Daily walking of at least 10 minutes, better 20 minutes to get an effect.

- Foot deformities in children (clubfoot, duck gait, varus, valgus)
- The most important phases of gait development in children
- What are the most common types of gait disorders in children?
- Symptoms of Clubfoot
- Treatment of clubfoot
- treatment methods
- Conservative therapy
- Useful tips
- Causes in children and triggers of pathology
- Main symptoms and types of flat feet in children
- Treatment of clubfoot
- Operations for clubfoot
- prevention of scoliosis
- Video – exercises for scoliosis in children
- Possible causes
- Make a mistake - make a pump!
- THERE IS NO MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS FOR CLUBFOOT. THE TERM 'CLUBFOOT' USUALLY REFERS TO ONE OF TWO CONDITIONS – CLUBFOOT OR VARUS FOOT DEFORMITY.
- CAUSES AND TYPES OF VARUS DEFECTS
- Treatment
- The most important
- Clubfoot Treatment
- Prevention of clubfoot
Foot deformities in children (clubfoot, duck gait, varus, valgus)
Children's gait differs from that of an adult. At different stages of a child's growth, these or other anomalies are age-related changes that correct themselves with age. Still, it's always important to watch out for problems that require treatment.
- Clubfoot (clubfoot), internal rotation of the legs
- 'Duck walk' (stand on toes), external rotation of the legs
- Metatarsus adductus (midfoot adduction, lowering of the midfoot level)
- shin twist
- Internal rotation of the thigh
- Varus and valgus deformities of the knee joints
- Clubfoot in children
- Tiptoe walking
The most important phases of gait development in children
- By 6 months most children are able to roll onto their side and sit up with support.
- Babies can crawl at 8-9 months
- At 9-12 months, your child will be able to stand on their feet. At this age, children can walk with help, but cannot yet walk on their own.
- At 11-16 months, children can walk without additional support.
- By age 2, most children can climb stairs and jump in place.
- By age 3, most children can take turns walking up and down stairs and standing on one leg
- By age 4 most children can take turns walking up and down stairs and hopping on one leg.
What are the most common types of gait disorders in children?
The most common gait disorders in children include:
Clubfoot, an adduction of the feet, does not usually cause serious problems. This problem is temporary and in most cases does not require orthopedic correction or treatment. The biggest problem with clubfoot can be difficulty putting on shoes or cosmetic setbacks during puberty.
It is important to distinguish clubfoot from clubfoot. Clubfoot (as opposed to clubfoot) is a serious orthopedic pathology (deformity of the foot caused by a dysplastic process of connective tissue). These children require orthopedic and/or surgical treatment.
Symptoms of Clubfoot
As early as the 16th week of pregnancy, congenital clubfoot can be detected by fetal ultrasound screening. But even after the birth of the child, the following symptoms can be noticed:
- The toes are curved inwards.
- The toe is pointing down and the heel is higher than the toe.
- The hock is twisted outwards.
- The tibia and joint are stiff.
The following symptoms are easy to spot in older children:
- Strong stepping on the shoes.
- Abnormal gait (foot appears to curve inward).
- Lumps, calluses, blisters under the big toe.
- The child complains of discomfort when walking.
Treatment of clubfoot
The cause of clubfoot is only identified in one in five cases. In most cases, it is a congenital disorder caused by heredity or maternal errors during pregnancy.
However, clubfoot can also occur in a healthy child in the first two years of life. The causes of the deformity can be different: the consequences of trauma, polio, rickets, muscle hypertension, increased load on the musculoskeletal system, ill-fitting footwear and others.
Treatment of clubfoot depends on an accurate diagnosis and the type of deformity. It is extremely important to determine the severity of the condition and try to determine the cause. Come to us at the KIT Multispecialty Medical Center for the examination and treatment of clubfoot. Our specialists will find the best treatment option for you.
Foot deformities can be corrected in a variety of ways. Depending on the severity and the individual physiology of the patient, the following methods can be effective:
- tight bandaging,
- plaster casts,
- therapeutic massage,
- PHYSIOTHERAPY,
- Physiotherapy,
- paraffin compresses,
- selection of orthopedic footwear,
- surgical treatment,
- Ponseti method (3-step therapy for children up to 2 years old).
The specialists in our clinic develop an individual therapy plan that can combine several of the above methods. This will increase its effectiveness and speed up your child's recovery.
treatment methods
How to correct clubfoot in a child – for this, conservative and surgical methods are used, depending on the stage of the disease. The therapeutic tactics are determined by the podiatrist, and the therapy is carried out under his supervision.
