Danger!!! The problem is less noticeable if the child has clubfoot on one foot. It is unnatural to position the foot with an inward rotation, lowering the outer edge and lifting the inner edge.

- How to correct a clubfoot in a child?
- Possible causes
- Clubfoot recurrence: causes and symptoms
- Do recurrences occur after clubfoot treatment with the Ponseti method?
- What are the causes of recurrences?
- Prevention of clubfoot recurrence
- What should parents do to reduce the chances of clubfoot recurring?
- Which orthosis is best for preventing clubfoot recurrence?
- OSTEOPATHY AND CLUB FOOT TREATMENT
- TREATMENT OF CLUB FOOT
- OSTEOPATHY AND TREATMENT OF CLUB FOOT
- Clubfoot in children 1 year old
- Treatment of clubfoot in one-year-old children
- causes
- Congenital valgus foot
- Acquired clubfoot
- Types of Clubfoot
- atypical shape
- What is the disease?
- Causes of acquired clubfoot
- causes
- Congenital clubfoot
- Acquired clubfoot
- Types of Clubfoot
- atypical shape
- prevention
- Treatment in Naberezhnye Chelny
How to correct a clubfoot in a child?
Ever since we were little, we've known the nursery rhyme about the bear with the clubfoot. But the problem of clubfoot can occur not only in the bear, but also in Teddybear, Seryoshka, Aneka, Taneka and other children, regardless of their names. In this blog article we will try to understand what clubfoot is, how to recognize it and how to fix it.
The term refers to a foot deformity in which the foot deviates inward from the axis of the lower limbs. Simply put, they are turned inward from the foot, although they are usually a straight extension of the foot.
Possible causes
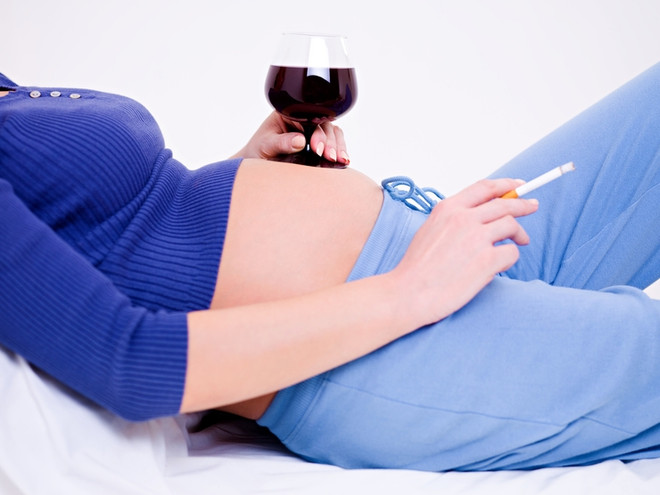
Experts distinguish between congenital and acquired clubfoot. The former can already be seen on ultrasound during pregnancy. The reason for this is not yet known exactly. Physiology may be to blame - a tight uterus putting pressure on the baby, lack of water, or breech presentation. There is also evidence that severe stress or the use of alcohol or drugs during pregnancy may play a role in the development of the condition. However, the abnormality can also be genetic.
The disease can also appear after birth. Causes include fractures and irregular bone fusions, stunted growth, burns, and tumors. In fairness, these cases are much rarer than congenital cases.
Depending on its complexity, the disease is divided into three stages. At the first stage, it is often corrected manually, but at the third stage, the mobility of the joints is already limited and treatment with conservative methods is no longer acceptable.
Clubfoot recurrence: causes and symptoms
Do recurrences occur after clubfoot treatment with the Ponseti method?
Of course, even with the Ponseti method, about 1 in 4 patients under the age of 5 will experience recurrence of clubfoot. And in most cases, they can be easily corrected. A short plaster cast and an achillotomy with transfer of the tibialis anterior tendon are usually sufficient. The scope of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and is determined by the attending physician. After 5 years of age, the probability of recurrence decreases to 5 % of the total number of recurrences and occurs during pubertal growth.
What are the causes of recurrences?
Recurrences of congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system are treated by orthopedists worldwide. Clubfoot is no exception. A loss of correction during the growth phase occurs in 25 % of the children.
Difficult recurrences result from incorrect treatment of the clubfoot or incomplete correction.
As a rule, however, recurrences are due to errors in the last phase of clubfoot treatment - wearing the orthosis.
Syndromes and combinations of neurological and musculoskeletal disorders rarely result in loss of correction. In discussions with parents of children who have had clubfoot recurrence, failure to follow orthodontic protocols is a common occurrence. This is the main cause of recurrence.
