Clubfoot recurrences occur after treatment with any method. Statistically speaking, there are currently the fewest clubfoot recurrences after treatment with the Ponseti method. This fact has been noted by many pediatric orthopedists in their studies. The most important protection against a relapse is wearing the orthosis according to a set routine. When wearing the orthoses, parents have many questions about the correctness of wearing the orthoses, the duration of wearing the orthoses, etc. There are parents of children with healed clubfoot who neglect the doctor's recommendations, as a result of which these children have a have a high risk of relapse. Ignacio Ponseti himself found in his research that relapses occur less often in families that strictly follow the doctor's recommendations.

- Congenital clubfoot: causes, symptoms, treatment
- Causes of congenital clubfoot
- Causes of congenital clubfoot
- How is the diagnosis made?
- Treatment of congenital clubfoot in newborns
- Help for the project 'Towards life
- Our patients
- Anastasia
- Miroslav
- Alexander
- Maria
- Filipp
- The more complex forms of recurrence include those that have developed:
- Towards specialists
- Glazova Natalia Alekseevna
- Gromov Ilya Valeryevich
- Maxim Vavilov
- Congenital clubfoot in children. Treatment
- Symptoms of clubfoot in a newborn:
- Importance of treatment, negative consequences of a neglected disease
- Project 'Towards Life' for children's health
- How quickly should a club foot be treated?
- What are the symptoms of clubfoot?
- Caused
- Treatment
- Prevention of recurrence
- preventive measures
Congenital clubfoot: causes, symptoms, treatment
Clubfoot is a musculoskeletal disorder in which the foot deforms and deviates inward. Congenital clubfoot is usually congenital, so it is especially important to treat it as soon as possible after the child is born. Congenital clubfoot can be detected during an ultrasound scan as early as the third month of pregnancy.
Many parents ask themselves: why does the baby have congenital clubfoot? How can this be determined? Let's try to understand this.
Causes of congenital clubfoot
There has been a lot of research into this condition, but to date the exact causes are unknown. There are currently three theories that this defect could have arisen:
- Mechanically. Proponents of this version believe that it occurs due to excessive compression of the foot by the walls of the uterus (cause of compression – tightness, lack of water, tumor, brainless position of the baby).
- Neuromuscular. In this case, the cause is seen in abnormal development of the fetus, which is due to external negative factors: drug use, alcohol consumption, smoking during pregnancy, infectious diseases, constant stress, medications, electromagnetic radiation.
- Genetically conditioned. Proponents of this theory believe that clubfoot is inherited.
Causes of congenital clubfoot

To date, doctors and scientists do not agree on what specific factor causes this birth defect. It is believed that the disease develops in the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy, as the musculoskeletal system is formed at this time. However, inheritance cannot be ruled out: entire families are known in which clubfoot is passed on from generation to generation.

In Japan, clubfoot is not considered a serious defect. Many people in the Land of the Rising Sun find him very charming and excuse him for giving them a certain 'patina of infantilism'.
Another Japanese theory suggests that clubfoot is a psychosomatic reaction of a 'closed' child raised in deprivation for a long time.
Main risk factors for congenital clubfoot:
- Presence of tumors in the uterus that put pressure on the child (e.g. a large fibroid).
- Malformations.
- Pregnancy-related infectious diseases or poisoning (alcohol or drugs).
- Neuromuscular diseases.
Depending on the severity, clubfoot is divided into three stages: mild, moderate and severe. The mild form of clubfoot is considered a 'nice' defect because the range of motion of the ankle joint is preserved and can be easily corrected. The moderate form requires more correction, and the severe form makes it impossible to move the joint at all.
How is the diagnosis made?
A congenital clubfoot is often diagnosed by a pediatrician or neonatologist in the first days of life. However, if the symptoms of the defect appear only after the baby has started walking, the clubfoot is diagnosed as acquired (for example, it can be caused by vitamin D deficiency or trauma).