Conservative therapy
It is advisable to begin treating clubfoot in children by identifying and treating the cause of the condition. In most cases, the cause lies in sports activities that lead to foot injuries or in long-term static loading of the feet. These should be avoided altogether or the movement reduced.
The next step is to normalize the child's weight. Clubfoot often develops in overweight children. Therefore, make sure that the child gets enough exercise and that the diet is checked. Meat and fish products, fruit and vegetables should dominate the menu. Limit fast carbs - candy, cookies, fizzy drinks. Foods containing ascorbic acid and B vitamins should be consumed.
Children with clubfoot must wear orthopedic shoes. These must be selected individually after consultation with a podiatrist. Children's therapeutic shoes are often custom-made. You must meet the following requirements:
- They must be precisely tailored to the size of the foot;
- You must have a stuck heel;
- have a rigid, ridged sole;
- Heel height of no more than two centimeters.
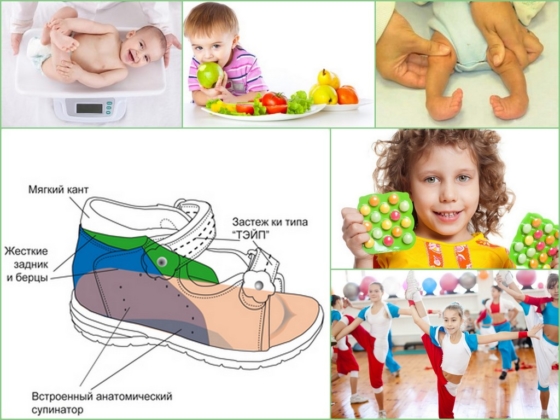

It is recommended to wear the shoes daily and change them as the foot grows. The shoes must be made of natural material.
Read more:Important!!!
Children under the age of three should wear shoes without supinators, because at this age the natural layer of fat plays its part.
Useful tips
Gymnastic exercises and massage for the clubfoot should be performed daily. The doctor gives the parents the necessary exercises so that they can help the child to do them correctly.
Therapeutic gymnastics, as a rule, is carried out at home. It requires special equipment:
Important!
Treatment is most effective when the child practices barefoot.
Clubfoot exercises are performed lying down, sitting and standing. For small children, the exercises can be carried out in the form of games. Training always begins with a warm-up: the child is encouraged to walk in circles, shifting from one foot to the other while standing still. After a five-minute warm-up phase, begin the physiotherapeutic exercise:
- Place the child in a chair so that their feet are close to the floor. Encourage the child to roll a stick or small ball around the soles of their feet;
- Put small objects - toys, pens - in front of the child on the chair. Ask the child to pick them up with their toes;
- Pass a small ball to the child in the chair and ask them to push the ball with the soles of their feet. Hold the ball for a few seconds;
- Ask the child to stand on the floor. Ask them to alternately lift the toes and heels of their feet;
- Standing on the floor, roll from heel to toe and vice versa;
- Walk on the inside and outside of the foot, then on the heels and toes;
- The child lies on the floor, raises his legs and bends them in his knees. Rotate the feet clockwise and then counterclockwise;
- Ask the child, lying on their back, to lift their feet and use their fingers to draw numbers, letters, and geometric shapes in the air;
- Lay the child on the bed and ask them to crush the sheet with the soles of their feet.
After the exercise, walk on a spiked rubber mat and give your child a warm foot bath. Put a decoction of chamomile, lovage and sage in the bath.
Causes in children and triggers of pathology
There are many situations that affect the health of children's feet in one way or another. The main factors that can provoke the development of the disease, but still do not guarantee its occurrence:
- heredity – if mom or dad had such problems, the child also needs to immediately buy preventive footwear and do therapeutic exercises;
- foot injuries;
- Excessive stress (due to high body weight or initial obesity, heavy lifting, constant weight lifting);
- Rickets;
- Muscle weakness due to insufficient physical development, lack of exercise;
- paralysis (e.g. cerebral palsy).
Studies have shown that city kids who wear shoes consistently (instead of being barefoot) are more likely to be affected by this condition than their rural peers. In addition, the lack of physical activity, which is replaced by smartphones and computers, affects posture, which also contributes to the frequency of lower limb problems.
Main symptoms and types of flat feet in children
Most symptoms are visible to the naked eye. They can be recognized by parents:
- Uneven cracking of heels in a child over 5 years old;
- Complaints of tiredness when walking, back and leg pain;
- clubfoot;
- Stepping on the inside edges of the sole.