- The child stays in the orthosis for less time than recommended. This problem occurs in the first days of wearing the orthosis or, on the contrary, at the end of treatment, at the age of 2-3 years. In the first case, parents take pity on the crying child, uncomfortable and not used to wearing such shoes, and remove the orthosis. In the second case, they lose vigilance: the feet look good, so they stop putting the orthosis on the child at bedtime and don't go to the doctor. But the child is actively growing, so after 3-6 months of such a regimen, the risk of clubfoot recurrence increases significantly.
- Errors in wearing orthoses.
- Wrong size.
Prevention of clubfoot recurrence
What should parents do to reduce the chances of clubfoot recurring?
- Make sure you follow the orthosis wearing schedule.
Parents should be aware that after the cast and achillotomy, clubfoot treatment is not over but has moved into the maintenance phase. The most important thing in clubfoot prophylaxis is therefore still the plaster cast and the observation by the treating doctor. The orthopedist actively monitors the children until they stop growing.
The easiest and safest way is to wear braces. These are shoes that are attached to a rail at a specific angle that is adjusted as the child grows. At this stage, the main task of parents is to wear braces correctly and strictly adhere to the orthodontic regime. In the first 3 months, the child must wear these shoes 23 hours a day. After that, according to the wearing protocol, the time in the braces is gradually reduced, and then they only need to be worn for all types of sleep. A child who goes to kindergarten at the age of two can stay there without braces. However, wearing the braces at home is mandatory.
Studies have shown that families who have followed the brace-wearing protocol and strictly followed the doctor's recommendations are less likely to relapse.
Which orthosis is best for preventing clubfoot recurrence?
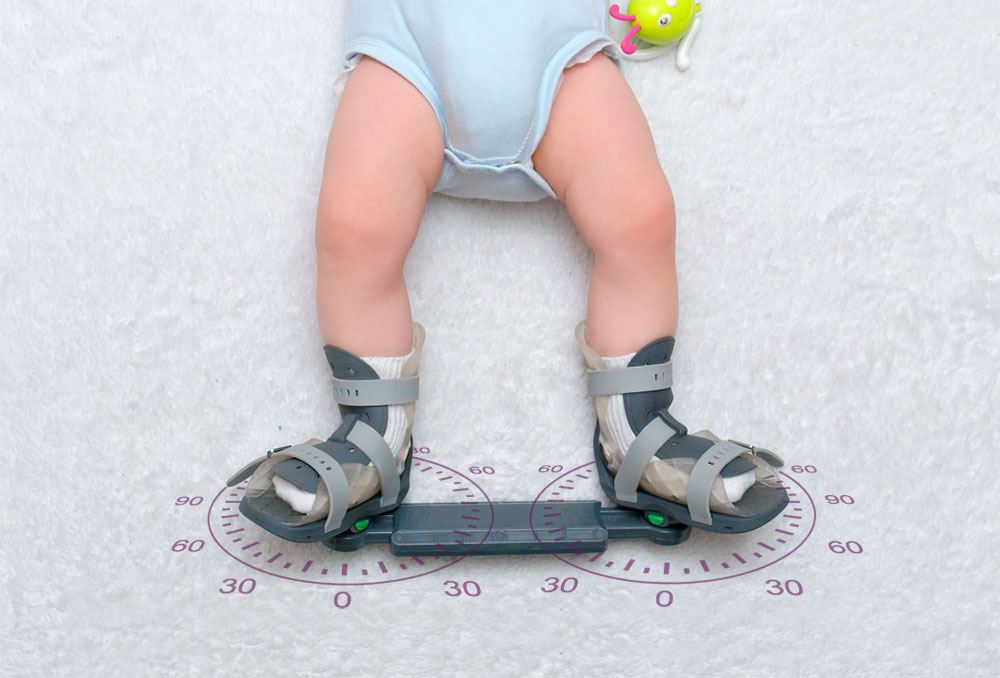

An orthosis with a static bar is recommended. Currently, orthoses Kinetic Pro (from Russia), Mitchell (from Great Britain) and Alfa-flex (from Germany) are very popular in Russia. In addition, I would like to point out that setting dorsiflexion to 15-20 degrees for the clubfoot and 0 degrees for the vertical and oblique ramus is very important for relapse prevention. The Landes Kinetic Pro Braces feature a ball-and-socket mechanism that allows the dorsiflexion angle to be individually adjusted for the specific therapy. This characteristic distinguishes them very positively from their foreign counterparts. Of course, the low price of the Kinetic Pro models is also a strong argument in their favor.