Another possible cause of worsening hip dysplasia is pulling the legs too tight, which can lead to a 'star effect'.
Instrumental examinations are used to confirm the diagnosis. X-rays of the feet in anteroposterior and lateral views as well as a 3D CT scan can be performed on the child as early as 3 months of age.
Immediately after birth, the child is examined using an ultrasound. The most important sign of clubfoot is the parallel position of the heel bone and ankle bone.
Treatment of congenital clubfoot in newborns
Traditionally, a combination of conservative and surgical procedures are used to correct clubfoot. Both therapies require a lot of physiotherapy, physical therapy and massage and can last into adolescence, but do not guarantee complete correction of the condition. A child whose movements are restricted will develop an irregular gait over the course of his or her life. If the problem of effective treatment of right and left clubfoot is not addressed in time, it will lead to shortening of the limbs.
The Ponseti method is becoming increasingly popular and leads to complete healing in 80-90 cases. It is used to begin the correction of foot deformities in children in the first months after birth. The Ponseti method divides all phases of treatment of congenital clubfoot into three stages:
- Correction with plaster casts (4-8 bandages depending on the complexity of the deformity).
- Small traumatic crossing of the Achilles tendon to lengthen it.
- Maintaining the correction/treatment result by wearing orthopedic shoes (braces).
Help for the project 'Towards life
If you know from an ultrasound scan that your baby needs treatment for congenital clubfoot, it makes sense to use the time until your baby is born. Even before birth, you can choose a pediatric orthopedist who treats congenital club feet using the Ponseti method, who has experience in dealing with similar problems, and the medical institution where the doctor will carry out the treatment. Talk to parents of children with clubfoot on forums. If you are convinced that it is possible to get rid of a clubfoot without consequences, come to our clinic. We gently and effectively help your child grow up healthy by overcoming clubfoot on one or both sides.
As part of the 'Towards Life' project, you will receive help from highly qualified doctors. They have mastered the advanced Ponseti technique, which virtually eliminates recurrence. Many children around the world and in Russia have already been successfully treated with this method. Therapy as part of the project is free! To make an appointment and if you have any questions, please call us 8 (800) 555-84-21 Weekdays 9:00 a.m. – 7:00 p.m. (Moscow time).
Our patients
Anastasia



Diagnosis: Congenital bilateral severe atypical clubfoot
Treating doctor: Maxim Vavilov
Miroslav



Diagnosis: Congenital bilateral severe clubfoot
Treating doctor: Maxim Vavilov
Alexander



Diagnosis: Congenital right-sided severe clubfoot
Treating doctor: Maxim Vavilov
Maria



Diagnosis: Congenital bilateral clubfoot
Treating doctor: Maxim Vavilov
Filipp
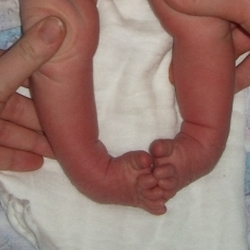


