the chest as possible. When walking, both crutches should be moved at the same time. Support yourself first on the crutch and then on your good leg.
Always keep an eye on the crutch. Always check the connection to the rest of the crutch.
Nourishment

Recovery is hardly possible without a balanced diet. During this time, the body has a high need for vitamins and minerals, which should be supplied both through food and through special vitamin-mineral complexes.
The diet should be varied. Meals should be rich in protein. Fish and meat (lean meat) intake should be increased. It is important to include calcium in the diet, which can be easily obtained from dairy products, oatmeal, sesame seeds and parsley. Vitamins C, D and B can be obtained from liver, citrus fruits and fish oil. However, salty, fatty and sugary foods should be avoided. Carbonated drinks are contraindicated as they leach calcium from the body. The consumption of alcohol is also prohibited.
indications
Osteosynthesis of the lower leg is indicated in the following cases:
- in open fractures;
- Severe displacement of bone fragments (by 0.5 bone diameter or more);
- Segmental or displaced fractures;
- Polytrauma (lower leg fracture in combination with other injuries);
- if muscles, tendons, vessels or nerves are damaged or compressed by bone fragments and there is a high risk of such complications;
- For soft tissues trapped between bone fragments;
- If conservative treatment of the fracture is unsuccessful (secondary dislocation, incorrect joint);
- in some complex fractures with significant displacement and/or rotation of the bone fragments.
Preparation
Before the operation, the patient undergoes a thorough diagnostic examination. This is necessary to clarify the subtleties of the injury, as well as individual body characteristics that can lead to unforeseen situations during surgical treatment. The minimum scope of the examinations includes:
- X-ray of the tibia, with CT or MRI if not sufficiently informative;
- ECG, X-ray fluoroscopy;
- testing for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis;
- general blood and urine tests, blood chemistry, coagulation and blood group tests;
- Consultations with the surgeon, the anesthesiologist and the general practitioner.
If the patient has chronic illnesses, the diagnosis can be expanded.
Complications due to inadequate treatment

A hip fracture is an injury with an increased risk of complications. Prolonged immobility, especially in old age, increases the likelihood of developing neuroses, dementia and psychopathic conditions. Without proper treatment, the risk of death is 10 percent in the first month after the injury and up to 30 percent in the first year after a hip fracture. That is why it is so important to follow all recommendations and start exercising as early as possible. Other possible complications of a hip fracture include:
- pulmonary embolism;
- hospital-acquired pneumonia;
- increased risk of infection;
- limited mobility and quality of life;
- high risk of hip fracture recurrence.
A so-called false joint can also occur: the fracture does not heal or does not heal properly. Another dangerous disease is fat embolism. It occurs as a result of a surgical procedure. Sometimes the injury is complicated by tissue or nerve tears caused by the sharp edges of the fragments. As the fractures heal, local blood flow may deteriorate. During the recovery period, patients complain of discomfort caused by the metal structures in the hip.
prevention

Hip fractures are common worldwide, but there is no uniform injury prevention tactic. A common cause of fractures is usually osteoporosis. It is important to recognize this condition early and initiate appropriate treatment. People over 40 should undergo regular examinations to assess the condition of their bone tissue. It's also worth:
- Quit smoking - this habit significantly increases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Seek medical advice in a timely manner. In this way, infections or cancers that affect bone density can be detected early.
Take bone-strengthening medications. These include calcium and vitamin D. Chondroprostheses are also recommended for the prevention of hip fractures, but not all specialists consider them effective.
Read more:- Bones of the tarsal bone of the hand.
- tibial joint.
- What is the connection between the femur and tibia?.
- tibia and fibula.
- Fracture of the 5th metatarsal.
- Fractures of the tarsal bones.
- fibula.
- Photo: Outer malleolus fracture.