OSTEOPATHY AND CLUB FOOT TREATMENT
If you discover that your child has clubfoot, it is worth taking your newborn to an osteopath as soon as possible after discharge from the delivery room.
An osteopath can fix clubfoot problems in children by guiding the joints and bones in the right direction.
The effect of such manipulations is visible after about a week, so a second session (if necessary) for the 7th-8th. Already a few days after a child's first visit to an osteopath, results can be seen.
The sooner corrective therapy is done, the fewer problems your child will have in the future.
TREATMENT OF CLUB FOOT
Clubfoot treatment must be timely. It should be started as early as possible.
Parents need to be patient because clubfoot treatment is a long and demanding process.
- Gymnastics,
- Massage,
- osteopathy,
- Physiotherapy,
- the use of orthopedic shoes in old age,
- plaster casts and special splints,
- Surgery.
However, surgical intervention is a very serious procedure and is recommended only when conservative treatment is ineffective.
OSTEOPATHY AND TREATMENT OF CLUB FOOT
If you find symptoms of clubfoot in a newborn, according to the principle of treating it as early as possible, it is advisable to take the child to an osteopath immediately after discharge from the hospital, or to visit this specialist directly in the maternity hospital, if it is occupied.
The earlier a correction is made, the faster progress will be made.
Osteopathy is so effective for clubfoot and other congenital injuries that positive results can be seen after just two or three sessions. Infants have very flexible and supple ligaments and are very treatable.
However, it is worth remembering that the treatment process is lengthy and one should not stop halfway. Treatment should be completed when the foot is in a stable and normal position.
During a visit to the osteopath, an experienced therapist will help the bones in the child's foot move into proper position and correct changes that have not yet caused clinical symptoms.
With clubfoot, the osteopath uncovers the cause of the condition and uses manual methods that are individually tailored to each child.
Clubfoot in children 1 year old
From 0 to 12 months of age, both congenital and acquired forms of the disease can be diagnosed. The former are often diagnosed during fetal development, and therapy is then started after birth, on doctor's orders.
Acquired disorders are diagnosed after the fourth month of life (before that, the inwardly rotated and upward arch of the foot can be a deviation from the norm). Often the diagnosis is made closer to the time when the child begins to walk independently. Ideally, the foot should be able to walk again before the first steps are taken.
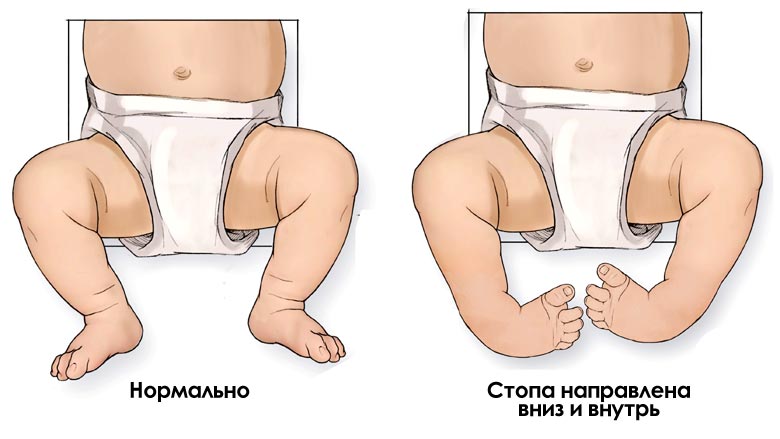
Treatment of clubfoot in one-year-old children
Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment can be conservative or surgical, using a combination of both tactics in the latter case. In mild to moderate cases, the mobility of the ankle is unrestricted or only slightly restricted. Restoration of foot function and shape can be improved with comprehensive treatment.
- Massage.
- Corrective exercises for 5-7 minutes.
- Manual therapy.
- Soft bandaging according to the Fink-Ettingen method consolidates the results achieved with passive exercises and chiropractic exercises.
- With a moderately severe lesion, the treatment is carried out according to the Ponseti method. A plaster cast is placed on the leg at intervals of 5-7 days. Each step causes a slight change and the leg is fixed in a new position until the anatomical norm is reached.
- Wearing orthotics - devices in the form of shoes that affect the position of the sole - is effective. For example, an orthosis is a pair of shoes with a metal plate in between. It fixes the physiologically correct position of muscles, joints and ligaments and does not allow the child to voluntarily change them.
causes
Congenital valgus foot
mechanical causes Clubfoot Causes During Pregnancy. Because the fetal skeleton is not fully developed, the baby's bones can deform slightly when pressed against the wall of the uterus. Most commonly, this is due to low water content or misalignment of the baby in the womb.