Diagnosis: Congenital bilateral clubfoot
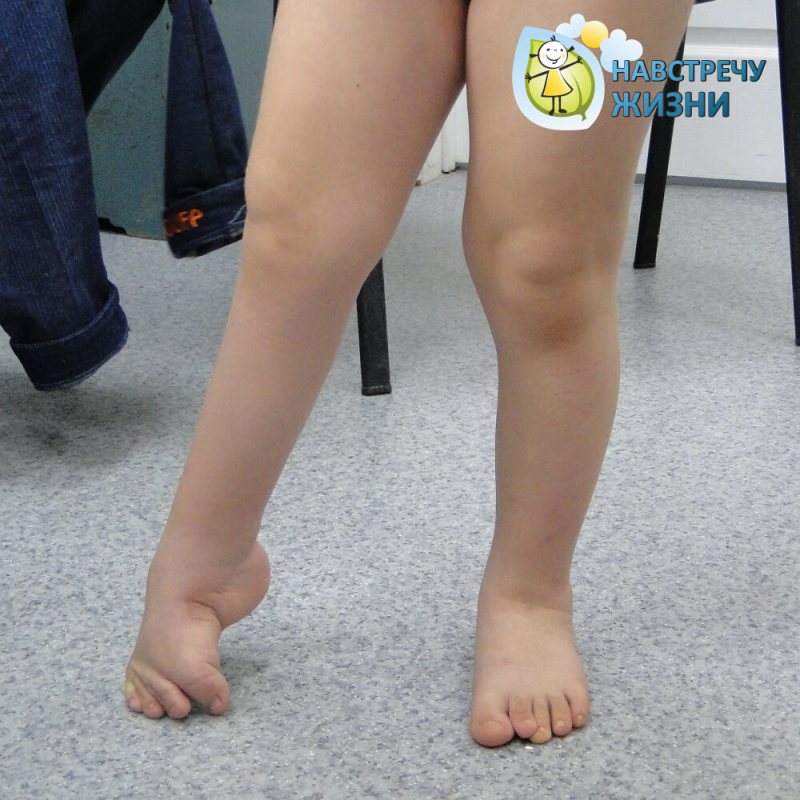
The more complex forms of recurrence include those that have developed:
- Improper treatment of clubfoot, in which a plaster cast can lead to a secondary deformity;
- incomplete correction during treatment, when it is not possible to cure the clubfoot by staged casting and achillotomy (5 cases per 100 patients);
- Recurrences after surgical treatment (the presence of a skin-tightening scar does not always allow correction of the deformity with plaster);
- Non-diapathic clubfoot.
Recurrences of this form can be observed between the ages of 0 and 15 years. The treatment plan is determined by the specialist after direct examination and the results of additional tests.
Treatment of any recurrence begins with gradual casting to reduce surgical intervention. The choice of surgical correction method depends on the results of the plaster cast.
Experts point out that the decision to undergo surgery is influenced by the biomechanics of the foot. If the biomechanics are intact and the deformity is mobile, correction of the deformity with a cast and tendon/muscle lengthening by offloading the foot is possible.
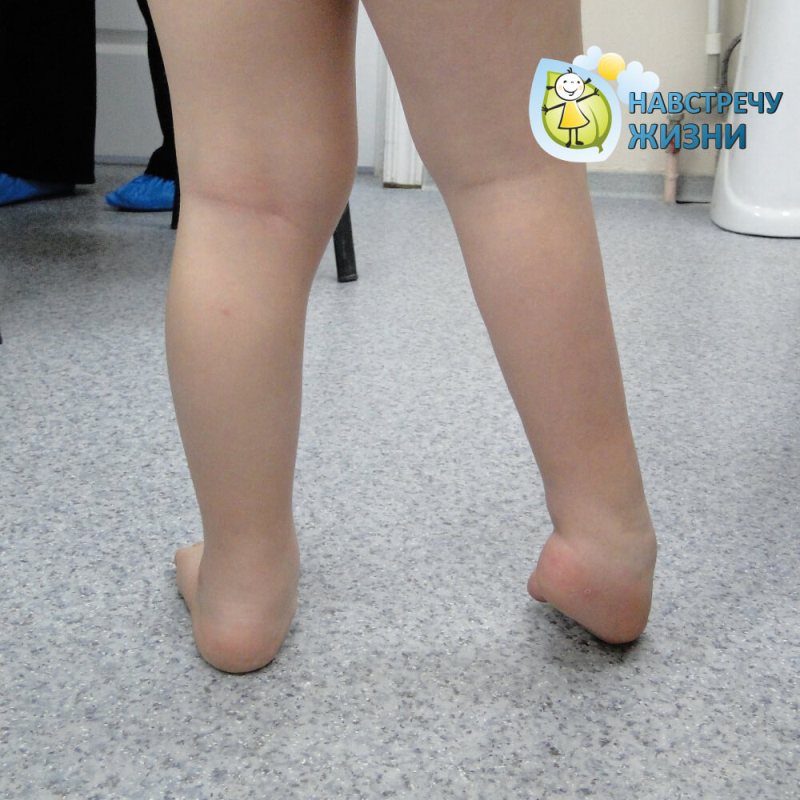
If the biomechanics of the foot are disturbed, pediatric orthopedists suggest bone surgery (osteotomies, arthrodeses). The choice of treatment plan is left to the treating physician.
If you have any questions about the treatment of clubfoot of any form and age, please contact [email protected].
Towards specialists

Glazova Natalia Alekseevna

Gromov Ilya Valeryevich
Candidate of Medical Sciences, pediatric traumatologist and orthopedist