If any of these traits are noticed or reappear, you should definitely make an appointment with your family doctor or orthopedist and seek advice about the condition.
Moms and dads can decide for themselves in which direction the clubfoot goes:
Treatment of clubfoot
How do you correct a clubfoot? Therapy is always lengthy, complex and individually tailored. Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
- Cast - effective up to 60%;
- corrective massage – performed at the initial stage or before applying the plaster cast;
- paraffin application;
- Ponseti method – special plaster casts with an effectiveness of about 90 %;
- Wearing splints, orthopedic constructions and special shoes.
Physiotherapy for children, therapeutic massage for children and gymnastics are also indicated.
Operations for clubfoot
Surgical treatment is used for congenital and severe forms when conservative treatment does not bring the desired result. The operation consists of plastic surgery of the aponeurosis, the ligaments and the tendons of the foot. The operation can be performed on a child at least one year old. During the rehabilitation period, children are prescribed physiotherapy, massage and physiotherapy.
A pregnant woman should eat a nutritious diet and lead a healthy lifestyle. After the child is born, her gait should be monitored. Swimming can help prevent clubfoot.
Preventive measures include:
- more frequent walking barefoot on uneven ground;
- choosing the right size and shoes so that the foot is well supported;
- Don't wear shoes with cracked or wrinkled heels;
- Timely treatment of abnormalities in pregnancy;
- Wear proper, non-compressive footwear with a raised insole on the inside of the foot and a sturdy heel counter;
- Massage feet to strengthen muscles.
It is good to eat fish, dairy and milk products. If clubfoot is suspected, you should consult a pediatric traumatologist.
prevention of scoliosis
To prevent the disease, children should be introduced to physical activity as early as possible: exercise regularly, play more than on the computer, spend more time outdoors. It is important to monitor how much time your child spends in front of the television, computer or gadgets as these are the most likely causes of scoliosis.
The child's bed should be adapted to their height and as comfortable as possible. It is advisable to choose an orthopedic mattress and a moderately firm mattress so that the spine does not bend during sleep.
The table at which the child studies and the chair should also be selected according to the child's height and should be stable and comfortable. Pay attention to your child's posture when sitting at the table.
Video – exercises for scoliosis in children
Possible causes
Newborn scoliosis is often due to mechanical causes, e.g. B. low water pressure or incorrect positioning of the fetus during the mother's pregnancy. The increased pressure causes the walls of the uterus to press the legs harder against the fetus. Often the cause of clubfoot is a neuromuscular abnormality in fetal development:
- abnormalities caused by avitaminosis;
- lack of nerve fibers;
- abnormalities in the formation of muscles and ligaments in the first few weeks of life;
- Toxicity due to maternal use of drugs during pregnancy.
If a parent had clubfoot in childhood, the child's developmental abnormalities are due to hereditary factors. The problem of how to correct clubfoot has a genetic cause - triple pairs of chromosomes (Edwards syndrome) leading to clubfoot. If the question of how to correct a clubfoot is not addressed, later musculoskeletal problems can arise: from incorrect foot support, increasing loads, weight gain, wearing unsuitable footwear, injuries and foot diseases. How to treat clubfoot in children depends not so much on the cause of its formation, the most important thing is the timely elimination of the pathology.
Make a mistake - make a pump!
You explain to the child that you will help him monitor the correctness of the exercise. As soon as the child makes a mistake, clap your hands and it must e.g. B. Do five push-ups. However, if he has noticed the mistake and clapped his hands himself, the push-ups are omitted. This is a simple way to teach your child to stop clapping, slurping or saying the word 'pancake'. ….
The trick is very effective, but don't let it take too long. The deal is worth more than the money. Explain to your child that push-ups are not a punishment but an extra exercise to get stronger and that your child is just doing them out of inattention.
THERE IS NO MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS FOR CLUBFOOT. THE TERM 'CLUBFOOT' USUALLY REFERS TO ONE OF TWO CONDITIONS – CLUBFOOT OR VARUS FOOT DEFORMITY.
Clubfoot is a serious congenital disorder characterized by abnormal foot alignment (turning inwards), clubfoot toes, restricted ankle mobility, and restricted knee joint mobility. Clubfoot is usually diagnosed in infants. The condition is treated using a variety of methods, including massage, gymnastics, and plaster casts. In some cases, clubfoot in infants is corrected with surgery.