Genetic' causes are caused by chromosomal mutations occurring more than once in the same family. If an older relative has or had clubfoot, there is an increased risk of developing the disease in the family.
Musculoskeletal causes are also associated with the fact that the problem is acquired in the womb. It can be caused by a mineral deficiency, the pregnant woman's use of alcohol, drugs, or medication that are harmful to the fetus, or by developmental abnormalities that are beyond her control.
Acquired clubfoot
In childhood, clubfoot is usually acquired during the first attempts to walk. It is important to pay attention to how the child positions their feet when walking because acquired clubfoot is usually caused by inattentive parents. Other causes can be:
- Rickets;
- History of diseases (e.g. polio);
- Developmental disorders due to vitamin deficiency or genetic predisposition;
- Improperly fitting footwear;
- foot injuries (abnormal bone healing after a fracture);
- CNS diseases, etc.
Types of Clubfoot
The typical clubfoot does not extend beyond the foot and does not affect the rest of the skeleton in the early stages. It is caused by defects in muscles, tendons and ligaments. There are 3 degrees of severity in this form of clubfoot, the first two of which can be treated well on an outpatient or hospital basis, while the third requires surgery:
- Grade 1 are minor changes in the foot that can be managed independently, relying on treatment prescribed by the doctor, such as massage and therapeutic exercise;
- At grade 2, the muscles are less stretchy and more difficult to treat, so a home massage therapist is always needed. a massage therapist at home or in the clinic, the use of paraffin packs and even plaster casts;
- Grade 3: joint mobility is reduced, bones and muscles are severely deformed, and it is almost impossible to treat such a problem without surgery.
atypical shape
Atypical clubfoot extends beyond the foot and affects all or part of the musculoskeletal system. In 90 % cases, it occurs during pregnancy due to hereditary diseases. The atypical form can appear:
- Mild severity - if tibia retains mobility - treated well;
- Moderate severity - the child's leg movements are limited but possible - is treated with special physical therapy and sometimes surgery;
- Severe severity - pathological changes that cannot be treated with physical therapy - can only be treated with surgery.
What is the disease?
The foot deformity can be congenital or acquired. The first form occurs during fetal development. Possible causes:
- Bad habits of mother - alcohol, smoking, drugs;
- work in a harmful occupation;
- malnutrition, vitamin deficiency;
- Incorrect positioning of the fetus;
- low water content;
- abnormal bone development;
- spinal nerve abnormalities;
- toxoplasmosis;
- hip dysplasia;
- genetic disorders.
Congenital clubfoot has mild, moderate, and severe symptoms. The first two are often not recognized on the infant's initial examination, while the latter, characterized by twisting of the bones of the lower limbs, are immediately noticeable. Parents should pay attention to the foot is too short, there is a transverse groove in the sole, the toes are turned inward, and the tissue is swollen.

Causes of acquired clubfoot
Acquired clubfoot develops as the child grows due to various factors:
- Trauma, burns, tumors of the bones, muscles and ligaments;
- complications after infectious diseases;
- paralysis due to neurological problems;
- Bone growth disorders of the lower limbs and foot;
- injuries, spinal diseases;
- Rickets;
- Poliomyelitis;
- uncomfortable shoes;
- overweight.
Acquired clubfoot in children is much less common and easier to correct. If a child 'shuffles' their foot, hobbles, has a slipping gait, and has their knees turned in, parents should not wait to see a podiatrist.
Early detection of a congenital foot defect is the key to correcting it. When a child starts to walk, the bones are soft and flexible and can be easily corrected. As the child grows older, the foot undergoes profound changes that are very difficult or impossible to correct.
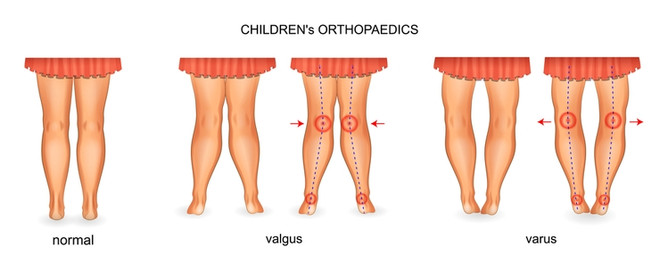
Clubfoot can be detected in infants in the womb with an ultrasound scan of the fetus. If the neonatologist suspects clubfoot during the initial evaluation of the newborn, they will refer the child to an orthopedist. He will assess the mobility and position of the joints and recommend a comprehensive examination. Treatment of clubfoot must be carried out under his guidance and supervision.