Maxim Vavilov
Dr. med., orthopedic traumatologist, President of the Russian Ponseti Society, Associate Chair in Pediatric Surgery at the YSMU.
г. 15, Pobedy St., Yaroslavl, Russia.
8-800-555-84-21, +7 (4852) 72-01-35, VKontakte group
© 2006-2023, Project 'Towards Life'.
Support, advertising and website development – Perspektiva
Congenital clubfoot in children. Treatment

Clubfoot in children is a congenital pathology of the bones and soft tissues of the child's foot that develops prenatally. The anomaly can be detected by ultrasound in the expectant mother in the 8th to 12th week of pregnancy. Congenital clubfoot can be effectively treated immediately after birth, otherwise it can lead to disability. Clubfoot can also be a manifestation of other diseases, e.g. B. a vertebral arch cleft in the lumbar spine, and it can be combined with hip dysplasia.
Symptoms of clubfoot in a newborn:
- The foot is smaller and the heel is significantly smaller than in a healthy foot;
- The forefoot is directed downwards;
- The plantar surface of the clubfoot faces the other foot;
- The foot is turned outwards (supinated), with the sole pointing downwards.
A newborn with a congenital clubfoot should be evaluated by an orthopedic surgeon. Conservative and surgical methods are used to treat clubfoot in children.
During conservative treatment, the orthopedist prescribes medications, among other things.
If the foot deformity is large or the parents are late to the doctor, surgery is performed. It should be noted that the operation is carried out when the child is 6 months old. With the Ponzetti treatment method, surgical treatment is carried out earlier.
Importance of treatment, negative consequences of a neglected disease
Timely treatment of clubfoot in children can correct the situation. Experienced orthopedic surgeons know how to effectively treat clubfoot in children and bring the child back to full life. Orthopedic shoes - braces - must be worn for a short period of time, gradually reducing the wearing time. After the main part of the treatment, from the first months after birth until the age of two, the child only wears the shoes at night. With the Ponseti method, there are almost no relapses, the muscles remain flexible and strong, and the procedure is minimally traumatic. The wound heals quickly, without scarring, pulling skin or discomfort when wearing shoes, which is not the case with surgical treatment of a neglected pathology.
Congenital clubfoot in infants should preferably be corrected in the first few months after birth, when the tendons and muscles are most stretched. Once the child begins to walk, the pathology becomes more complicated and the standard Ponseti method may no longer be sufficient, requiring additional surgery with tendon transplantation. Advanced disease can lead to the following
- Muscular dystrophy;
- joint dysfunction;
- subluxation of bones;
- scoliosis;
- loss of ability to walk properly;
- Disability.
Project 'Towards Life' for children's health
When a child's feet develop abnormally, parents wonder how to treat clubfoot in their growing child so that the defect can be corrected quickly and without relapses. The answer lies in the unique 'Towards Life' project, created specifically to support children in need. The qualifications and experience of the doctors involved as well as the treatment using advanced methods guarantee the success of the therapy. The children we have helped are growing up healthy and are not lagging behind their peers in terms of development.
The clubfoot treatment is free for all children in the project. Thanks to financial support from the charitable foundation Rusfond, the children receive qualified medical assistance without having to pay for a cast, operation or materials. Patients from other cities who come to Yaroslavl for long-term treatment are provided with accommodation for the duration of their stay. If you would like to know how you can have your child's clubfoot treated free of charge as part of the 'Towards Life' project, please contact us by email or telephone. Calls from Russia are free of charge.
If you have any questions, you can get advice by phone:
8 (800) 555-84-21
on weekdays from 9 a.m. to 7 p.m. Moscow time
How quickly should a club foot be treated?
An untreated clubfoot will certainly make it difficult for the child to learn to walk properly, so doctors usually recommend treating it almost immediately after birth. Fortunately, most experienced clubfoot doctors usually successfully treat clubfoot without surgery.
The following measures, among others, are recommended for prevention
– wearing orthopedic insoles
– Shoes should be comfortable and of the right size; In some cases, orthopedic therapeutic shoes may also be recommended.
– Regular massages, massage mats can be used; Due to their natural nubs, they are ideal for massaging bare feet.