A varus deformity is a condition characterized by a curvature of the axes and arches of the foot, where they look inward'. The lower leg can also have an O-shaped curvature. With a varus deformity, the weight of the body is unevenly distributed, which puts additional strain on certain muscle groups and ligaments. When a child has clubfoot, it is difficult to run, jump, trip, and fall while walking. It is a varus foot deformity that is most common in children. So let's look at the causes, types, treatment and prevention options.
CAUSES AND TYPES OF VARUS DEFECTS
There are two main types of varus foot deformities: congenital i acquired. The first form is diagnosed in children from birth, and treatment is recommended from an early age as well. Congenital clubfoot in children can be caused by the following factors:
- Genetic predisposition to the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
- coexisting flat feet;
- lack of calcium and vitamin D in the body;
- excess weight that puts undue stress on the feet;
- endocrine system problems associated with diabetes;
- Rickets;
- sedentary lifestyle, lack of exercise leading to muscle weakness in foot and ankle;
- wearing inferior, uncomfortable and unsuitable footwear.
Treatment
Correcting a clubfoot is not a quick process. Even in adults, after years of trying to treat the problem in childhood, symptoms of an incompletely treated condition, such as: B. a limp on one foot, can be detected when walking. Treatment of children depends on the severity of the disease, the stage at which the parents present themselves in the clinic and the presence of complications. The overall success of the treatment depends on these factors.
IMPORTANT: The choice of treatment is at the discretion of the physician. It depends on the results achieved in each stage.
In mild to moderate cases, conservative techniques are used when treating a child with clubfoot. Massages with ozokerite can be used, which have a warming effect and can relax the posterior and inner muscles of the lower leg in areas with increased tone. The massage begins with relaxing, stroking movements, after which the therapist moves on to more intense and active movements. It takes multiple massage sessions to get rid of a child's foot defect.
The most important
Congenital clubfoot is a common malformation of the intrauterine musculoskeletal system. It can be unilateral or bilateral. It occurs most frequently in boys. The defect must be corrected as it severely impairs the patient's function later in life.
Various techniques have been proposed for treatment. Conservative methods are based on massage, physiotherapy, elastic bandages and orthopedic constructions. If your child has clubfoot, the most effective method is three-step Ponseti patching - a three-step treatment of the condition that results in positive dynamics in almost all patients.
Clubfoot Treatment
There are two treatment methods, depending on the degree of curvature.
- Conservative treatment. It is used most frequently. In the mildest form of the disease, it consists of massage and physical therapy. For the intermediate degree, which is the most common, the pediatric orthopedist prescribes treatment using the Ponseti method. Plaster casts are placed on different parts of the leg to correct the position of the ankle.
Conservative treatment methods include:
- special therapeutic exercises for clubfoot;
- massages;
- bandaging with soft flannel;
- plaster casts;
- electrostimulation;
- Physiotherapy in the form of paraffin, mud, magnetic therapy or pine baths.
After the treatment, a prophylactic bandage – special shoes – is put on. Continued physical therapy is also recommended.
- surgical treatment. It is indicated for severe curvature, when the disease was recognized late and standard therapy is ineffective. The surgeon corrects the tendons, muscles, and sometimes the bones of the foot. After the operation, the foot is fixed with a plaster cast. For a full recovery, massage and therapeutic exercises are recommended. In addition, it is important to choose the right footwear for clubfoot. They must be made of quality materials, have a high firm back and good supinator.
Prevention of clubfoot
There is no guaranteed effective prevention of congenital clubfoot. This is especially true for children in whose families there is a genetic predisposition to this disease. However, to reduce the risk of developing a deformity, the expectant mother should follow a few simple rules:
- Take care of their health and at the slightest sign of infection, consult a doctor;
- Eat a healthy diet so she gets all the vitamins and minerals she needs;
- Avoid stress.
After the birth of the child, the position of the legs should be observed. The changes during sleep are particularly noticeable when the baby is maximally relaxed. To prevent orthopedic foot diseases in children, orthopedic mats and high-quality shoes with a solid insole are often used. A very important factor is a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. Vitamin D can be included in the diet after consulting the pediatrician.
Clubfoot is a deformity that is reversible in nearly 100% of cases. The most important thing is to diagnose the misalignment early and seek professional help. An experienced orthopedic surgeon at Daily Medical can quickly identify and correct the problem.
- Clubfoot in 7-year-old children.
- What is clubfoot?.
- Footwear for children's clubfoot.
- Therapeutic exercises for scoliosis.
- Congenital clubfoot.
- Why does a child develop clubfoot?.
- clubfoot.
- 1 year old child with clubfoot.