Acquired clubfoot develops in children between the ages of 3 and 14 and is almost asymptomatic in the early stages. At the first disturbing symptoms, a comprehensive examination must be carried out:
- X-rays of the ankle and foot to determine the degree of deformation of the bones and joints;
- General blood and urine tests – important for assessing the child's health.
causes
Congenital clubfoot
mechanical causes Causes of clubfoot during pregnancy. Because the fetal skeleton is not yet fully formed, the baby's bones can deform slightly when pressed against the walls of the uterus. The most common causes for this are not enough water or the wrong position of the baby in the uterus.
Genetic causes are caused by chromosomal mutations that occur more than once in the same family. If an older relative has or had clubfoot, the risk of the disease running in the family is increased.
Musculoskeletal causes are also associated with the fact that the problem is acquired in the womb. It can be caused by a mineral deficiency, the pregnant woman's use of alcohol, drugs, or medication that are harmful to the fetus, or by developmental abnormalities that are beyond her control.
Acquired clubfoot
In childhood, clubfoot is usually acquired with the first attempts to walk. It is important to observe the position of the child's foot while walking. Inattentive parents are usually to blame for acquired clubfoot. Other causes can be:
- inflammation of the bunions;
- childhood diseases (e.g. polio);
- Developmental disorders due to vitamin deficiency or genetic predisposition;
- ill-fitting shoes;
- foot injuries (abnormal bone healing after a fracture);
- CNS diseases, etc.
Types of Clubfoot
The typical clubfoot does not extend beyond the foot and does not affect the rest of the skeleton in the early stages. It is caused by defects in muscles, tendons and ligaments. There are 3 degrees of severity in this form of clubfoot, the first two of which can be treated well on an outpatient or hospital basis, while the third requires surgery:
- Grade 1 are minor changes in the foot that can be managed independently by relying on treatment prescribed by the doctor, such as: B. Massage and therapeutic exercise;
- At grade 2, the muscles are less flexible and less easy to treat, so a home massage therapist is essential a massage therapist at home or in a clinic, the use of paraffin packs or even plaster casts;
- Grade 3: joint mobility is reduced, bones and muscles are severely deformed, and it is almost impossible to treat such a problem without surgery.
atypical shape
Atypical clubfoot extends beyond the foot and affects all or part of the musculoskeletal system. In 90 percent of cases, it occurs during pregnancy due to hereditary diseases. The atypical form can appear:
- Mild severity—when the tibia retains mobility—is easily treatable;
- Moderate severity - the child's leg movements are limited but possible - treatable with special physical therapy and sometimes with surgery;
- Severe severity - pathological changes that cannot be treated with physiotherapy - only surgery can eliminate them.
prevention
It is important to understand that there are no treatments that can prevent the occurrence of clubfoot in both children and adults 100 %. If a family member fell ill with this pathology, then no preventive measures can affect a person's genome. Still, the risk of children developing clubfoot can be reduced by the mother herself if she follows a few simple rules:
- No stress during pregnancy.
- Consume only healthy foods and products rich in calcium. This element plays an active role in the formation of the fetal skeleton.
- Complete renunciation of all unhealthy habits.
- Regular check-ups with a specialist.
- Take care of your own health and consult a doctor if you suspect an infection.
For the child, regular massages and therapeutic exercises are useful as preventive measures.
Treatment in Naberezhnye Chelny
Clubfoot is a disease that can be effectively treated. In this situation, it is important not to waste time and consult a doctor at the first suspicion of the disease. Early stage clubfoot can be treated using traditional methods in both children and adults. At the Center for Reconstructive Medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny, experienced specialist Damir Nadirovich Uzarov conducts massage sessions for clubfoot. An orthopaedist/traumatologist helps with the timely diagnosis and puts together an individual correction program. To make an appointment or to clarify questions, please call +7 (8552) 78-09-35, +7 (953) 482-66-62.

Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that results from a disruption in the inhibitory processes in the brain. In practice, this disorder is manifested by a subjective feeling of lack of sleep, which significantly affects a person's quality of life. What causes insomnia in humans and how can it be treated?
Medical observations show that about 8 % of all visits to neurologists are due to spinal canal stenosis.
2017 – 2023 © The Center for Restorative Medicine All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part prohibited without permission!
License No.: LO-16-01-006209 from 08/24/2017 to carry out the therapeutic activity of Balsam + GmbH.
Read more:- What is clubfoot?.
- Clubfoot in 7-year-old children.
- Congenital clubfoot.
- Why does a child develop clubfoot?.
- clubfoot.
- 1 year old child with clubfoot.
- Clubfoot in children therapeutic exercises 7 years old.
- Footwear for children's clubfoot.