What are the symptoms of clubfoot?
There are different variants of clubfoot with different degrees of severity. Many cases are discovered during prenatal diagnosis; other forms of clubfoot are not recognized immediately, i.e. before birth. The most common variants of clubfoot in children include deformities in which:
- The upper part of the child's foot is curved downward and/or inward. This causes the arch of the foot to enlarge, which also causes the child's heel to turn inward.
- In severe cases of clubfoot, the child's foot may be severely twisted, as if it were upside down.
- Sometimes the foot or the foot is slightly shorter than the other foot. If the deviation is not severe, it can be corrected with corrective orthopedic shoes.
- In many cases of clubfoot, the corresponding calf muscles and the muscles of the affected lower limbs are also underdeveloped.
Caused
There are several theories about the origin of congenital clubfoot, but none of them can fully explain the etiology of the disease. The cause of congenital clubfoot is still unclear. There is also no evidence that the condition is hereditary. Only rarely do parents report the presence of similar malformations in relatives.
The diagnosis is simple and can be made during the first examination of the child in the maternity hospital. The diagnosis of clubfoot can be made during a routine ultrasound scan of the fetus in utero. In this way, the expectant mother can prepare mentally and prepare for the treatment of her unborn child. The examination also includes a discussion with a neurologist and, if necessary, with a geneticist.
Treatment
The Ponseti method is the gold standard in the treatment of congenital clubfoot. Treatment includes elimination of the main part of the deformity with a gradual cast for 5-8 weeks, followed by percutaneous achillotomy and complete correction of the deformity. Further maintenance of the achieved correction is carried out by wearing a cast for 3 weeks after the achillotomy and then a special orthopedic orthosis (corset). In the first 3 months, the orthosis is worn practically around the clock (23 hours per day), after which it is only worn during the day and at night to sleep. This method is recognized by pediatric orthopedists worldwide. When the technique is used correctly, excellent and good results are achieved in 80-90 cases.
In some cases, when the extensor muscles of the foot are weak (the child tilts the forefoot slightly inward when walking), it is necessary to restore the muscular balance of the foot. For this purpose, the attachment point of the tibialis anterior muscle is moved to the outside of the foot. The procedure is minimally traumatic and restores active extension and correct alignment of the foot during walking. The operation is usually performed between the ages of 3-5.
In rare cases of recurrence of the deformity, which can occur with a severe form of clubfoot and non-compliance with orthodontic measures, as well as in advanced forms of the disease (late treatment), the MacKey operation is performed. This is an operation on the soft tissues of the foot to restore the normal relative position of the bones in the foot. MacKey surgery is performed between the ages of 3-6 years.
In advanced cases, corrective osteotomies or three-part foot arthrodeses are performed between the ages of 7 and 12 years.
Prevention of recurrence
Modern medicine assumes that clubfoot is due to muscle and tendon changes throughout the leg. A stretching treatment simply compensates for the shortening and stiffening of the foot. As for the change in structure, it remains the same and can be aggravated by recurrence. To prevent possible recurrence in a timely manner, a plaster cast is applied and corrective surgery is performed. In exceptional cases, a comprehensive clubfoot correction is carried out.
After the clubfoot is corrected, the foot looks slightly different. In unilateral clubfoot, one foot is one or two sizes smaller than the other and the calf muscle of the affected limb is thinner. This type of defect does not affect the function of the limb.
preventive measures
In order to exclude the development of clubfoot in the newborn, the following is recommended to the expectant mother, among others
- early prevention and treatment before and during pregnancy;
- to undergo special massage techniques;
- not to strain the muscles of the lower limbs;
- to wear special orthopedic shoes with a good insole;
- walking barefoot on morning dew, lake/river sand and uneven ground.
The above recommendations are guidelines only and should not be used without prior medical approval.
© 2017 – 2023 MCC Proxima.
All rights reserved.
The information on this website and the price list do not constitute a public offer.
© 2017 - 2023 MCC 'Proxima'. All rights reserved.
The information on this page and the price list do not constitute a public offer.
- The Ponseti method.
- 1 year old child with clubfoot.
- What is clubfoot?.
- Clubfoot in 7-year-old children.
- clubfoot.
- Why does a child develop clubfoot?.
- Ponseti breeches.
- Clubfoot Treatment.
